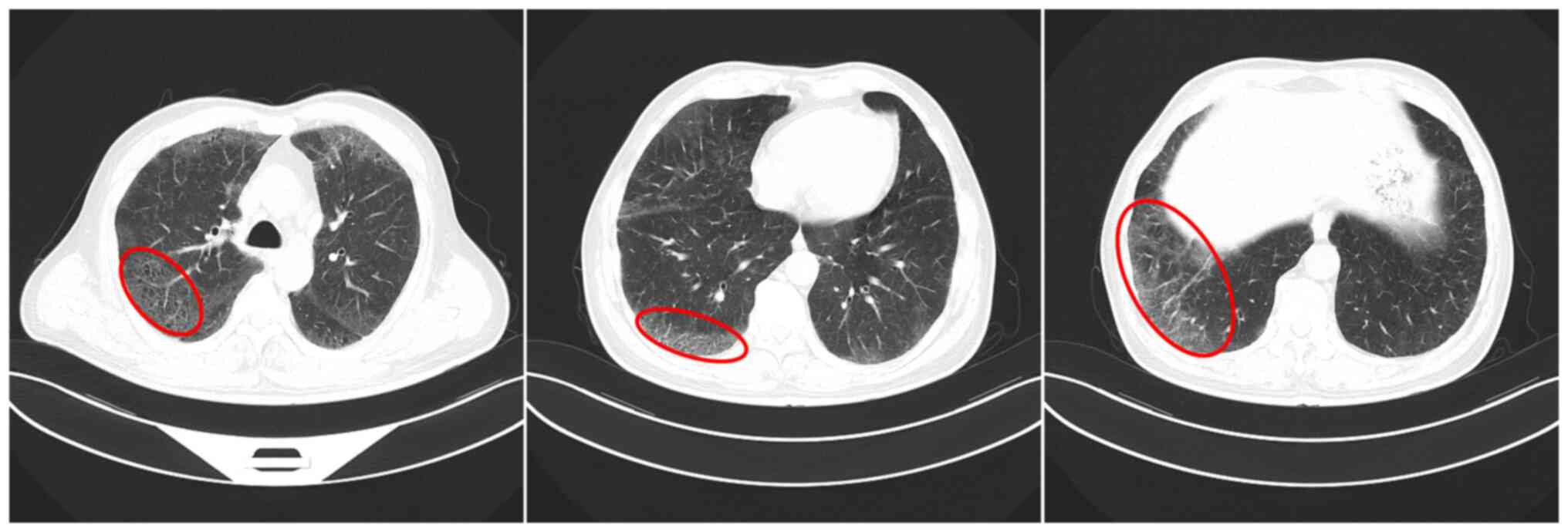
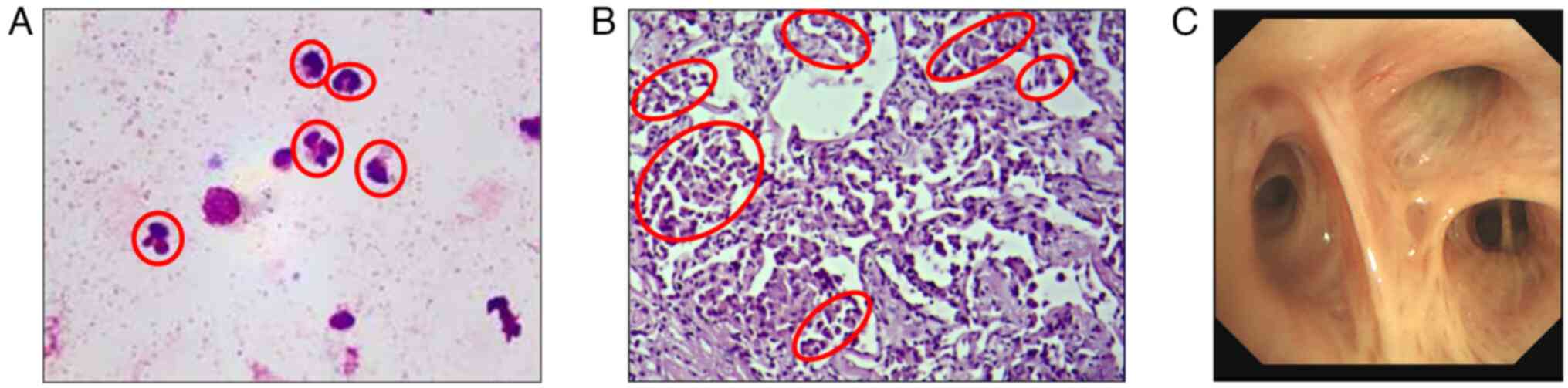
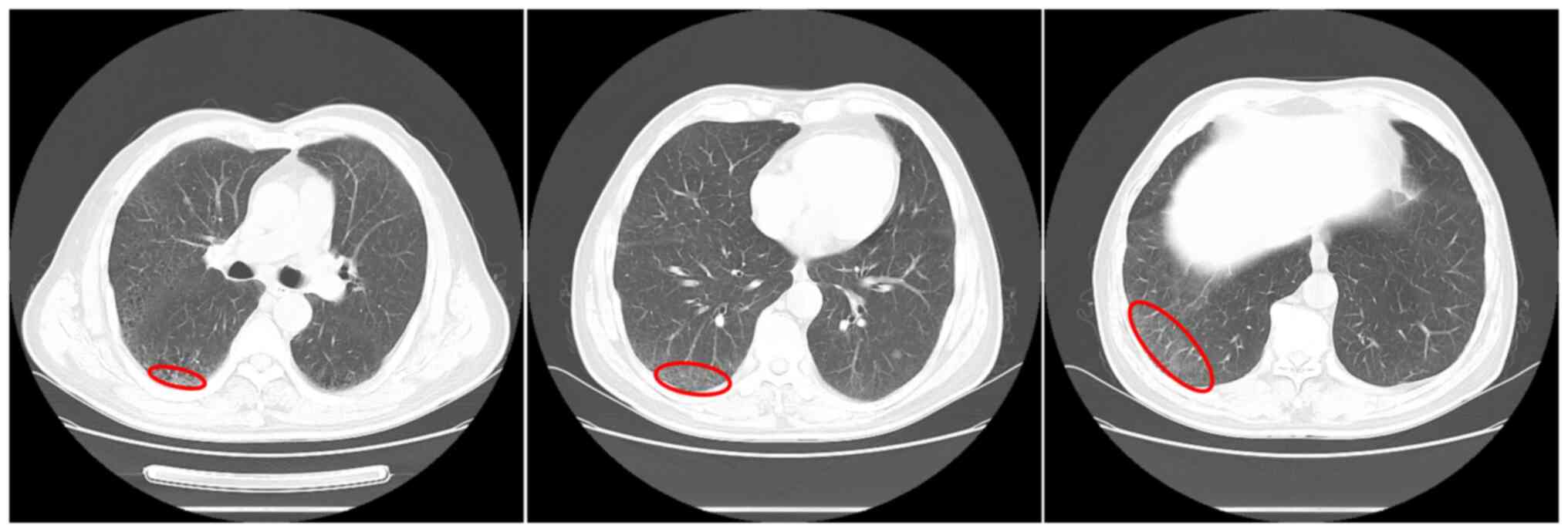
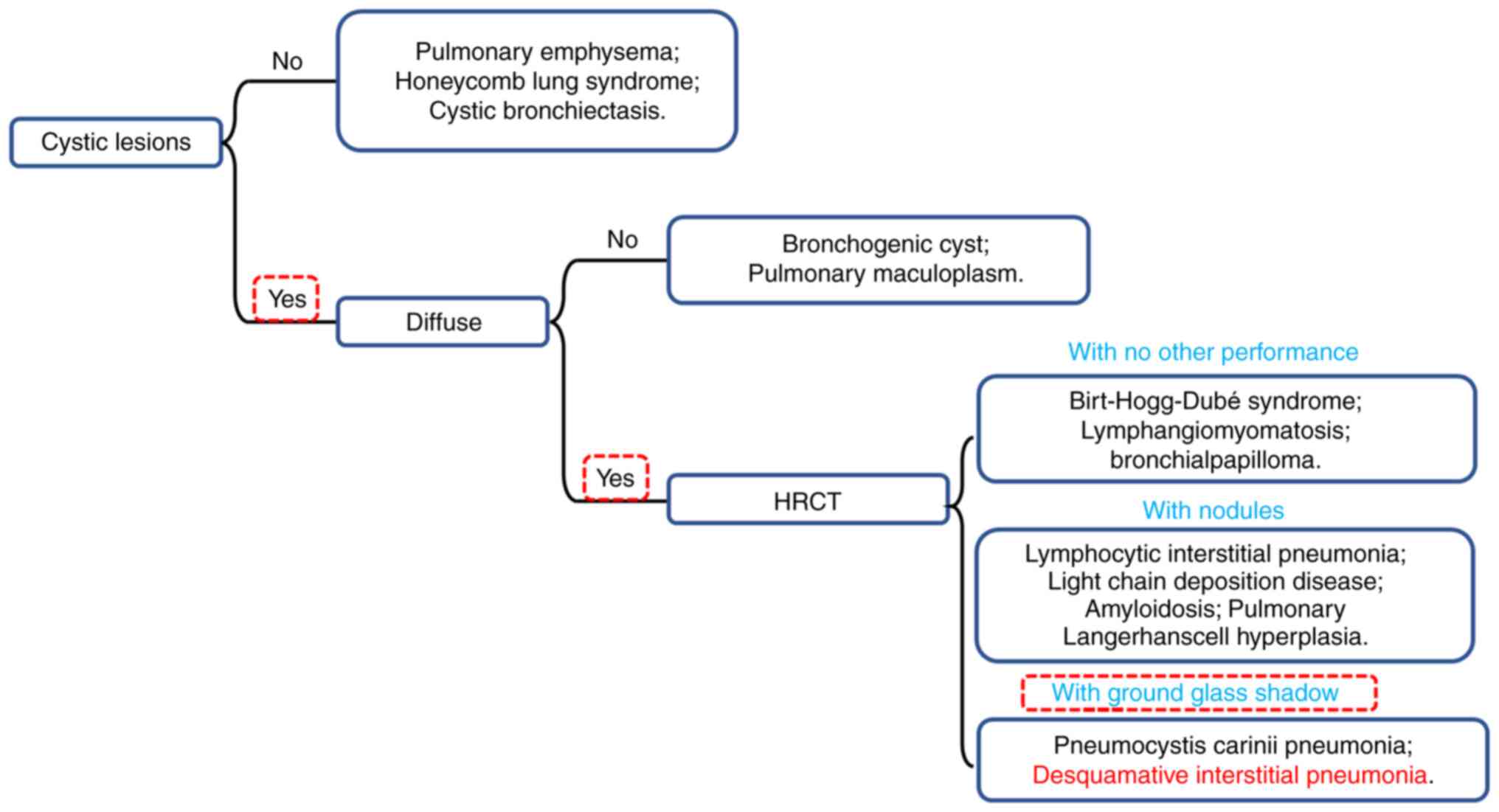
|
1
|
Panchabhai TS, Farver C and Highland KB:
Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia. Clin Chest Med. 37:463–474.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Radzikowska E: Update on pulmonary
Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Front Med (Lausanne).
7(582581)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Diken ÖE, Şengül A, Beyan AC, Ayten Ö,
Mutlu LC and Okutan O: Desquamative interstitial pneumonia: Risk
factors, laboratory and bronchoalveolar lavage findings,
radiological and histopathological examination, clinical features,
treatment and prognosis. Exp Ther Med. 17:587–595. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Obaidat B, Yazdani D, Wikenheiser-Brokamp
KA and Gupta N: Diffuse cystic lung diseases. Respir Care.
65:111–126. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ryu JH, Tian X, Baqir M and Xu K: Diffuse
cystic lung diseases. Front Med. 7:316–327. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liebow AA, Steer A and Billingsley JG:
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Am J Med. 39:369–404.
1965.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Godbert B, Wissler MP and Vignaud JM:
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia: An analytic review with an
emphasis on aetiology. Eur Respir Rev. 22:117–123. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hino T, Lee KS, Yoo H, Han J, Franks TJ
and Hatabu H: Interstitial lung abnormality (ILA) and nonspecific
interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). Eur J Radiol Open.
8(100336)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wells AU, Nicholson AG and Hansell DM:
Challenges in pulmonary fibrosis. 4: Smoking-induced diffuse
interstitial lung diseases. Thorax. 62:904–910. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Blin T, De Muret A, Teulier M, Ferreira M,
Vincent M, Catinon M, Legras A, Diot P and Marchand-Adam S:
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia induced by metal exposure. A
case report and literature review. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung
Dis. 37:79–84. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Serrano Gotarredona MP, Navarro Herrero S,
Gómez Izquierdo L and Rodríguez Portal JA: Smoking-related
interstitial lung disease. Radiologia (Engl Ed). 64 (Suppl
3):S277–S289. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Moreno García MJ, López-Herce Cid J,
Rodríguez Sánchez C, Alvarado Ortega F, Carrasco S and Ruza Tarrió
F: Desquamative interstitial pneumonia. An Esp Pediatr. 23:431–437.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Medenica M and Medenica M: Desquamative
interstitial pneumonia with clinical, radiological and histologic
correlation. Radiol Case Rep. 14:505–509. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yamakawa H, Suido Y, Sadoyama S, Yamanaka
Y, Ikeda S, Kitamura H, Baba T, Okudela K, Takemura T and Ogura T:
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia complicated with IgG4-related
lung disease. Intern Med. 56:1553–1556. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Margaritopoulos GA, Harari S, Caminati A
and Antoniou KM: Smoking-related idiopathic interstitial pneumonia:
A review. Respirology. 21:57–64. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hagmeyer L and Randerath W:
Smoking-related interstitial lung disease. Dtsch Arztebl Int.
112:43–50. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lougheed MD, Roos JO, Waddell WR and Munt
PW: Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis and diffuse alveolar
damage in textile workers. Potential role of mycotoxins. Chest.
108:1196–1200. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nemery B: Metal toxicity and the
respiratory tract. Eur Respir J. 3:202–219. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cottin V: Desquamative interstitial
pneumonia: Still orphan and not always benign. Eur Respir Rev.
29(200183)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lovrenski A, Eri Ž, Tegeltija D,
Kašiković-Lečić S and Panjković M: Desquamative interstitial
pneumonia: A case report. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 142:602–606.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ishimoto H, Sakamoto N, Ozasa M, Tsutsui
S, Hara A, Kido T, Yamaguchi H, Yamamoto K, Obase Y, Ishimatsu Y
and Mukae H: Idiopathic desquamative interstitial pneumonia
diagnosed using transbronchial lung cryobiopsy: A case report.
Respir Med Case Rep. 34(101523)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sousa V and Carvalho L: DIP (desquamative
interstitial pneumonia): As a tobacco-associated disease-case
report. Rev Port Pneumol. 10:431–435. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Portuguese).
|
|
23
|
Miyaoka M, Hatanaka K, Iwazaki M and
Nakamura N: Pulmonary adenocarcinoma mimicking desquamative
interstitial pneumonia: Report of 2 cases with genetic analysis.
Int J Surg Pathol. 26:655–659. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Neacşu F, Vârban AŞ, Simion G, Şurghie R,
Pătraşcu OM, Sajin M, Dumitru M and Vrînceanu D: Lung cancer
mimickers-a case series of seven patients and review of the
literature. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 62:697–704. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Furuya K, Yasumori K, Takeo S, Sakino I,
Uesugi N, Momosaki S and Muranaka T: Lung CT: Part 1, mimickers of
lung cancer-spectrum of CT findings with pathologic correlation.
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 199:W454–W463. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Batra K and Adams TN: Imaging features of
idiopathic interstitial lung diseases. J Thorac Imaging. 38 (Suppl
1):S19–S29. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
American Thoracic Society; European
Respiratory Society. American thoracic society/European respiratory
society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of
the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. This joint statement of the
American thoracic society (ATS), and the European respiratory
society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001
and by the ERS executive committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 165:277–304. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hellemons ME, Moor CC, von der Thüsen J,
Rossius M, Odink A, Thorgersen LH, Verschakelen J, Wuyts W,
Wijsenbeek MS and Bendstrup E: Desquamative interstitial pneumonia:
A systematic review of its features and outcomes. Eur Respir Rev.
29(190181)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Craig PJ, Wells AU, Doffman S, Rassl D,
Colby TV, Hansell DM, Du Bois RM and Nicholson AG: Desquamative
interstitial pneumonia, respiratory bronchiolitis and their
relationship to smoking. Histopathology. 45:275–282.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Katzenstein AL, Mukhopadhyay S, Zanardi C
and Dexter E: Clinically occult interstitial fibrosis in smokers:
Classification and significance of a surprisingly common finding in
lobectomy specimens. Hum Pathol. 41:316–325. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ryu JH, Colby TV, Hartman TE and Vassallo
R: Smoking-related interstitial lung diseases: A concise review.
Eur Respir J. 17:122–132. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vassallo R: Diffuse lung diseases in
cigarette smokers. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 33:533–542.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Deutsch GH, Young LR, Deterding RR, Fan
LL, Dell SD, Bean JA, Brody AS, Nogee LM, Trapnell BC, Langston C,
et al: Diffuse lung disease in young children: Application of a
novel classification scheme. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
176:1120–1128. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jarrot PA, Mahmoudi R, Novella JL and
Manckoundia P: Pneumonia due to Yersinia enterocolitica. Med Mal
Infect. 43:38–39. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
35
|
He H and Wunderink RG: Staphylococcus
aureus pneumonia in the community. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
41:470–479. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Radzikowska E: Pulmonary Langerhans' cell
histiocytosis in adults. Adv Respir Med. 85:277–289.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shaw B, Borchers M, Zander D and Gupta N:
Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Semin Respir Crit Care
Med. 41:269–279. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu KF, Xu W, Liu S, Yu J, Tian X, Yang Y,
Wang ST, Zhang W, Feng R and Zhang T: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis.
Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 41:256–268. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
McCarthy C, Gupta N, Johnson SR, Yu JJ and
McCormack FX: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Pathogenesis, clinical
features, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Respir Med.
9:1313–1327. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pitt J: Lymphocytic interstitial
pneumonia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 38:89–95. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Daccord C, Good JM, Morren MA, Bonny O,
Hohl D and Lazor R: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Eur Respir Rev.
29(200042)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|