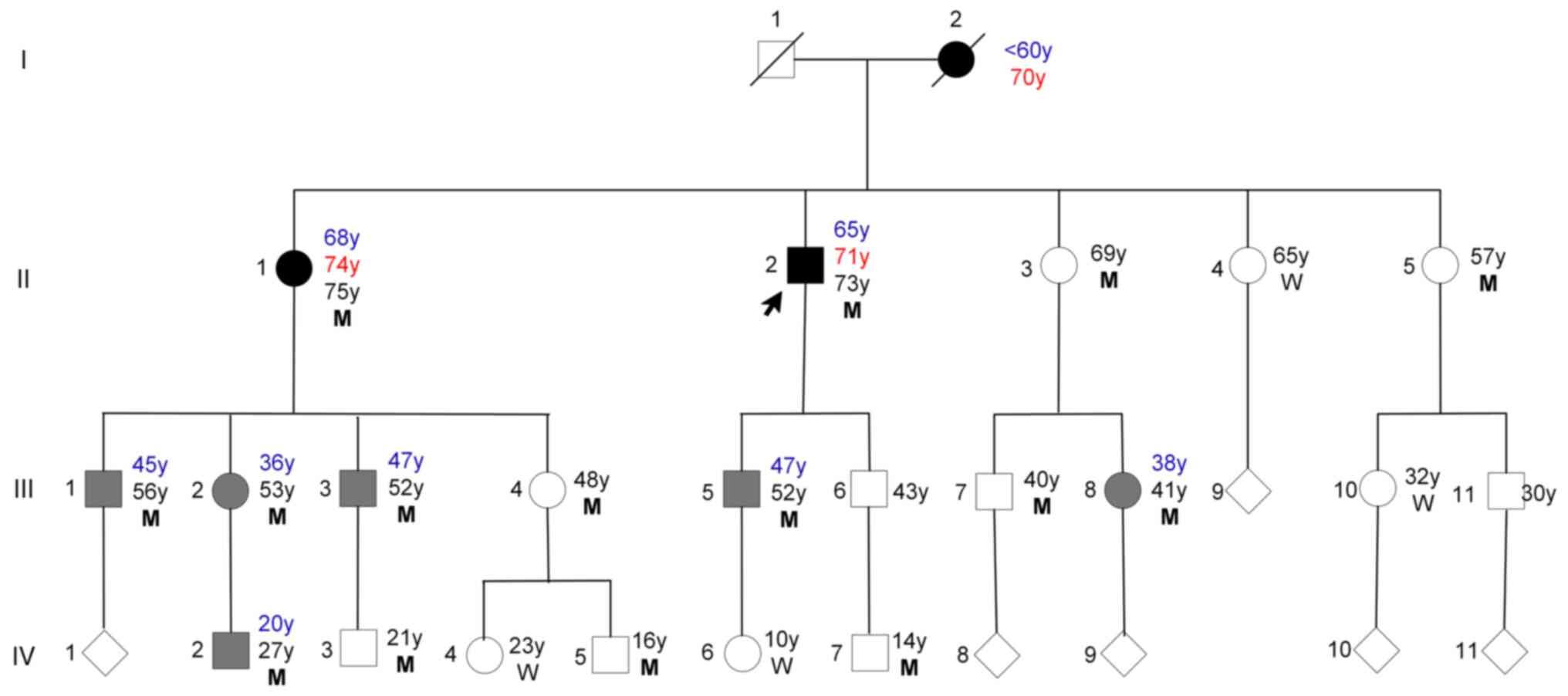
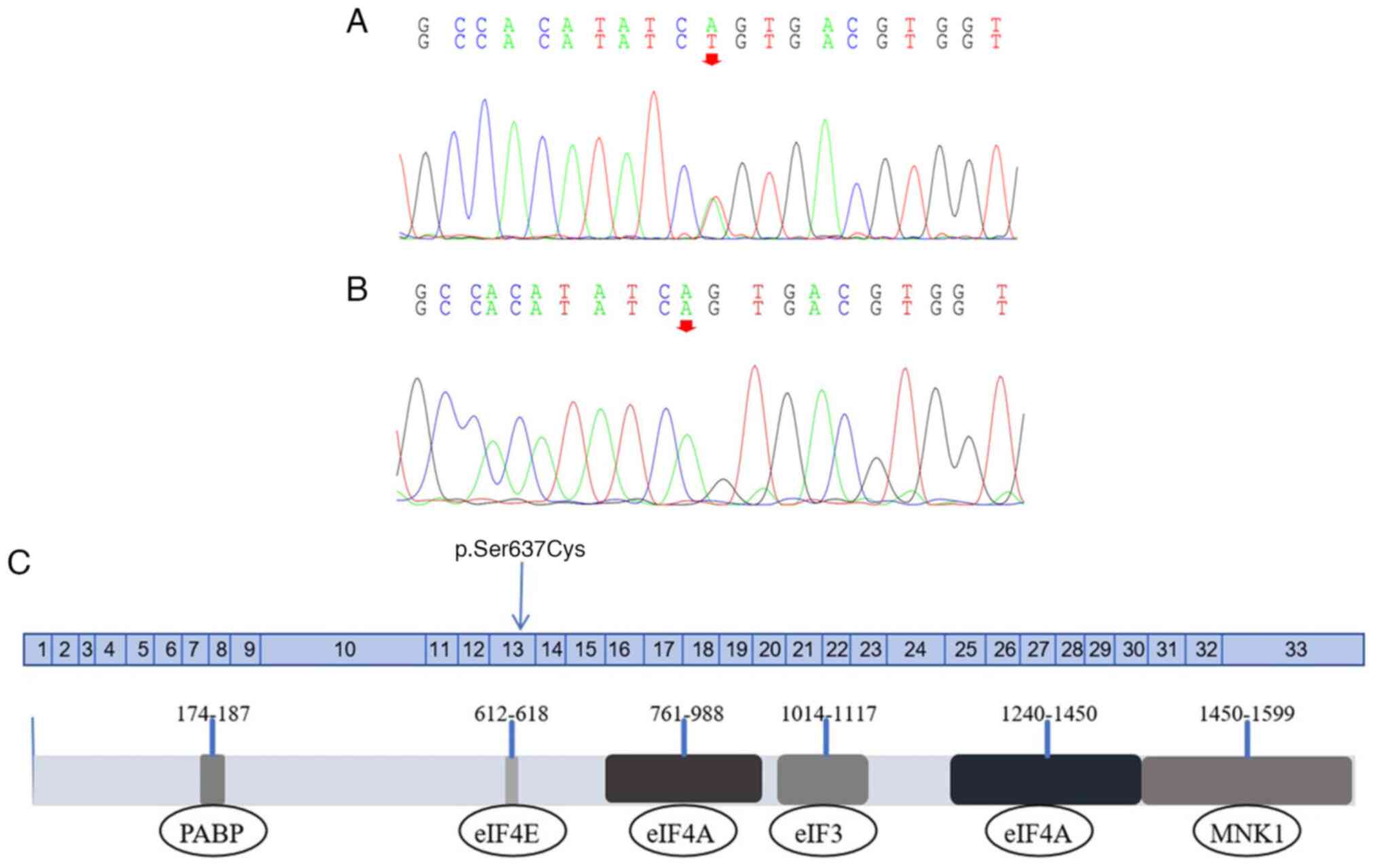
|
1
|
Nussbaum RL and Ellis CE: Alzheimer's
disease and Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 348:1356–1364.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hayes MT: Parkinson's disease and
Parkinsonism. Am J Med. 132:802–807. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fereshtehnejad SM, Zeighami Y, Dagher A
and Postuma RB: Clinical criteria for subtyping Parkinson's
disease: Biomarkers and longitudinal progression. Brain.
140:1959–1976. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bhatia KP, Bain P, Bajaj N, Elble RJ,
Hallett M, Louis ED, Raethjen J, Stamelou M, Testa CM and Deuschl
G: Tremor Task Force of the International Parkinson and Movement
Disorder Society. Consensus Statement on the classification of
tremors. From the task force on tremor of the International
Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov Disord. 33:75–87.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Song P, Zhang Y, Zha M, Yang Q, Ye X, Yi Q
and Rudan I: The global prevalence of essential tremor, with
emphasis on age and sex: A meta-analysis. J Glob Health.
11(04028)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Louis ED and Ferreira JJ: How common is
the most common adult movement disorder? Update on the worldwide
prevalence of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 25:534–541.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
de Lau LM and Breteler MM: Epidemiology of
Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 5:525–535. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Clarimón J and Kulisevsky J: Parkinson's
disease: From genetics to clinical practice. Curr Genomics.
14:560–567. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Funayama M, Ohe K, Amo T, Furuya N,
Yamaguchi J, Saiki S, Li Y, Ogaki K, Ando M, Yoshino H, et al:
CHCHD2 mutations in autosomal dominant late-onset Parkinson's
disease: A genome-wide linkage and sequencing study. Lancet Neurol.
14:274–282. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lesage S, Drouet V, Majounie E,
Deramecourt V, Jacoupy M, Nicolas A, Cormier-Dequaire F, Hassoun
SM, Pujol C, Ciura S, et al: Loss of VPS13C function in
autosomal-recessive Parkinsonism causes mitochondrial dysfunction
and increases PINK1/Parkin-Dependent mitophagy. Am J Hum Genet.
98:500–513. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nalls MA, Blauwendraat C, Vallerga CL,
Heilbron K, Bandres-Ciga S, Chang D, Tan M, Kia DA, Noyce AJ, Xue
A, et al: Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and
heritable risk for Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis of
genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 18:1091–1102.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Puschmann A: New genes causing hereditary
Parkinson's disease or Parkinsonism. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
17(66)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang N, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Zhang R, He Y, Zhou
Y, Xu Q, Sun Q, Yan X, Guo J and Tang B: Systematically analyzing
rare variants of autosomal-dominant genes for sporadic Parkinson's
disease in a Chinese cohort. Neurobiol Aging. 76:215.e1–215.e7.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yan R and Rhoads RE: Human protein
synthesis initiation factor eIF-4 gamma is encoded by a single gene
(EIF4G) that maps to chromosome 3q27-qter. Genomics. 26:394–398.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jackson RJ, Hellen CU and Pestova TV: The
mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation and principles of
its regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:113–127. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Raught B, Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Imataka H,
Morino S, Gradi A, Aebersold R and Sonenberg N: Serum-stimulated,
Rapamycin-sensitive phosphorylation sites in the eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 4GI. EMBO J. 19:434–444.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ramírez-Valle F, Braunstein S, Zavadil J,
Formenti SC and Schneider RJ: eIF4GI links nutrient sensing by mTOR
to cell proliferation and inhibition of autophagy. J Cell Biol.
181:293–307. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Haimov O, Sehrawat U, Tamarkin-Ben Harush
A, Bahat A, Uzonyi A, Will A, Hiraishi H, Asano K and Dikstein R:
Dynamic interaction of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4G1)
with eIF4E and eIF1 Underlies Scanning-Dependent and -independent
translation. Mol Cell Biol. 38:e00139–18. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Howard A and Rogers AN: Role of
translation initiation factor 4G in lifespan regulation and
age-related health. Ageing Res Rev. 13:115–124. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vosler PS, Gao Y, Brennan CS, Yanagiya A,
Gan Y, Cao G, Zhang F, Morley SJ, Sonenberg N, Bennett MV and Chen
J: Ischemia-induced calpain activation causes eukaryotic
(translation) initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4GI) degradation, protein
synthesis inhibition, and neuronal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:18102–18107. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Algarni M and Fasano A: The overlap
between Essential tremor and Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat
Disord. 46 (Suppl 1):S101–S104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tarakad A and Jankovic J: Essential Tremor
and Parkinson's disease: Exploring the relationship. Tremor Other
Hyperkinet Mov (NY). 8(589)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chartier-Harlin MC, Dachsel JC,
Vilariño-Güell C, Lincoln SJ, Leprêtre F, Hulihan MM, Kachergus J,
Milnerwood AJ, Tapia L, Song MS, et al: Translation initiator
EIF4G1 mutations in familial Parkinson disease. Am J Hum Genet.
89:398–406. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gialluisi A, Reccia MG, Modugno N, Nutile
T, Lombardi A, Di Giovannantonio LG, Pietracupa S, Ruggiero D,
Scala S, Gambardella S, et al: Identification of sixteen novel
candidate genes for late onset Parkinson's disease. Mol
Neurodegener. 16(35)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gibb WR and Lees AJ: The relevance of the
Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J
Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 51:745–752. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hoehn MM and Yahr MD: Parkinsonism: Onset,
progression and mortality. Neurology. 17:427–442. 1967.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Goetz CG, Tilley BC, Shaftman SR, Stebbins
GT, Fahn S, Martinez-Martin P, Poewe W, Sampaio C, Stern MB, Dodel
R, et al: Movement disorder Society-sponsored revision of the
Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale
presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov Disord.
23:2129–2170. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Norris D, Clark MS and Shipley S: The
mental status examination. Am Fam Physician. 94:635–641.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XC, Liu RH, Wang T, Wang Y, Jiang Y,
Chen DD, Wang XY, Hou TS and Kong QX: A novel missense mutation in
SPAST causes hereditary spastic paraplegia in male members of a
family: A case report. Mol Med Rep. 27(79)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu YD, Ma MY, Hu XB, Yan H, Zhang YK,
Yang HX, Feng JH, Wang L, Zhang H, Zhang B, et al: Brain proteomic
profiling in intractable epilepsy caused by TSC1 truncating
mutations: A small sample study. Front Neurol.
11(475)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fromer M, Moran JL, Chambert K, Banks E,
Bergen SE, Ruderfer DM, Handsaker RE, McCarroll SA, O'Donovan MC,
Owen MJ, et al: Discovery and statistical genotyping of copy-number
variation from whole-exome sequencing depth. Am J Hum Genet.
91:597–607. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Oldridge DA, Diskin SJ and Zhang
NR: CODEX: A normalization and copy number variation detection
method for whole exome sequencing. Nucleic Acids.
43(e39)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L,
Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS and Sunyaev SR: A
method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat
Methods. 7:248–249. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the
deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 11:361–362. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al:
Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence
variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College
of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular
Pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–424. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tsai FM, Lin YJ, Cheng YC, Lee KH, Huang
CC, Chen YT and Yao A: PrimerZ: Streamlined primer design for
promoters, exons and human SNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W63–W65.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu X, Wang N, Chen C, Wu PY, Piao S, Geng
D and Li Y: Swallow tail sign on susceptibility map-weighted
imaging (SMWI) for disease diagnosing and severity evaluating in
Parkinsonism. Acta Radiol. 62:234–242. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim DS, Tung GA, Akbar U and Friedman JH:
The evaluation of the swallow tail sign in patients with
Parkinsonism and gait disorders. J Neurol Sci.
428(117581)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W,
Olanow CW, Oertel W, Obeso J, Marek K, Litvan I, Lang AE, et al:
MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Mov
Disord. 30:1591–1601. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Deng H, Wu Y and Jankovic J: The EIF4G1
gene and Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 132:73–78.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Damier P, Hirsch EC, Agid Y and Graybiel
AM: The substantia nigra of the human brain. I. Nigrosomes and the
nigral matrix, a compartmental organization based on calbindin D
(28K) immunohistochemistry. Brain. 122:1421–1436. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cosottini M, Frosini D, Pesaresi I,
Donatelli G, Cecchi P, Costagli M, Biagi L, Ceravolo R, Bonuccelli
U and Tosetti M: Comparison of 3T and 7T susceptibility-weighted
angiography of the substantia nigra in diagnosing Parkinson
disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 36:461–466. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Schwarz ST, Afzal M, Morgan PS, Bajaj N,
Gowland PA and Auer DP: The ‘swallow tail’ appearance of the
healthy nigrosome-a new accurate test of Parkinson's disease: A
case-control and retrospective cross-sectional MRI study at 3T.
PLoS One. 9(e93814)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Villa N, Do A, Hershey JW and Fraser CS:
Human eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) protein binds to
eIF3c, -d, and -e to promote mRNA recruitment to the ribosome. J
Biol Chem. 288:32932–32940. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sonenberg N and Hinnebusch AG: Regulation
of translation initiation in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and biological
targets. Cell. 136:731–745. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lesage S, Condroyer C, Klebe S, Lohmann E,
Durif F, Damier P, Tison F, Anheim M, Honoré A, Viallet F, et al:
EIF4G1 in familial Parkinson's disease: Pathogenic mutations or
rare benign variants? Neurobiol Aging. 33:2233.e1–2233.e5.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Schulte EC, Mollenhauer B, Zimprich A,
Bereznai B, Lichtner P, Haubenberger D, Pirker W, Brücke T, Molnar
MJ, Peters A, et al: Variants in eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 4G1 in sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurogenetics.
13:281–285. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li K, Tang BS, Guo JF, Lou MX, Lv ZY, Liu
ZH, Tian Y, Song CY, Xia K and Yan XX: Analysis of EIF4G1 in ethnic
Chinese. BMC Neurol. 13(38)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen Y, Chen K, Song W, Chen X, Cao B,
Huang R, Zhao B, Guo X, Burgunder J, Li J and Shang HF: VPS35
Asp620Asn and EIF4G1 Arg1205His mutations are rare in Parkinson
disease from southwest China. Neurobiol Aging. 34:1709.e7–e8.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Blanckenberg J, Ntsapi C, Carr JA and
Bardien S: EIF4G1 R1205H and VPS35 D620N mutations are rare in
Parkinson's disease from South Africa. Neurobiol Aging.
35:445.e1–e3. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gagliardi M, Annesi G, Tarantino P,
Nicoletti G and Quattrone A: Frequency of the ASP620ASN mutation in
VPS35 and Arg1205His mutation in EIF4G1 in familial Parkinson's
disease from South Italy. Neurobiol Aging. 35:2422.e1–e2.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kumari U and Tan EK: LRRK2 in Parkinson's
disease: Genetic and clinical studies from patients. FEBS J.
276:6455–6463. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Marchetti B, Tirolo C, L'Episcopo F,
Caniglia S, Testa N, Smith JA, Pluchino S and Serapide MF:
Parkinson's disease, aging and adult neurogenesis: Wnt/β-catenin
signalling as the key to unlock the mystery of endogenous brain
repair. Aging Cell. 19(e13101)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lunati A, Lesage S and Brice A: The
genetic landscape of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol (Paris).
174:628–643. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Bandres-Ciga S, Diez-Fairen M, Kim JJ and
Singleton AB: Genetics of Parkinson's disease: An introspection of
its journey towards precision medicine. Neurobiol Dis.
137(104782)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Polymeropoulos MH, Higgins JJ, Golbe LI,
Johnson WG, Ide SE, Di Iorio G, Sanges G, Stenroos ES, Pho LT,
Schaffer AA, et al: Mapping of a gene for Parkinson's disease to
chromosome 4q21-q23. Science. 274:1197–1199. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pirooznia SK, Rosenthal LS, Dawson VL and
Dawson TM: Parkinson disease: Translating insights from molecular
mechanisms to neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev. 73:33–97.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|