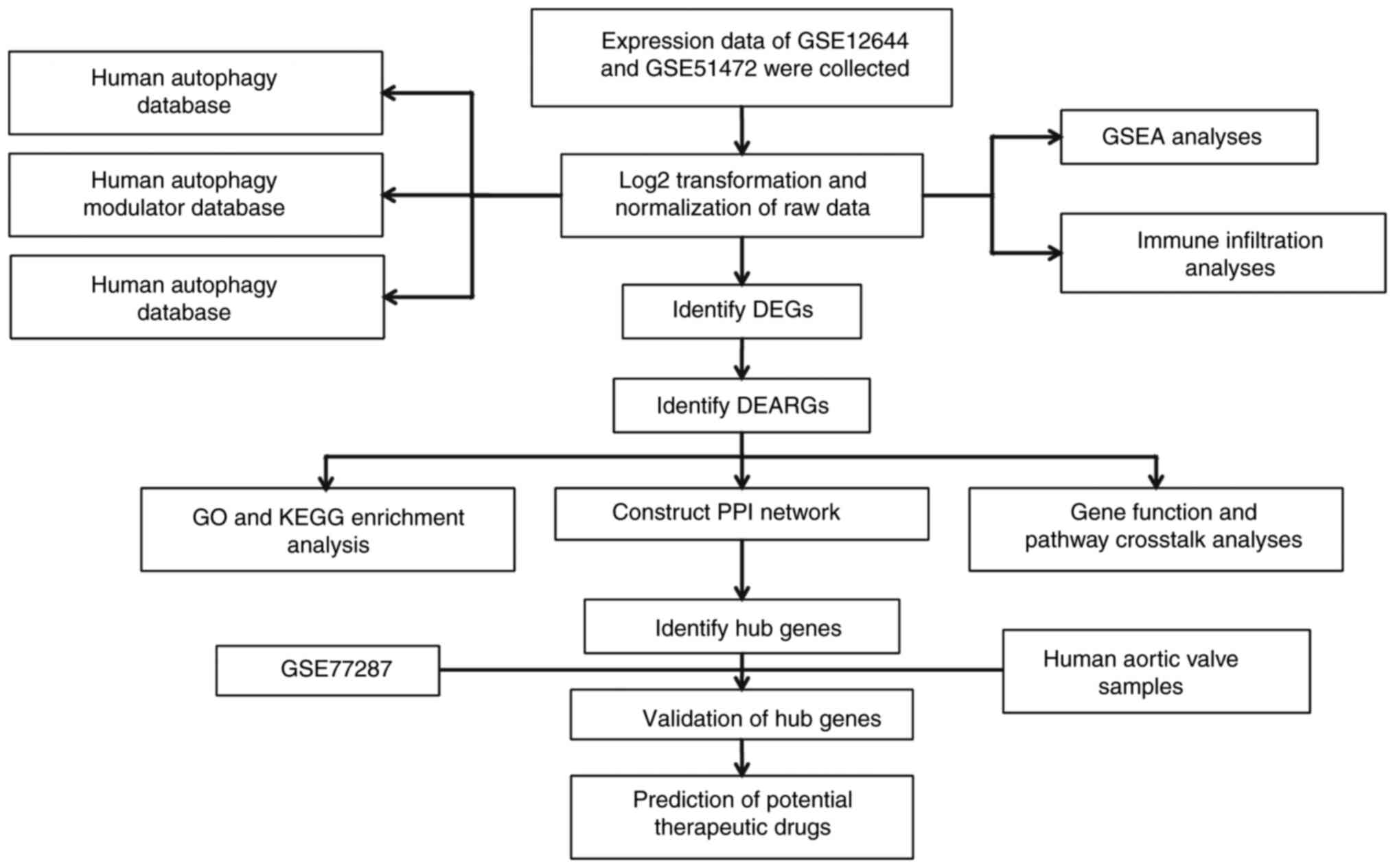
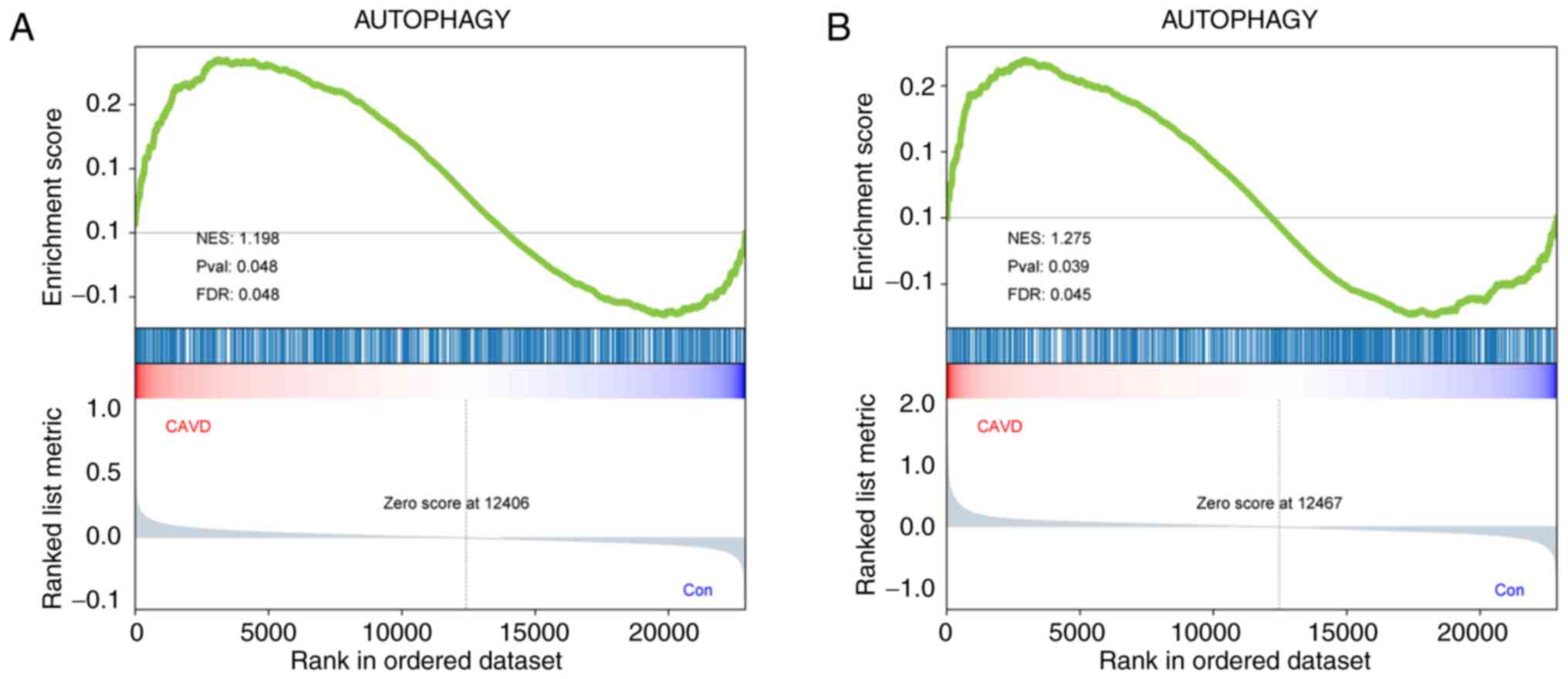
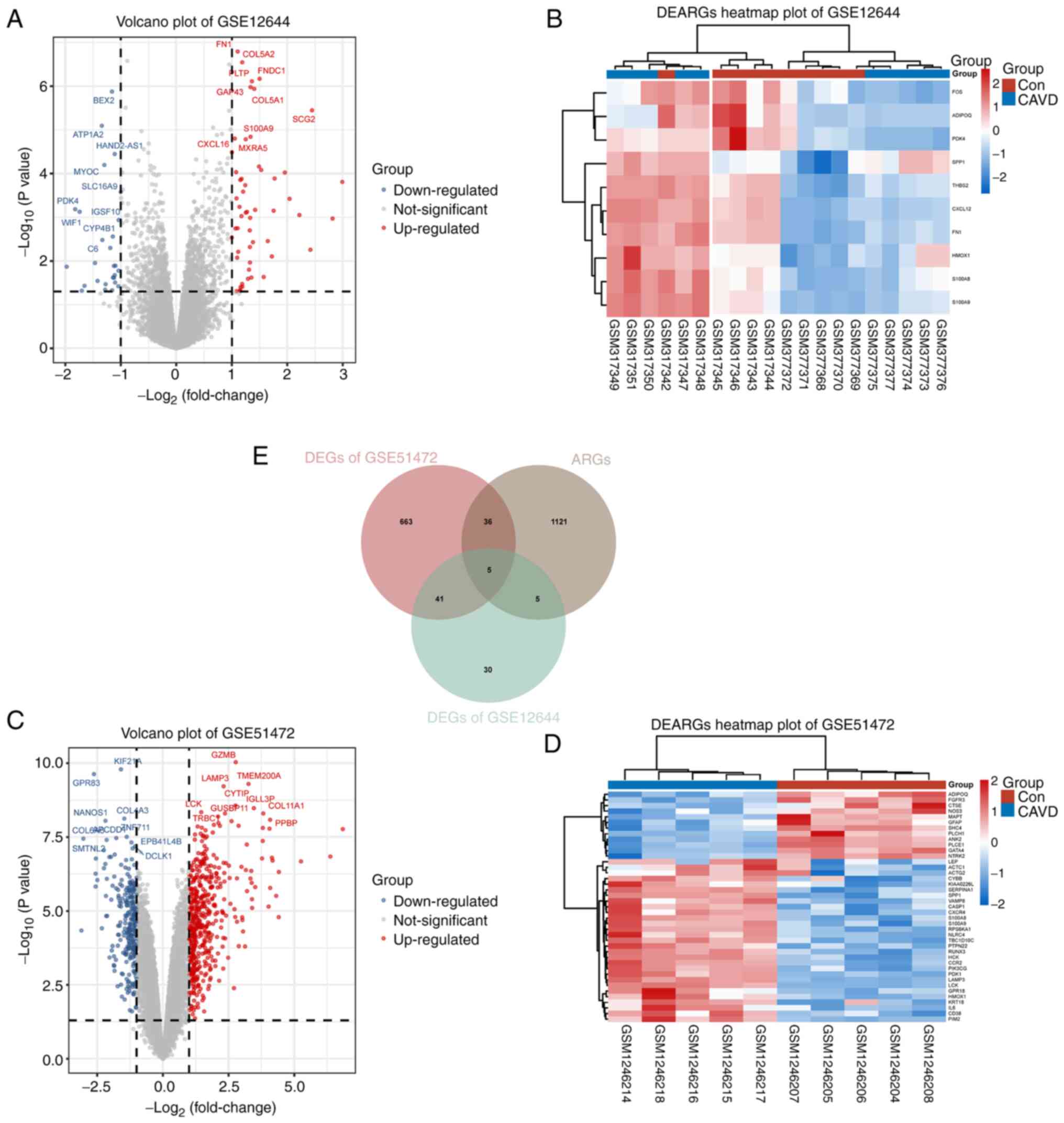
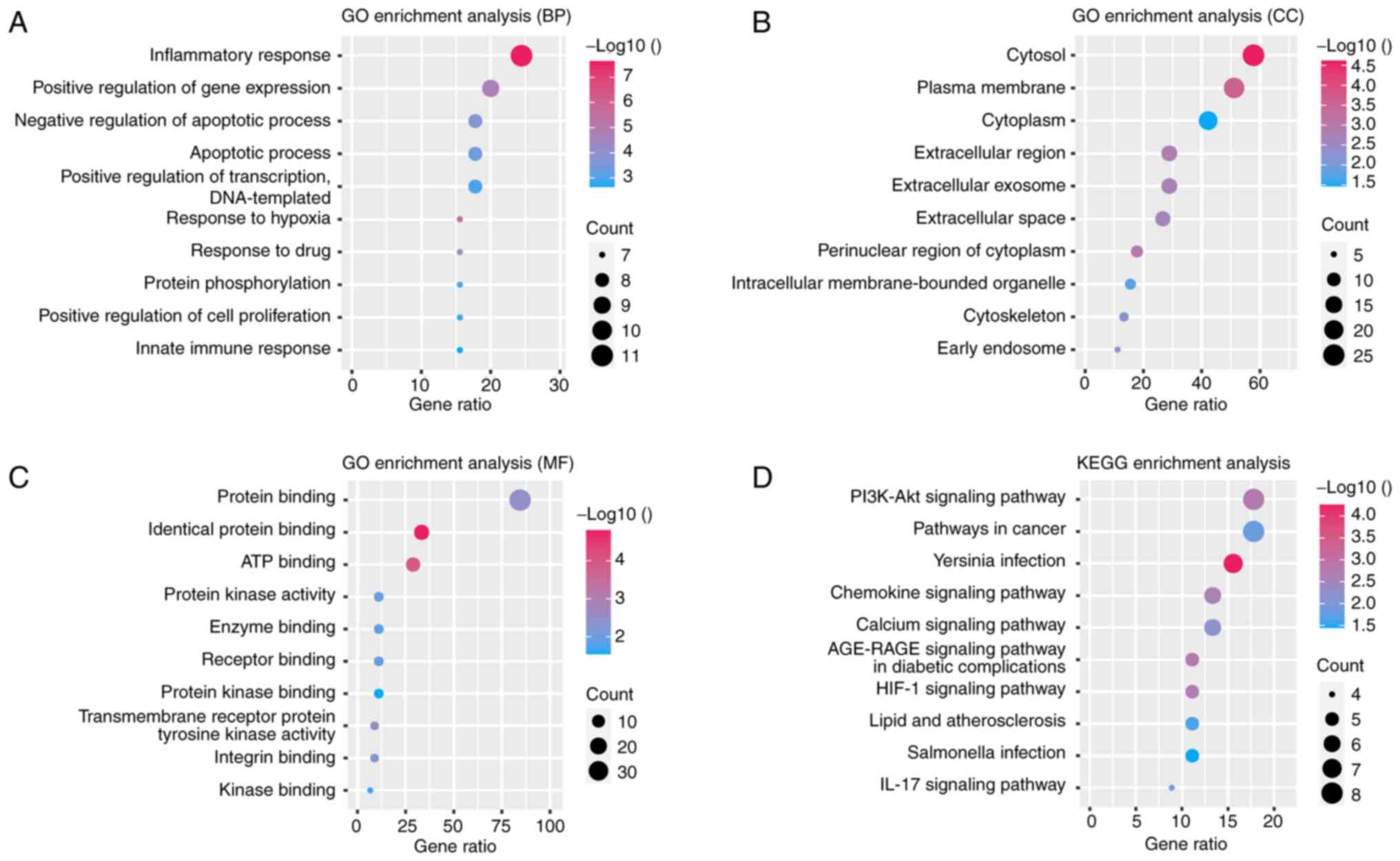
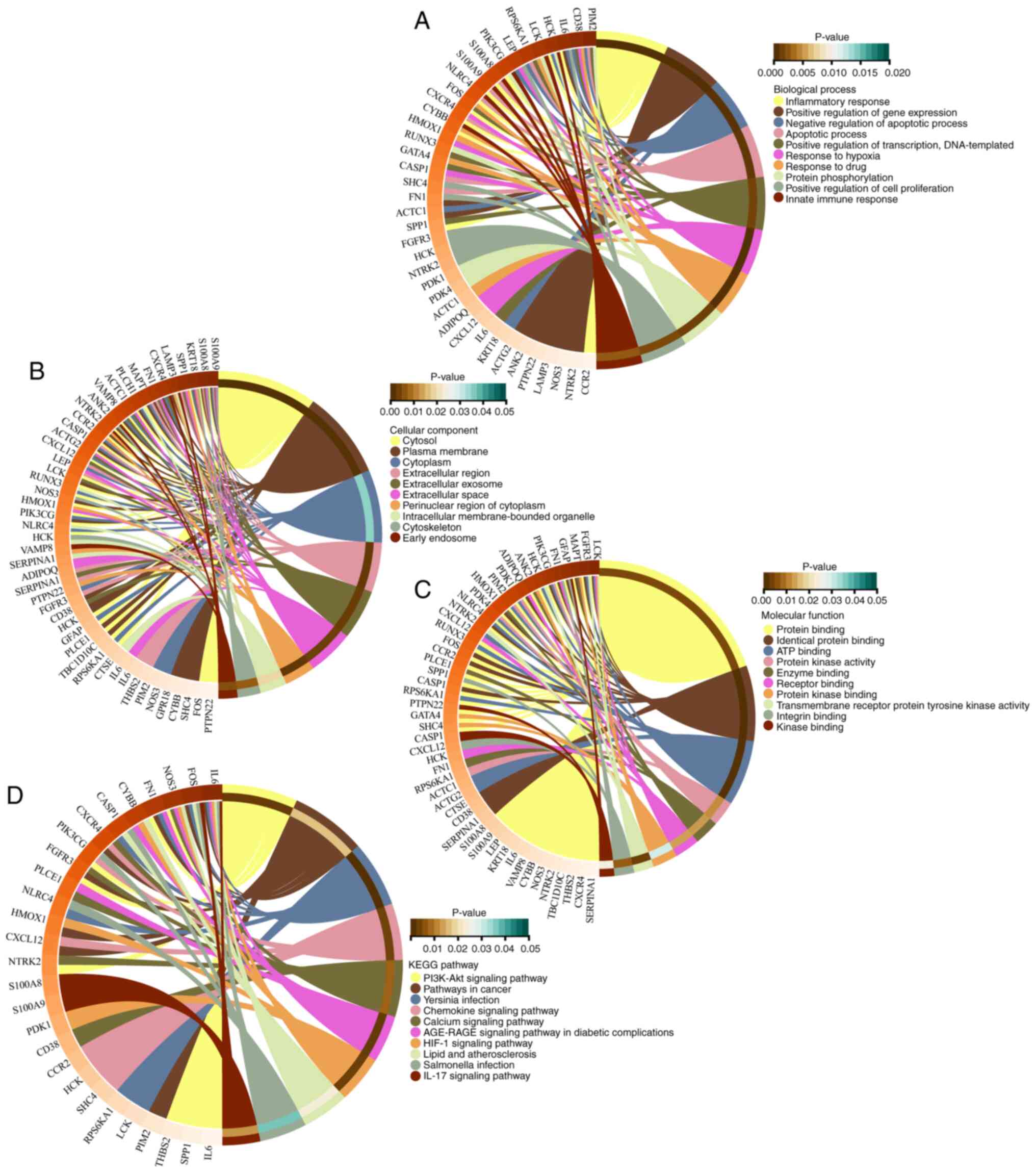
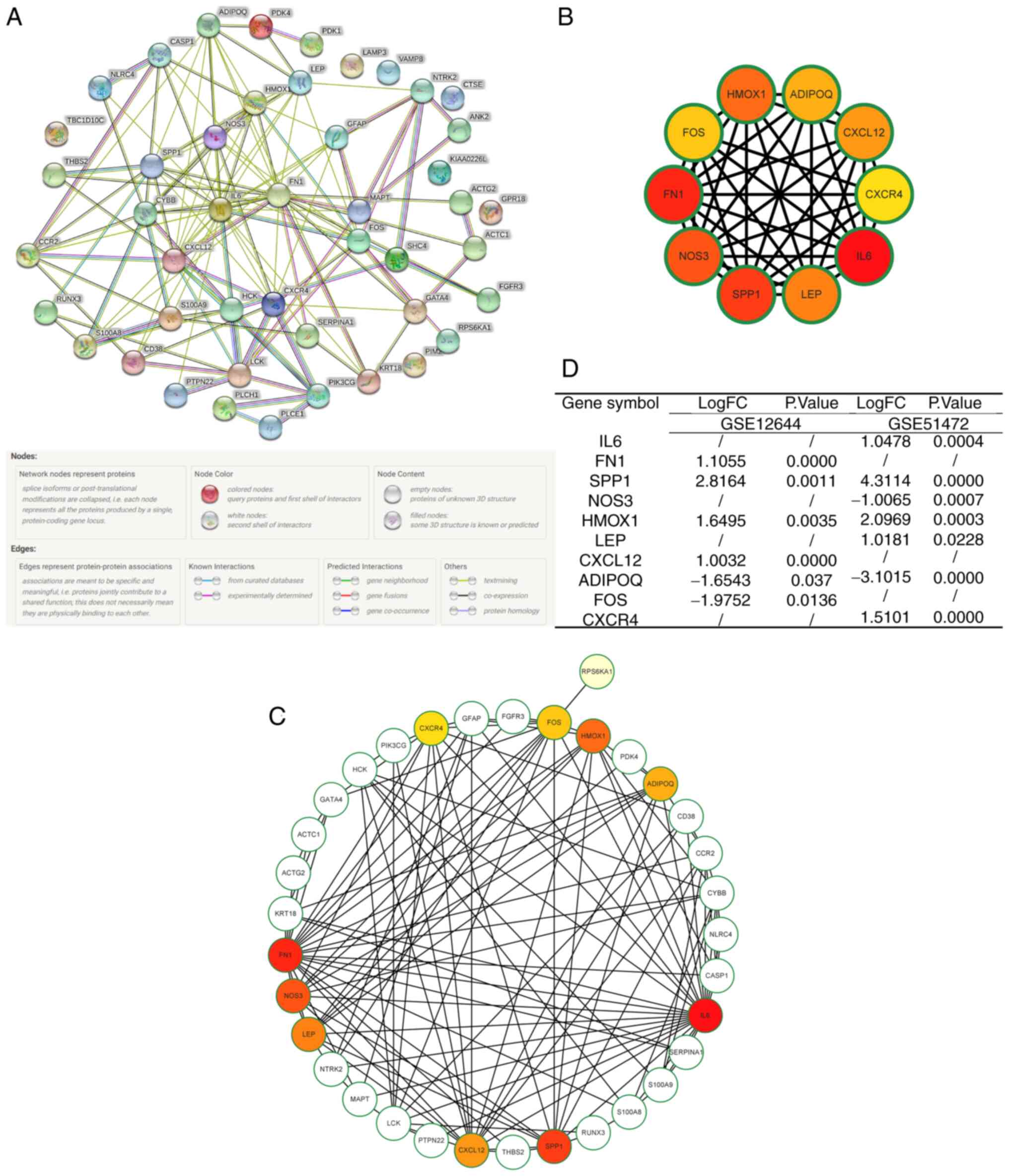
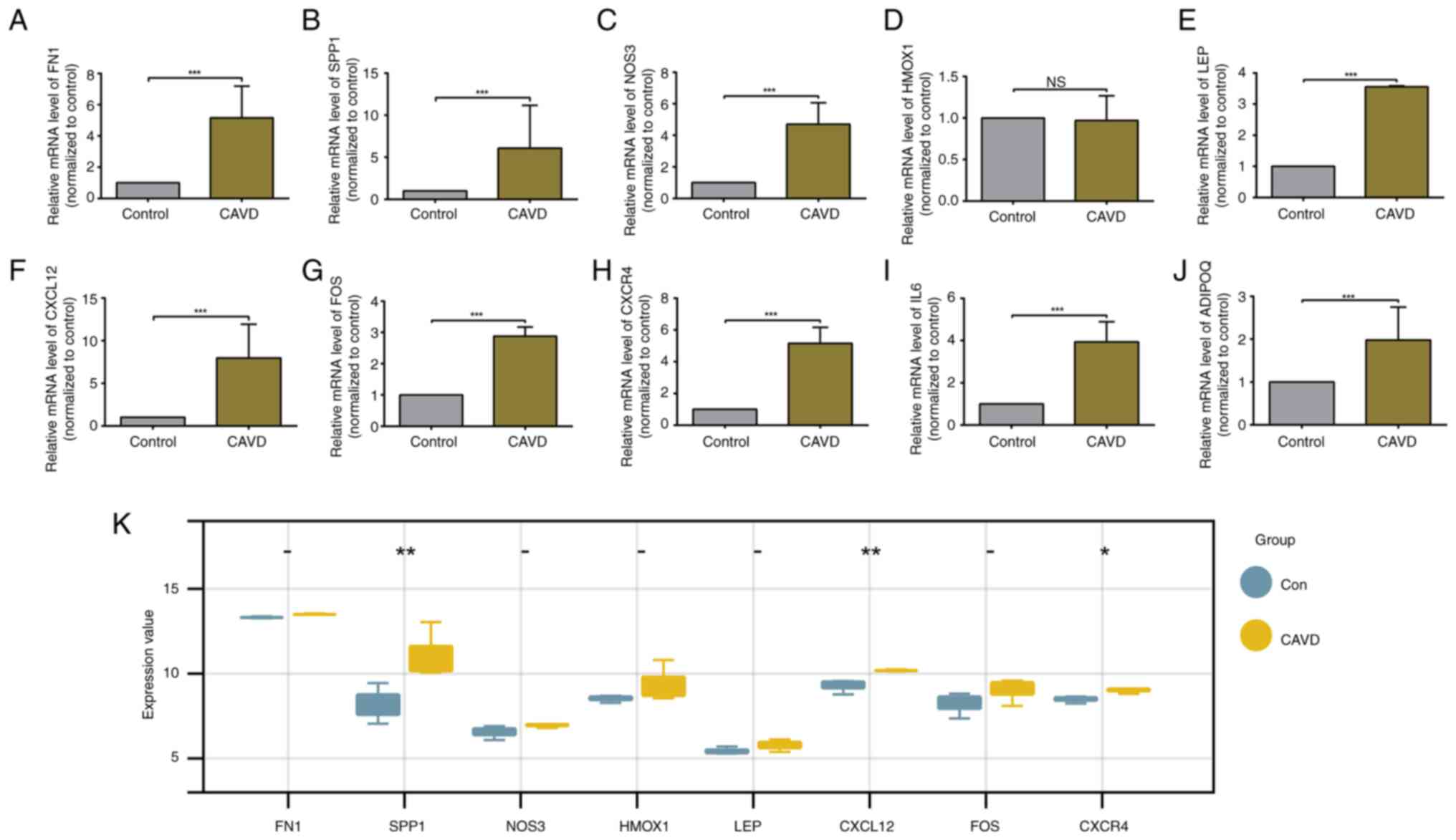
|
1
|
Chen Y, Xiao F and Wang R: Calcified
aortic valve disease complicated with and without diabetes
mellitus: The underlying pathogenesis. Rev Cardiovasc Med.
23(7)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lindman BR, Clavel MA, Mathieu P, Iung B,
Lancellotti P, Otto CM and Pibarot P: Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat
Rev Dis Primers. 2(16006)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kraler S, Blaser MC, Aikawa E, Camici GG
and Lüscher TF: Calcific aortic valve disease: From molecular and
cellular mechanisms to medical therapy. Eur Heart J. 43:683–697.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jiang T, Hasan SM, Faluk M and Patel J:
Evolution of transcatheter aortic valve replacement | review of
literature. Curr Probl Cardiol. 46(100600)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim KH and Lee MS: Autophagy-a key player
in cellular and body metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 10:322–337.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Levine B, Mizushima N and Virgin HW:
Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 469:323–335.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Clarke AJ and Simon AK: Autophagy in the
renewal, differentiation and homeostasis of immune cells. Nat Rev
Immunol. 19:170–183. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nixon RA: The role of autophagy in
neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 19:983–997. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Marsh T and Debnath J: Autophagy
suppresses breast cancer metastasis by degrading NBR1. Autophagy.
16:1164–1165. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G and Galluzzi
L: Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res.
120:1812–1824. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luciani A, Schumann A, Berquez M, Chen Z,
Nieri D, Failli M, Debaix H, Festa BP, Tokonami N, Raimondi A, et
al: Impaired mitophagy links mitochondrial disease to epithelial
stress in methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency. Nat Commun.
11(970)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Peng S, Xu LW, Che XY, Xiao QQ, Pu J, Shao
Q and He B: Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory response, attenuates
lipid deposition, and improves the stability of vulnerable
atherosclerotic plaques by modulating autophagy. Front Pharmacol.
9(438)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Michiels CF, Kurdi A, Timmermans JP, De
Meyer GRY and Martinet W: Spermidine reduces lipid accumulation and
necrotic core formation in atherosclerotic plaques via induction of
autophagy. Atherosclerosis. 251:319–327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen HY, Xiao ZZ, Ling X, Xu RN, Zhu P and
Zheng SY: ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and
promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
regulating autophagy. Mol Med. 27(14)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nandi SS, Katsurada K, Sharma NM, Anderson
DR, Mahata SK and Patel KP: MMP9 inhibition increases autophagic
flux in chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
319:H1414–H1437. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang B, Nie J, Wu L, Hu Y, Wen Z, Dong L,
Zou MH, Chen C and Wang DW: AMPKα2 protects against the development
of heart failure by enhancing mitophagy via PINK1 phosphorylation.
Circ Res. 122:712–729. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Zheng Q, Wang K, Luo J, Wang Z, Li
H, Liu Z, Dong N and Shi J: Sam68 promotes osteogenic
differentiation of aortic valvular interstitial cells by
TNF-α/STAT3/autophagy axis. J Cell Commun Signal. 17:863–879.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Carracedo M, Persson O, Saliba-Gustafsson
P, Artiach G, Ehrenborg E, Eriksson P, Franco-Cereceda A and Bäck
M: Upregulated autophagy in calcific aortic valve stenosis confers
protection of valvular interstitial cells. Int J Mol Sci.
20(1486)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bossé Y, Miqdad A, Fournier D, Pépin A,
Pibarot P and Mathieu P: Refining molecular pathways leading to
calcific aortic valve stenosis by studying gene expression profile
of normal and calcified stenotic human aortic valves. Circulation.
Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2:489–498. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rysä J: Gene expression profiling of human
calcific aortic valve disease. Genom Data. 7:107–108.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang NN, Dong J, Zhang L, Ouyang D, Cheng
Y, Chen AF, Lu AP and Cao DS: HAMdb: A database of human autophagy
modulators with specific pathway and disease information. J
Cheminform. 10(34)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Moussay E, Kaoma T, Baginska J, Muller A,
Van Moer K, Nicot N, Nazarov PV, Vallar L, Chouaib S, Berchem G and
Janji B: The acquisition of resistance to TNFα in breast cancer
cells is associated with constitutive activation of autophagy as
revealed by a transcriptome analysis using a custom microarray.
Autophagy. 7:760–770. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Homma K, Suzuki K and Sugawara H: The
autophagy database: An all-inclusive information resource on
autophagy that provides nourishment for research. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D986–D990. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lin G, Chai J, Yuan S, Mai C, Cai L,
Murphy RW, Zhou W and Luo J: VennPainter: A tool for the comparison
and identification of candidate genes based on venn diagrams. PLoS
One. 11(e0154315)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yoo M, Shin J, Kim J, Ryall KA, Lee K, Lee
S, Jeon M, Kang J and Tan AC: DSigDB: Drug signatures database for
gene set analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:3069–3071. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Broeders W, Bekkering S, El Messaoudi S,
Joosten LAB, van Royen N and Riksen NP: . Innate immune cells in
the pathophysiology of calcific aortic valve disease: Lessons to be
learned from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease? Basic Res
Cardiol. 117(28)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mathieu P and Boulanger MC: Basic
mechanisms of calcific aortic valve disease. Can J Cardiol.
30:982–993. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kostyunin AE, Yuzhalin AE, Ovcharenko EA
and Kutikhin AG: Development of calcific aortic valve disease: Do
we know enough for new clinical trials? J Mol Cell Cardiol.
132:189–209. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gould ST, Srigunapalan S, Simmons CA and
Anseth KS: Hemodynamic and cellular response feedback in calcific
aortic valve disease. Circ Res. 113:186–197. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xie W, Shan Y, Wu Z, Liu N, Yang J, Zhang
H, Sun S, Chi J, Feng W, Lin H and Guo H: Herpud1 deficiency
alleviates homocysteine-induced aortic valve calcification. Cell
Biol Toxicol. 39:2665–2684. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Biasizzo M and Kopitar-Jerala N: Interplay
between NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy. Front Immunol.
11(591803)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu H, Che X, Zheng Q, Wu A, Pan K, Shao A,
Wu Q, Zhang J and Hong Y: Caspases: A molecular switch node in the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci.
10:1072–1083. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xue JF, Shi ZM, Zou J and Li XL:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of
articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats
with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1252–1261.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lépine S, Allegood JC, Park M, Dent P,
Milstien S and Spiegel S: Sphingosine-1-phosphate
phosphohydrolase-1 regulates ER stress-induced autophagy. Cell
Death Differ. 18:350–361. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Peacock JD, Huk DJ, Ediriweera HN and
Lincoln J: Sox9 transcriptionally represses Spp1 to prevent matrix
mineralization in maturing heart valves and chondrocytes. PLoS One.
6(e26769)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Grootaert MO, da Costa Martins PA, Bitsch
N, Pintelon I, De Meyer GR, Martinet W and Schrijvers DM: Defective
autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells accelerates senescence
and promotes neointima formation and atherogenesis. Autophagy.
11:2014–2032. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ma Q, Zhang N, You Y, Zhu J, Yu Z, Chen H,
Xie X and Yu H: CXCR4 blockade in macrophage promotes angiogenesis
in ischemic hindlimb by modulating autophagy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
169:57–70. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Priego AR, Parra EG, Mas S,
Morgado-Pascual JL, Ruiz-Ortega M and Rayego-Mateos S: Bisphenol A
modulates autophagy and exacerbates chronic kidney damage in mice.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(7189)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Samiei N, Hosseini S, Maleki M, Moradi L,
Joghataei MT and Arabian M: Modulatory role of SIRT1 and resistin
as therapeutic targets in patients with aortic valve stenosis. Arch
Med Res. 50:333–341. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ohlsson C, Langenskiöld M, Smidfelt K,
Poutanen M, Ryberg H, Norlén AK, Nordanstig J, Bergström G and
Tivesten Å: Low progesterone and low estradiol levels associate
with abdominal aortic aneurysms in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
107:e1413–e1425. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Feng Y, Chen Y, Wu X, Chen J, Zhou Q, Liu
B, Zhang L and Yi C: Interplay of energy metabolism and autophagy.
Autophagy. 20:4–14. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fang J, Qian Y, Chen J, Xu D, Cao N, Zhu
G, Hu W, Hu H, Qian N, Yang S, et al: Human antigen R regulates
autophagic flux by stabilizing autophagy-associated mRNA in
calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovasc Res. 119:2117–2129.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|