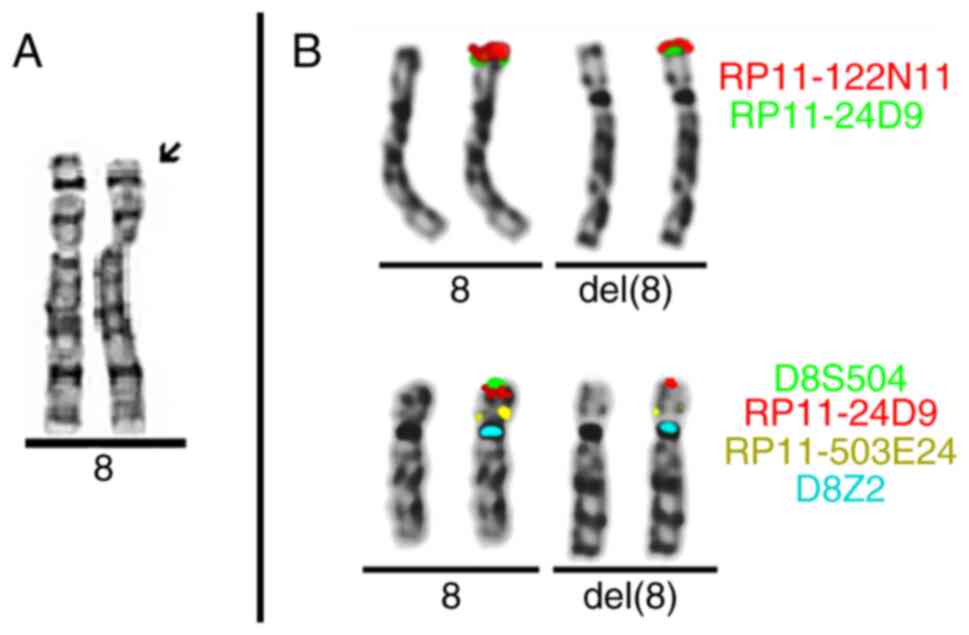
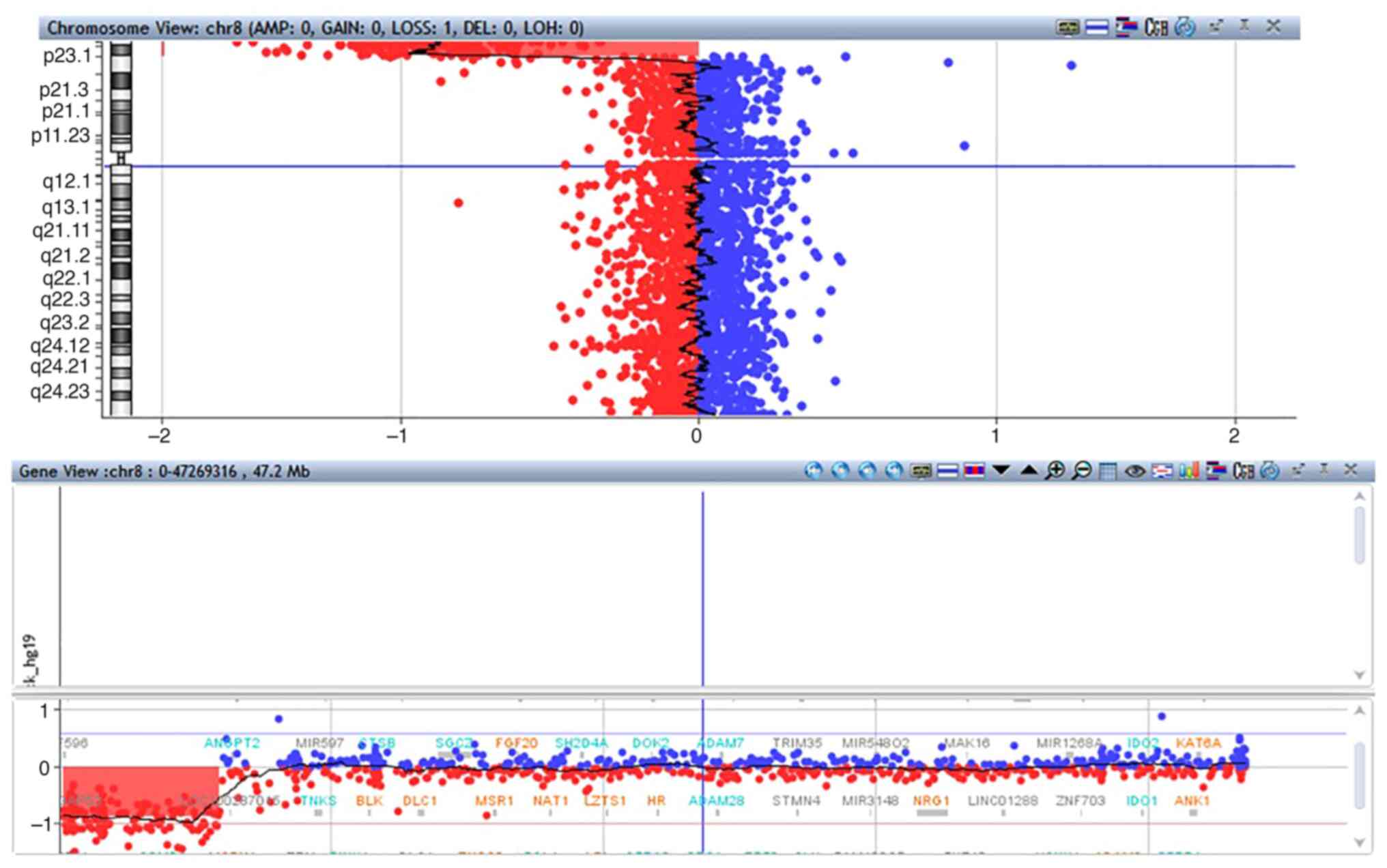
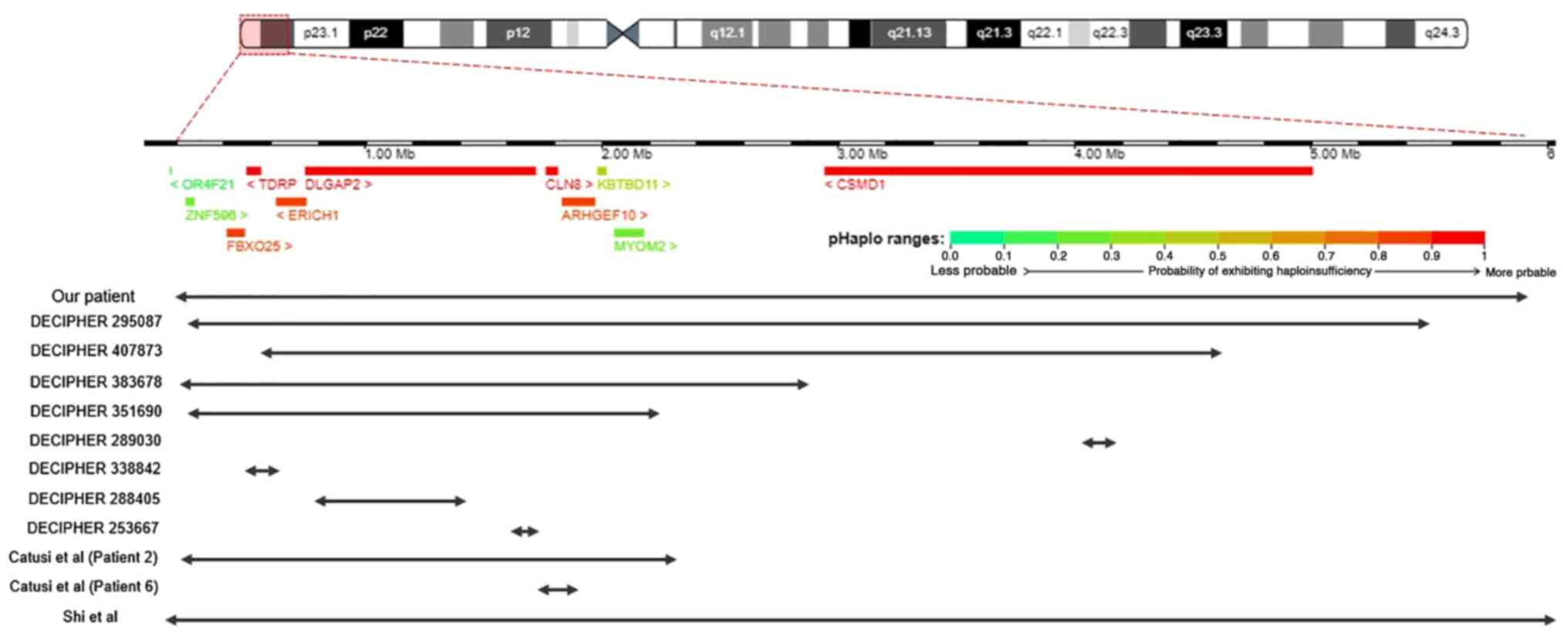
|
1
|
Yu S, Fiedler S, Stegner A and Graf WD:
Genomic profile of copy number variants on the short arm of human
chromosome 8. Eur J Hum Genet. 18:1114–1120. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shi S, Lin S, Chen B and Zhou Y: Isolated
chromosome 8p23.2-pter deletion: Novel evidence for developmental
delay, intellectual disability, microcephaly and neurobehavioral
disorders. Mol Med Rep. 16:6837–6845. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Páez MT, Yamamoto T, Hayashi K, Yasuda T,
Harada N, Matsumoto N, Kurosawa K, Furutani Y, Asakawa S, Shimizu N
and Matsuoka R: Two patients with atypical interstitial deletions
of 8p23.1: Mapping of phenotypical traits. Am J Med Genet A.
146A:1158–1165. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Catusi I, Garzo M, Capra AP, Briuglia S,
Baldo C, Canevini MP, Cantone R, Elia F, Forzano F, Galesi O, et
al: 8p23.2-pter microdeletions: Seven new cases narrowing the
candidate region and review of the literature. Genes (Basel).
12(652)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Die-Smulders CE, Engelen JJ,
Schrander-Stumpel CT, Govaerts LC, de Vries B, Vles JS, Wagemans A,
Schijns-Fleuren S, Gillessen-Kaesbach G and Fryns JP: Inversion
duplication of the short arm of chromosome 8: Clinical data on
seven patients and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet.
59:369–374. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
García-Santiago FA, Martínez-Glez V,
Santos F, García-Miñaur S, Mansilla E, Meneses AG, Rosell J,
Granero ÁP, Vallespín E, Fernández L, et al: Analysis of
invdupdel(8p) rearrangement: Clinical, cytogenetic and molecular
characterization. Am J Med Genet A. 167A:1018–1025. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wat MJ, Shchelochkov OA, Holder AM, Breman
AM, Dagli A, Bacino C, Scaglia F, Zori RT, Cheung SW, Scott DA and
Kang SH: Chromosome 8p23.1 deletions as a cause of complex
congenital heart defects and diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Med Genet
A. 149A:1661–1677. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ballarati L, Cereda A, Caselli R,
Selicorni A, Recalcati MP, Maitz S, Finelli P, Larizza L and
Giardino D: Genotype-phenotype correlations in a new case of 8p23.1
deletion and review of the literature. Eur J Med Genet. 54:55–59.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Burnside RD, Pappas JG, Sacharow S,
Applegate C, Hamosh A, Gadi IK, Jaswaney V, Keitges E, Phillips KK,
Potluri VR, et al: Three cases of isolated terminal deletion of
chromosome 8p without heart defects presenting with a mild
phenotype. Am J Med Genet A. 161A:822–828. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu Y, Ji T, Wang J, Xiao J, Wang H, Li J,
Gao Z, Yang Y, Cai B, Wang L, et al: Submicroscopic subtelomeric
aberrations in Chinese patients with unexplained developmental
delay/mental retardation. BMC Med Genet. 11(72)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Verhoeven K, De Jonghe P, Van de Putte T,
Nelis E, Zwijsen A, Verpoorten N, De Vriendt E, Jacobs A, Van
Gerwen V, Francis A, et al: Slowed conduction and thin myelination
of peripheral nerves associated with mutant rho guanine-nucleotide
exchange factor 10. Am J Hum Genet. 73:926–932. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mole SE, Williams RE and Goebel HH:
Correlations between genotype, ultrastructural morphology and
clinical phenotype in the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses.
Neurogenetics. 6:107–126. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Passantino R, Cascio C, Deidda I, Galizzi
G, Russo D, Spedale G and Guarneri P: Identifying protein partners
of CLN8, an ER-resident protein involved in neuronal ceroid
lipofuscinosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:529–540. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rasmussen AH, Rasmussen HB and
Silahtaroglu A: The DLGAP family: Neuronal expression, function and
role in brain disorders. Mol Brain. 10(43)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kraus DM, Elliott GS, Chute H, Horan T,
Pfenninger KH, Sanford SD, Foster S, Scully S, Welcher AA and
Holers VM: CSMD1 is a novel multiple domain complement-regulatory
protein highly expressed in the central nervous system and
epithelial tissues. J Immunol. 176:4419–4430. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gayed EMAE, Rizk MS, Ramadan AN and Bayomy
NR: mRNA expression of the CUB and sushi multiple domains 1 (CSMD1)
and its serum protein level as predictors for psychosis in the
familial high-risk children and young adults. ACS Omega.
6(24128)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|