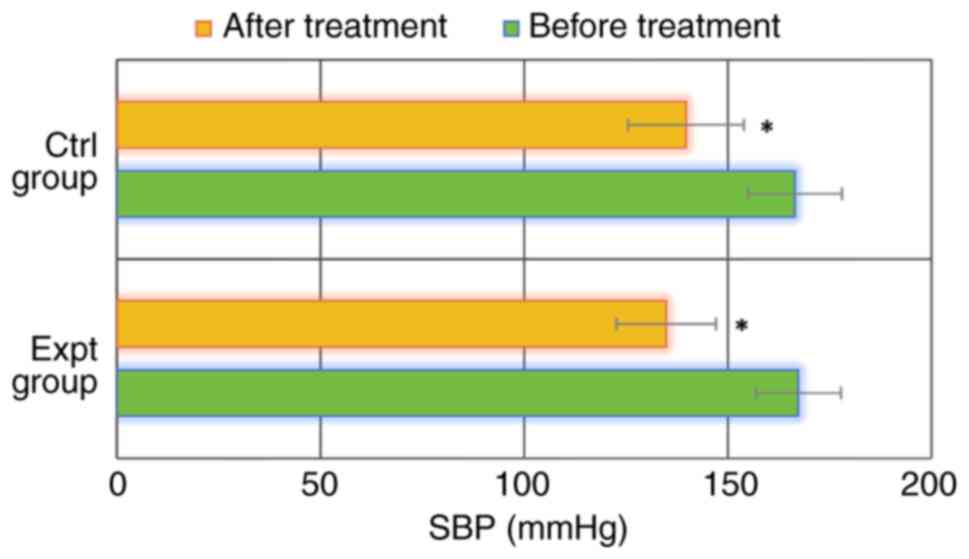
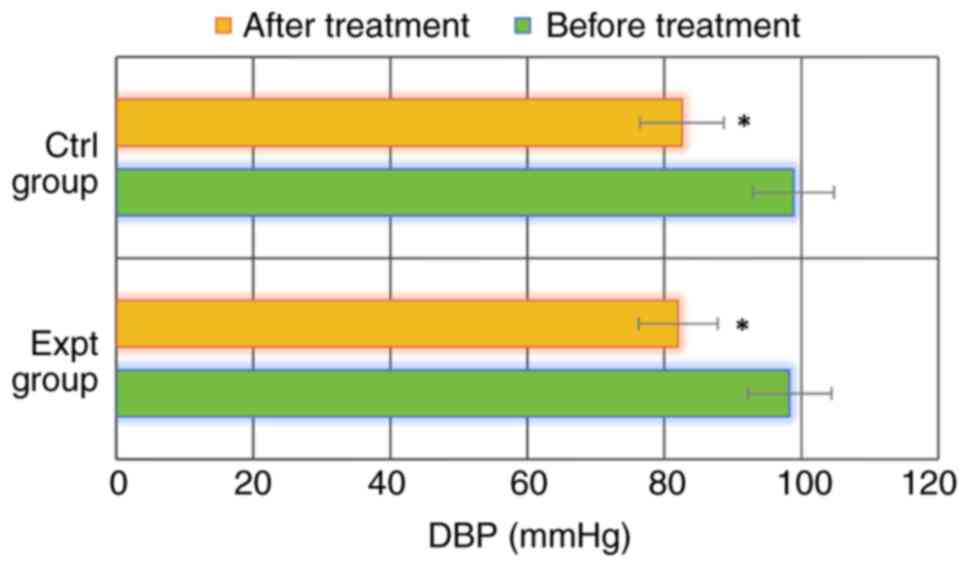
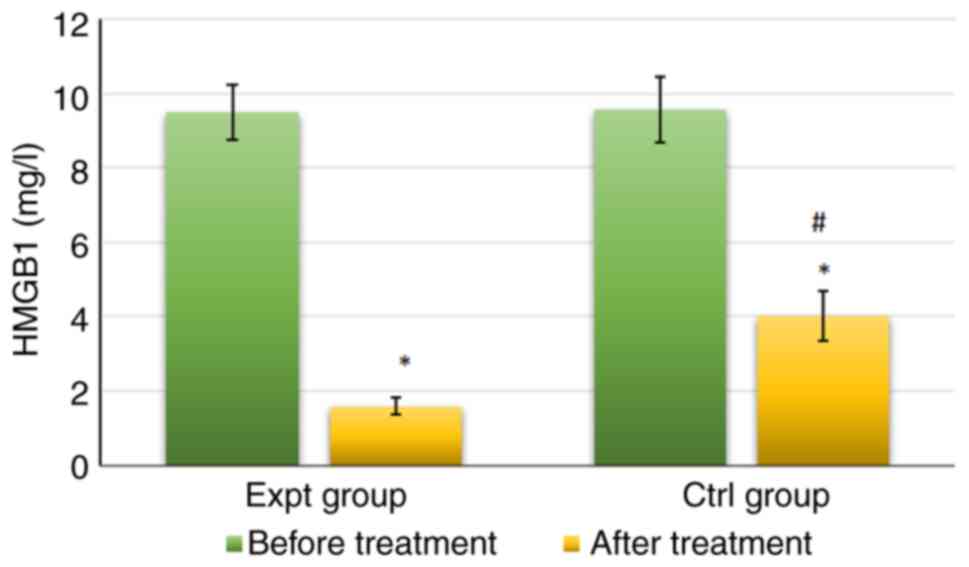
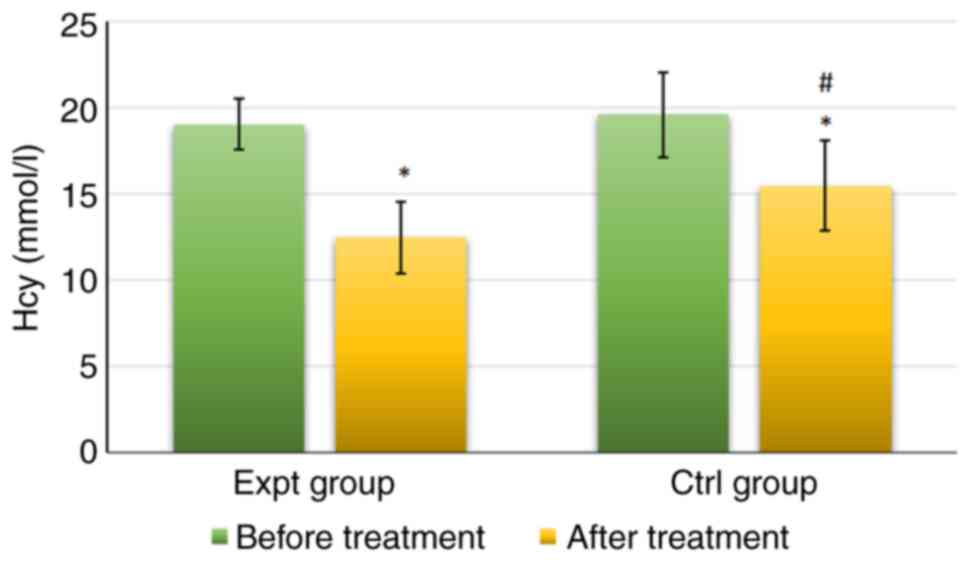
|
1
|
Magee LA, Brown MA, Hall DR, Gupte S,
Hennessy A, Karumanchi SA, Kenny LC, McCarthy F, Myers J, Poon LC,
et al: The 2021 International Society for the Study of Hypertension
in Pregnancy classification, diagnosis & management
recommendations for international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens.
27:148–169. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Corrigan L, O'Farrell A, Moran P and Daly
D: Hypertension in pregnancy: Prevalence, risk factors and outcomes
for women birthing in Ireland. Pregnancy Hypertens. 24:1–6.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Brown MA, Magee LA, Kenny LC, Karumanchi
SA, McCarthy FP, Saito S, Hall DR, Warren CE, Adoyi G and Ishaku S:
International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy
(ISSHP). The hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: ISSHP
classification, diagnosis & management recommendations for
international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens. 13:291–310.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tan JS, Liu NN, Guo TT, Hu S and Hua L:
Genetic predisposition to COVID-19 may increase the risk of
hypertension disorders in pregnancy: A two-sample Mendelian
randomization study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 26:17–23. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ma XL, Zhai X, Liu JW, Xue XX, Guo SZ, Xie
H, Chen JX, Zhao HH and Wang W: Study on the biological basis of
hypertension and syndrome with liver-fire hyperactivity based on
data mining technology. World J Tradit Chin Med. 4:176–180.
2018.
|
|
6
|
Thombre Kulkarni M, Holzman C, Wasilevich
E, Luo Z, Scheid J and Allswede M: Pregnancy hypertension and its
associations with pre-pregnancy depression, anxiety,
antidepressants, and anxiolytics. Pregnancy Hypertens. 16:67–74.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen L, Shortreed SM, Easterling T,
Cheetham TC, Reynolds K, Avalos LA, Kamineni A, Holt V, Neugebauer
R, Akosile M, et al: Identifying hypertension in pregnancy using
electronic medical records: The importance of blood pressure
values. Pregnancy Hypertens. 19:112–118. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ives CW, Sinkey R, Rajapreyar I, Tita ATN
and Oparil S: Preeclampsia-Pathophysiology and Clinical
Presentations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol.
76:1690–1702. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ishikuro M, Murakami K, Yokozeki F, Onuma
T, Noda A, Ueno F, Obara T and Kuriyama S: Hypertension in
pregnancy as a possible factor for child autistic behavior at two
years old. Pregnancy Hypertens. 25:88–90. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Avorgbedor F, Silva S, McCoy TP,
Blumenthal JA, Merwin E, Seonae Y and Holditch-Davis D:
Hypertension and infant outcomes: North Carolina pregnancy risks
assessment monitoring system data. Pregnancy Hypertens. 28:189–193.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ukah UV, De Silva DA, Payne B, Magee LA,
Hutcheon JA, Brown H, Ansermino JM, Lee T and von Dadelszen P:
Prediction of adverse maternal outcomes from pre-eclampsia and
other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A systematic review.
Pregnancy Hypertens. 11:115–123. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cheu LA, Drexler K and Kominiarek MA:
Using m-Health apps to diagnose hypertension in pregnancy.
Pregnancy Hypertens. 22:99–100. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sahni S, Palkar AV, Rochelson BL, Kępa W
and Talwar A: Pregnancy and pulmonary arterial hypertension: A
clinical conundrum. Pregnancy Hypertens. 5:157–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fletcher B, Chappell LC, Lavallee L,
Wilson HM, Stevens R, Mackillop L, McManus RJ and Tucker KL:
Changes to management of hypertension in pregnancy, and attitudes
to self-management: An online survey of obstetricians, before and
following the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 26:54–61. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Du Q, Jovanović S, Tulić L, Tulić I and
Jovanović A: Pregnancy-induced hypertension is associated with
down-regulation of Kir6.1 in human myometrium. Pregnancy Hypertens.
18:96–98. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Badon SE, Dublin S, Nance N, Hedderson MM,
Neugebauer R, Easterling T, Cheetham TC, Chen L, Holt VL and Avalos
LA: Gestational weight gain and adverse pregnancy outcomes by
pre-pregnancy BMI category in women with chronic hypertension: A
cohort study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 23:27–33. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Naeh A and Ray JG: Pregnancy hypertension:
An international journal of women's cardiovascular health-Reply:
Letter to the editor. Pregnancy Hypertens. 30(96)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lu CQ, Lin J, Yuan L, Zhou JG, Liang K,
Zhong QH, Huang JH, Xu LP, Wu H, Zheng Z, et al: Pregnancy induced
hypertension and outcomes in early and moderate preterm infants.
Pregnancy Hypertens. 14:68–71. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Myerscough PR: Infant growth and
development after treatment of maternal hypertension. Lancet.
1(883)1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vidyasagar S, Kumar S and Morton A:
Screening for primary aldosteronism in pregnancy. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 25:171–174. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nash CM and Shetty N: Current state of
affairs: A study regarding diagnosis, treatment and use of home
blood pressure monitoring for hypertension in pregnancy. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 24:96–99. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gasnier R, Valério EG, Vettorazzi J,
Martins-Costa SH, Barros EG and Ramos JG: Calcium-to-creatinine
ratio in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Pregnancy Hypertens.
2:59–64. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu JF and Nightingale CH: Magnesium
sulfate in eclampsia and pre-eclampsia: Pharmacokinetic principles.
Clin Pharmacokinet. 38:305–314. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Okusanya BO, Oladapo OT, Long Q,
Lumbiganon P, Carroli G, Qureshi Z, Duley L, Souza JP and
Gülmezoglu AM: Clinical pharmacokinetic properties of magnesium
sulphate in women with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. BJOG.
123:356–366. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Wang DJ, Zhang Y, Zhang YX and Zhang
R: Regulation of magnesium sulfate combined with nifedipine and
labetalol on disease-related molecules in serum and placenta in the
treatment of preeclampsia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:5062–5070.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Podymow T and August P: Antihypertensive
drugs in pregnancy. Semin Nephrol. 31:70–85. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
DeSisto CL, Robbins CL, Ritchey MD, Ewing
AC, Ko JY and Kuklina EV: Hypertension at delivery
hospitalization-United States, 2016-2017. Pregnancy Hypertens.
26:65–68. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nzelu D, Dumitrascu-Biris D, Hunt KF,
Cordina M and Kametas NA: Pregnancy outcomes in women with previous
gestational hypertension: A cohort study to guide counselling and
management. Pregnancy Hypertens. 12:194–200. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mhiri R, Mvogo A, Kamga A, Yassinguezo S,
Fagla H, Dotou D and Kallel H: Epidemiology and maternal prognosis
of hypertension disorders of pregnancy in French Guiana. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 20:96–101. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rodrigues Â, Barata C, Marques I and
Almeida MC: Diagnosis of White Coat Hypertension and pregnancy
outcomes. Pregnancy Hypertens. 14:121–124. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Akbar MIA, Adibrata MA, Aditiawarman
Aryananda RA, Angsar MD and Dekker G: Maternal and perinatal
outcome related to severity of chronic hypertension in pregnancy.
Pregnancy Hypertens. 16:154–160. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bowen L, Pealing L, Tucker K, McManus RJ
and Chappell LC: Adherence with blood pressure self-monitoring in
women with pregnancy hypertension, and comparisons to clinic
readings: A secondary analysis of OPTIMUM-BP. Pregnancy Hypertens.
25:68–74. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nguyen NTT, Kurtovic K, Mitchell C,
Evangelista M, Del Valle R, McWay Boling S and Hughes BL: Improving
treatment of severe hypertension in pregnancy and postpartum using
a hypertensive pathway. Pregnancy Hypertens. 30:1–6.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Easterling T, Mundle S, Bracken H,
Parvekar S, Mool S, Magee LA, von Dadelszen P, Shochet T and
Winikoff B: Oral antihypertensive regimens (nifedipine retard,
labetalol, and methyldopa) for management of severe hypertension in
pregnancy: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
394:1011–1021. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gupta A, Nayak D, Sharma J and
Keepanasseril A: Comparing the efficacy of oral labetalol with oral
amlodipine in achieving blood pressure control in women with
postpartum hypertension: Randomized controlled trial (HIPPO
study-Hypertension In Pregnancy & Postpartum
Oral-antihypertensive therapy). J Hum Hypertens. 37:1056–1062.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Muhammad S, Usman H, Dawha YM, Yahya A,
Yekeen A and Bako B: Comparison of intravenous labetalol and
hydralazine for severe hypertension in pregnancy in Northeastern
Nigeria: A randomized controlled trial. Pregnancy Hypertens.
29:1–6. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
He Y, Tian J, Blizzard L, Oddy WH, Dwyer T
and Venn AJ: Associations of childhood adiposity and changes in
adiposity status from childhood to adulthood with pregnancy
hypertension. Pregnancy Hypertens. 19:218–225. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Zhang H, Chen Q, Jiao F, Shi C,
Pei M, Lv J, Zhang H, Wang L and Gong Z: TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation
signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and
acute kidney injury. Cell Prolif. 53(e12829)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu X, Piao HN, Aosai F, Zeng XY, Cheng JH,
Cui YX, Li J, Ma J, Piao HR, Jin X and Piao LX: Arctigenin protects
against depression by inhibiting microglial activation and
neuroinflammation via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and TNF-α/TNFR1/NF-κB
pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 177:5224–5245. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Webster LM, Reed K, Myers JE, Burns A,
Gupta P, Patel P, Wiesender C, Seed PT and Nelson-Piercy C and
Nelson-Piercy C: Quantifying adherence to antihypertensive
medication for chronic hypertension during pregnancy. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 17:12–14. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Gressner AM, Lahme B, Meurer SK, Gressner
O and Weiskirchen R: Variable expression of cystatin C in cultured
trans-differentiating rat hepatic stellate cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:731–738. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xu CC, Fu GX, Liu QQ and Zhong Y:
Association between cystatin C and heart failure with preserved
ejection fraction in elderly Chinese patients. Z Gerontol Geriatr.
51:92–97. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dikovskaya MA, Russkikh GS, Loktev KV,
Johnston TP, Gevorgyan MM, Voronina NP, Chernykh VV, Trunov AN and
Korolenko TA: Cystatin C and cystatin SN as possible soluble tumor
markers in malignant uveal melanoma. Radiol Oncol. 56:83–91.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xu B, Charlton F, Makris A and Hennessy A:
PP042. Anti-hypertensive drugs hydralazine, clonidine and labetalol
improve trophoblast integration into endothelial cellular networks
in vitro. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2(264)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu B, Bobek G, Makris A and Hennessy A:
Antihypertensive methyldopa, labetalol, hydralazine, and clonidine
reversed tumour necrosis factor-α inhibited endothelial nitric
oxide synthase expression in endothelial-trophoblast cellular
networks. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 44:421–427. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tooher J, Thornton C, Makris A, Korda A,
Ogle R, Horvath J and Hennessy A: PP102. Hypertension in pregnancy
and long term cardiovascular mortality outcomes. Pregnancy
Hypertens. 2(295)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
MacCarthy EP and Bloomfield SS: Labetalol:
A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses and
adverse effects. Pharmacotherapy. 3:193–219. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Visser VS, Hermes W, Twisk J, Franx A, van
Pampus MG, Koopmans C, Mol BWJ and de Groot CJM: Prognostic model
for chronic hypertension in women with a history of hypertensive
pregnancy disorders at term. Pregnancy Hypertens. 10:118–123.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Magee LA, Rey E, Asztalos E, Hutton E,
Singer J, Helewa M, Lee T, Logan AG, Ganzevoort W, Welch R, et al:
Management of non-severe pregnancy hypertension-A summary of the
CHIPS Trial (Control of Hypertension in Pregnancy Study) research
publications. Pregnancy Hypertens. 18:156–162. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Oogaki Y, Ozawa R, Seshima K, Shinoda R,
Torii Y, Takahashi H, Iwata H, Kuwayama T and Shirasuna K: Uncaria
tomentosa extract (AC-11) improves pregnancy hypertension together
with suppression of sFlt-1 and sEng. Pregnancy Hypertens.
26:127–132. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hauspurg A, Countouris ME, Jeyabalan A,
Hubel CA, Roberts JM, Schwarz EB and Catov JM: Risk of hypertension
and abnormal biomarkers in the first year postpartum associated
with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy among overweight and obese
women. Pregnancy Hypertens. 15:1–6. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|