|
1
|
Kuznia AL, Hernandez AK and Lee LU:
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Common questions and answers. Am
Fam Physician. 101:19–23. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Addai D, Zarkos J and Bowey AJ: Current
concepts in the diagnosis and management of adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 36:1111–1119. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hefti F: Pathogenesis and biomechanics of
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). J Child Orthop. 7:17–24.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Smit TH: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:
The mechanobiology of differential growth. JOR Spine.
3(e1115)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lin J, Wong CKH, Cheung JPY, Cheung PWH
and Luo N: Psychometric performance of proxy-reported EQ-5D youth
version 5-level (EQ-5D-Y-5L) in comparison with three-level
(EQ-5D-Y-3L) in children and adolescents with scoliosis. Eur J
Health Econ. 23:1383–1395. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kaviani R, Londono I, Parent S, Moldovan F
and Villemure I: Growth plate cartilage shows different strain
patterns in response to static versus dynamic mechanical
modulation. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 15:933–946. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Swany LM, Larson AN, Milbrandt TA, Sanders
JO, Neal KM, Blakemore LC, Newton PO, Pahys JM, Cahill PJ and
Alanay A: Inter- and intra-rater reliability and accuracy of
sanders skeletal maturity staging system when used by surgeons
performing vertebral body tethering. Spine Deform. 10:97–106.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gargano G, Oliva F, Migliorini F and
Maffulli N: Melatonin and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: The
present evidence. Surgeon. 20:e315–e321. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liang ZT, Guo CF, Li J and Zhang HQ: The
role of endocrine hormones in the pathogenesis of adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. FASEB J. 35(e21839)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chmielewska M, Janusz P, Andrusiewicz M,
Kotwicki T and Kotwicka M: Methylation of estrogen receptor 2
(ESR2) in deep paravertebral muscles and its association with
idiopathic scoliosis. Sci Rep. 10(22331)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wise CA: What causes AIS? Ask the genome!
Stud Health Technol Inform. 280:3–8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu B, Zhao S, Liu L, Du H, Zhao H, Wang
S, Niu Y, Li X and Qiu G: Deciphering disorders Involving Scoliosis
COmorbidities (DISCO) study group et al. Aberrant
interaction between mutated ADAMTSL2 and LTBP4 is associated with
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Gene. 814(146126)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sharma S, Gao X, Londono D, Devroy SE,
Mauldin KN, Frankel JT, Brandon JM, Zhang D, Li QZ, Dobbs MB, et
al: Genome-wide association studies of adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis suggest candidate susceptibility genes. Hum Mol Genet.
20:1456–1466. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhao L, Roffey DM and Chen S: association
between the estrogen receptor beta (ESR2) Rs1256120 single
nucleotide polymorphism and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
42:871–878. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kotwicki T, Janusz P, Andrusiewicz M,
Chmielewska M and Kotwicka M: Estrogen receptor 2 gene polymorphism
in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:E1599–E1607.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dai J, Lv ZT, Huang JM, Cheng P, Fang H
and Chen AM: Association between polymorphisms in vitamin D
receptor gene and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A meta-analysis.
Eur Spine J. 27:2175–2183. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Goździalska A, Jaśkiewicz J, Knapik-Czajka
M, Drąg J, Gawlik M, Cieśla M, Kulis A, Zarzycki D and Lipik E:
Association of calcium and phosphate balance, vitamin D, PTH, and
calcitonin in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 41:693–697. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Suh KT, Eun IS and Lee JS: Polymorphism in
vitamin D receptor is associated with bone mineral density in
patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J.
19:1545–1550. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guan M, Wang H, Fang H, Zhang C, Gao S and
Zou Y: Association between IGF1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism
(rs5742612) and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A meta-analysis.
Eur Spine J. 26:1624–1630. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang Y, Wu Z, Zhao T, Wang H, Zhao D,
Zhang J, Wang Y, Ding Y and Qiu G: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
and the single-nucleotide polymorphism of the growth hormone
receptor and IGF-1 genes. Orthopedics. 32(411)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nelson LM, Ward K and Ogilvie JW: Genetic
variants in melatonin synthesis and signaling pathway are not
associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 36:37–40. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nowak R, Kwiecien M, Tkacz M and Mazurek
U: Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling in
paravertebral muscles in juvenile and adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Biomed Res Int. 2014(594287)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Aulisa L, Papaleo P, Pola E, Angelini F,
Aulisa AG, Tamburrelli FC, Pola P and Logroscino CA: Association
between IL-6 and MMP-3 gene polymorphisms and adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis: A case-control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
32:2700–2702. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao J, Yang M and Li M: Association of
IL-6 and MMP-3 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis: A meta-analysis. J Genet. 95:573–579.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Norris JM, Simpson BS, Ball R, Freeman A,
Kirkham A, Parry MA, Moore CM, Whitaker HC and Emberton M: A
modified newcastle-ottawa scale for assessment of study quality in
genetic urological research. Eur Urol. 79:325–326. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
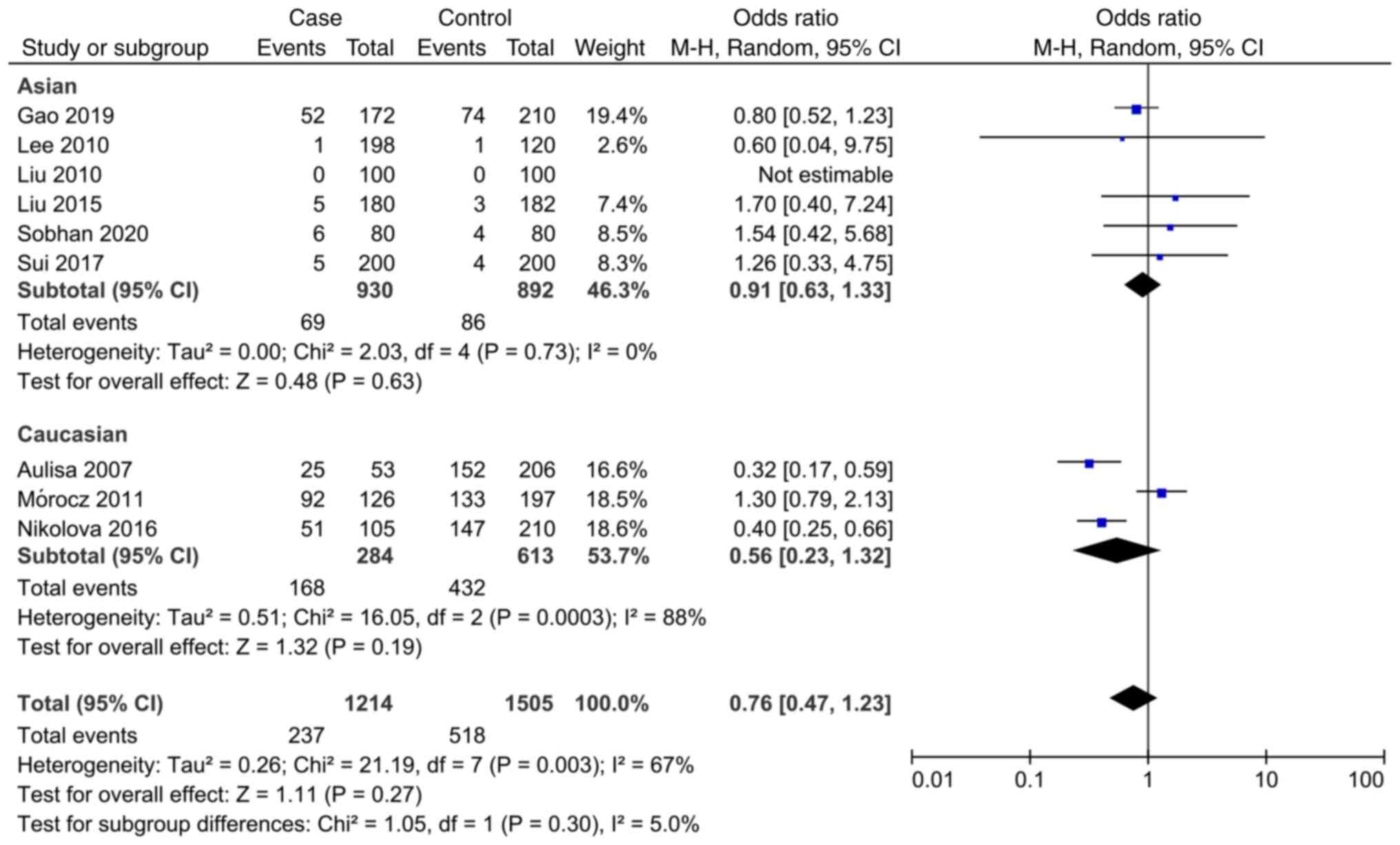
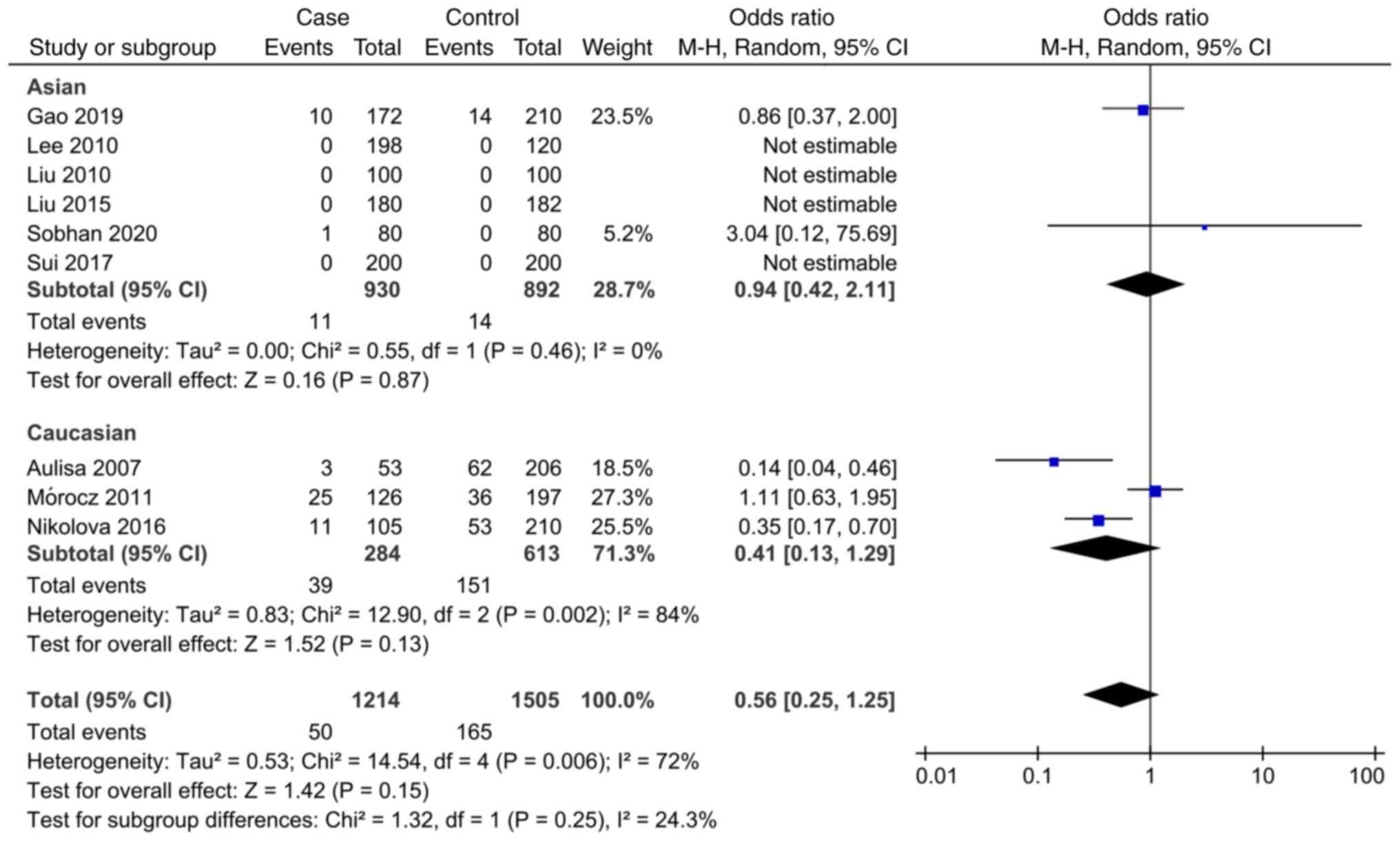
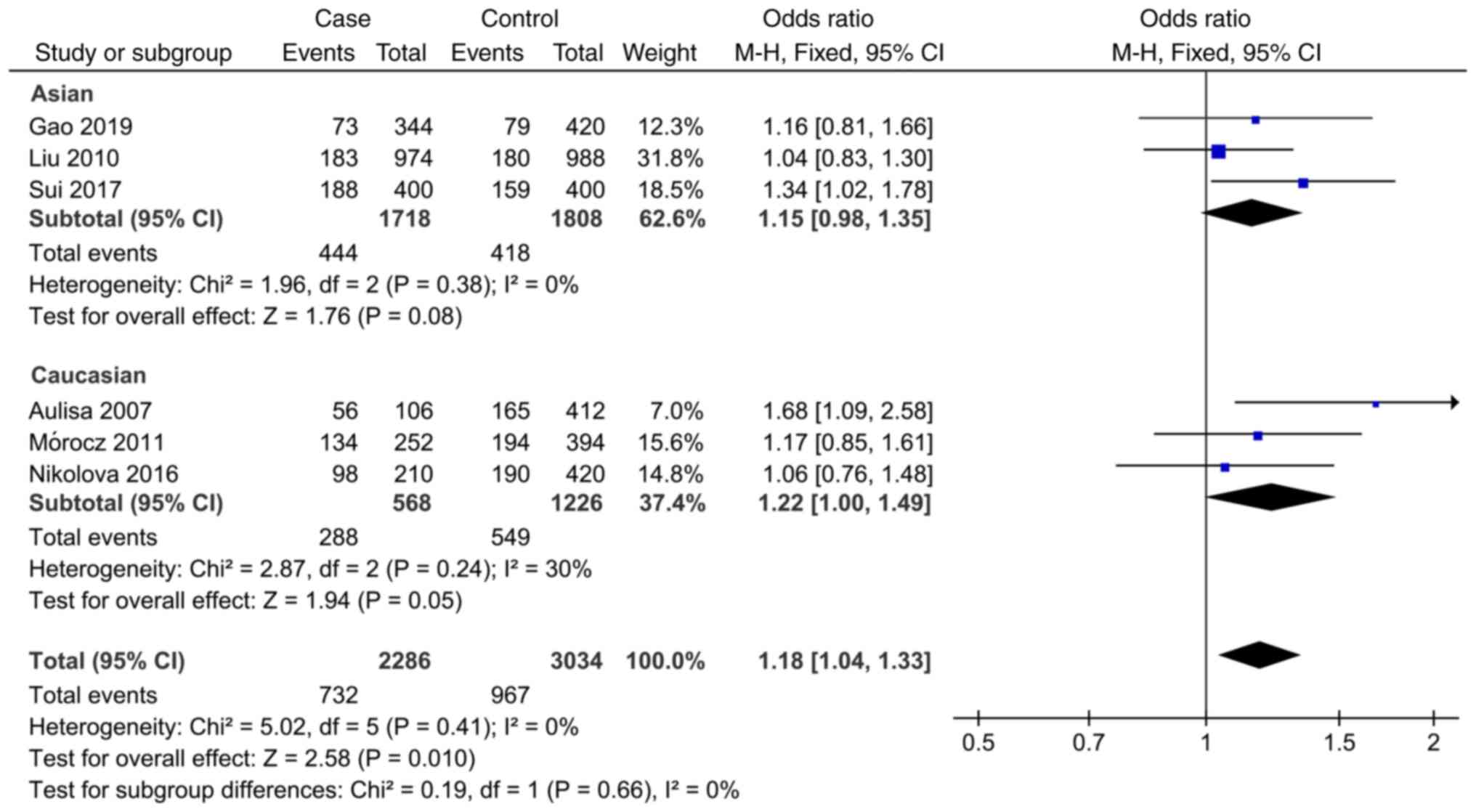
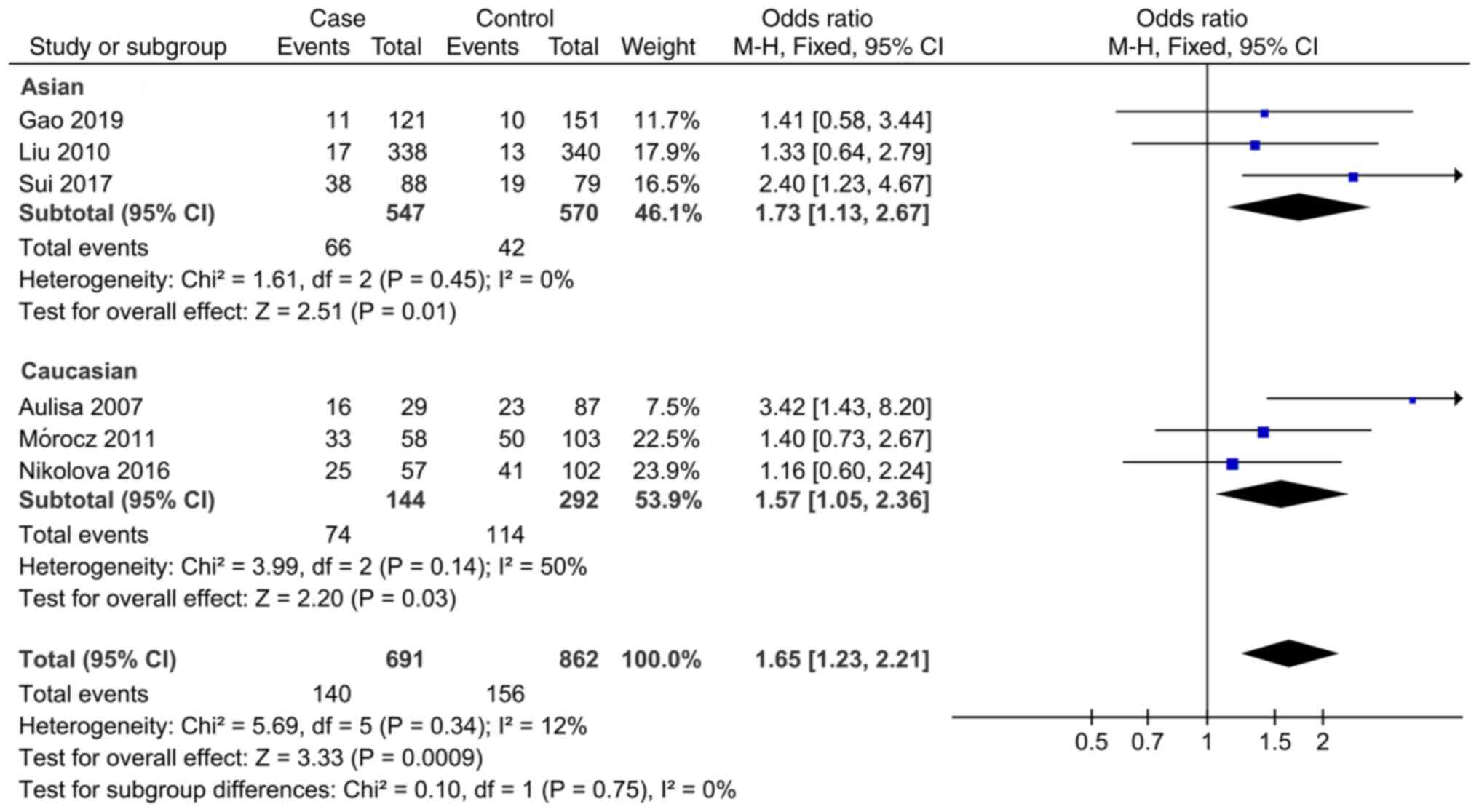
Sobhan MR, Mahdinezhad-Yazdi M, Dastgheib
SA, Ahrar H, Aghili K and Neamatzadeh H: Association of the
IL-6-174G > C (rs1800795) polymorphism with adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis: Evidence from a case-control study and
meta-analysis. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 55:17–26.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
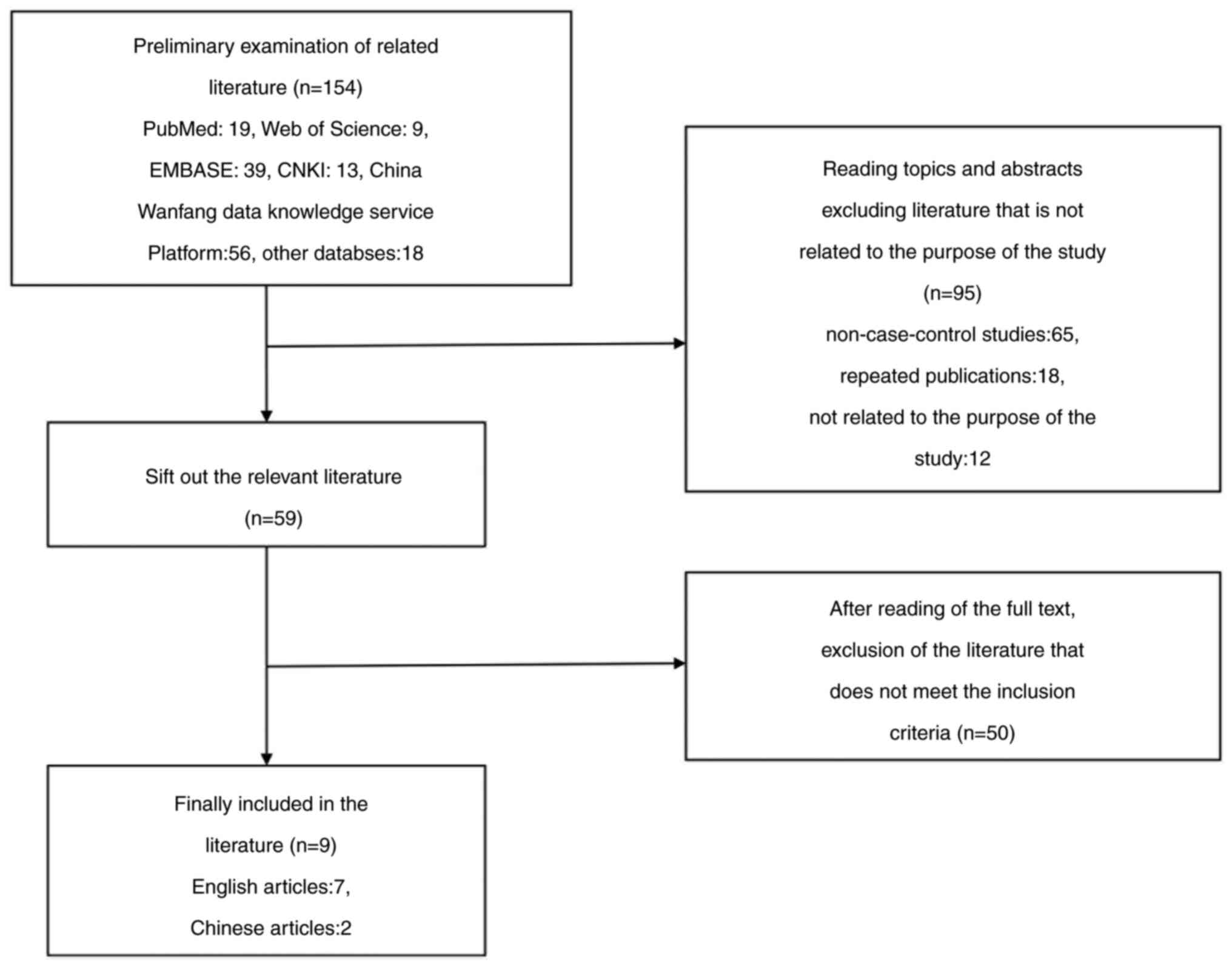
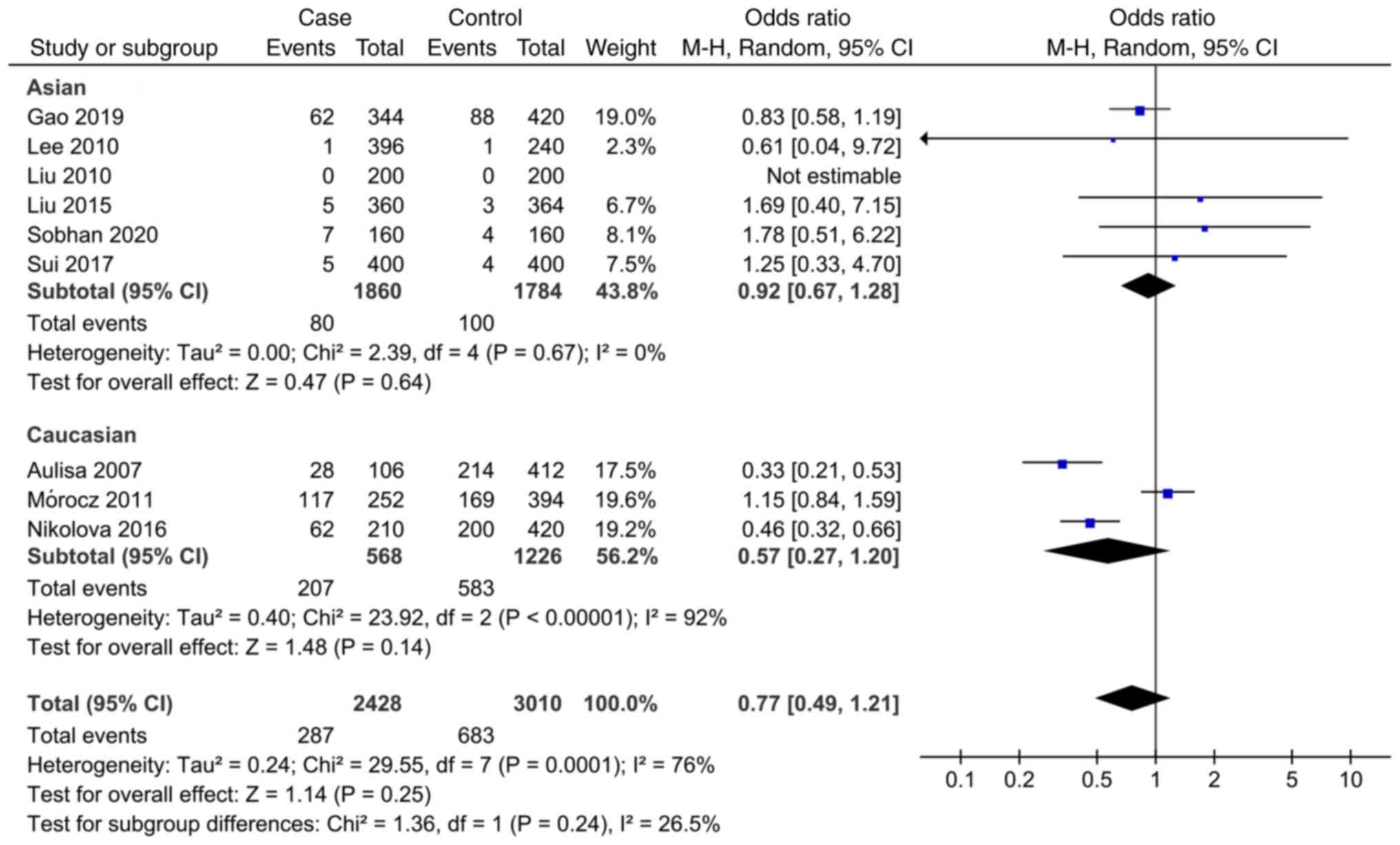
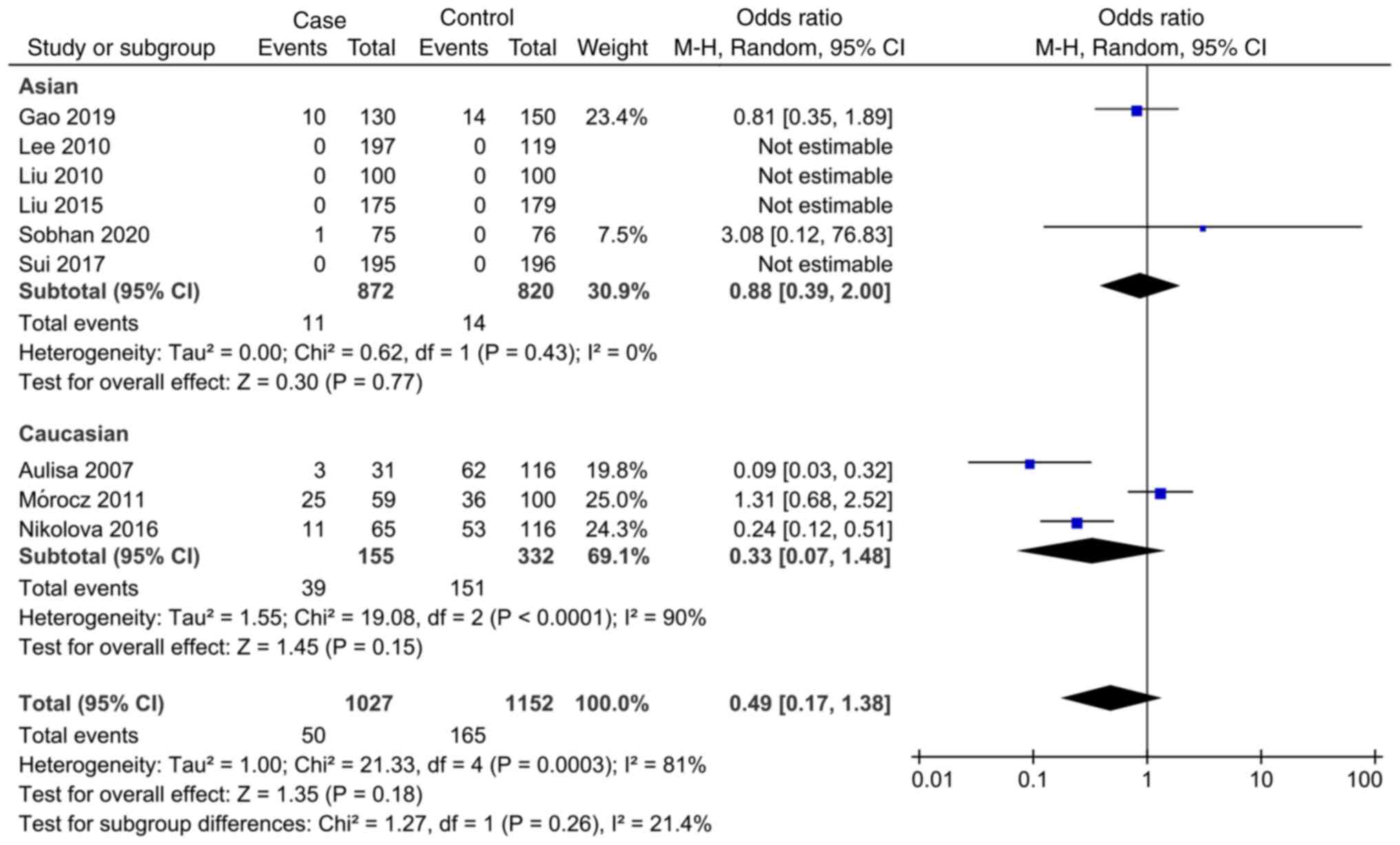
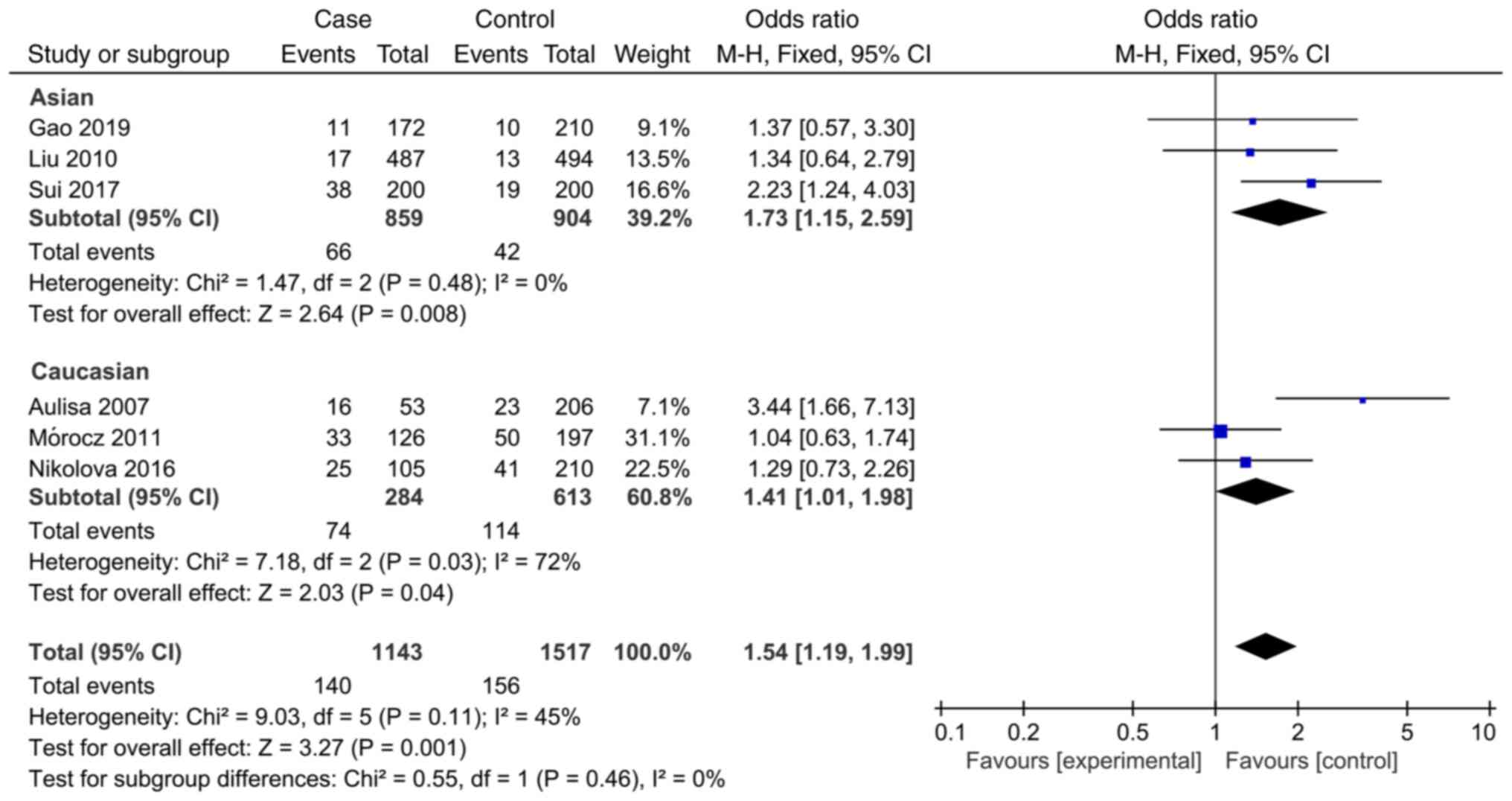
Gao S: Study on the relationship between
Interleukin-6, Matrix metalloproteinase-3 Gene Polymorphism and
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Doctoral thesis, Zhengzhou
University, 2019. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFDLAST2019&filename=1019115140.nh.
|
|
28
|
Sui W, Yang J, Huang Z, Wang Q, Fan H and
Deng Y: Polymorphisms in promoter regions of MMP-3 and IL-6 genes
are not associated to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) gender
bias. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 30:559–563. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nikolova ST, Yablanski VT, Vlaev EN,
Stokov LD, Savov AS, Kremensky IM and Loukanov AR: Association
between IL-6 and MMP3 common genetic polymorphisms and idiopathic
scoliosis in Bulgarian patients: A case-control study. Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 41:785–791. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu S: Association between Gene
Polymorphism and Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Northern
Chinese Han population. Doctoral thesis, Peking Union Medical
College, 2015. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFDLAST2015&filename=1015353939.nh.
|
|
31
|
Mórocz M, Czibula A, Grózer ZB, Szécsényi
A, Almos PZ, Raskó I and Illés T: Association study of BMP4, IL6,
Leptin, MMP3, and MTNR1B gene promoter polymorphisms and adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:E123–E130.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Tang NLS, Cao XB, Liu WJ, Qiu XS,
Cheng JCY and Qiu Y: Lack of association between the promoter
polymorphisms of MMP-3 and IL-6 genes and adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis: A case-control study in a Chinese Han population. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 35:1701–1705. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee JS, Suh KT and Eun IS: Polymorphism in
interleukin-6 gene is associated with bone mineral density in
patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg
Br. 92:1118–1122. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Labrom FR, Izatt MT, Askin GN, Labrom RD,
Claus AP and Little JP: Quantifying typical progression of
adolescent idiopathic Scoliosis: Longitudinal three-dimensional MRI
measures of disc and vertebral deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
48:1642–1651. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tang NLS, Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA, Qiu Y, Lam
TP, Cheng JCY and Hadley-Miller N: A decade in review after
idiopathic scoliosis was first called a complex trait-a tribute to
the late Dr. Yves Cotrel for his support in studies of etiology of
scoliosis. Genes (Basel). 12(1033)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang Y, Yang M, Shi D, Chen K, Zhao J, He
S, Bai Y, Shen P and Ni H: Single-cell RNA Seq reveals cellular
landscape-specific characteristics and potential etiologies for
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. JOR Spine. 4(e1184)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Khanshour AM, Kou I, Fan Y, Einarsdottir
E, Makki N, Kidane YH, Kere J, Grauers A, Johnson TA, Paria N, et
al: Genome-wide meta-analysis and replication studies in multiple
ethnicities identify novel adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
susceptibility loci. Hum Mol Genet. 27:3986–3998. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kreiner FF, Kraaijenhof JM, von Herrath M,
Hovingh GKK and von Scholten BJ: Interleukin 6 in diabetes, chronic
kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and
therapeutic perspectives. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 18:377–389.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Albrakati A, Alsharif KF, Al Omairi NE,
Alsanie WF, Almalki ASA, Elmageed ZY, Elshopakey GE, Lokman MS,
Bauomy AA, Moneim AE and Kassab RB: Neuroprotective efficiency of
prodigiosins conjugated with selenium nanoparticles in rats exposed
to chronic unpredictable mild stress is mediated through
antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and
neuromodulatory activities. Int J Nanomedicine. 16:8447–8464.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yamamoto Y, Kokubo Y, Nakajima H, Honjoh
K, Watanabe S and Matsumine A: Distribution and polarization of
hematogenous macrophages associated with the progression of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
47:E149–E158. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Schmidli MR, Sadowska A, Cvitas I,
Gantenbein B, Lischer HEL, Forterre S, Hitzl W, Forterre F and
Wuertz-Kozak K: Fibronectin fragments and inflammation during
canine intervertebral disc disease. Front Vet Sci.
7(547644)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen J, Mei Z, Huang B, Zhang X, Liu J,
Shan Z, Wang J, Wang X and Zhao F: IL-6/YAP1/β-catenin signaling is
involved in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol.
234:5964–5971. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zawilla NH, Darweesh H, Mansour N, Helal
S, Taha FM, Awadallah M and El Shazly R: Matrix
metalloproteinase-3, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, and
occupational risk factors in lumbar disc degeneration. J Occup
Rehabil. 24:370–381. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Takahashi M, Haro H, Wakabayashi Y,
Kawa-uchi T, Komori H and Shinomiya K: The association of
degeneration of the intervertebral disc with 5a/6a polymorphism in
the promoter of the human matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene. J Bone
Joint Surg Br. 83:491–495. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Nikolova S, Dikova M, Dikov D, Djerov A,
Dzhebir G, Atanasov V, Savov A and Kremensky I: Role of the IL-6
gene in the etiopathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Anal Cell
Pathol (Amst). 2015(621893)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ng PTT, Tucker K, Zahir SF, Izatt MT,
Straker L and Claus A: Comparison of physiological and behavioral
nutrition-related factors in people with and without adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis, from cohort data at 8 to 20 years. JBMR Plus.
8(ziad013)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Qin X, Sun K, Xu W, Gao J, Jiang H, Chen
W, Zhang L, Li Z, Li W, Yuan P, et al: An evidence-based guideline
on treating lumbar disc herniation with traditional Chinese
medicine. J Evid Based Med. 17:187–206. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Burger M, Coetzee W, du Plessis LZ,
Geldenhuys L, Joubert F, Myburgh E, van Rooyen C and Vermeulen N:
The effectiveness of Schroth exercises in adolescents with
idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. S Afr
J Physiother. 75(904)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|