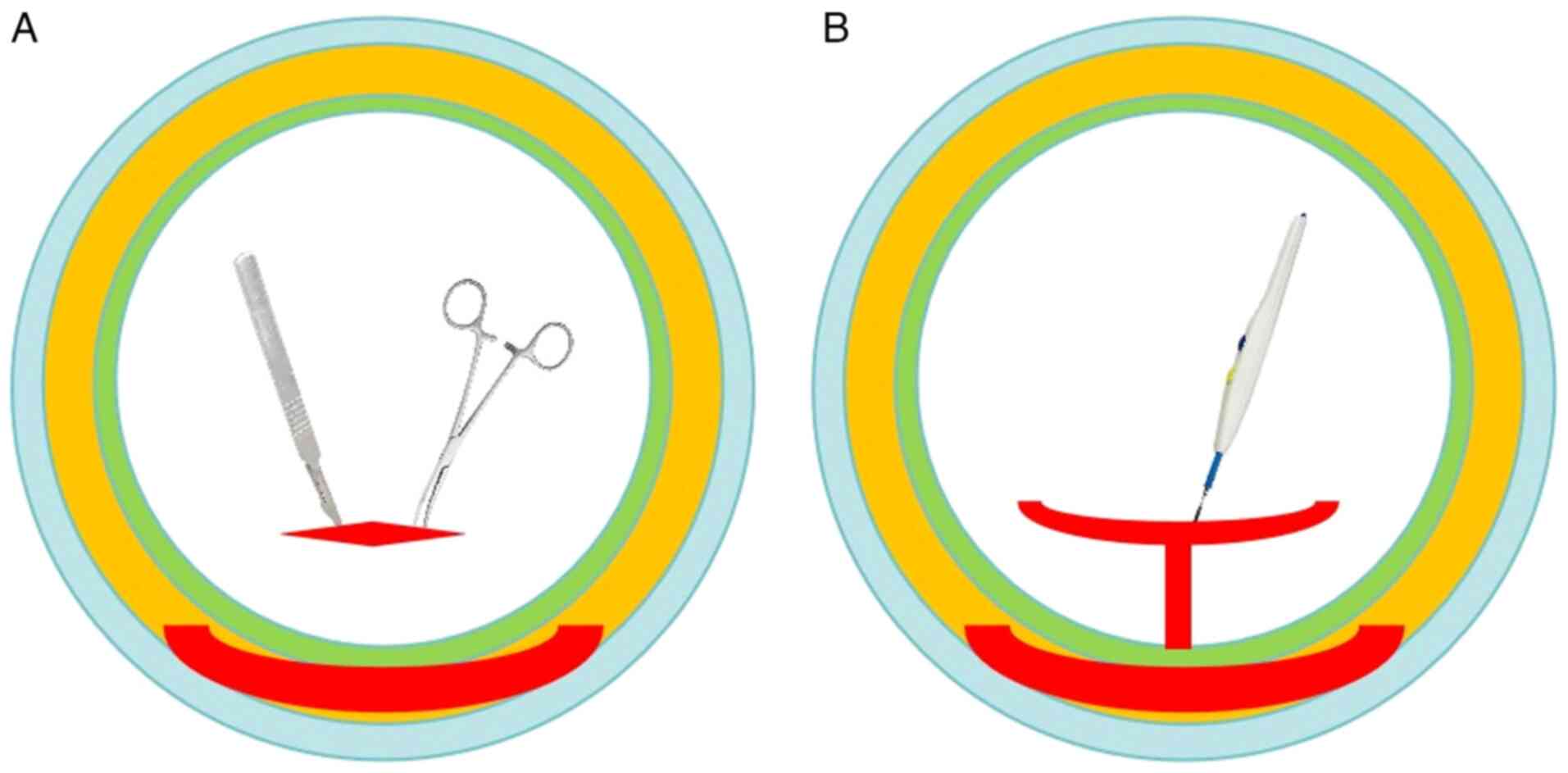
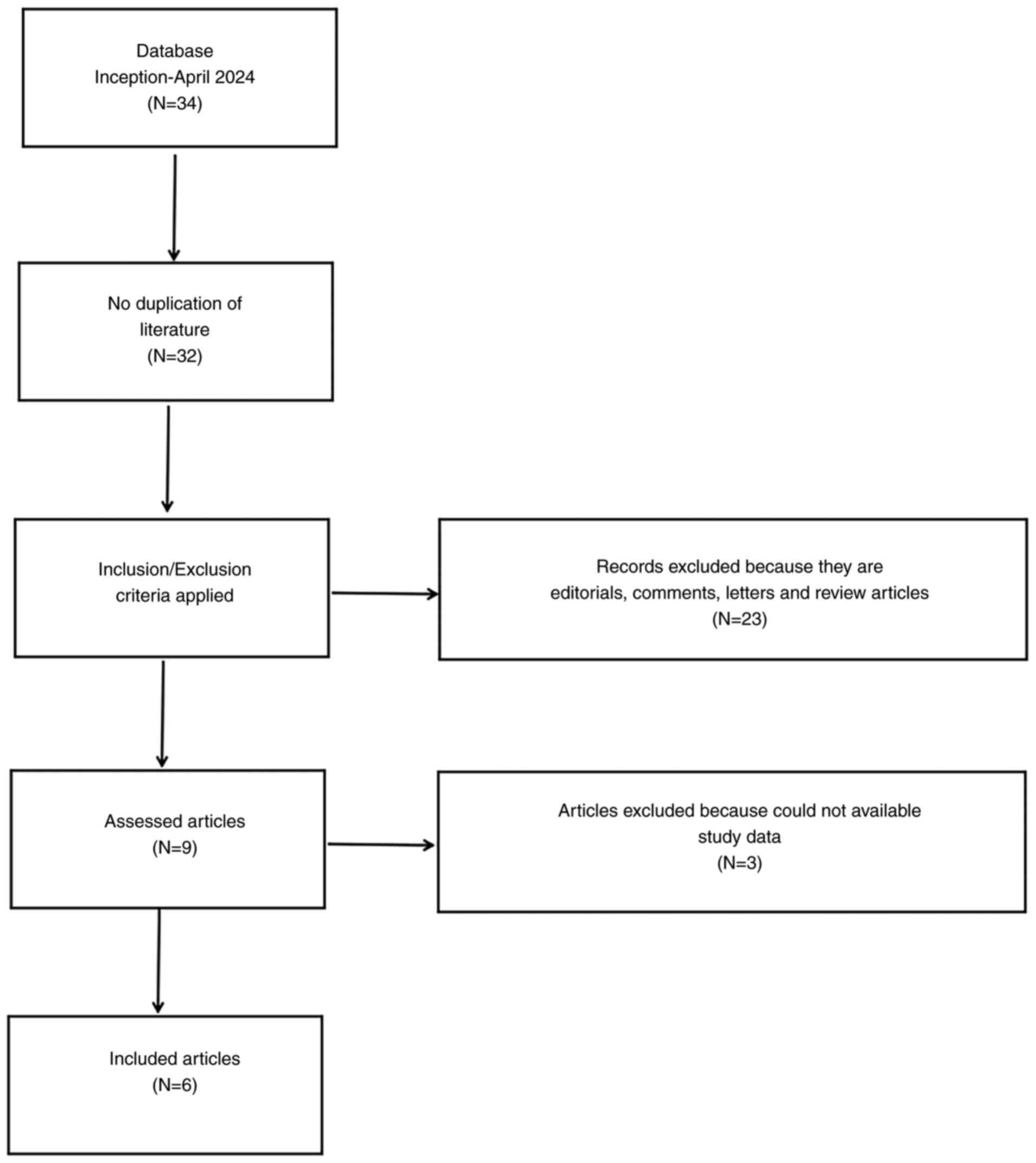
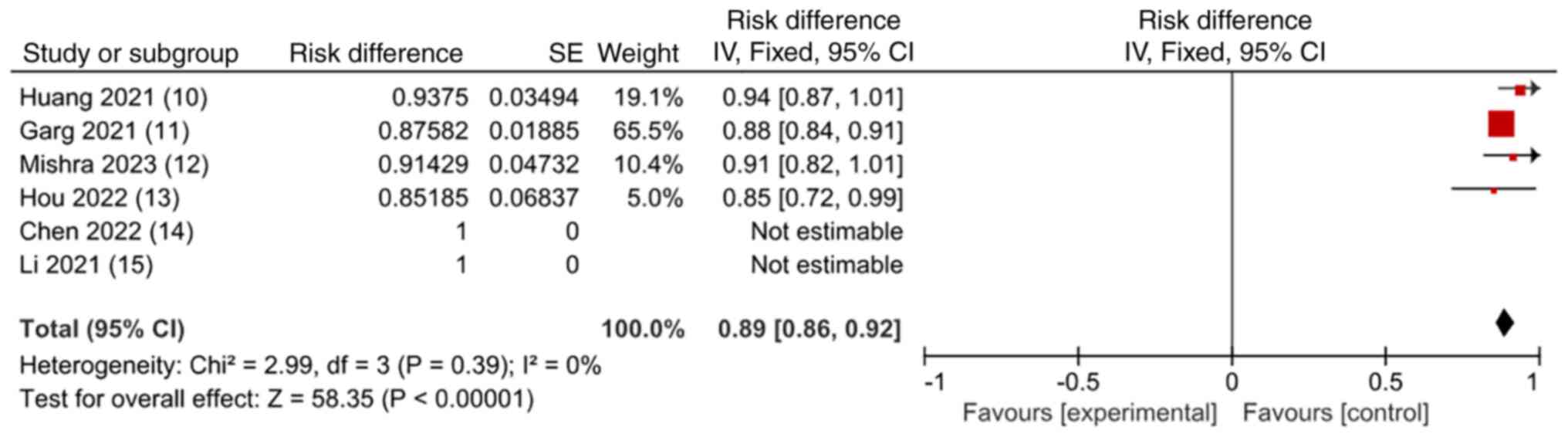
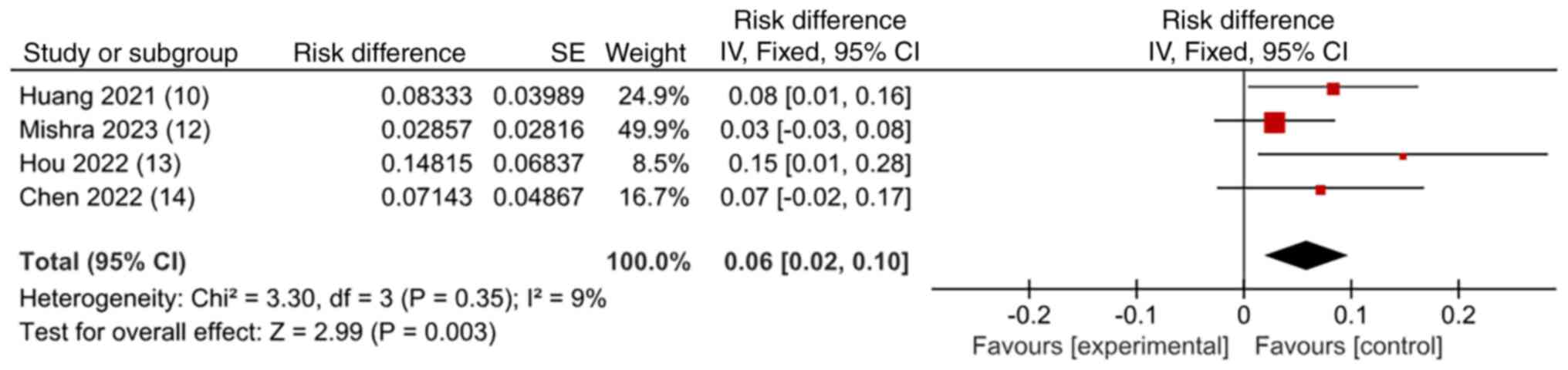
|
1
|
Felt-Bersma RJ and Bartelsman JF:
Haemorrhoids, rectal prolapse, anal fissure, peri-anal fistulae and
sexually transmitted diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
23:575–592. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cooper CR and Keller DS: Response to
letter to the editor on ‘Resident's Corner: Perianal Fistulas’. Dis
Colon Rectum. 63(e515)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ribaldone DG, Resegotti A, Pellicano R,
Astegiano M, Saracco GM and Morino M: The role of topical therapy
for perianal fistulizing Crohn's disease: Are we forgetting
something? Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 65:130–135.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Garg P, Sodhi SS and Garg N: Management of
complex cryptoglandular anal fistula: Challenges and solutions.
Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 13:555–567. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Abramowitz L, Soudan D, Souffran M,
Bouchard D, Castinel A, Suduca JM, Staumont G, Devulder F, Pigot F,
Ganansia R, et al: The outcome of fistulotomy for anal fistula at 1
year: A prospective multicentre French study. Colorectal Dis.
18:279–285. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Regusci L, Fasolini F, Meinero P, Caccia
G, Ruggeri G, Serati M and Braga A: Video-Assisted anal fistula
treatment (VAAFT) for complex anorectal fistula: Efficacy and risk
factors for failure at 3-year follow-up. Tech Coloproctol.
24:741–746. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Narang SK, Keogh K, Alam NN, Pathak S,
Daniels IR and Smart NJ: A systematic review of new treatments for
cryptoglandular fistula in ano. Surgeon. 15:30–39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin H, Jin Z, Zhu Y, Diao M and Hu W: Anal
fistula plug vs rectal advancement flap for the treatment of
complex cryptoglandular anal fistulas: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of studies with long-term follow-up. Colorectal Dis.
21:502–515. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Garg P: Transanal opening of
intersphincteric space (TROPIS)-A new procedure to treat high
complex anal fistula. Int J Surg. 40:130–134. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang B, Wang X, Zhou D, Chen S, Li B,
Wang Y and Tai J: Treating highly complex anal fistula with a new
method of combined intraoperative endoanal ultrasonography (IOEAUS)
and transanal opening of intersphincteric space (TROPIS). Wideochir
Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 16:697–703. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Garg P, Kaur B and Menon GR: Transanal
opening of the intersphincteric space: A novel sphincter-sparing
procedure to treat 325 high complex anal fistulas with long-term
follow-up. Colorectal Dis. 23:1213–1224. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mishra S, Thakur DS, Somashekar U, Verma A
and Sharma D: The management of complex fistula in ano by transanal
opening of the intersphincteric space (TROPIS): Short-term results.
Ann Coloproctol: Mar 31, 2023 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
13
|
Hou XT, Chen H, Chen YN and Zhang R:
Transanal opening of intersphincteric space to treat complex anal
fistula. Mod Med J. 50:588–591. 2022.
|
|
14
|
Chen XQ, Ren YY, Li YY, Sun F, Zhao YC and
Jin X: Clinical efficacy of anal sphincter otomy (TROPIS) in the
treatment of high sphincter type anal fistula. Journal of
Colorectal & Anal Surgery. 28:479–487. 2022.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Li YB, Chen JH, Wang MD, Fu J, Zhou BC, Li
DG, Zeng HQ and Pang LM: Transanal opening of intersphincteric
space for Fistula-in-Ano. Am Surg. 88:1131–1136. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wlodarczyk M, Wlodarczyk J,
Sobolewska-Wlodarczyk A, Trzcinski R, Dziki L and Fichna J: Current
concepts in the pathogenesis of cryptoglandular perianal fistula. J
Int Med Res. 49(300060520986669)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jeong HY, Song SG, Nam WJ and Lee JK:
puborectalis muscle involvement on magnetic resonance imaging in
complex fistula: A new perspective on diagnosis and treatment. Ann
Coloproctol. 37:51–57. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jayne DG, Scholefield J, Tolan D, Gray R,
Senapati A, Hulme CT, Sutton AJ, Handley K, Hewitt CA, Kaur M, et
al: A multicenter randomized controlled trial comparing safety,
efficacy and cost-effectiveness of the surgisis anal fistula plug
versus surgeon's preference for transsphincteric Fistula-in-Ano:
The FIAT Trial. Ann Surg. 273:433–441. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Eisenhammer S: The internal anal
sphincter; its surgical importance. S Afr Med J. 27:266–270.
1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garcia-Aguilar J, Belmonte C, Wong WD,
Goldberg SM and Madoff RD: Anal fistula surgery. Factors associated
with recurrence and incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 39:723–729.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jordan J, Roig JV, Garcia-Armengol J,
Garcia-Granero E, Solana A and Lledo S: Risk factors for recurrence
and incontinence after anal fistula surgery. Colorectal Dis.
12:254–260. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Garg P: A new understanding of the
principles in the management of complex anal fistula. Med
Hypotheses. 132(109329)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Garg P: Intersphincteric component in a
complex Fistula-in-Ano is like an abscess and should be treated
like one. Dis Colon Rectum. 61(e26)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang H, Zhou ZY, Hu B, Liu DC, Peng H,
Xie SK, Su D and Ren DL: Clinical significance of 2 deep posterior
perianal spaces to complex cryptoglandular fistulas. Dis Colon
Rectum. 59:766–774. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Emile SH, Elfeki H, Shalaby M and Sakr A:
A Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of
video-assisted anal fistula treatment (VAAFT). Surg Endosc.
32:2084–2093. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gottgens KW, Smeets RR, Stassen LP, Beets
G and Breukink SO: Systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical
interventions for high cryptoglandular perianal fistula. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 30:583–593. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cestaro G, De Rosa M and Gentile M:
Treatment of fistula in ano with fibrin glue: Preliminary results
from a prospective study. Minerva Chir. 69:225–228. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Damin DC, Rosito MA, Contu PC and Tarta C:
Fibrin glue in the management of complex anal fistula. Arq
Gastroenterol. 46:300–303. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Emile SH, Khan SM, Adejumo A and Koroye O:
Ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract (LIFT) in treatment of
anal fistula: An updated systematic review, meta-analysis and
meta-regression of the predictors of failure. Surgery. 167:484–492.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Prosst RL and Joos AK: Short-term outcomes
of a novel endoscopic clipping device for closure of the internal
opening in 100 anorectal fistulas. Tech Coloproctol. 20:753–758.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Matos D, Lunniss PJ and Phillips RK: Total
sphincter conservation in high fistula in ano: Results of a new
approach. Br J Surg. 80:802–804. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sainio P: A manometric study of anorectal
function after surgery for anal fistula, with special reference to
incontinence. Acta Chir Scand. 151:695–700. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Soltani A and Kaiser AM: Endorectal
advancement flap for cryptoglandular or Crohn's fistula-in-ano. Dis
Colon Rectum. 53:486–495. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Uribe N, Balciscueta Z, Minguez M, Martin
MC, Lopez M, Mora F and Primo V: ‘Core out’ or ‘curettage’ in
rectal advancement flap for cryptoglandular anal fistula. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 30:613–619. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Omar W, Alqasaby A, Abdelnaby M, Youssef
M, Shalaby M, Anwar Abdel-Razik M and Emile SH: Drainage seton
versus external anal sphincter-sparing seton after rerouting of the
fistula tract in the treatment of complex anal fistula: A
randomized controlled trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 62:980–987.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
El-Said M, Emile S, Shalaby M, Abdel-Razik
MA, Elbaz SA, Elshobaky A, Elkaffas H and Khafagy W: Outcome of
Modified Park's technique for treatment of complex anal fistula. J
Surg Res. 235:536–542. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Garg P, Song J, Bhatia A, Kalia H and
Menon GR: The efficacy of anal fistula plug in fistula-in-ano: A
systematic review. Colorectal Dis. 12:965–970. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Garg P, Kaur B, Goyal A, Yagnik VD, Dawka
S and Menon GR: Lessons learned from an audit of 1250 anal fistula
patients operated at a single center: A retrospective review. World
J Gastrointest Surg. 13:340–354. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mei Z, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Liu P, Ge M, Du P,
Yang W and He Y: Risk Factors for Recurrence after anal fistula
surgery: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 69:153–164. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Garg P, Kaur B, Singla K, Menon GR and
Yagnik VD: A simple protocol to effectively manage anal fistulas
with no obvious internal opening. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 14:33–44.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yagnik VD, Kaur B, Dawka S, Sohal A, Menon
GR and Garg P: Non-Locatable internal opening in anal fistula
associated with acute abscess and its definitive management by garg
protocol. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 15:189–198. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Rojanasakul A, Booning N, Huimin L,
Pongpirul K and Sahakitrungruang C: Intersphincteric exploration
with ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract or attempted
closure of internal opening for acute anorectal abscesses. Dis
Colon Rectum. 64:438–445. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Garg P: Comparison between recent
sphincter-sparing procedures for complex anal fistulas-ligation of
intersphincteric tract vs transanal opening of intersphincteric
space. World J Gastrointest Surg. 14:374–382. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tang CL, Chew SP and Seow-Choen F:
Prospective randomized trial of drainage alone vs. drainage and
fistulotomy for acute perianal abscesses with proven internal
opening. Dis Colon Rectum. 39:1415–1417. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tian Z, Li YL, Nan SJ, Xiu WC and Wang YQ:
Video-assisted anal fistula treatment for complex anorectal
fistulas in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech
Coloproctol. 26:783–795. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|