|
1
|
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL and
Masson P: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 389:1238–1252.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Luyckx VA, Tonelli M and Stanifer JW: The
global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development
goals. Bull World Health Organ. 96:414–422D. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Khanmohammadi S, Tavolinejad H,
Aminorroaya A, Rezaie Y, Ashraf H and Vasheghani-Farahani A:
Association of lipid accumulation product with type 2 diabetes
mellitus, hypertension, and mortality: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 21:1943–1973.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Raposo MA, Guimarães NS and Tupinambás U:
Lipid accumulation product index to predict metabolic syndrome in
people living with HIV. Clin Med Res. 18:120–125. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gai Z, Wang T, Visentin M, Kullak-Ublick
GA, Fu X and Wang Z: Lipid accumulation and chronic kidney disease.
Nutrients. 11(722)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bobulescu IA: Renal lipid metabolism and
lipotoxicity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 19:393–402.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rosenstein K and Tannock LR: Dyslipidemia
in chronic kidney disease. In: Endotext. Feingold KR, Anawalt B,
Blackman MR, et al. (eds.) MDText.com, Inc., South
Dartmouth (MA), 2000.
|
|
8
|
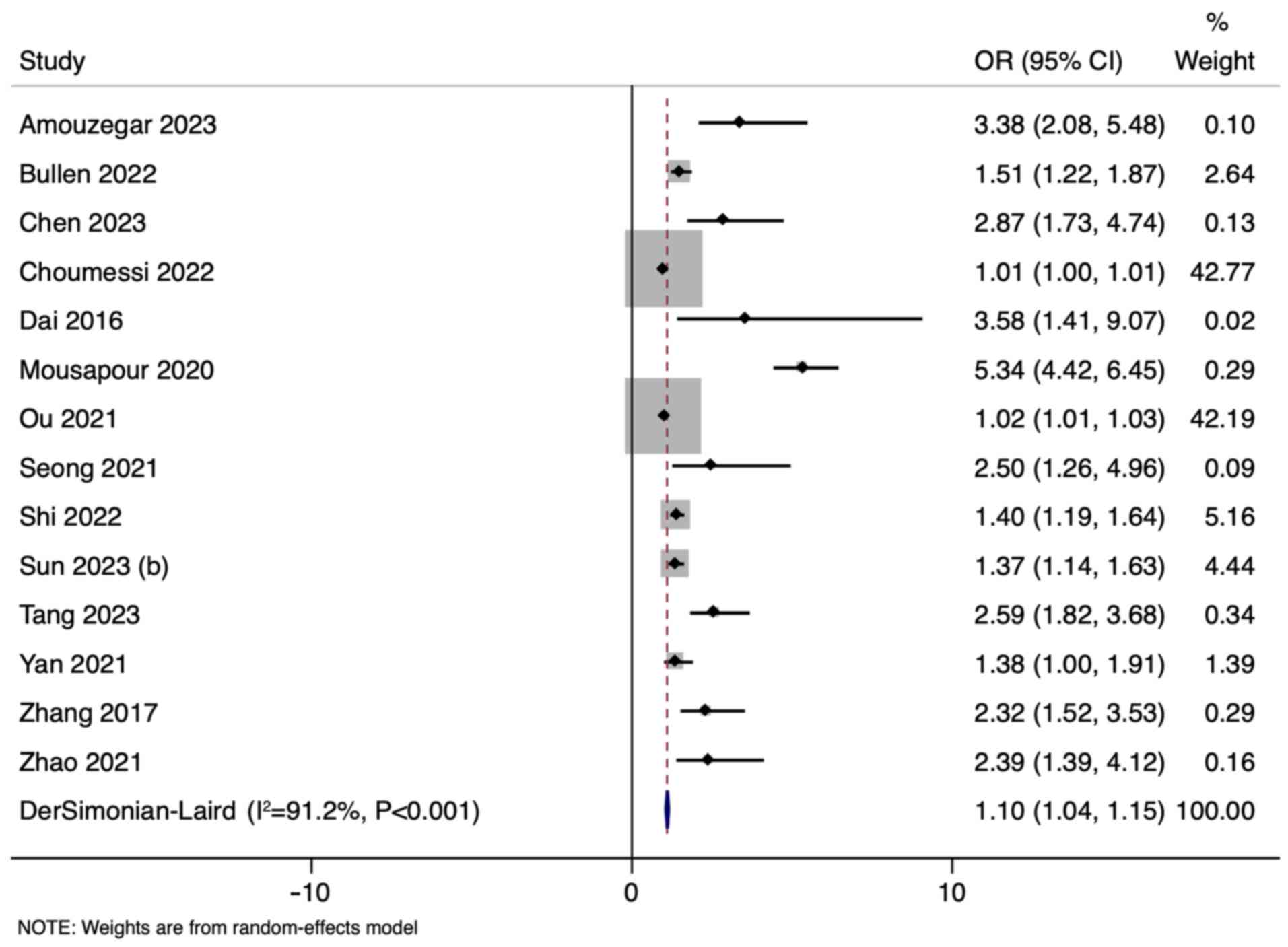
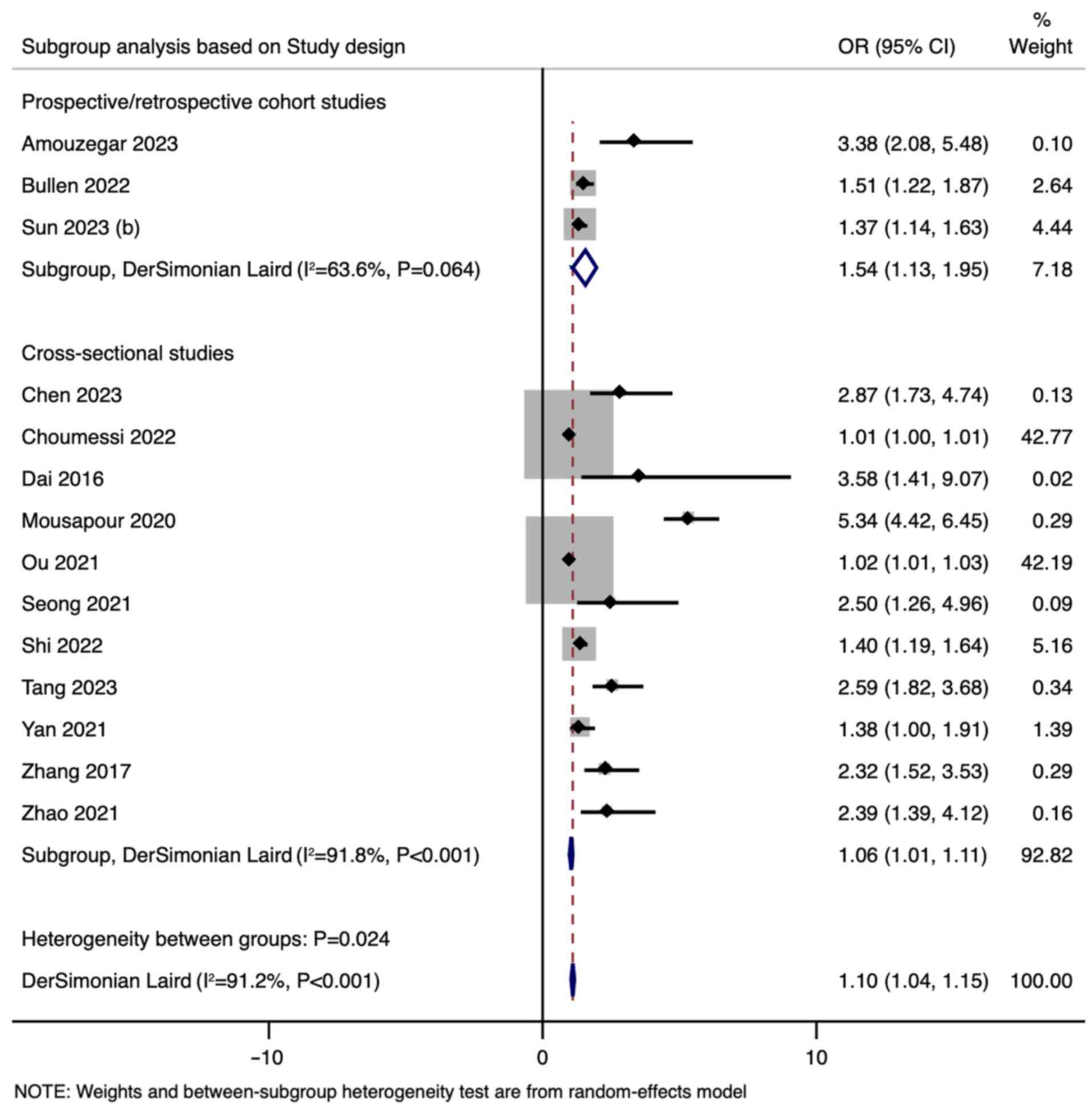
Bullen AL, Katz R, Kumar U, Gutierrez OM,
Sarnak MJ, Kramer HJ, Shlipak MG, Ix JH, Judd SE, Cushman M and
Garimella PS: Lipid accumulation product, visceral adiposity index
and risk of chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol.
23(401)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
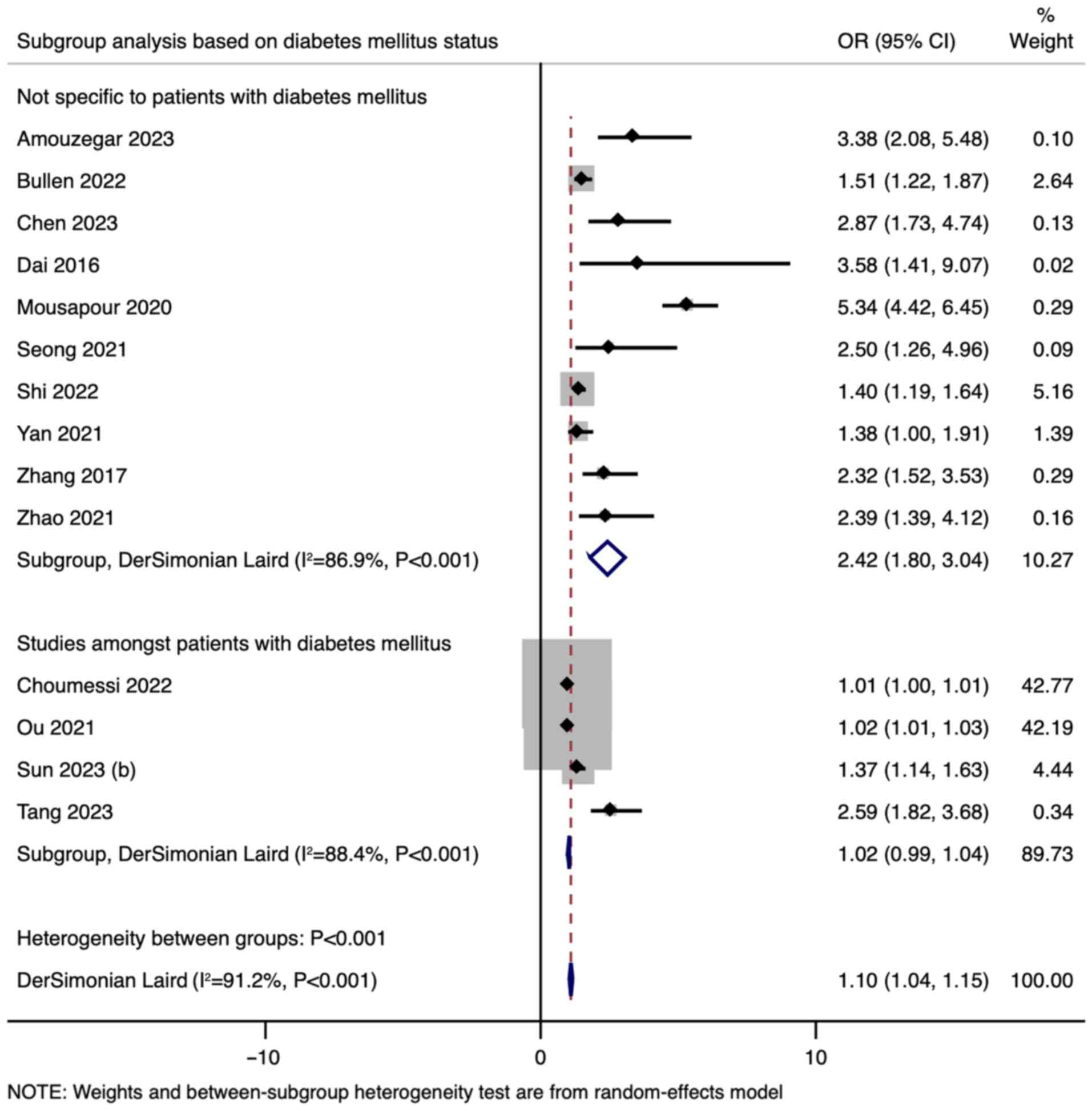
Sun Y, Yan Y, Liao Y, Chu C, Guo T, Ma Q,
Wang Y, Wang D, Jia H and Mu J: The new visceral adiposity index
outperforms traditional obesity indices as a predictor of
subclinical renal damage in Chinese individuals: A cross-sectional
study. BMC Endocr Disord. 23(78)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tang M, Yao S, Cao H, Wei X, Zhen Q, Tan
Y, Liu F, Wang Y, Peng Y and Fan N: Interrelation between the lipid
accumulation product index and diabetic kidney disease in patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
14(1224889)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma
K, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Zoungas S, Rossing P, Groop PH and Cooper ME:
Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
1(15018)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sun Z, Wang K, Yun C, Bai F, Yuan X, Lee Y
and Lou Q: Correlation between the variability of different obesity
indices and diabetic kidney disease: A retrospective cohort study
based on populations in Taiwan. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
16:2791–2802. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lo CK, Mertz D and Loeb M:
Newcastle-Ottawa scale: Comparing reviewers' to authors'
assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol. 14(45)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vogelgesang F, Schlattmann P and Dewey M:
The evaluation of bivariate mixed models in meta-analyses of
diagnostic accuracy studies with SAS, Stata and R. Methods Inf Med.
57:111–119. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J,
Welch VA, Higgins JP and Thomas J: Updated guidance for trusted
systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
10(ED000142)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Choumessi AT, Saha BUF, Navti LK, Tibi AS,
Njeck AT and Nantia EA: Assessment of visceral adiposity index and
lipid accumulation product index as markers of chronic kidney
disease among diabetic and hypertensive patients at the Bamenda
Regional Hospital, Cameroon: A cross-sectional study. Pan Afr Med
J. 42(228)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao S, Ren Z, Yu S, Chi C, Tang J,
Maimaitiaili R, Teliewubai J, Li J, Xu Y and Zhang Y: Association
between lipid accumulation product and target organ damage in
elderly population: The northern Shanghai study. Clin Interv Aging.
16:1769–1776. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu P, Meng X, Kan R, Wang Z and Yu X:
Association between metabolic scores for visceral fat and chronic
kidney disease: A cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13(1052736)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi Y, Hu L, Li M, Zhou W, Wang T, Zhu L,
Bao H, Cheng X and Li P: Association between the surrogate markers
of insulin resistance and chronic kidney disease in Chinese
hypertensive patients. Front Med (Lausanne).
9(831648)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yan P, Xu Y, Miao Y, Tang Q, Wu Y, Bai X,
Zhang Z, Li Q and Wan Q: Association of lipid accumulation product
with chronic kidney disease in Chinese community adults: A report
from the REACTION study. Lipids Health Dis. 20(131)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen T, Wang X, Wang X, Chen H, Xiao H,
Tang H, Feng L, Xiang Z, Zou H and Shao X: Comparison of novel
metabolic indices in estimation of chronic kidney diseases in a
southern Chinese population. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
13:4919–4927. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Seong JM, Lee JH, Gi MY, Son YH, Moon AE,
Park CE, Sung HH and Yoon H: Gender difference in the association
of chronic kidney disease with visceral adiposity index and lipid
accumulation product index in Korean adults: Korean national health
and nutrition examination survey. Int Urol Nephrol. 53:1417–1425.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jin J, Woo H, Jang Y, Lee WK, Kim JG, Lee
IK, Park KG and Choi YK: Novel Asian-specific visceral adiposity
indices are associated with chronic kidney disease in Korean
adults. Diabetes Metab J. 47:426–436. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mousapour P, Barzin M, Valizadeh M,
Mahdavi M, Azizi F and Hosseinpanah F: Predictive performance of
lipid accumulation product and visceral adiposity index for renal
function decline in non-diabetic adults, an 8.6-year follow-up.
Clin Exp Nephrol. 24:225–234. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Amouzegar A, Honarvar M, Masoumi S, Tohidi
M, Mehran L and Azizi F: Sex-specific trajectories of insulin
resistance markers and reduced renal function during 18 years of
follow-up: TLGS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 108:e230–e239.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang K, Li Q, Chen Y, Wang N and Lu Y:
Visceral adiposity and renal function: An observational study from
SPECT-China. Lipids Health Dis. 16(205)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dai D, Chang Y, Chen Y, Chen S, Yu S, Guo
X and Sun Y: Visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation
product index: Two alternate body indices to identify chronic
kidney disease among the rural population in northeast China. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 13(1231)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ou YL, Lee MY, Lin IT, Wen WL, Hsu WH and
Chen SC: Obesity-related indices are associated with albuminuria
and advanced kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ren Fail.
43:1250–1258. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fang T, Zhang Q, Wang Y and Zha H:
Diagnostic value of visceral adiposity index in chronic kidney
disease: A meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. 60:739–748.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Suh SH and Kim SW: Dyslipidemia in
patients with chronic kidney disease: An updated overview. Diabetes
Metab J. 47:612–629. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Anoop SS, Dasgupta R, Rebekah G, Jose A,
Inbakumari MP, Finney G and Thomas N: Lipid accumulation product
(LAP) as a potential index to predict risk of insulin resistance in
young, non-obese Asian Indian males from southern India:
Observations from hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies. BMJ
Open Diabetes Res Care. 9(e002414)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hallan SI, Ritz E, Lydersen S, Romundstad
S, Kvenild K and Orth SR: Combining GFR and albuminuria to classify
CKD improves prediction of ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1069–1077.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jallow AW, Bah AN, Bah K, Hsu CY and Chu
KC: Machine learning approach for chronic kidney disease risk
prediction combining conventional risk factors and novel metabolic
indices. Appl Sci. 12(12001)2022.
|