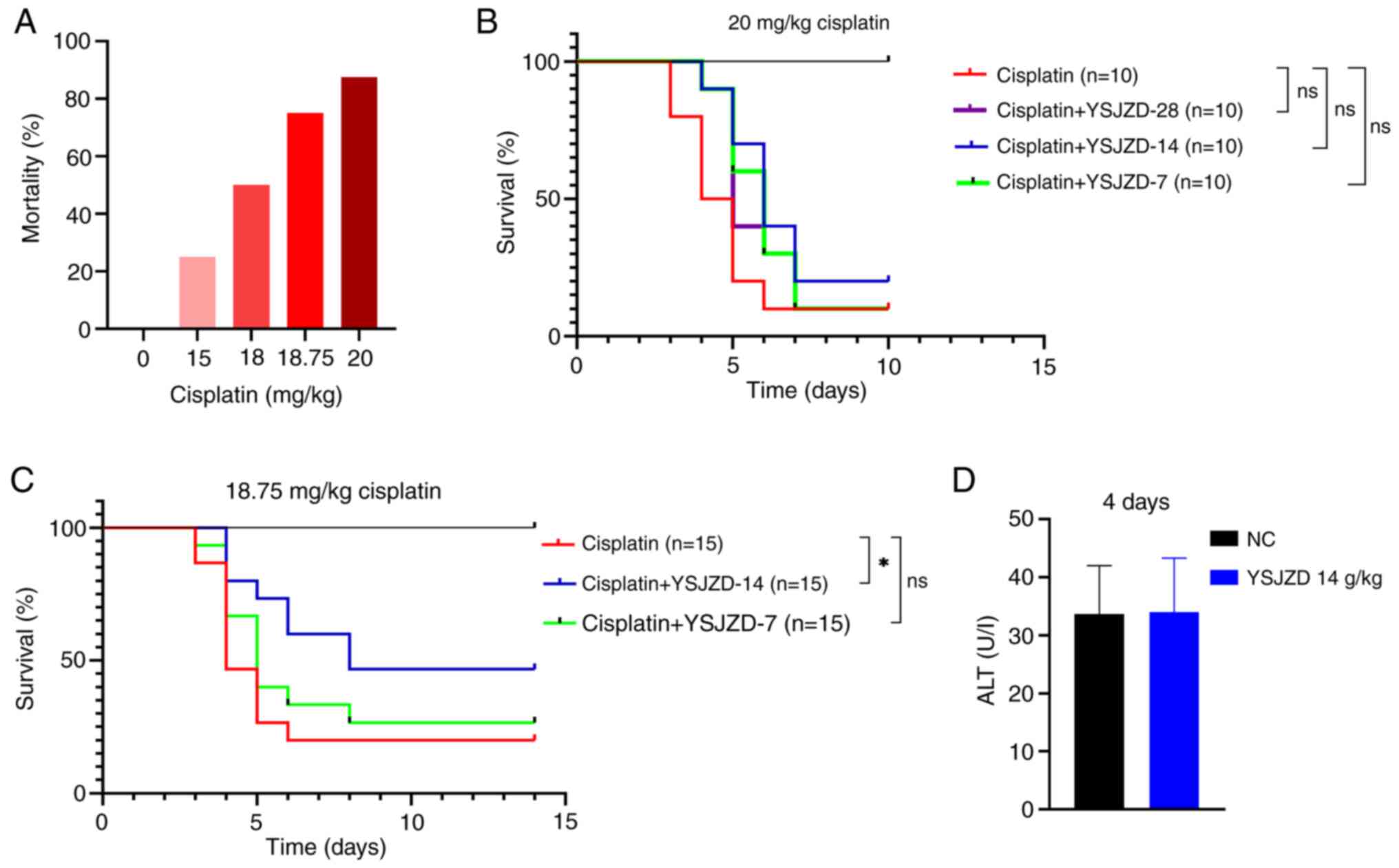
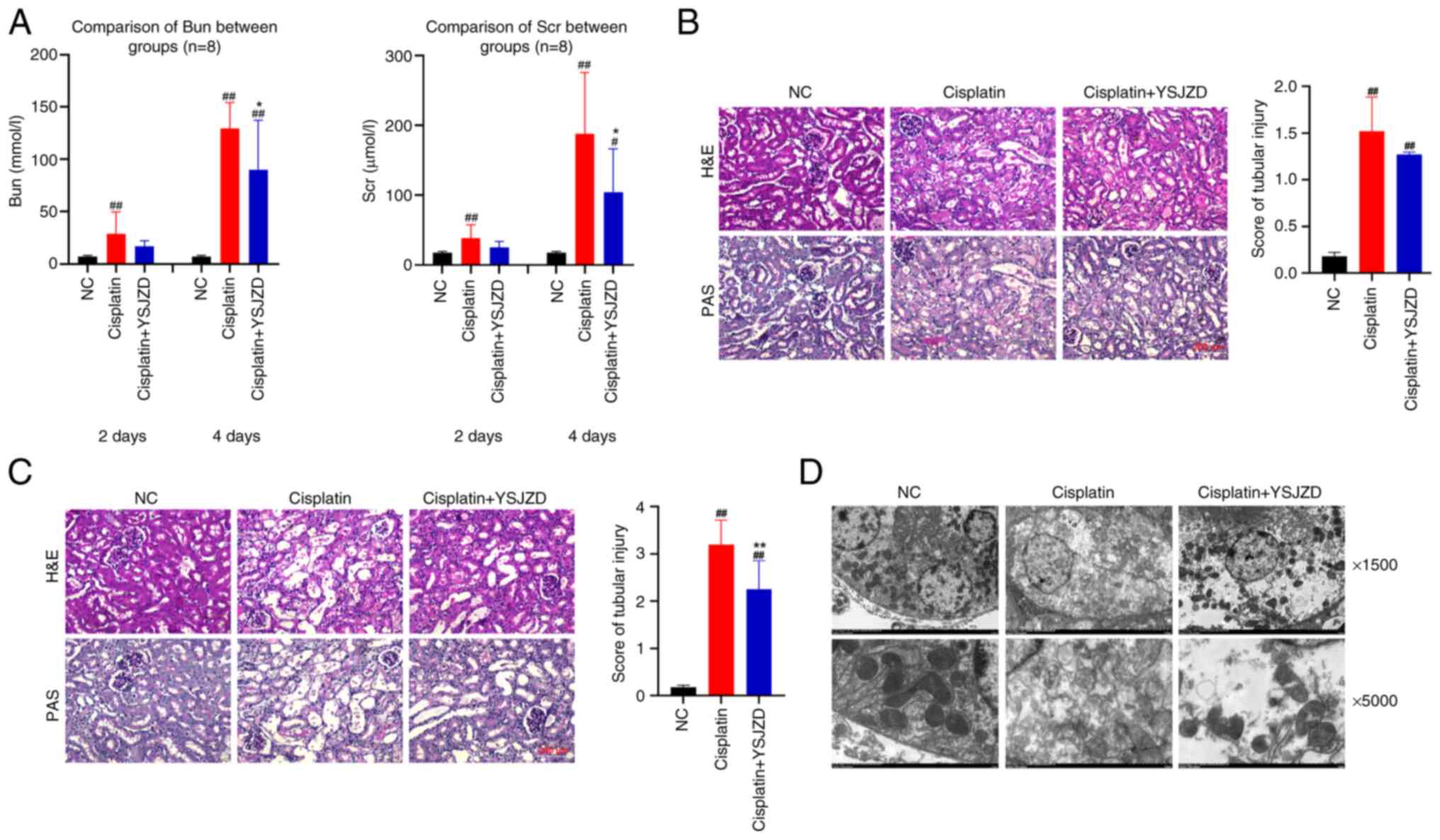
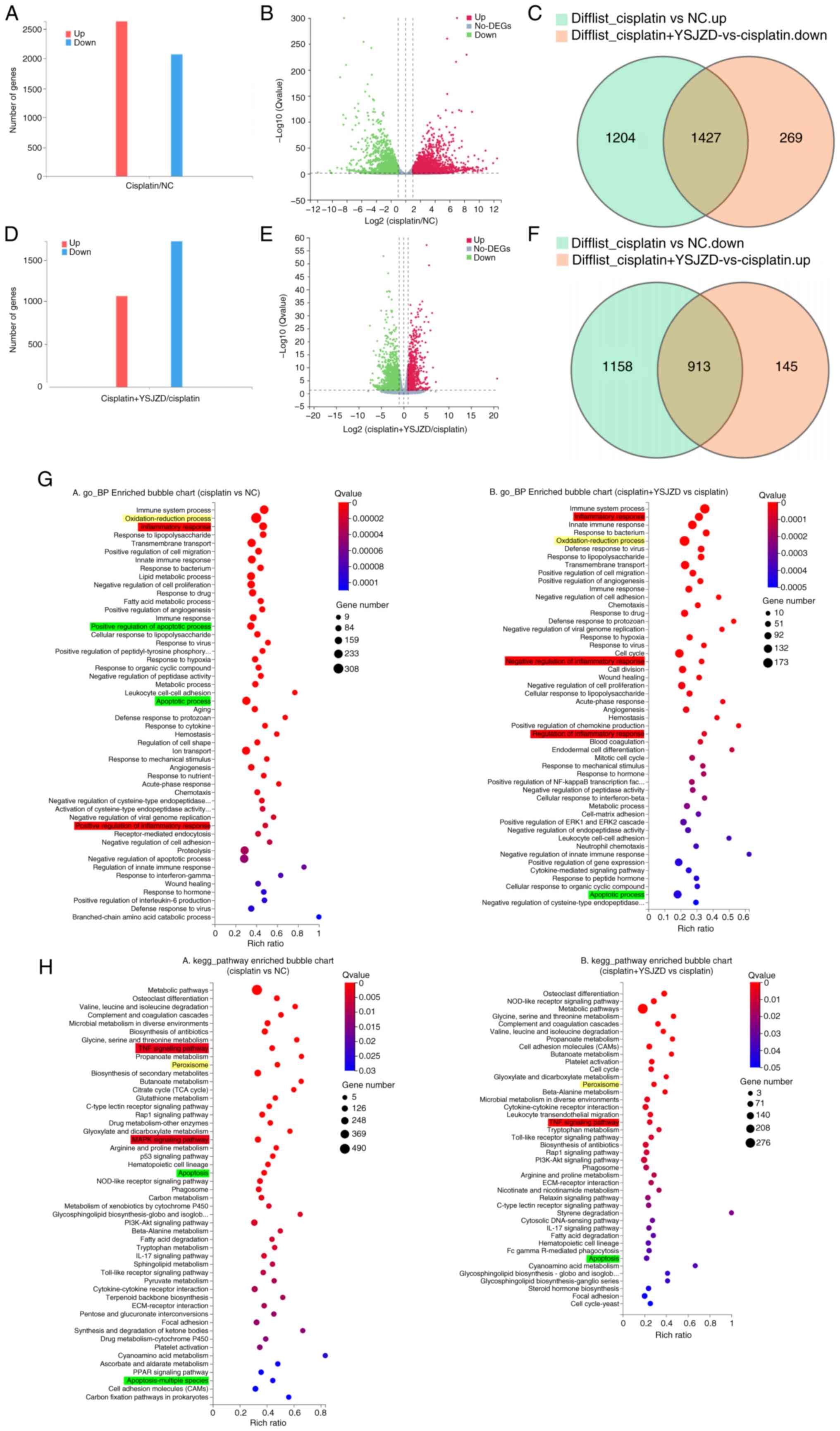
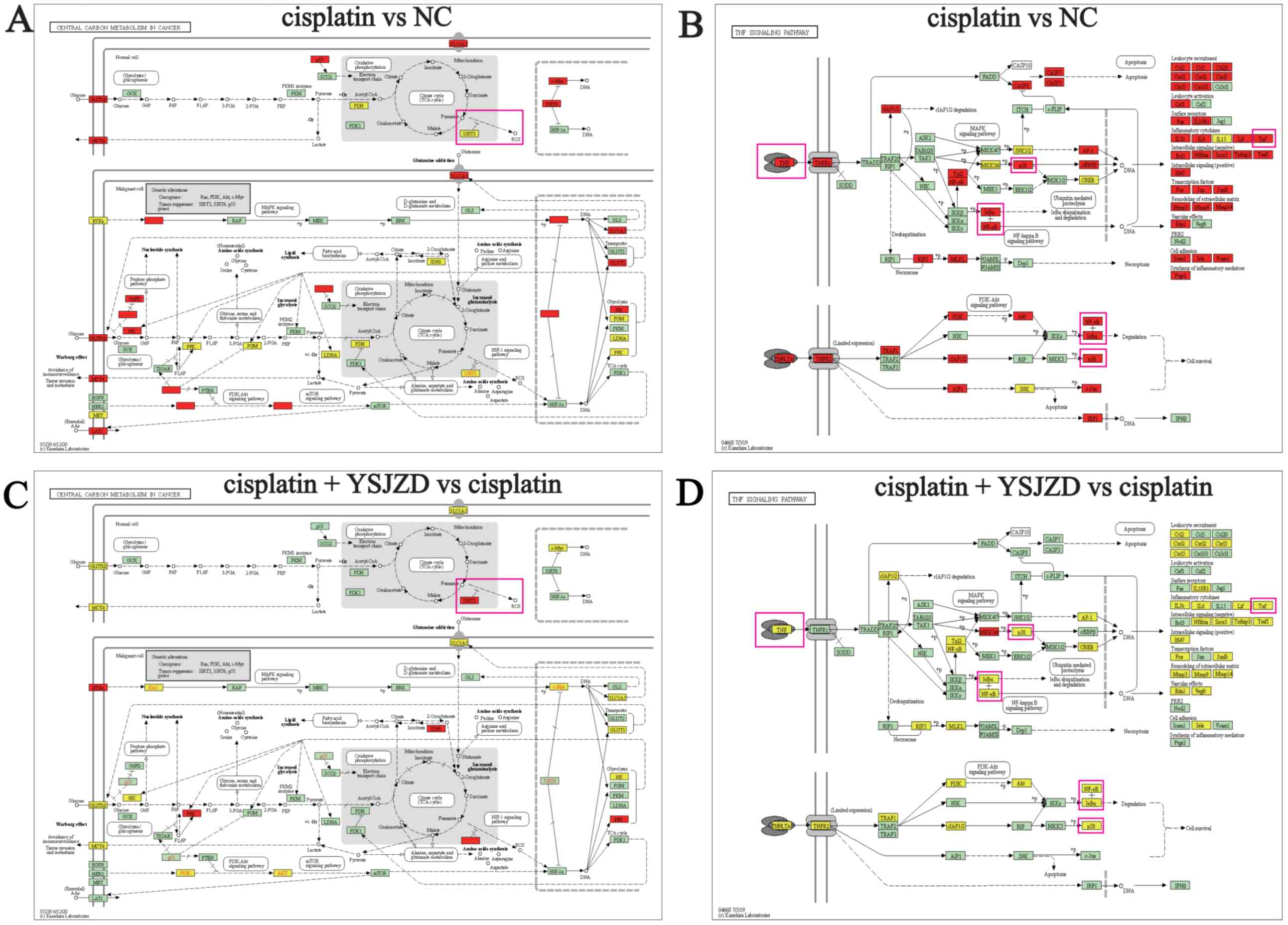
|
1
|
Zhang Q, Qi J, Luo Q, Wu M, Zhang L, Qin L
and Nie X: Yishen Xiezhuo formula ameliorates the development of
cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by attenuating renal tubular
epithelial cell senescence. Ann Transl Med. 10(1392)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Volarevic V, Djokovic B, Jankovic MG,
Harrell CR, Fellabaum C, Djonov V and Arsenijevic N: Molecular
mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the
knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity. J Biomed Sci.
26(25)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Oliveira BM, de Almeida LF, Deluque AL,
Souza CS, Maciel ALD, Francescato HDC, Costa RS, Giovanini C, de
Paula FJA and Coimbra TM: Calcitriol reduces the inflammation,
endothelial damage and oxidative stress in AKI caused by cisplatin.
Int J Mol Sci. 23(15877)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu L, Liu W, Li S, Bai M, Zhou Y, Jiang Z,
Jia Z, Huang S, Zhang A and Gong W: Flavonoid derivative DMXAA
attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury independent of
STING signaling. Clin Sci (Lond). 137:435–452. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
McSweeney KR, Gadanec LK, Qaradakhi T, Ali
BA, Zulli A and Apostolopoulos V: Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced
acute kidney injury: Pathological mechanisms, pharmacological
interventions and genetic mitigations. Cancers (Basel).
13(1572)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen
KN and Edelstein CL: Recent advances in models, mechanisms,
biomarkers and interventions in cisplatin-induced acute kidney
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3011)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Qi L, Luo Q, Zhang Y, Jia F, Zhao Y and
Wang F: Advances in toxicological research of the anticancer drug
cisplatin. Chem Res Toxicol. 32:1469–1486. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fang CY, Lou DY, Zhou LQ, Wang JC, Yang B,
He QJ, Wang JJ and Weng QJ: Natural products: Potential treatments
for cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
42:1951–1969. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mapuskar KA, Steinbach EJ, Zaher A, Riley
DP, Beardsley RA, Keene JL, Holmlund JT, Anderson CM, Zepeda-Orozco
D, Buatti JM, et al: Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in
cisplatin-induced kidney injury. Antioxidants (Basel).
10(1329)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sears SM and Siskind LJ: Potential
therapeutic targets for cisplatin-induced kidney injury: Lessons
from other models of AKI and Fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
32:1559–1567. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xu YF, Ruan SW, Lin JM and Zhang Z: Yishen
Jiangzhuo Granules affect tubulointerstitial fibrosis via a
mitochondrion-mediated apoptotic pathway. Chin J Integr Med.
21:928–937. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu SY, Bian RL and Chen X: Experimental
methodology of Pharmacology. People's Medical Publishing House,
Beijing, 2002.
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Chang Y, Han Z, Ma K, Zeng X and
Li L: Estrogen protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
by regulating Th17/Treg cell immune balance. Dis Markers.
2022(7812099)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ranasinghe R, Mathai ML and Zulli A:
Cisplatin for cancer therapy and overcoming chemoresistance.
Heliyon. 8(e10608)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu Z, Zhang M, Wang W, Zhou S, Yu M, Qiu
X, Jiang S, Wang X, Tang C, Li S, et al: Dihydromyricetin
attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by reducing
oxidative stress, inflammation and ferroptosis. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 473(116595)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chou YN, Lee MM, Deng JS, Jiang WP, Lin JG
and Huang GJ: Water extract from brown strain of flammulina
velutipes alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by
attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy via
PI3K/AKT pathway regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 24(9448)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Linkermann A, Bräsen JH, Darding M, Jin
MK, Sanz AB, Heller JO, De Zen F, Weinlich R, Ortiz A, Walczak H,
et al: Two independent pathways of regulated necrosis mediate
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:12024–12029. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Perse M and Veceric-Haler Z:
Cisplatin-induced rodent model of kidney injury: Characteristics
and challenges. Biomed Res Int. 2018(1462802)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ozkok A, Ravichandran K, Wang Q,
Ljubanovic D and Edelstein CL: NF-κB transcriptional inhibition
ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). Toxicol
Lett. 240:105–113. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim C, Kwak W, Won DH, Kim J, Hwang DB,
Kim N, Kang M, Jeon Y, Park YI, Park JW and Yun JW: Loss of Dact2
alleviates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through regulation of
the Igfl-MAPK pathway axis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 39:3197–3217.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yuan H, Zhao Y, Li S, Qin J and Yu X:
Madecassoside ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by
inhibiting activation of the mitogen activated protein kinase
pathway. Environ Toxicol. 38:1473–1483. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ramesh G and Reeves WB: p38 MAP kinase
inhibition ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in mice. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 289:F166–F174. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ramesh G and Reeves WB: TNF-alpha mediates
chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin
nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 110:835–842. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang B, Ramesh G, Norbury CC and Reeves
WB: Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int.
72:37–44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ramesh G, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS and
Reeves WB: Endotoxin and cisplatin synergistically stimulate
TNF-alpha production by renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 292:F812–F819. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pan Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Zhang Z, He Y, Zhao
Q, Yang H and Zhou P: A proteoglycan isolated from Ganoderma
lucidum attenuates diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting oxidative
stress-induced renal fibrosis both in vitro and in vivo. J
Ethnopharmacol. 310(116405)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lu XH, Zhang J and Xiong Q: Suppressive
effect erythropoietin on oxidative stress by targeting
AMPK/Nox4/ROS pathway in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Transpl
Immunol. 72(101537)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ma Q, Xu Y, Tang L, Yang X, Chen Z, Wei Y,
Shao X, Shao X, Xin Z, Cai B, et al: Astragalus polysaccharide
attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing
oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed Res Int.
2020(2851349)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Wang B, Guo F, Huang R, Liang Y,
Li L, Tao S, Yin T, Fu P and Ma L: FFAR4 improves the senescence of
tubular epithelial cells by AMPK/SirT3 signaling in acute kidney
injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7(384)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huang Z, Li Q, Yuan Y, Zhang C, Wu L, Liu
X, Cao W, Guo H, Duan S, Xu X, et al: Renalase attenuates
mitochondrial fission in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via
modulating sirtuin-3. Life Sci. 222:78–87. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Ye Z, Lai W, Rao J, Huang W, Zhang
X, Yao Z and Lou T: Activation of sirtuin 3 by silybin attenuates
mitochondrial dysfunction in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.
Front Pharmacol. 8(178)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Morigi M, Perico L, Rota C, Longaretti L,
Conti S, Rottoli D, Novelli R, Remuzzi G and Benigni A: Sirtuin
3-dependent mitochondrial dynamic improvements protect against
acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest. 125:715–726. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zi Y, Wang X, Zi Y, Yu H, Lan Y, Fan Y,
Ren C, Liao K and Chen H: Cigarette smoke induces the ROS
accumulation and iNOS activation through deactivation of
Nrf-2/SIRT3 axis to mediate the human bronchial epithelium
ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 200:73–86. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wen L, Wei Q, Livingston MJ, Dong G, Li S,
Hu X, Li Y, Huo Y and Dong Z: PFKFB3 mediates tubular cell death in
cisplatin nephrotoxicity by activating CDK4. Transl Res. 253:31–40.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee D, Yamabe N, Lee H, Lim Lee H, Kim DW,
Wook Lee J and Sung Kang K: Necrostatins regulate apoptosis,
necroptosis, and inflammation in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity
in LLC-PK1 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 48(128256)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Oh GS, Kim HJ, Shen A, Lee SB, Khadka D,
Pandit A and So HS: Cisplatin-induced kidney dysfunction and
perspectives on improving treatment strategies. Electrolyte Blood
Press. 12:55–65. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|