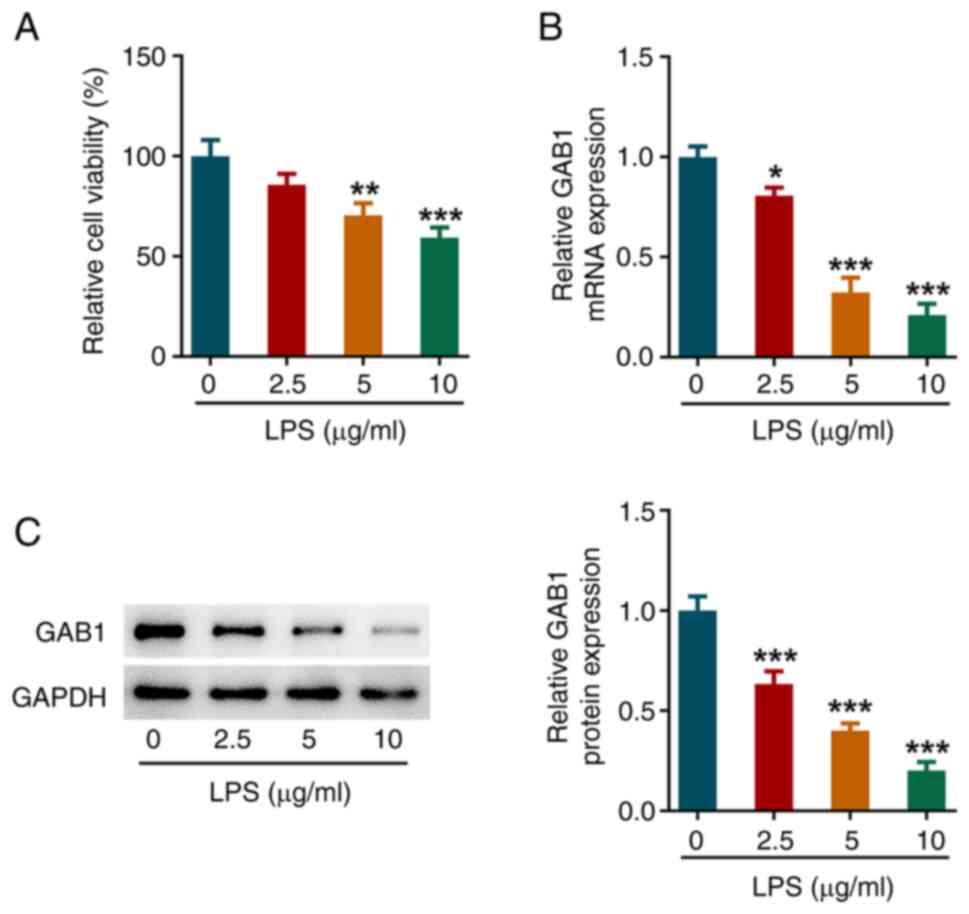
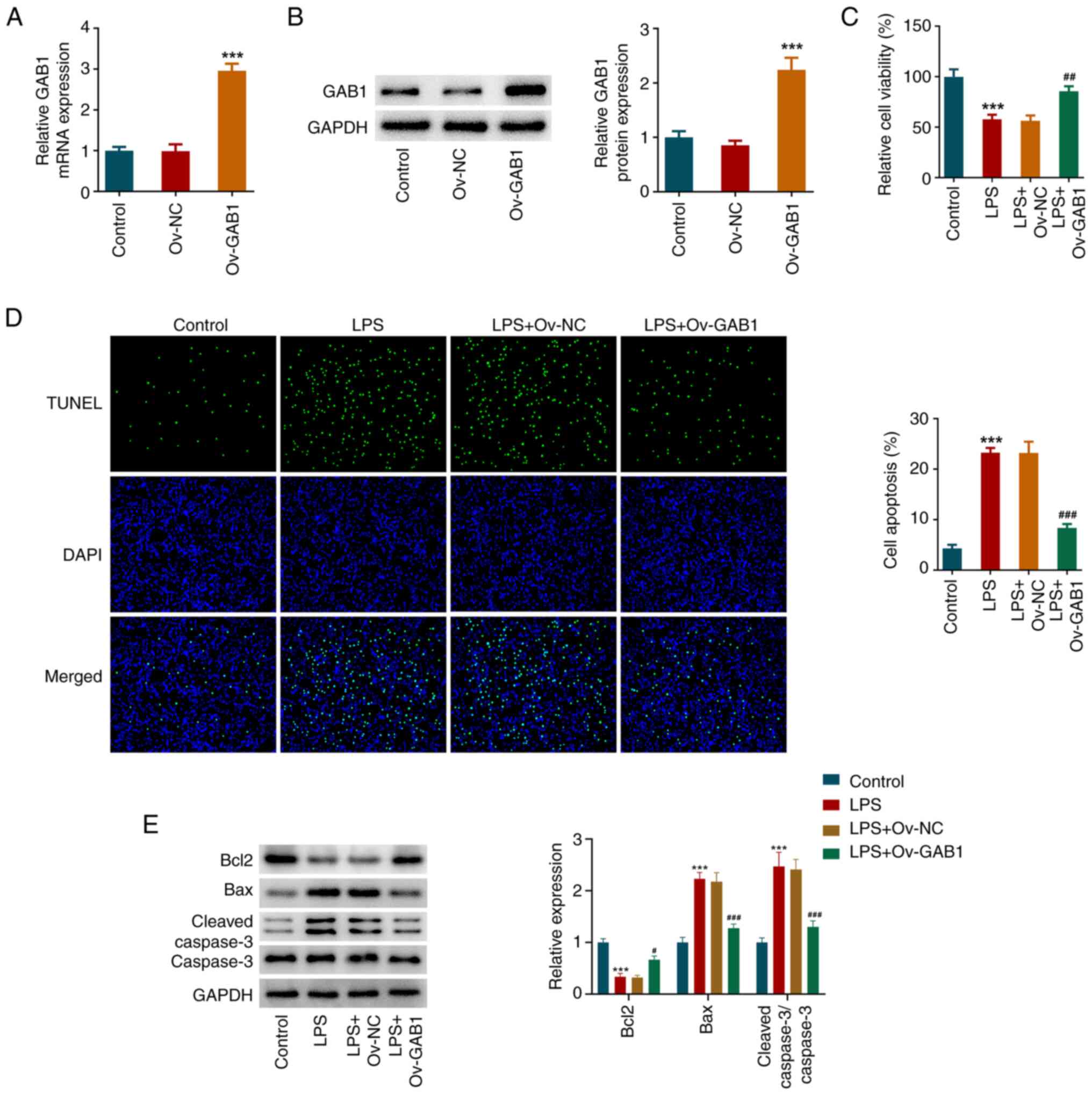
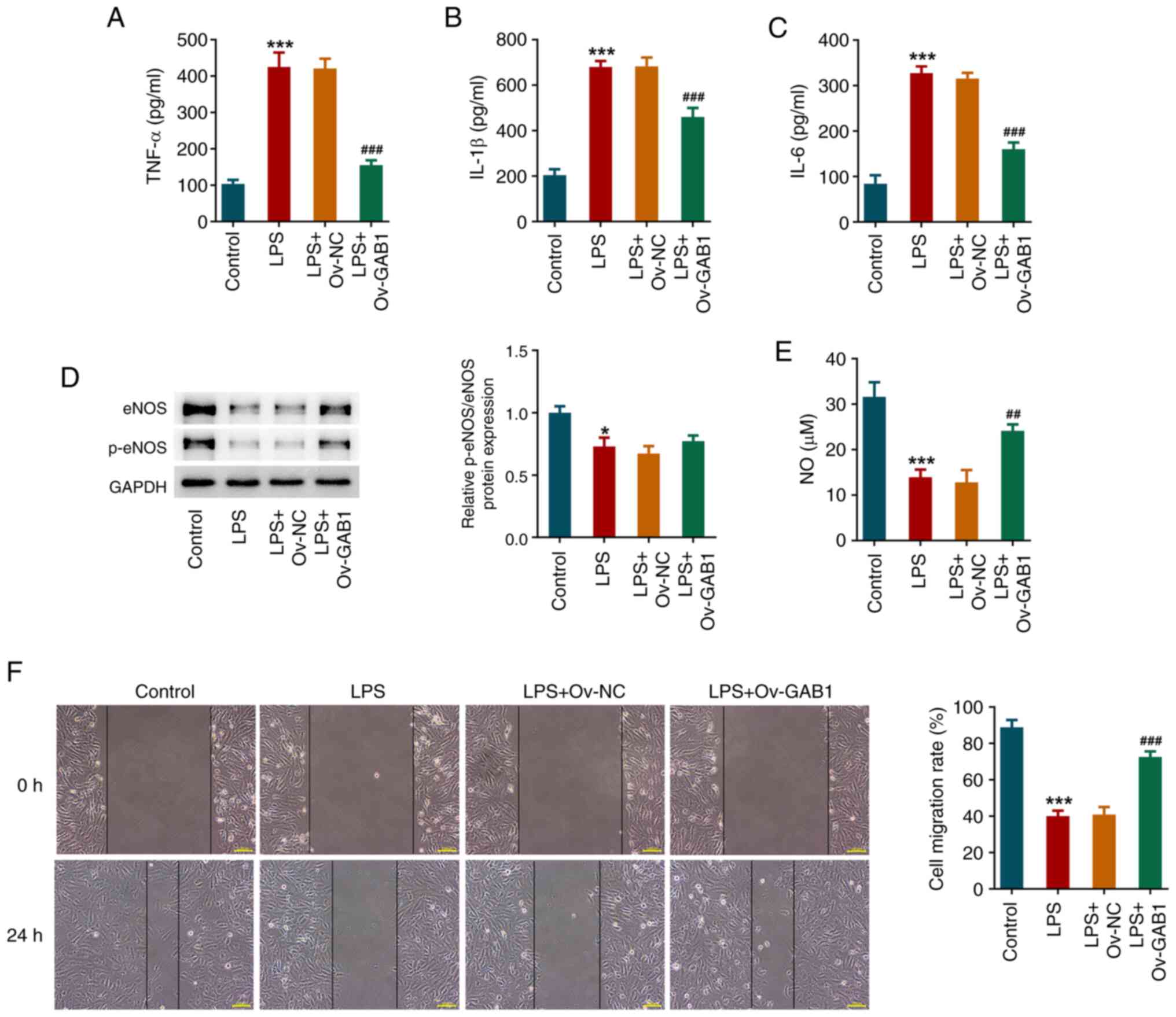
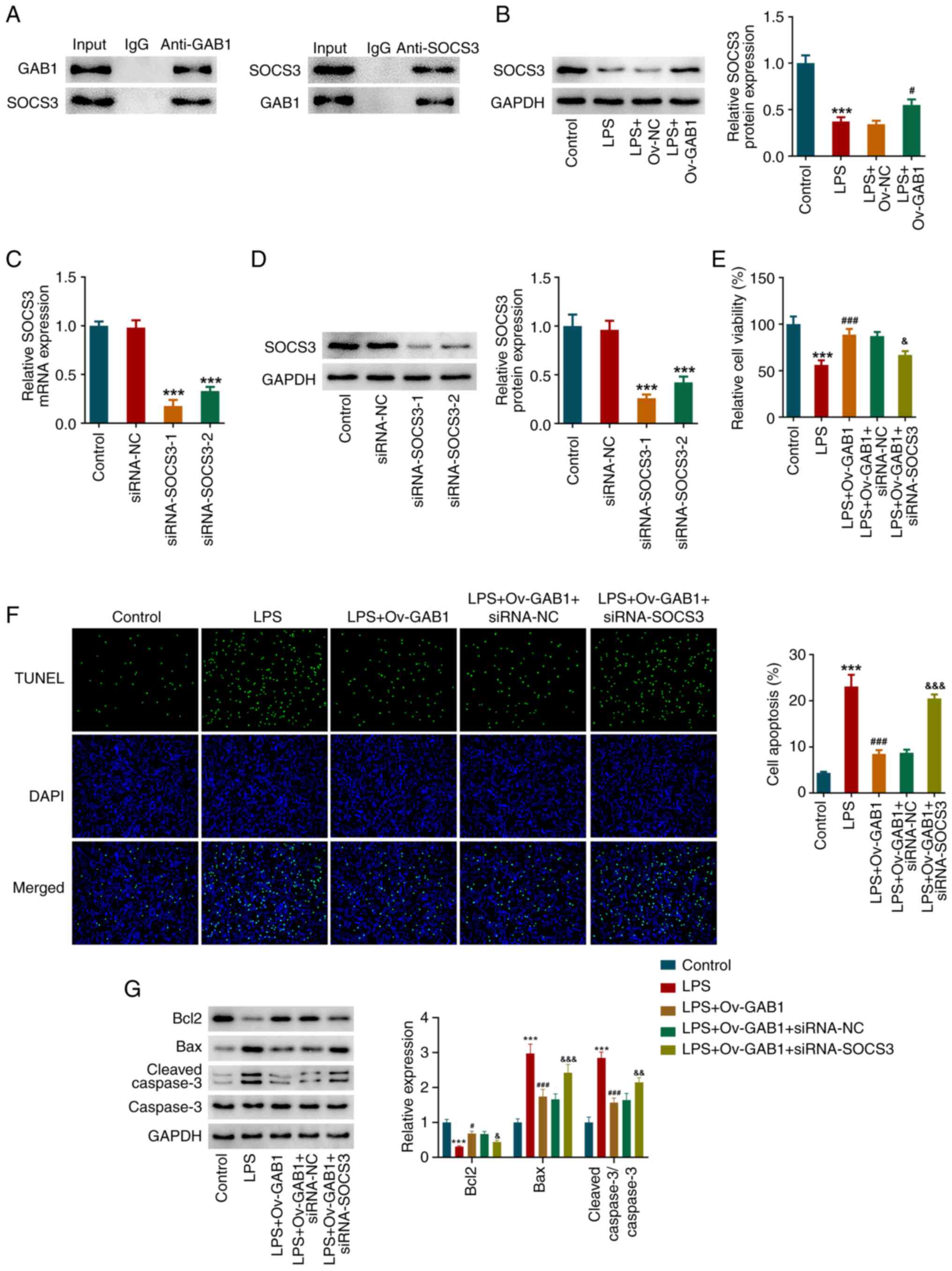
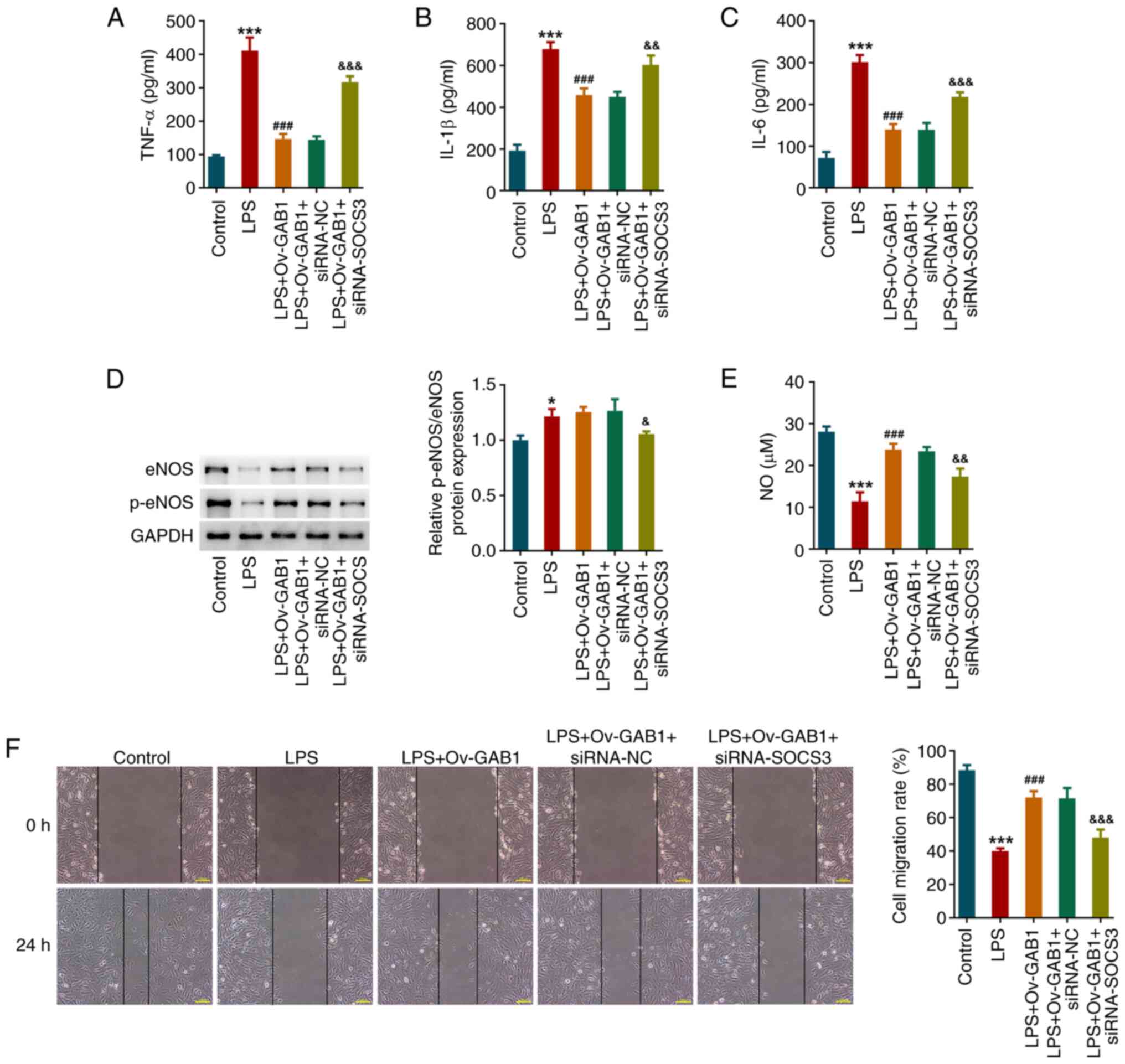
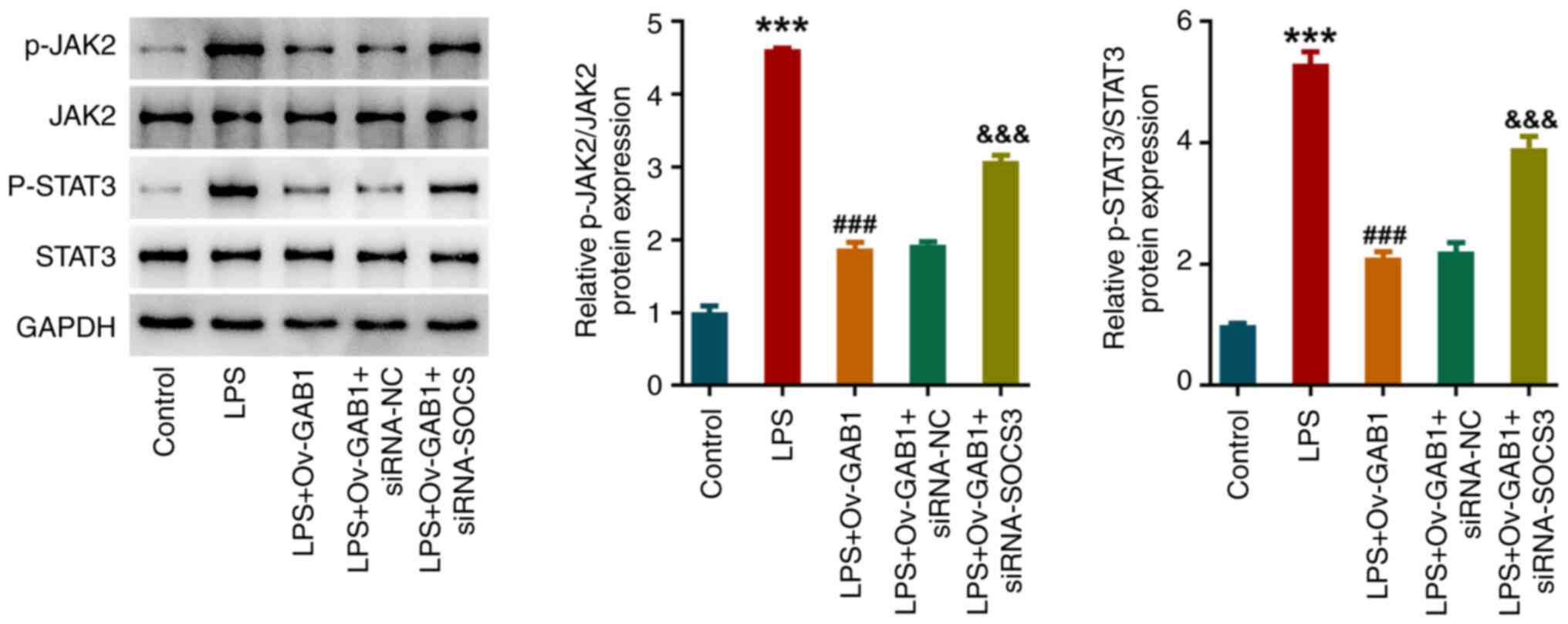
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli
M, Coopersmith CM, French C, Machado FR, Mcintyre L, Ostermann M,
Prescott HC, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International
guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit
Care Med. 49:e1063–e1143. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Seymour CW, Kennedy JN, Wang S, Chang CCH,
Elliott CF, Xu Z, Berry S, Clermont G, Cooper G, Gomez H, et al:
Derivation, validation, and potential treatment implications of
novel clinical phenotypes for sepsis. JAMA. 321:2003–2017.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xie J, Wang H, Kang Y, Zhou L, Liu Z, Qin
B, Ma X, Cao X, Chen D, Lu W, et al: The epidemiology of sepsis in
Chinese ICUs: A national cross-sectional survey. Crit Care Med.
48:e209–e218. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL,
Scicluna BP and Netea MG: The immunopathology of sepsis and
potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:407–420.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lelubre C and Vincent JL: Mechanisms and
treatment of organ failure in sepsis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:417–427.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vincent JL, Ince C and Pickkers P:
Endothelial dysfunction: A therapeutic target in bacterial sepsis?
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 25:733–748. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gu H and Neel BG: The ‘Gab’ in signal
transduction. Trends Cell Biol. 13:122–130. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sun L, Zhu H and Zhang K: GAB1 alleviates
septic lung injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 49:94–103. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Qiu N, Xu X and He Y: LncRNA TUG1
alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting
miR-34b-5p/GAB1. BMC Pulm Med. 20(49)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xiong Y, Wang Y, Tian H, Li Y, Xu Q and He
Z: Circ-PRKCI alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced human kidney 2
cell injury by regulating miR-106b-5p/GAB1 axis. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 78:523–533. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Higuchi K, Nakaoka Y, Shioyama W, Arita Y,
Hashimoto T, Yasui T, Ikeoka K, Kuroda T, Minami T, Nishida K, et
al: Endothelial Gab1 deletion accelerates angiotensin II-dependent
vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E
knockout mice. Circ J. 76:2031–2040. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 402-408:2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kolluru GK, Siamwala JH and Chatterjee S:
eNOS phosphorylation in health and disease. Biochimie.
92:1186–1198. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aird WC: The role of the endothelium in
severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood.
101:3765–3777. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Page AV and Liles WC: Biomarkers of
endothelial activation/dysfunction in infectious diseases.
Virulence. 4:507–516. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Joffre J, Hellman J, Ince C and
Ait-Oufella H: Endothelial responses in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 202:361–370. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Yin M, Zhang H, Ni W, Pierce RW,
Zhou HJ and Min W: BMX represses thrombin-PAR1-mediated endothelial
permeability and vascular leakage during early sepsis. Circ Res.
126:471–485. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang L, Li Y, Cheng Z, Lv Z, Luo S and
Xia Y: PCSK9 promotes endothelial dysfunction during sepsis via the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and NLRP3 pathways. Inflammation. 46:115–128.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhao L, Hu J, Zheng P, Mi B, Chen Z, Zhao
X, Wu J and Wang Y: PAR1 regulates sepsis-induced vascular
endothelial barrier dysfunction by mediating ERM phosphorylation
via the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
124(110992)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Janaszak-Jasiecka A, Siekierzycka A,
Płoska A, Dobrucki IT and Kalinowski L: Endothelial dysfunction
driven by hypoxia-the influence of oxygen deficiency on no
bioavailability. Biomolecules. 11(982)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Carow B and Rottenberg ME: SOCS3, a major
regulator of infection and inflammation. Front Immunol.
5(58)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jin D, Liu Y, Sun F, Wang X, Liu X and He
Z: Restoration of skilled locomotion by sprouting corticospinal
axons induced by co-deletion of PTEN and SOCS3. Nat Commun.
6(8074)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Martino N, Ramos RB, Lu S, Leyden K,
Tomaszek L, Sadhu S, Fredman G, Jaitovich A, Vincent PA and Adam
AP: Endothelial SOCS3 maintains homeostasis and promotes survival
in endotoxemic mice. JCI Insight. 6(e147280)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Martino N, Bossardi Ramos R, Chuy D,
Tomaszek L and Adam AP: SOCS3 limits TNF and endotoxin-induced
endothelial dysfunction by blocking a required autocrine
interleukin-6 signal in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 323:C556–C569. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jaśkiewicz A, Domoradzki T and Pająk B:
Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway-can we compare it to the two faces
of the God Janus? Int J Mol Sci. 21(8261)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu Q, Wang H, Li X and Leng B: Effects of
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation on sepsis-induced kidney
injury. Minerva Med. 113:350–352. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhen G, Liang W, Jia H and Zheng X:
Melatonin relieves sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Minerva Med. 113:983–989.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu Y, Li D, Huang Y, Sun Y, Zhou H, Ye F,
Yang H, Xu T, Quan S and Pan J: Pretreatment with eupatilin
attenuates inflammation and coagulation in sepsis by suppressing
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Inflamm Res. 16:1027–1042.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Durham GA, Williams JJL, Nasim MT and
Palmer TM: Targeting SOCS proteins to control JAK-STAT signalling
in disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40:298–308. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gao Y, Zhao H, Wang P, Wang J and Zou L:
The roles of SOCS3 and STAT3 in bacterial infection and
inflammatory diseases. Scand J Immunol. 88(e12727)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|