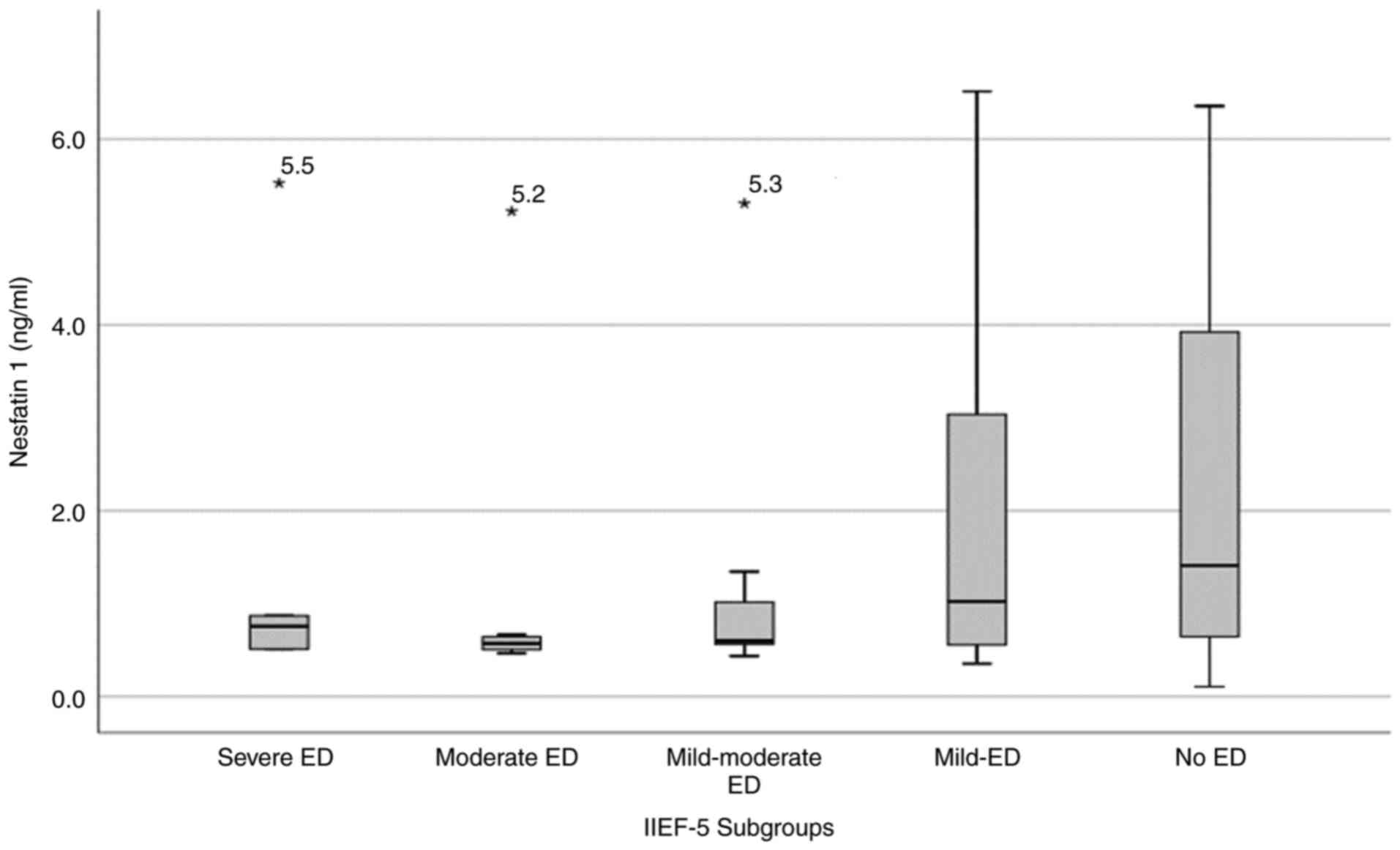
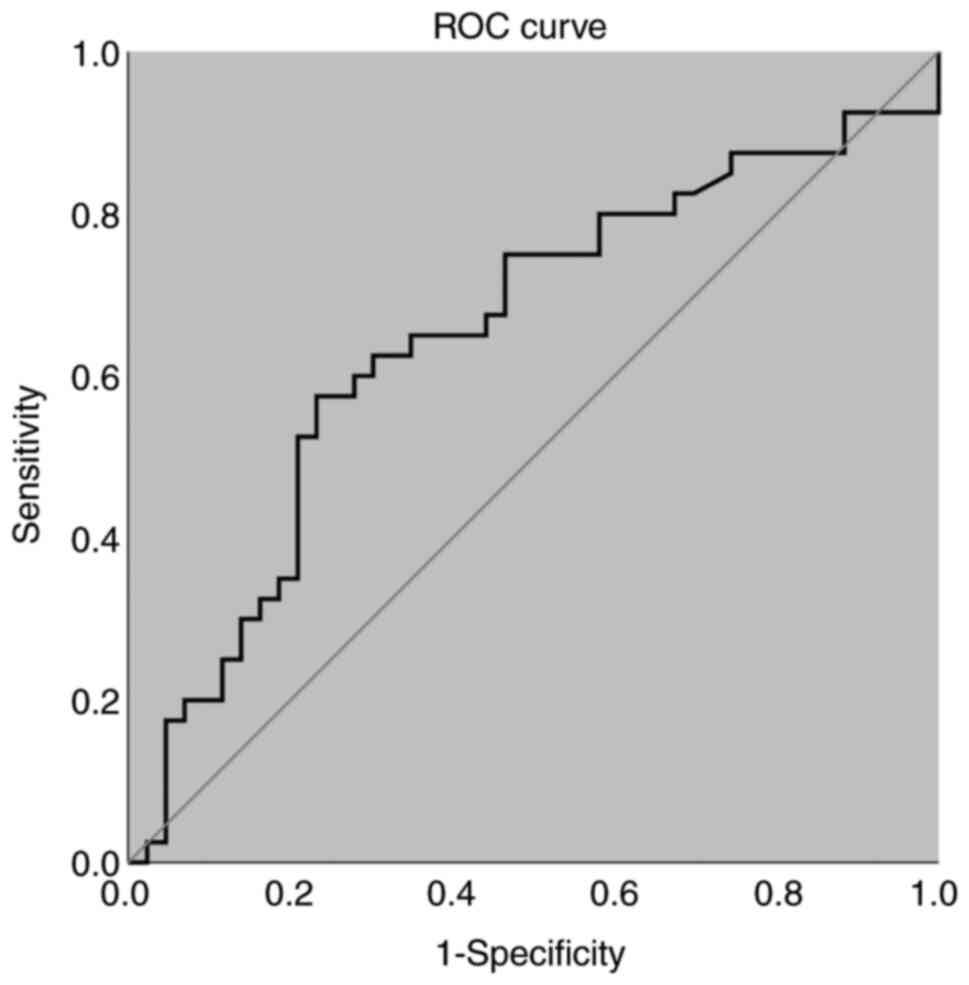
|
1
|
NIH Consensus Conference Impotence. NIH
consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA. 270:83–90.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sexual and Reproductive Health-Management
of erectile dysfunction-Uroweb.
|
|
3
|
Cho JW and Duffy JF: Sleep, sleep
disorders, and sexual dysfunction. World J Mens Health. 37:261–275.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shamloul R and Ghanem H: Erectile
dysfunction. Lancet. 381:153–65. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gratzke C, Angulo J, Chitaley K, Dai YT,
Kim NN, Paick JS, Simonsen U, Uckert S, Wespes E, Andersson KE, et
al: Anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of erectile
dysfunction. J Sex Med. 7:445–475. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Salonia A, Bettocchi C, Boeri L,
Capogrosso P, Carvalho J, Cilesiz NC, Cocci A, Corona G,
Dimitropoulos K, Gül M, et al: European association of urology
guidelines on sexual and reproductive health-2021 update: Male
sexual dysfunction. Eur Urol. 80:333–357. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Carson CC and Dean JD: Management of
Erectile Dysfunction in Clinical Practice. Springer Medical
Publishing, New York, NY, 2006.
|
|
8
|
Rosen RC: Psychogenic erectile
dysfunction. Classification and management. Urol Clin North Am.
28:269–278. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pastuszak AW: Current diagnosis and
management of erectile dysfunction. Curr Sex Health Rep. 6:164–176.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Janmohamed S and Bouloux PG: Endocrinology
of male sexual dysfunction. In: Male Sexual Dysfunction. Wiley,
Hoboken, NJ, pp30-47, 2017.
|
|
11
|
Sun W, Bi LK, Xie DD and Yu DX: Serum
nesfatin-1 is associated with testosterone and the severity of
erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. 52(e13634)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ragab A, Ahmed MH, Reda Sayed A,
EldinAbdelbary DAK and GamalEl Din SF: Serum nesfatin-1 level in
men with diabetes and erectile dysfunction correlates with
generalized anxiety disorder-7: A prospective comparative study.
Andrology. 11:307–315. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Oh IS, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi
S, Inoue K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto M, Imaki T, Hashimoto K, et al:
Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the
hypothalamus. Nature. 443:709–712. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yamawaki H, Takahashi M, Mukohda M, Morita
T, Okada M and Hara Y: A novel adipocytokine, nesfatin-1 modulates
peripheral arterial contractility and blood pressure in rats.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 418:676–681. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ozcan M, Gok ZB, Kacar E, Serhatlioglu I
and Kelestimur H: Nesfatin-1 increases intracellular calcium
concentration by protein kinase C activation in cultured rat dorsal
root ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett. 619:177–181. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao X, Zhang K, Song M, Li X, Luo L, Tian
Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Ling Y, et al: Role of Nesfatin-1 in the
Reproductive Axis of Male Rat. Sci Rep. 6(32877)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Barutcigil A and Tasatargil A: Effects of
nesfatin-1 on atrial contractility and thoracic aorta reactivity in
male rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. 40:414–420. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
World Medical Association. World medical
association declaration of helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Turunc T, Deveci S, Güvel S and
Peşkircioğlu L: The assessment of turkish validation with 5
question version of international index of erectile function
(IIEF-5). Turk J Urol. 33:45–49. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG and Buchner
A: G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the
social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods.
39:175–191. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Stengel A and Tache Y: Minireview:
Nesfatin-1-an emerging new player in the brain-gut, endocrine, and
metabolic axis. Endocrinology. 152:4033–4038. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Stengel A: Nesfatin-1-More than a food
intake regulatory peptide. Peptides. 72:175–183. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rupp SK, Wölk E and Stengel A: Nesfatin-1
Receptor: Distribution, signaling and increasing evidence for a G
protein-coupled receptor-A systematic review. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12(740174)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gonzalez R, Perry RL, Gao X, Gaidhu MP,
Tsushima RG, Ceddia RB and Unniappan S: Nutrient Responsive
Nesfatin-1 regulates energy balance and induces glucose-stimulated
insulin secretion in rats. Endocrinology. 152:3628–3637.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aydin S: Role of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 as a
Possible Biomarker. Curr Pharm Des. 19:6986–6992. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Şahin Z: Could the change of anorexigenic
function of nesfatin-1 during the day be associated with circadian
rhythm? Troia Med J. 2022.
|
|
27
|
Hatef A, Shajan S and Unniappan S:
Nutrient status modulates the expression of nesfatin-1 encoding
nucleobindin 2A and 2B mRNAs in zebrafish gut, liver and brain. Gen
Comp Endocrinol. 215:51–60. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
García-Galiano D, Pineda R, Ilhan T,
Castellano JM, Ruiz-Pino F, Sánchez-Garrido MA, Vazquez MJ,
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Romero-Ruiz A, Pinilla L, et al: Cellular
distribution, regulated expression, and functional role of the
anorexigenic peptide, NUCB2/Nesfatin-1, in the Testis.
Endocrinology. 153:1959–1971. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Riva M, Nitert MD, Voss U, Sathanoori R,
Lindqvist A, Ling C and Wierup N: Nesfatin-1 stimulates glucagon
and insulin secretion and beta cell NUCB2 is reduced in human type
2 diabetic subjects. Cell Tissue Res. 346:393–405. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Foo KS, Brauner H, Östenson CG and
Broberger C: Nucleobindin-2/nesfatin in the endocrine pancreas:
Distribution and relationship to glycaemic state. J Endocrinol.
204:255–263. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kadim BM and Hassan EA: Nesfatin-1-as a
diagnosis regulatory peptide in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Diabetes Metab Disord. 21:1369–1375. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu D, Yang M, Chen Y, Jia Y, Ma ZA, Boden
G, Li L and Yang G: Hypothalamic nesfatin-1/NUCB2 knockdown
augments hepatic gluconeogenesis that is correlated with inhibition
of mTOR-STAT3 signaling pathway in rats. Diabetes. 63:1234–1247.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hofmann T, Elbelt U, Ahnis A, Rose M,
Klapp BF and Stengel A: Sex-specific regulation of
NUCB2/nesfatin-1: Differential implication in anxiety in obese men
and women. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 60:130–137. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu GM, Xu ZQ and Ma HS:
Nesfatin-1/nucleobindin-2 is a potent prognostic marker and
enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in bladder
cancer. Dis Markers. 2018(4272064)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim J, Chung Y, Kim H, Im E, Lee H and
Yang H: The tissue distribution of Nesfatin-1/NUCB2 in mouse. Dev
Reprod. 18:301–309. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cheng YY, Zhao XM, Cai BP, Ma LN, Yin JY
and Song GY: Nesfatin-1 in newborns: Relationship with endocrine
and metabolic and anthropometric measures. J Pediatr Endocrinol
Metab. 25:727–732. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhai T, Li SZ, Fan XT, Tian Z, Lu XQ and
Dong J: Circulating Nesfatin-1 levels and type 2 diabetes: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res.
2017(7687098)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo Y, Liao Y, Fang G, Dong J and Li Z:
Increased nucleobindin-2 (NUCB2) transcriptional activity links the
regulation of insulin sensitivity in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Endocrinol Invest. 36:883–888. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Z, Li L, Yang M, Liu H, Boden G and
Yang G: Increased plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with
newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol
Diabetes. 120:91–95. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Algul S, Ozkan Y and Ozcelik O: Serum
nesfatin-1 levels in patients with different glucose tolerance
levels. Physiol Res. 65:979–985. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dai R, Deng G, Sun Z, Liu Z, Qian Y and
Han Y: Relation of serum and vitreous nesfatin-1 concentrations
with diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Lab Anal.
31(e22105)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li QC, Wang HY, Chen X, Guan HZ and Jiang
ZY: Fasting plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with type 1 and
type 2 diabetes mellitus and the nutrient-related fluctuation of
nesfatin-1 level in normal humans. Regul Pept. 159:72–77.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu F, Yang Q, Gao N, Liu F and Chen S:
Decreased plasma nesfatin-1 level is related to the thyroid
dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes
Res. 2014(128014)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Aydin MA, Aydogdu N, Tastekin E, Firat N
and Yalcinkaya Yavuz O: Investigation of the Relationship of
Nesfatin-1, Adropin Levels and Claudin-2, renalase immunoreactivity
with kidney function in an experimental hypertension model. P R
Health Sci J. 43:39–45. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kovalyova O, Ashcheulova T, Demydenko A,
Vizir M and Kochubiei O: Nesfatin-1 activity in patients with
essential hypertension and prediabetes, type 2 diabetes. Georgian
Med News. 44–49. 2017.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
46
|
Xu Y, Zhang H, Li Q, Lao K and Wang Y: The
role of nesfatin-1 expression in letrozole-induced polycystic
ovaries in the rat. Gynecol Endocrinol. 33:438–441. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sahin FK, Sahin SB, Ural UM, Cure MC,
Senturk S, Tekin YB, Balik G, Cure E, Yuce S and Kirbas A:
Nesfatin-1 and Vitamin D levels may be associated with systolic and
diastolic blood pressure values and hearth rate in polycystic ovary
syndrome. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 15:57–63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Varlı B, Şükür YE, Özmen B, Ergüder Bİ,
Sönmezer M, Berker B, Atabekoğlu C and Aytaç R: Anorexigenic
peptide (leptin, obestatin, nesfatin-1) levels and their impact on
assisted reproductive technology treatment outcomes in patients
with polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 48:368–373.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Alp E, Görmüş U, Güdücü N and Bozkurt S:
Nesfatin-1 levels and metabolic markers in polycystic ovary
syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 31:543–547. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sun J, Zhang D, Xu J, Chen C, Deng D, Pan
F, Dong L, Li S and Ye S: Circulating FABP4, nesfatin-1, and
osteocalcin concentrations in women with gestational diabetes
mellitus: A meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis.
19(199)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Almasi N, Zengin HY, Koç N, Uçakturk SA,
İskender Mazman D, Heidarzadeh Rad N and Fisunoglu M: Leptin,
ghrelin, nesfatin-1, and orexin-A plasma levels in girls with
premature thelarche. J Endocrinol Invest. 45:2097–2103.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
García-Galiano D, Navarro VM, Roa J,
Ruiz-Pino F, Sánchez-Garrido MA, Pineda R, Castellano JM, Romero M,
Aguilar E, Gaytán F, et al: The anorexigenic neuropeptide,
nesfatin-1, is indispensable for normal puberty onset in the female
rat. J Neurosci. 30:7783–7792. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chung Y, Kim H, Im E, Kim P and Yang H: Th
17 Cells and Nesfatin-1 are associated with Spontaneous Abortion in
the CBA/j x DBA/2 Mouse Model. Dev Reprod. 19:243–252.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kim J, Sun S, Lee D, Youk H and Yang H:
Gonadotropin regulates NUCB2/nesfatin-1 expression in the mouse
ovary and uterus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:602–607.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hofmann T, Stengel A, Ahnis A, Buße P,
Elbelt U and Klapp BF: NUCB2/nesfatin-1 is associated with elevated
scores of anxiety in female obese patients.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 38:2502–2510. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Chen K, Huang B, Feng J, Fan S, Hu Z, Ren
S, Tian H, Abdulkarem AL, Wang X, Tuo Y, et al: Nesfatin-1
regulates the phenotype transition of cavernous smooth muscle cells
by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to improve diabetic
erectile dysfunction. Heliyon. 10(e32524)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ranjan A, Choubey M, Yada T and Krishna A:
Direct effects of neuropeptide nesfatin-1 on testicular
spermatogenesis and steroidogenesis of the adult mice. Gen Comp
Endocrinol. 271:49–60. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim S, Sun S, Kim M, Ha J, Seok E and Yang
H: NUCB2/nesfatin-1 suppresses the acrosome reaction in sperm
within the mouse epididymis. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 27:120–128.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fazio L and Brock G: Erectile dysfunction:
Management update. Can Med Assoc J. 170:1429–1437. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Burnett AL: Nitric oxide in the penis:
Physiology and pathology. J Urol. 157:320–324. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Priviero FB, Leite R, Webb RC and Teixeira
CE: Neurophysiological basis of penile erection. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 28:751–755. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Mori Y, Shimizu H, Kushima H, Saito T,
Hiromura M, Terasaki M, Koshibu M, Ohtaki H and Hirano T:
Nesfatin-1 suppresses peripheral arterial remodeling without
elevating blood pressure in mice. Endocr Connect. 8:536–546.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Angelone T, Filice E, Pasqua T, Amodio N,
Galluccio M, Montesanti G, Quintieri AM and Cerra MC: Nesfatin-1 as
a novel cardiac peptide: Identification, functional
characterization, and protection against ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:495–509. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Seon S, Jeon D, Kim H, Chung Y, Choi N and
Yang H: Testosterone Regulates NUCB2 mRNA expression in male mouse
hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Dev Reprod. 21:71–78.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|