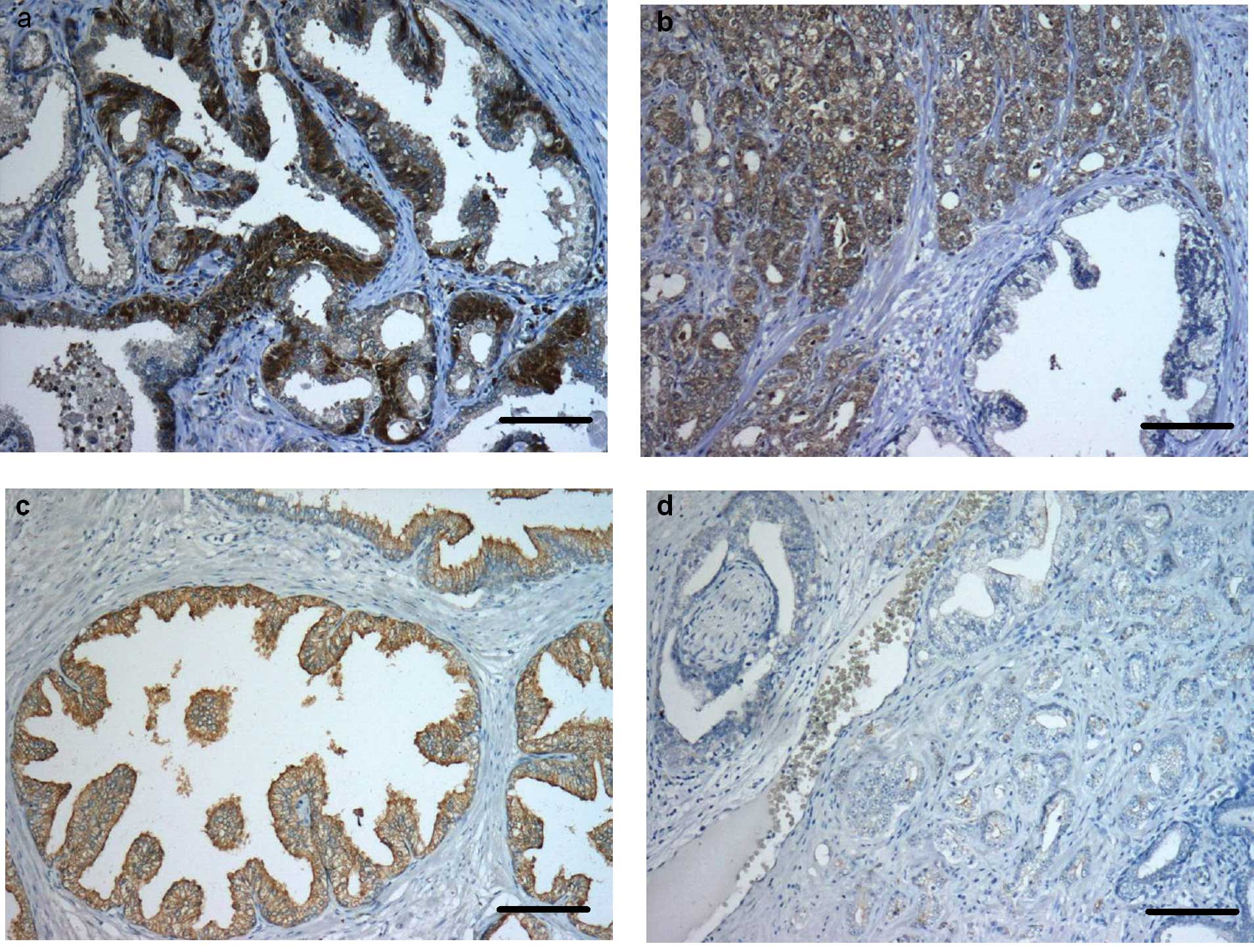
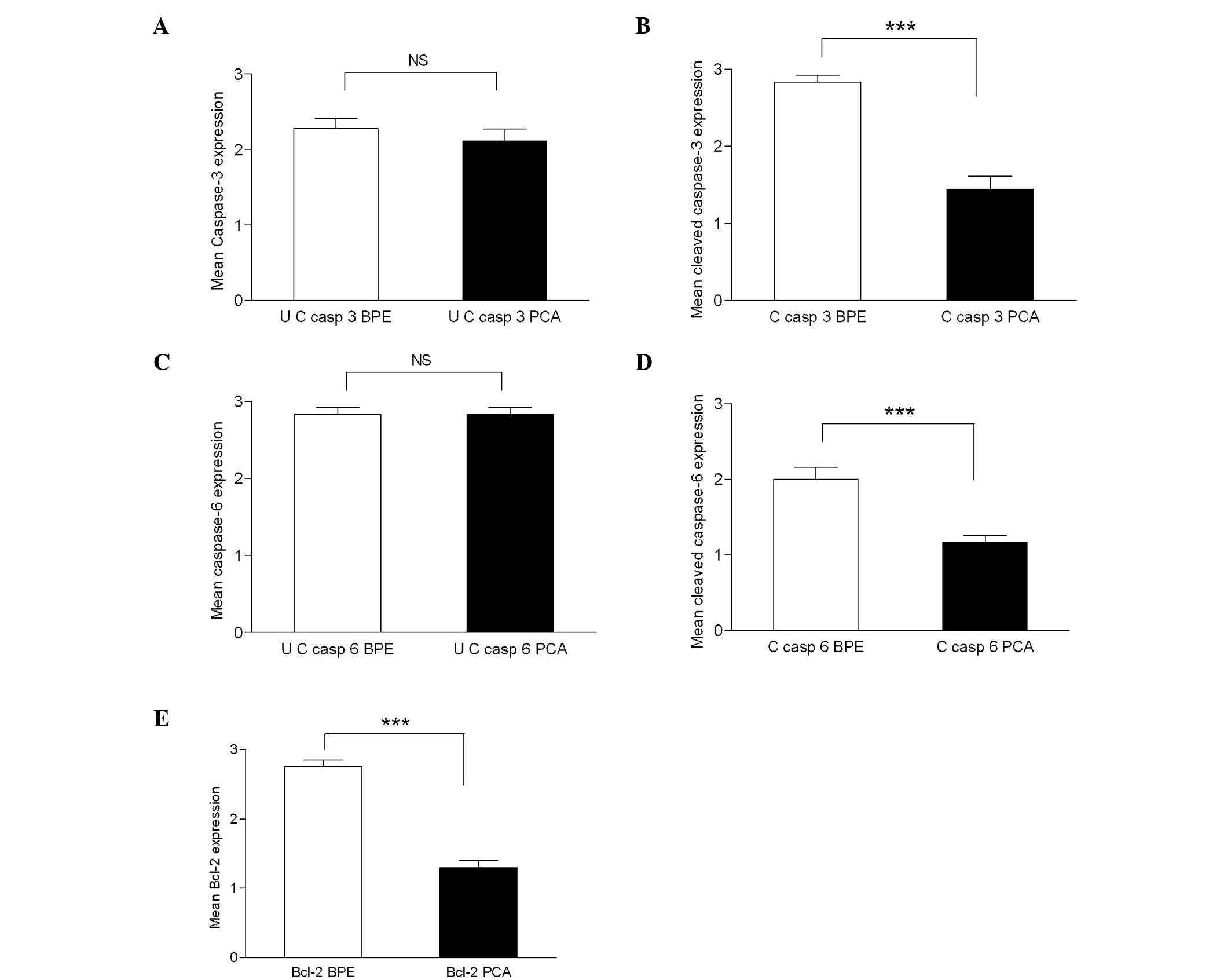
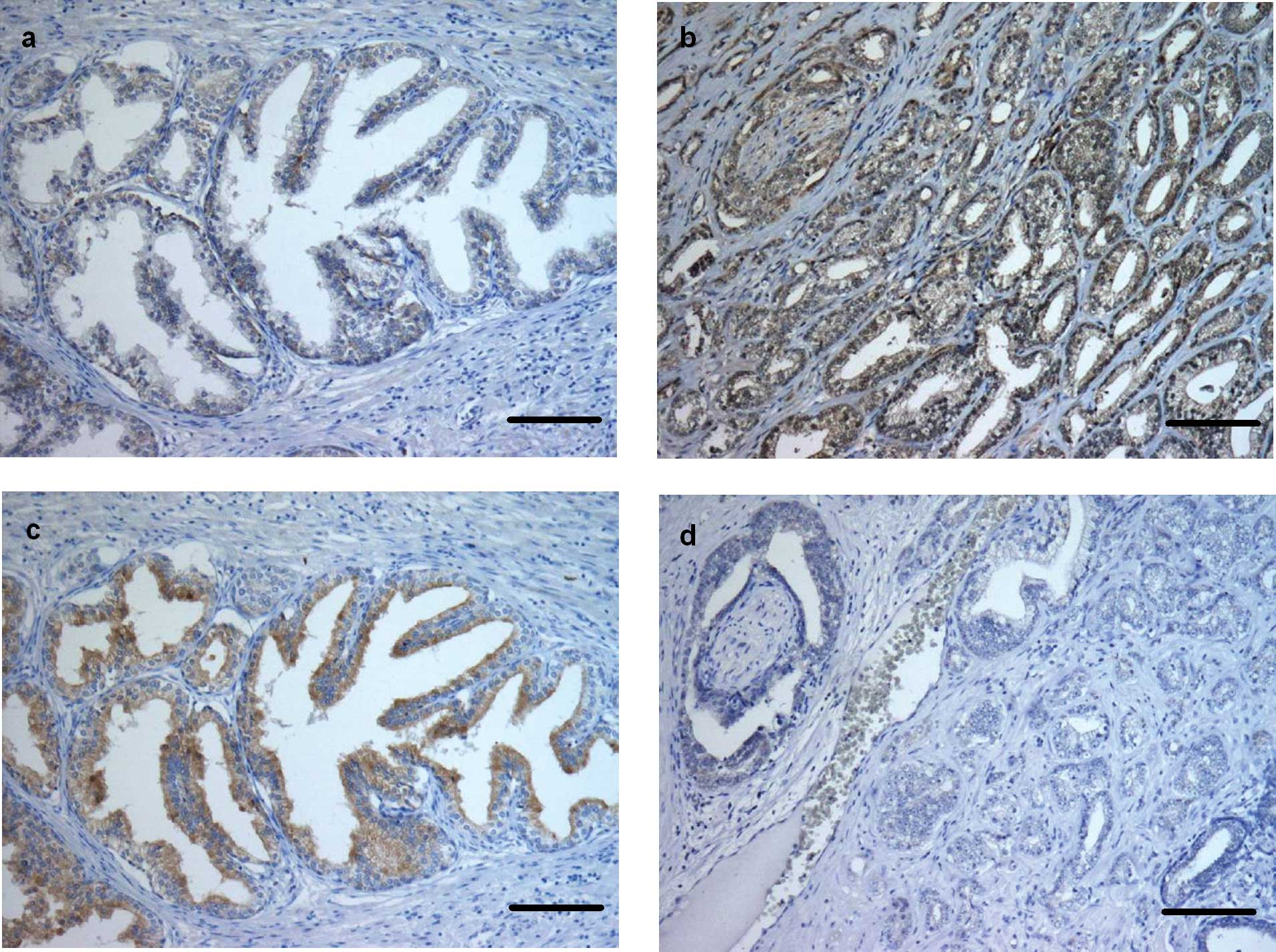
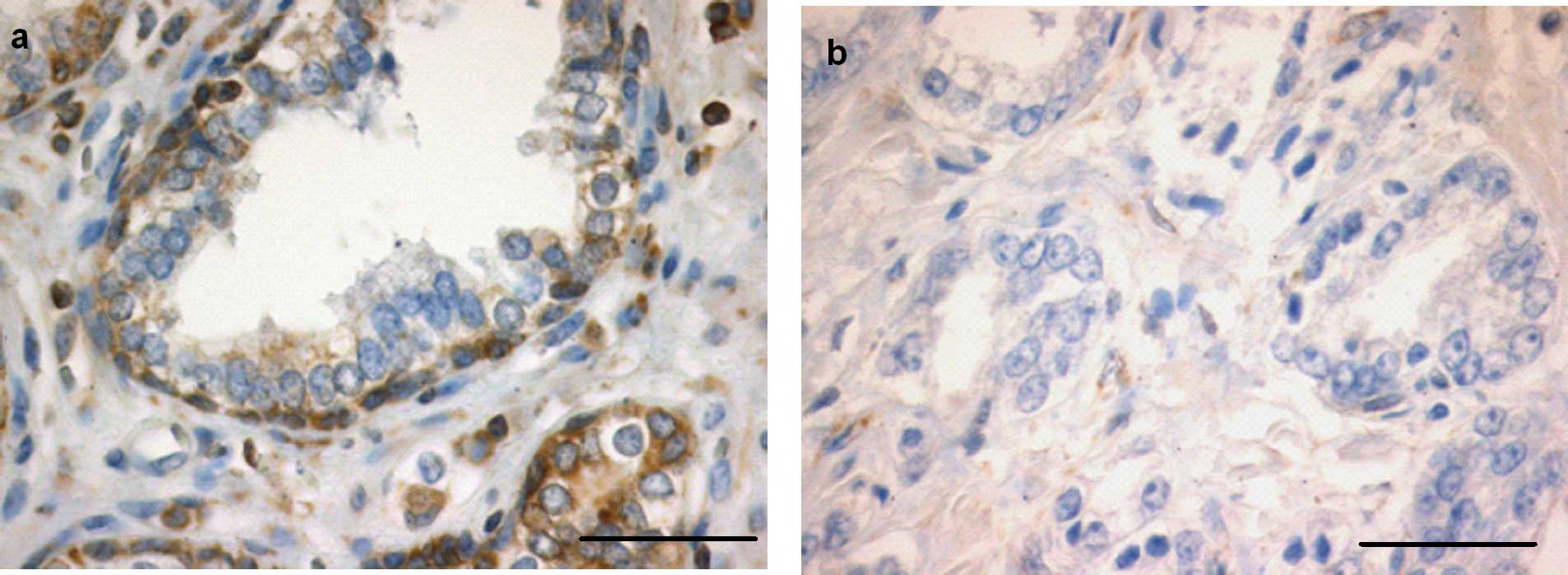
|
1.
|
Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S and Wingo
PA: Cancer statistics, 1999. CA Cancer J Clin. 49:8–31. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Slee EA, Adrain C and Martin SJ: Serial
killers: ordering caspase activation events in apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 6:1067–1074. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Woo M, Hakem R, Soengas MS, Duncan GS,
Shahinian A, Kagi D, Hakem A, McCurrach M, Khoo W, Kaufman SA,
Senaldi G, Howard T, Lowe SW and Mak TW: Essential contribution of
caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes.
Genes Dev. 12:806–819. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Harvey NL and Kumar S: The role of
caspases in apoptosis. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 62:107–128.
1998.
|
|
5.
|
Stegh AH and Peter ME: Apoptosis and
caspases. Cardiol Clin. 19:13–29. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Nunez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y and Inohara N:
Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene.
17:3237–3245. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen
C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH and Peter ME: Two
CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17:1675–1687. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Thornberry NA, Bull HG, Calaycay JR, et
al: A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for
interleukin-1 beta processing in monocytes. Nature. 356:768–774.
1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Stennicke HR, Deveraux QL, Humke EW, Reed
JC, Dixit VM and Salvesen GS: Caspase-9 can be activated without
proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem. 274:8359–8362. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB,
Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri
ES, Green DR and Martin SJ: Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated
caspase cascade: hierarchical activation of caspases-2, -3, -6, -7,
-8 and -10 in a caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol.
144:281–292. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Reed JC: Bcl-2 and the regulation of
programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 124:1–6. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Reed JC: Mechanisms of apoptosis. Am J
Pathol. 157:1415–1430. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Winter RN, Kramer A, Borkowski A and
Kyprianou N: Loss of caspase-1 and caspase-3 protein expression in
human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 61:1227–1232. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Gleason DF and Mellinger GT: Prediction of
prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological
grading and clinical staging. J Urol. 111:58–64. 1974.
|
|
17.
|
Mellinger GT, Gleason D and Bailar J III:
The histology and prognosis of prostatic cancer. J Urol.
97:331–337. 1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Woenckhaus C, Giebel J, Failing K, Fenic
I, Dittberner T and Poetsch M: Expression of AP-2alpha, c-kit and
cleaved caspase-6 and -3 in naevi and malignant melanomas of the
skin. A possible role for caspases in melanoma progression? J
Pathol. 201:278–287. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
McNeal JE: Normal histology of the
prostate. Am J Surg Pathol. 12:619–633. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
McNeal JE: Regional morphology and
pathology of the prostate. Am J Clin Pathol. 49:347–357.
1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
McNeal JE: Origin and development of
carcinoma in the prostate. Cancer. 23:24–34. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
McNeal JE: Origin and evolution of benign
prostatic enlargement. Invest Urol. 15:340–345. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Srodon M and Epstein JI: Central zone
histology of the prostate: a mimicker of high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol. 33:518–523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
O’Neill AJ, Boran SA, O’Keane C, Coffey
RN, Hegarty NJ, Hegarty P, Gaffney EF, Fitzpatrick JM and Watson
RW: Caspase 3 expression in benign prostatic hyperplasia and
prostate carcinoma. Prostate. 47:183–188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Sohn JH, Kim DH, Choi NG, Park YE and Ro
JY: Caspase-3/CPP32 immunoreactivity and its correlation with
frequency of apoptotic bodies in human prostatic carcinomas and
benign nodular hyperplasias. Histopathology. 37:555–560. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ananthanarayanan V, Deaton RJ, Yang XJ,
Pins MR and Gann PH: Alteration of proliferation and apoptotic
markers in normal and premalignant tissue associated with prostate
cancer. BMC Cancer. 6:732006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Vakkala M, Paakko P and Soini Y:
Expression of caspases 3, 6 and 8 is increased in parallel with
apoptosis and histological aggressiveness of the breast lesion. Br
J Cancer. 81:592–599. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kang JJ, Schaber MD, Srinivasula SM,
Alnemri ES, Litwack G, Hall DJ and Bjornsti MA: Cascades of
mammalian caspase activation in the yeast Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 274:3189–3198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Allsopp TE, McLuckie J, Kerr LE, Macleod
M, Sharkey J and Kelly JS: Caspase 6 activity initiates caspase 3
activation in cerebellar granule cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ.
7:984–993. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Reinhold WC, Kouros-Mehr H, Kohn KW,
Maunakea AK, Lababidi S, Roschke A, Stover K, Alexander J, Pantazis
P, Miller L, Liu E, Kirsch IR, Urasaki Y, Pommier Y and Weinstein
JN: Apoptotic susceptibility of cancer cells selected for
camptothecin resistance: gene expression profiling, functional
analysis and molecular interaction mapping. Cancer Res.
63:1000–1011. 2003.
|
|
31.
|
Lee SC, Chan J, Clement MV and Pervaiz S:
Functional proteomics of resveratrol-induced colon cancer cell
apoptosis: caspase-6-mediated cleavage of lamin A is a major
signaling loop. Proteomics. 6:2386–2394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM,
Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT, Tu SM and Campbell ML: Expression
of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with
emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
52:6940–6944. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Tu H, Jacobs SC, Borkowski A and Kyprianou
N: Incidence of apoptosis and cell proliferation in prostate
cancer: relationship with TGF-beta1 and bcl-2 expression. Int J
Cancer. 69:357–363. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Johnson MI, Robinson MC, Marsh C, Robson
CN, Neal DE and Hamdy FC: Expression of Bcl-2, Bax and p53 in
high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and localized
prostate cancer: relationship with apoptosis and proliferation.
Prostate. 37:223–229. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|