Spandidos Publications style
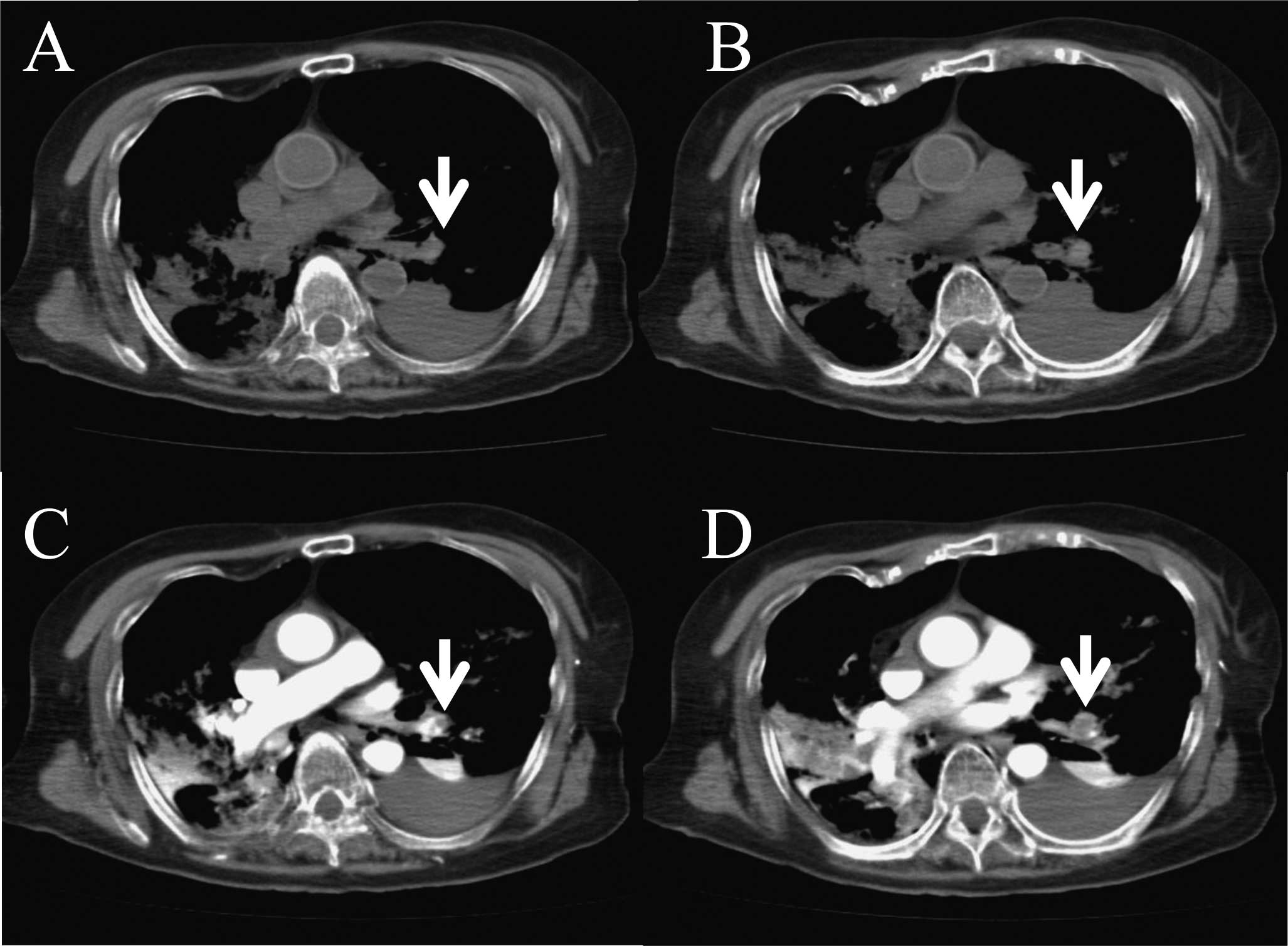
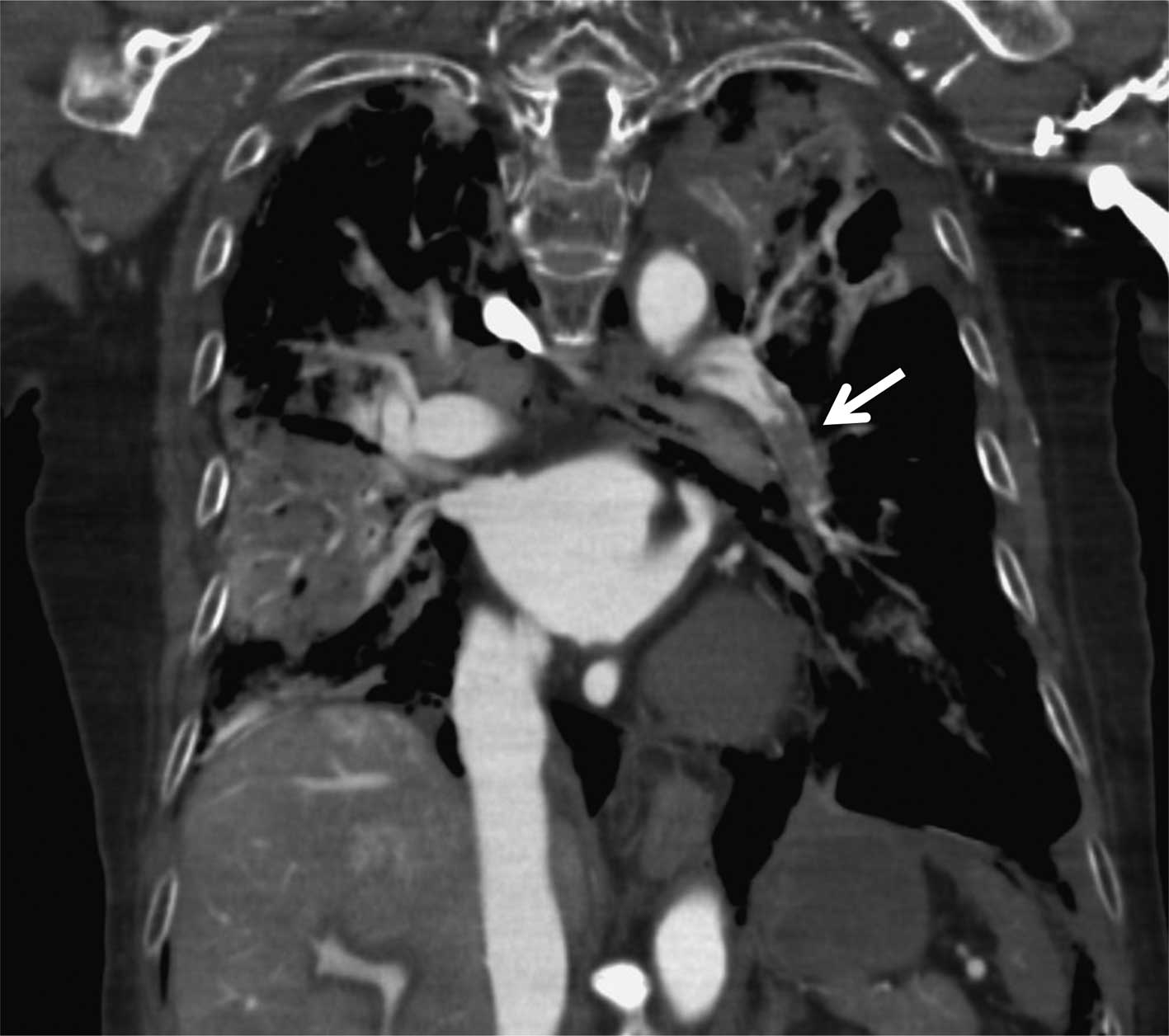
Kikuchi K, Kawahara K, Tsuji C, Tajima Y, Kuramoto T, Shihara M, Koga Y, Shiomi N, Uchikado H, Morimoto Y, Morimoto Y, et al: Post mortem contrast-enhanced computed tomography in a case of sudden death from acute pulmonary thromboembolism
. Exp Ther Med 1: 503-505, 2010.
APA
Kikuchi, K., Kawahara, K., Tsuji, C., Tajima, Y., Kuramoto, T., Shihara, M. ... Shigemori, M. (2010). Post mortem contrast-enhanced computed tomography in a case of sudden death from acute pulmonary thromboembolism
. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 1, 503-505. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm_00000079
MLA
Kikuchi, K., Kawahara, K., Tsuji, C., Tajima, Y., Kuramoto, T., Shihara, M., Koga, Y., Shiomi, N., Uchikado, H., Morimoto, Y., Miura, N., Mera, K., Ohno, Y., Miyagi, N., Hashiguchi, T., Maruyama, I., Hayabuchi, N., Nakayama, K., Shigemori, M."Post mortem contrast-enhanced computed tomography in a case of sudden death from acute pulmonary thromboembolism
". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 1.3 (2010): 503-505.
Chicago
Kikuchi, K., Kawahara, K., Tsuji, C., Tajima, Y., Kuramoto, T., Shihara, M., Koga, Y., Shiomi, N., Uchikado, H., Morimoto, Y., Miura, N., Mera, K., Ohno, Y., Miyagi, N., Hashiguchi, T., Maruyama, I., Hayabuchi, N., Nakayama, K., Shigemori, M."Post mortem contrast-enhanced computed tomography in a case of sudden death from acute pulmonary thromboembolism
". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 1, no. 3 (2010): 503-505. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm_00000079