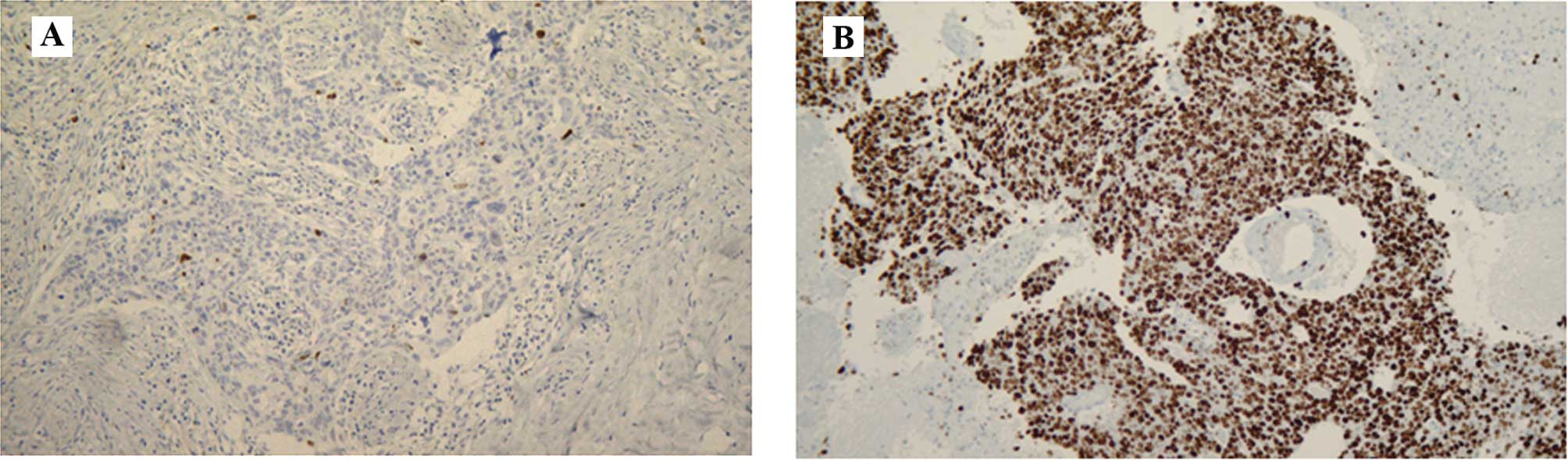
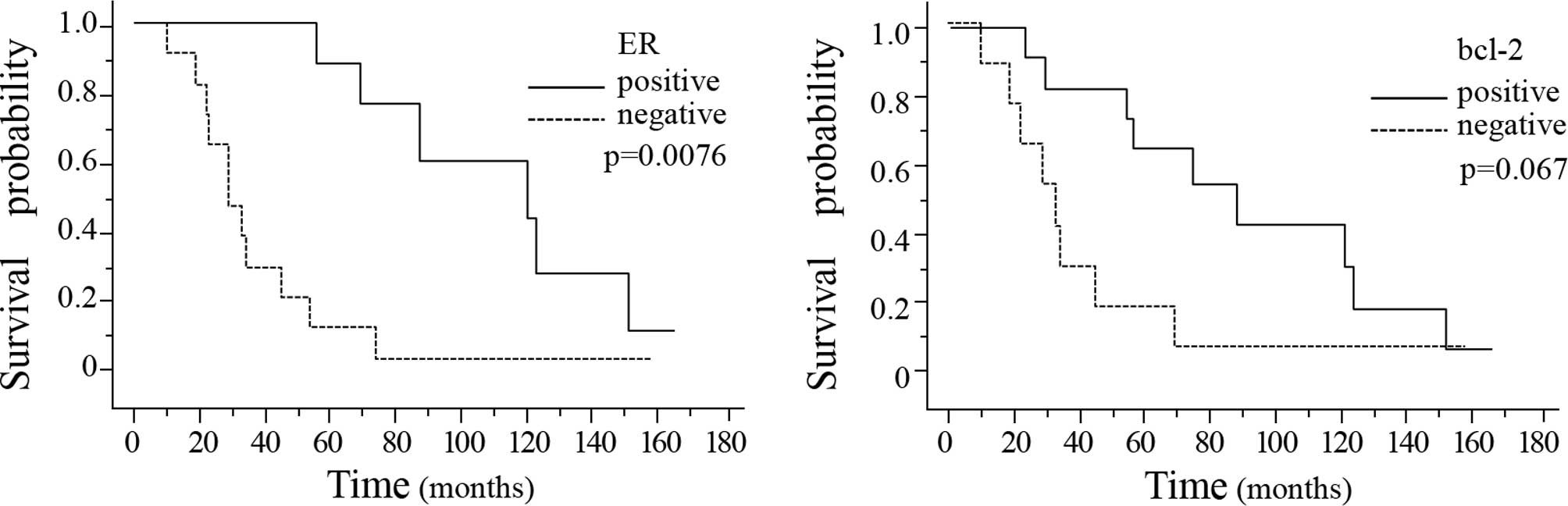
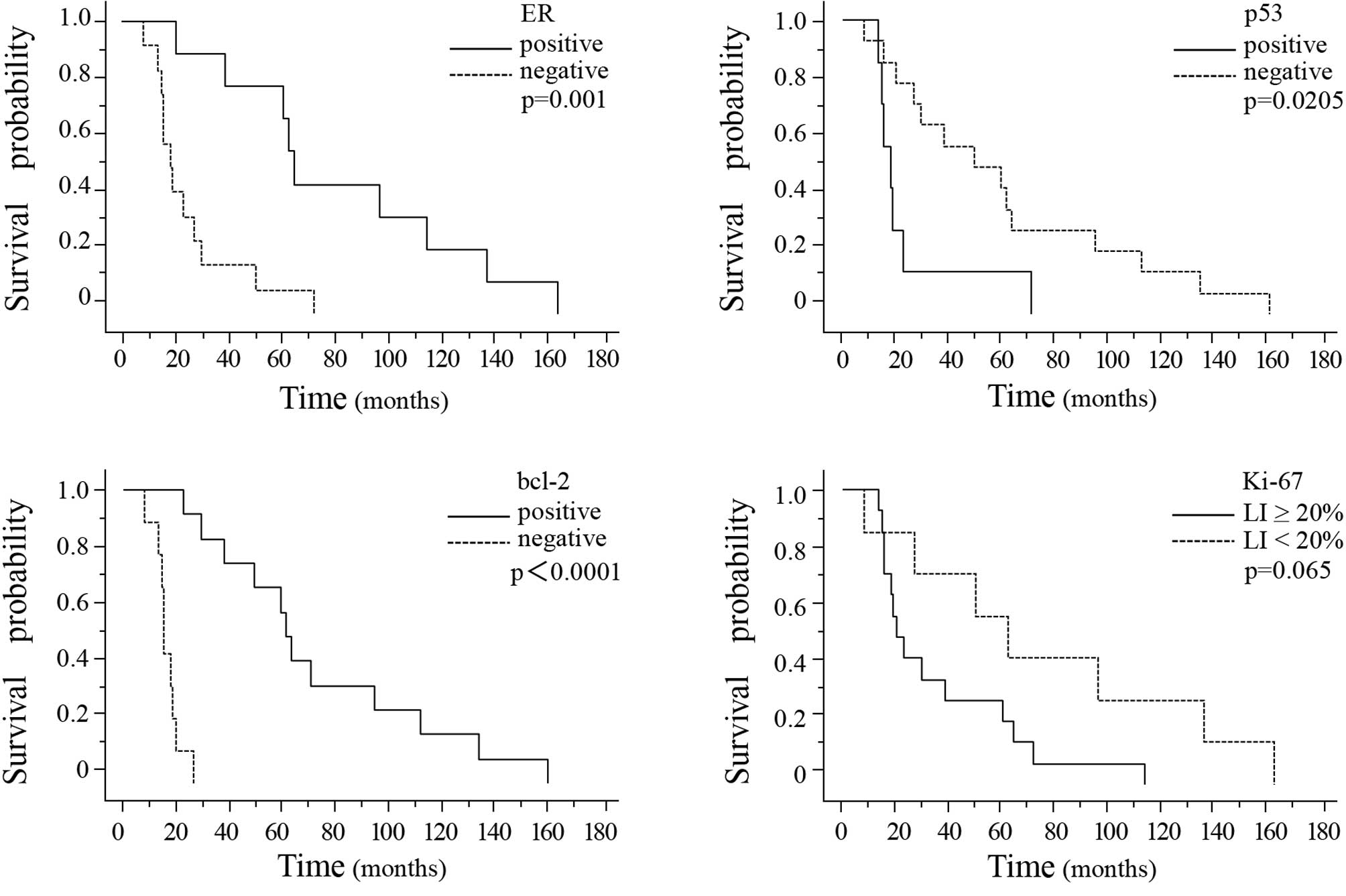
|
1.
|
Lin NU, Bellon JR and Winer EP: CNS
metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:3608–3617. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Shaffrey ME, Mut M, Asher AL, Burri SH,
Chahlavi A, Chang SM, Farace E, Fiveash JB, Lang FF, Lopes MB,
Markert JM, Schiff D, Siomin V, Tatter SB and Voqelbaum MA: Brain
metastasis. Curr Probl Surg. 41:665–741. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Engel J, Eckel R, Aydemir U, Aydemir S,
Kerr J, Schlesinger-Raab A, Dirschedl P and Holzel D: Determinants
and prognoses of locoregional and distant progression in breast
cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 55:1186–1195. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM,
Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Butt GT,
Tubbs RR, Casey G and Weil RJ: Breast cancers with brain metastases
are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal
cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Pathol.
30:1097–1103. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Ryberg M, Nielsen D, Osterlind K, Andersen
PK, Skovsgaard T and Dombernowsky P: Predictors of central nervous
system metastasis in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A
competing risk analysis of 579 patients treated with
epirubicin-based chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 91:217–225.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Evans AJ, James JJ, Cornford EJ, Chan SY,
Burrell HC, Pinder SE, Gutteridge E, Robertson JF, Hornbuckle J and
Cheung KL: Brain metastasis from breast cancer: identification of a
high-risk group. Clin Oncol. 16:345–349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Slimane K, Andre F, Delaloge S, Dunant A,
Perez A, Grenier J, Massard C and Spielmann M: Risk factors for
brain relapse in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
15:1640–1644. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Maki D and Grossman RI: Patterns of
disease spread in meta-static breast carcinoma: influence of
estrogen and progesterone receptor status. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
21:1064–1066. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH,
Schwab U and Stein H: Cell cycle analysis of a cell
proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 133:1710–1715.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Molino A, Micciolo R, Turazza M, Bonetti
F, Piubello Q, Bonetti A, Nortilli R, Pelosi G and Cetto GL: Ki-67
immunostaining in 322 primary breast cancers: associations with
clinical and pathological variables and prognosis. Int J Cancer.
74:433–437. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Railo M, Lundin J, Haglund C, von Smitten
K, von Boguslawsky K and Nordling S: Ki-67, p53, Er-receptors,
ploidy and S-phase as prognostic factors in T1 node negative breast
cancer. Acta Oncol. 36:369–374. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Pierga JY, Leroyer A, Viehl P, Mosseri V,
Chvillard S and Magdelenat H: Long term prognostic value of growth
fraction determination by Ki-67 immunostaining in primary operable
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 37:57–64. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Railo M, Nordling S, von Boguslawsky K,
Leivonen M, Kyllonen L and von Smitten K: Prognostic value of Ki-67
immunolabelling in primary operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
68:579–583. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Veronese SM, Gambacorta M, Gottardi O,
Scanzi F, Ferrari M and Lampertico P: Proliferation index as a
prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer. 71:3926–3931. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Caly M, Genin P, Al Ghuzlan A, Elie C,
Freneaux P, Klijanienko J, Rosty C, Sigal-Zafrani B,
Vincent-Salomoni A, Douggaz A, Zidane M and Sastre-Garau X:
Analysis of correlation between mitotic index, MIB1 score and
S-phase fraction as proliferation markers in invasive breast
carcinoma. Methodological aspects and prognostic value in a series
of 257 cases. Anticancer Res. 24:3283–3288. 2004.
|
|
16.
|
Petit T, Wilt M, Velten M, Millon R,
Rodier JF, Borel C, Mors R, Haegele P, Eber M and Ghnassia JP:
Comparative value of tumour grade hormonal receptors, Ki-67, HER-2
and topoisomerase II alpha status as predictive markers in breast
cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline-based
chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 40:205–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Bonetti A, Zaninelli M, Rodella S, Molino
A, Sperotto L, Piubello Q, Bonetti F, Nortilli R, Turazza M and
Cetto GL: Tumor proliferative activity and response to first-line
chemotherapy in advanced breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
38:289–297. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
MacGrogan G, Mauriac L, Durand M, Bonichon
F, Trojani M, De Mascarel I and Coindre JM: Primary chemotherapy in
breast invasive carcinoma: predictive value of the
immunohistochemical detection of hormonal receptors, p53, c-erbB-2,
MiB1, pS2 and GST pi. Br J Cancer. 74:1458–1465. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Aas T, Geisler S, Eide GE, Haugen DF,
Varhaug JE, Bassoe AM, Thorsen T, Berntsen H, Borresen-Dale AL,
Akslen LA and Lonning PE: Predictive value of tumor cell
proliferation in locally advanced breast cancer treated with
neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 39:438–446. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Shabani HK, Kitange G, Tsunoda K, Anda T,
Tokunaga Y, Shibata S, Kaminogo M, Hayashi T, Ayabe H and Iseki M:
Immunohistochemical expression of E-cadherin in metastatic brain
tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol. 20:7–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Buxant F, Anaf V, Simon P, Favt I and Noel
JC: Ki-67 immunostaining activity is higher in positive axillary
lymph nodes than in the primary breast tumor. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 75:1–3. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Cabibi D, Mustacchio V, Martorana A,
Tripodo C, Campione M, Calascibetta A, Sanguedolce R and Aragona F:
Lymph node metastases displaying lower Ki-67 immunostaining
activity than the primary breast cancer. Anticancer Res.
26:4357–4360. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lear-Kaul KC, Yoon HR,
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, McGavran L and Singh M: HER-2/neu status
in breast cancer metastases to central nervous system. Arch Pathol
Lab Med. 127:1451–1457. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Fuchs IB, Loebbecke M, Buhler H,
Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Heine B, Lichtenegger W and Schaller G:
HER2 in brain metastases: issues of concordance, survival, and
treatment. J Clin Oncol. 20:4130–4133. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ellis MJ, Coop A, Singh B, Tao Y,
Llombart-Cussac A, Janicke F, Mauriac L, Quebe-Fehling E,
Chaudri-Ross HA, Evans DB and Miller WR: Letrozole inhibits tumor
proliferation more effectively than tamoxifen independent of HER1/2
expression status. Cancer Res. 63:6523–6531. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Dunn JM, Hastrich DJ, Newcomb P, Webb JCJ,
Maitland NJ and Farndon JR: Correlation between p53 mutations and
antibody staining in breast carcinoma. Br J Surg. 80:1410–1412.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Thompson AM, Anderson TJ, Condie A,
Prosser J, Chetty U, Carter DC, Evans HJ and Steel CM: p53 allele
losses, mutations and expression in breast cancer and their
relationship to clinicopathological parameters. Int J Cancer.
50:528–532. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Borrensen AL, Hovig E, Smith-Sorensen B,
Malkin D, Lystad S, Andersen TI, Nesland JM, Isselbacher KJ and
Friend SH: Constant denaturation gel electrophoresis (CDGE) as a
rapid screening technique for p53 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 88:8405–8409. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Binder C, Marx D, Overhoff R, Binder L,
Schauer A and Hiddemann W: Bcl-2 protein expression in breast
cancer in relation to established prognostic factors and other
clinicopathological variables. Ann Oncol. 6:1005–1010.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Willsher
P, McClelland RA, Hoyle HB, Kyme SR, Finlay P, Blamey RW and
Nicholson RI: Immunocytochemical localization of bcl-2 protein in
human breast cancers and its relationship to a series of prognostic
markers and response to endocrine therapy. Int J Cancer.
59:619–628. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|