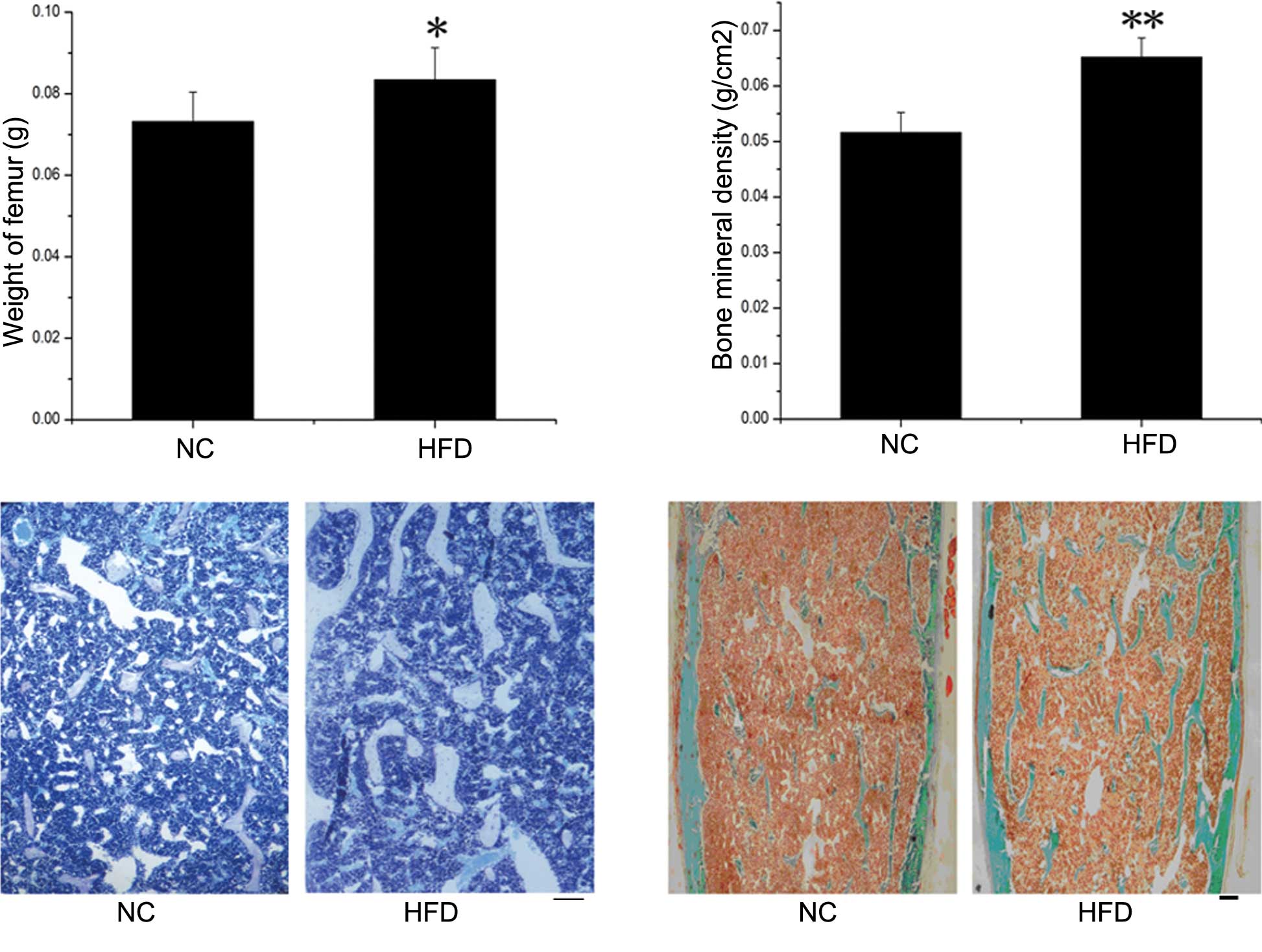
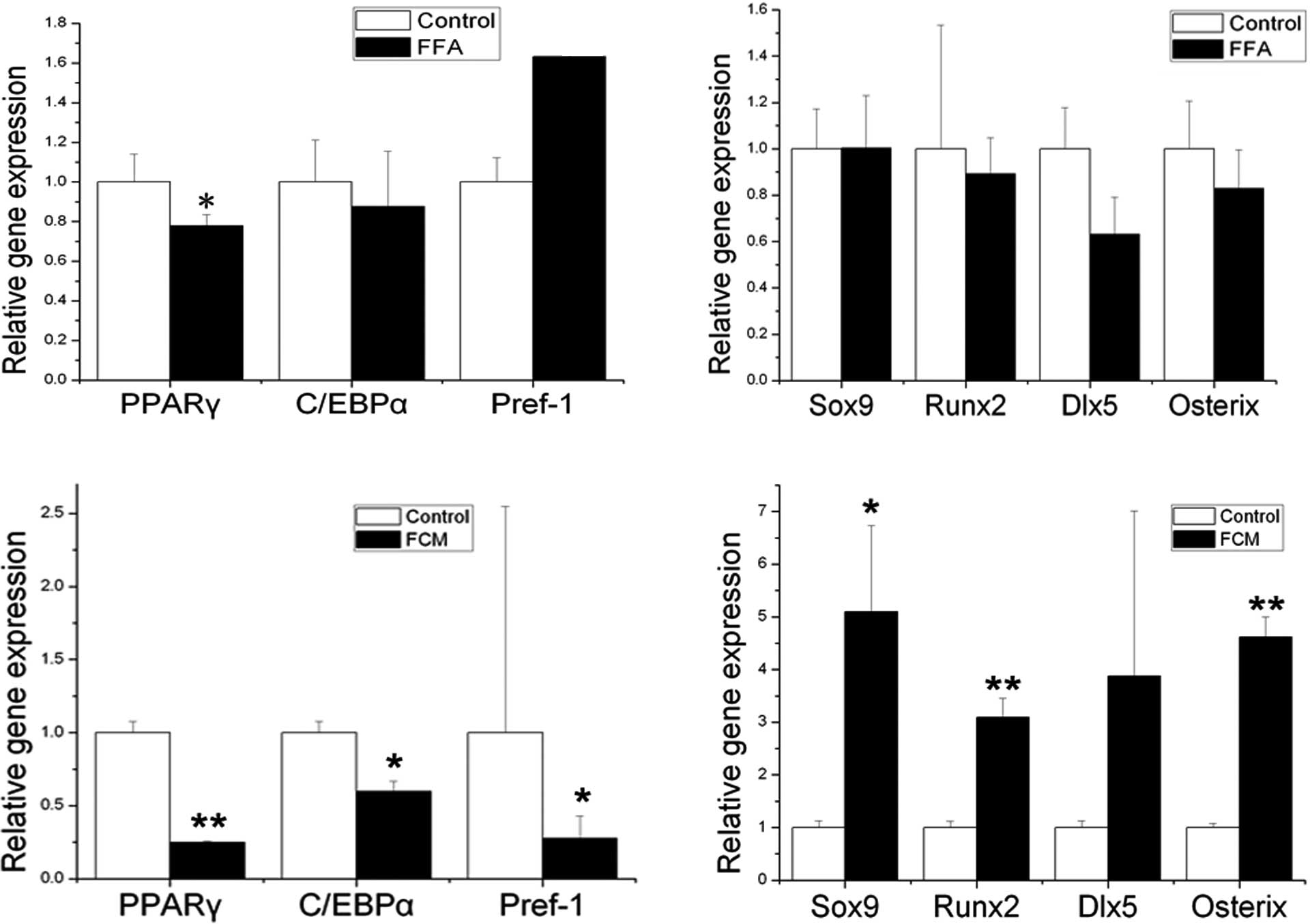
|
1.
|
Wellen KE and Hotamisligil GS:
Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin
Invest. 112:1785–1788. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Raisz LG: Pathogenesis of osteoporosis:
concepts, conflict, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 115:3318–3325.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Melton LJ III: Adverse outcomes of
osteoporotic fractures in the general population. J Bone Miner Res.
18:1139–1141. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Goulding A, Cannan R, Williams SM, Gold
EJ, Taylor RW and Lewis-Barned NJ: Bone mineral density in girls
with forearm fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 13:143–148. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Nagasaki K, Kikuchi T, Hiura M and
Uchiyama M: Obese Japanese children have low bone mineral density
after puberty. J Bone Miner Metab. 22:376–381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Clark EM, Ness AR and Tobias JH: Adipose
tissue stimulates bone growth in prepubertal children. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 91:2534–2541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Reid IR: Relationships among body mass,
its components, and bone. Bone. 31:547–555. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Gilsanz V, Chalfant J, Mo AO, Lee DC,
Dorey FJ and Mittelman SD: Reciprocal relations of subcutaneous and
visceral fat to bone structure and strength. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 94:3387–3393. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Devlin C, Leboy
PS and Owen ME: Evidence for an inverse relationship between the
differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow
stromal cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 102:341–351. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis
JA, Malluche H and Meunier PJ: Bone histomorphometry:
standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the
ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res.
2:595–610. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Reid IR: Relationships between fat and
bone. Osteoporos Int. 19:595–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Zhao LJ, Jiang H, Papasian CJ, Maulik D,
Drees B, Hamilton J, Deng HW and Zhao LJ: Correlation of obesity
and osteoporosis: effect of fat mass on the determination of
osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 23:17–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Boden G, She P, Mozzoli M, Cheung P,
Gumireddy K, Reddy P, Xiang X, Luo Z and Ruderman N: Free fatty
acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory
nuclear factor-κB pathway in rat liver. Diabetes. 54:3458–3465.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Soga T, Ohishi T, Matsui T, Saito T,
Matsumoto M, Takasaki J, Matsumoto S, Kamohara M, Hiyama H, Yoshida
S, Momose K, Ueda Y, Matsushime H, Kobori M and Furuichi K:
Lysophosphatidylcholine enhances glucose-dependent insulin
secretion via an orphan G protein-coupled receptor. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 326:744–751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yamada C, Yamada Y, Tsukiyama K, Yamada K,
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Tanaka K, Drucker DJ, Seino Y and Inagaki
N: The murine glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is essential for
control of bone resorption. Endocrinology. 149:574–579. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Grey A: Fatty acids and bone. Clinic Rev
Bone Miner Metab. 7:210–215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Cornish J, MacGibbon A, Lin JM, Watson M,
Callon KE, Tong PC, Dunford JE, van der Does Y, Williams GA, Grey
AB, Naot D and Reid IR: Modulation of osteoclastogenesis by fatty
acids. Endocrinology. 149:5688–5695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Watkins BA, Li Y, Allen KG, Hoffmann WE
and Seifert MF: Dietary ratio of (n-6)/(n-3) polyunsaturated fatty
acids alters the fatty acid composition of bone compartments and
biomarkers of bone formation in rats. J Nutr. 130:2274–2284.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Morley JE and Baumgartner RN:
Cytokine-related aging process. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
59:M924–M929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Steppan CM, Crawford DT, Chidsey-Frink KL,
Ke H and Swick AG: Leptin is a potent stimulator of bone growth in
ob/ob mice. Regul Pept. 92:73–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Frühbeck G: Intracellular signalling
pathways activated by leptin. Biochem J. 393:7–20. 2006.
|
|
23.
|
Luo XH, Guo LJ, Xie H, Yuan LQ, Wu XP,
Zhou HD and Liao EY: Adiponectin stimulates RANKL and inhibits OPG
expression in human osteoblasts through the MAPK signaling pathway.
J Bone Miner Res. 21:1648–1656. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Oshima K, Nampei A, Matsuda M, Iwaki M,
Fukuhara A, Hashimoto J, Yoshikawa H and Shimomura I: Adiponectin
increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating
osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:520–526. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Berger J, Tanen M, Elbrecht A,
Hermanowski-Vosatka A, Moller DE, Wright SD and Thieringer R:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligands inhibit
adipocyte 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression and
activity. J Biol Chem. 276:12629–12635. 2001.
|
|
26.
|
Shintani M, Nishimura H, Yonemitsu S,
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Inoue G, Yoshimasa Y and Nakao K:
Downregulation of leptin by free fatty acids in rat adipocytes:
effects of triacsin C, palmitate, and 2-bromopalmitate. Metabolism.
49:326–330. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|