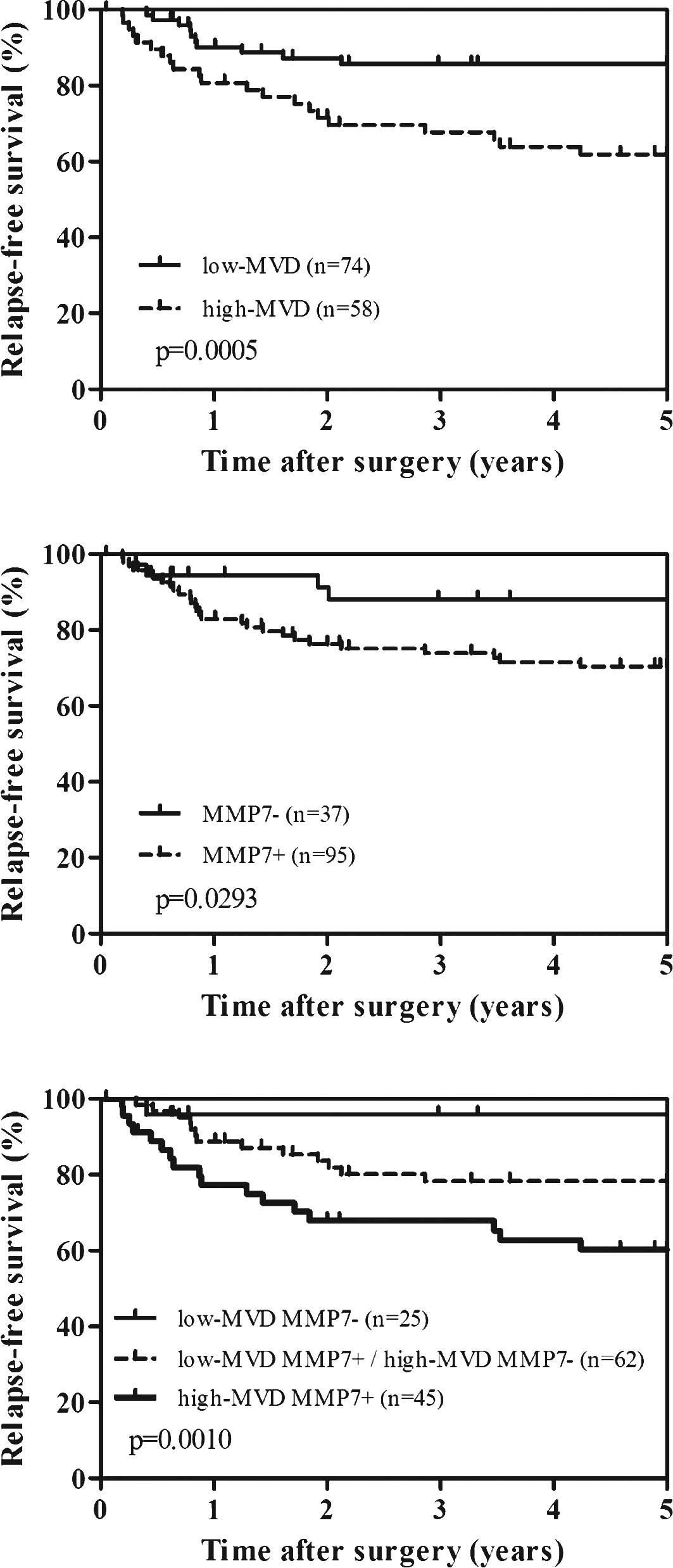
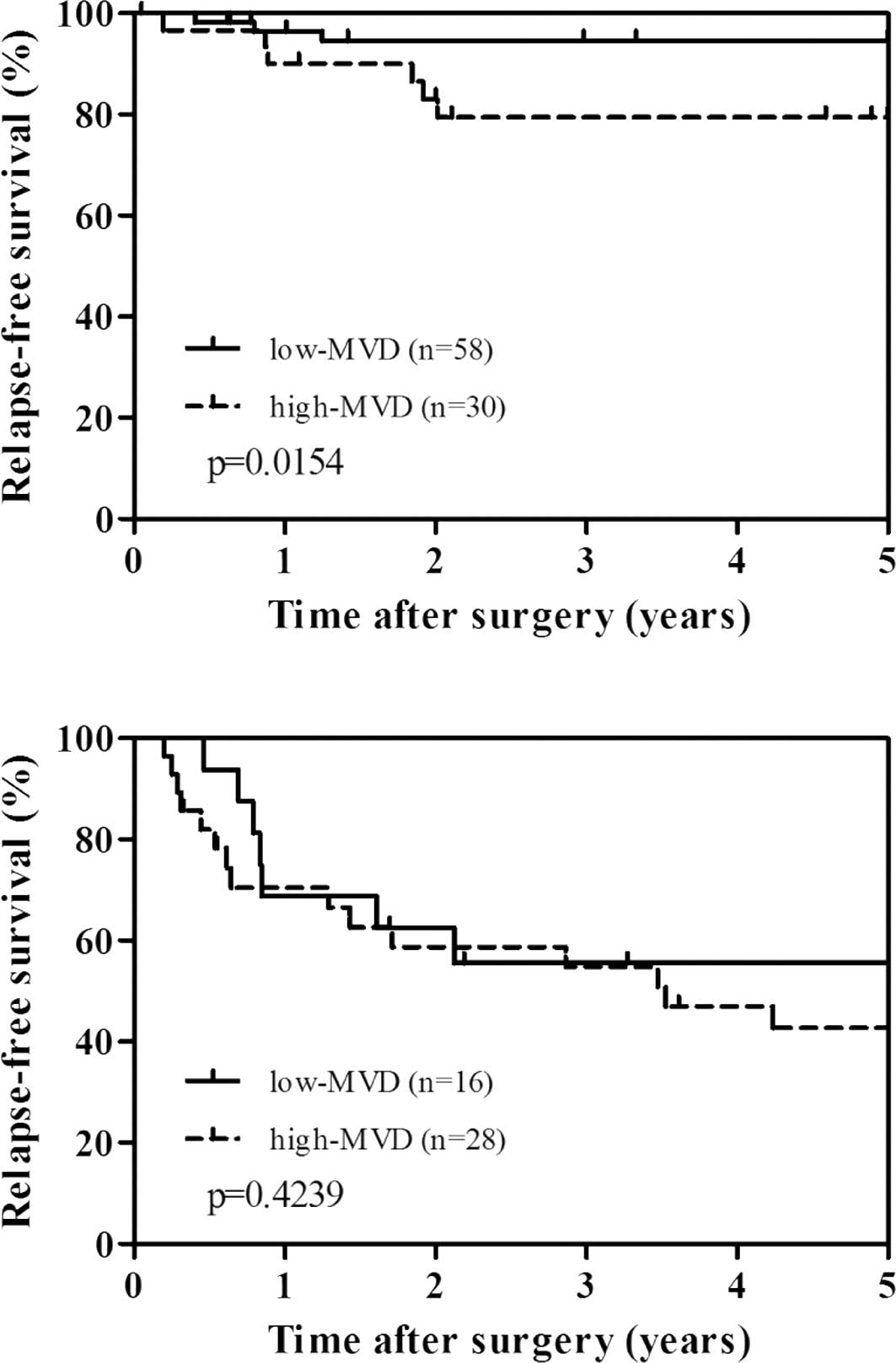
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Moriguchi S, Maehara Y, Korenaga D,
Sugimachi K and Nose Y: Risk factors which predict pattern of
recurrence after curative surgery for patients with advanced
gastric cancer. Surg Oncol. 1:341–346. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Dallas NA, Samuel S, Xia L, Fan F, Gray
MJ, Lim SJ and Ellis LM: Endoglin (CD105): a marker of tumor
vasculature and potential target for therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1931–1937. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Saad RS, Liu YL, Nathan G, Celebrezze J,
Medich D and Silverman JF: Endoglin (CD105) and vascular
endothelial growth factor as prognostic markers in colorectal
cancer. Mod Pathol. 17:197–203. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Mineo TC, Ambrogi V, Baldi A, Rabitti C,
Bollero P, Vincenzi B and Tonini G: Prognostic impact of VEGF,
CD31, CD34, and CD105 expression and tumour vessel invasion after
radical surgery for IB-IIA non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 57:591–597. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Zijlmans HJ, Fleuren GJ, Hazelbag S, Sier
CF, Dreef EJ, Kenter GG and Gorter A: Expression of endoglin
(CD105) in cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:1617–1626. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
El-Gohary YM, Silverman JF, Olson PR, Liu
YL, Cohen JK, Miller R and Saad RS: Endoglin (CD105) and vascular
endothelial growth factor as prognostic markers in prostatic
adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 127:572–579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Li C, Guo B, Wilson PB, Stewart A, Byrne
G, Bundred N and Kumar S: Plasma levels of soluble CD105 correlate
with metastasis in patients with breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
89:122–126. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Ding S, Li C, Lin S, Yang Y, Liu D, Han Y,
Zhang Y, Li L, Zhou L and Kumar S: Comparative evaluation of
microvessel density determined by CD34 or CD105 in benign and
malignant gastric lesions. Hum Pathol. 37:861–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Nikiteas NI, Tzanakis N, Theodoropoulos G,
Atsaves V, Christoni Z, Karakitsos P, Lazaris AC, Papachristodoulou
A, Klonaris C and Gazouli M: Vascular endothelial growth factor and
endoglin (CD-105) in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 10:12–17.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Roy R, Zhang B and Moses MA: Making the
cut: protease-mediated regulation of angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res.
312:608–622. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Overall CM and Kleifeld O: Tumour
microenvironment – opinion: validating matrix metalloproteinases as
drug targets and anti-targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:227–239. 2006.
|
|
13.
|
Ii M, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Maruyama Y and
Shinomura Y: Role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) in
human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp
Biol Med. 231:20–27. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Okayama H, Kumamoto K, Saitou K, Hayase S,
Kofunato Y, Sato Y, Miyamoto K, Nakamura I, Ohki S, Sekikawa K and
Takenoshita S: CD44v6, MMP-7 and nuclear Cdx2 are significant
biomarkers for prediction of lymph node metastasis in primary
gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 22:745–755. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association:
Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, 2nd English edition.
Gastric Cancer. 1:10–24. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis – correlation in invasive
breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991.
|
|
17.
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Huo N, Ichikawa Y, Kamiyama M, Ishikawa T,
Hamaguchi Y, Hasegawa S, Nagashima Y, Miyazaki K and Shimada H:
MMP-7 (matrilysin) accelerated growth of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Cancer Lett. 177:95–100. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Nishizuka I, Ichikawa Y, Ishikawa T,
Kamiyama M, Hasegawa S, Momiyama N, Miyazaki K and Shimada H:
Matrilysin stimulates DNA synthesis of cultured vascular
endothelial cells and induces angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Lett.
173:175–182. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lee S, Jilani SM, Nikolova GV, Carpizo D
and Iruela-Arispe ML: Processing of VEGF-A by matrix
metalloproteinases regulates bioavailability and vascular
patterning in tumors. J Cell Biol. 169:681–691. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Clasper S, Royston D, Baban D, Cao Y,
Ewers S, Butz S, Vestweber D and Jackson DG: A novel gene
expression profile in lymphatics associated with tumor growth and
nodal metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:7293–7303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Yoshitomi H, Kobayashi S, Ohtsuka M,
Kimura F, Shimizu H, Yoshidome H and Miyazaki M: Specific
expression of endoglin (CD105) in endothelial cells of intratumoral
blood and lymphatic vessels in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas.
37:275–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Shiozaki K, Harada N, Greco WR, Haba A,
Uneda S, Tsai H and Seon BK: Antiangiogenic chimeric anti-endoglin
(CD105) antibody: pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity in nonhuman
primates and effects of doxorubicin. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
55:140–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Tsujie M, Tsujie T, Toi H, Uneda S,
Shiozaki K, Tsai H and Seon BK: Anti-tumor activity of an
anti-endoglin monoclonal antibody is enhanced in immunocompetent
mice. Int J Cancer. 122:2266–2273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Fonsatti E, Nicolay HJ, Altomonte M, Covre
A and Maio M: Targeting cancer vasculature via endoglin/CD105: a
novel antibody-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategy in solid
tumours. Cardiovasc Res. 86:12–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|