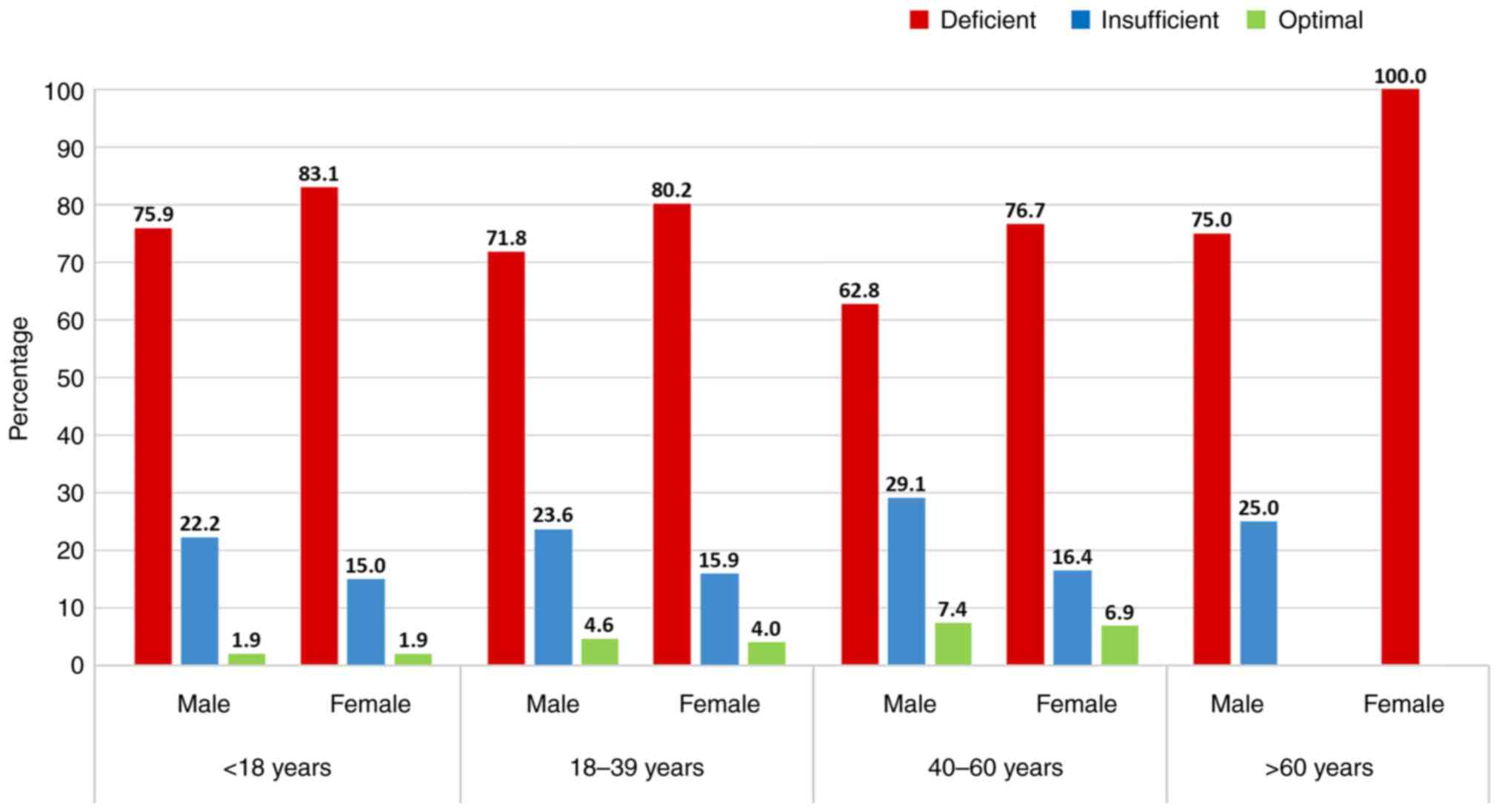
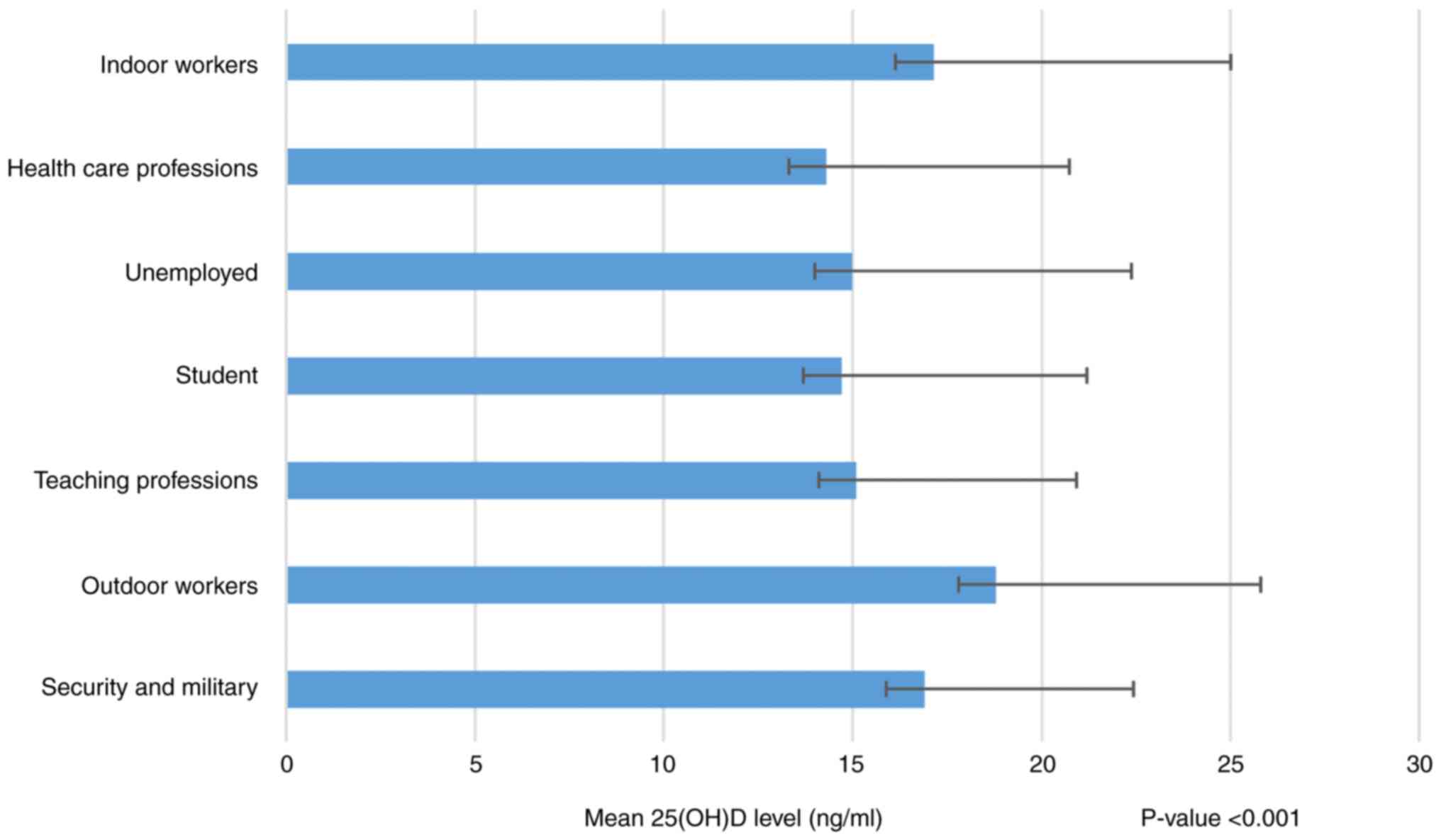
|
1
|
Al-Daghri NM: Vitamin D in Saudi Arabia:
Prevalence, distribution and disease associations. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 175:102–107. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gordon CM, DePeter KC, Feldman HA, Grace E
and Emans SJ: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among healthy
adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 158:531–537. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Holick MF: High prevalence of vitamin D
inadequacy and implications for health. In: Mayo Clinic
Proceedings. Vol 81. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp353-373, 2006.
|
|
4
|
Cashman KD: Vitamin D deficiency:
Defining, prevalence, causes, and strategies of addressing. Calcif
Tissue Int. 106:14–29. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tabrizi R, Moosazadeh M, Akbari M,
Dabbaghmanesh MH, Mohamadkhani M, Asemi Z, Heydari ST, Akbari M and
Lankarani KB: High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Iranian
population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Med Sci.
43:125–139. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Al-Dabhani K, Tsilidis KK, Murphy N, Ward
HA, Elliott P, Riboli E, Gunter M and Tzoulaki I: Prevalence of
vitamin D deficiency and association with metabolic syndrome in a
Qatari population. Nutr Diabetes. 7(e263)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duarte C, Carvalheiro H, Rodrigues AM,
Dias SS, Marques A, Santiago T, Canhão H, Branco JC and da Silva
JAP: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its predictors in the
Portuguese population: A nationwide population-based study. Arch
Osteoporos. 15(36)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mansoor S, Habib A, Ghani F, Fatmi Z,
Badruddin S, Mansoor S, Siddiqui I and Jabbar A: Prevalence and
significance of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among
apparently healthy adults. Clin Biochem. 43:1431–1435.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Forrest KY and Stuhldreher WL: Prevalence
and correlates of vitamin D deficiency in US adults. Nutr Res.
31:48–54. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cashman KD, Dowling KG, Škrabáková Z,
Gonzalez-Gross M, Valtueña J, De Henauw S, Moreno L, Damsgaard CT,
Michaelsen KF, Mølgaard C, et al: Vitamin D deficiency in Europe:
Pandemic? Am J Clin Nutr. 103:1033–1044. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari
HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH and Weaver CM:
Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin
D deficiency: An Endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:1911–1930. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Badawi A, Arora P, Sadoun E, Al-Thani AA
and Al Thani MH: Prevalence of vitamin d insufficiency in Qatar: A
systematic review. J Public Health Res. 1:229–235. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bolland MJ, Chiu WW, Davidson JS, Grey A,
Bacon C, Gamble GD and Reid IR: The effects of seasonal variation
of 25-hydroxyvitamin D on diagnosis of vitamin D insufficiency. N Z
Med J. 121:63–74. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rockell JEP, Skeaff CM, Williams SM and
Green TJ: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations of New
Zealanders aged 15 years and older. Osteoporos Int. 17:1382–1389.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Langlois K, Green-Finestone L, Little J,
Hidiroglou N and Whiting S: Vitamin D status of Canadians as
measured in the 2007 to 2009 Canadian health measures survey.
Health Rep. 21:47–55. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi HS, Oh HJ, Choi H, Choi WH, Kim JG,
Kim KM, Kim KJ, Rhee Y and Lim SK: Vitamin D insufficiency in
Korea-a greater threat to younger generation: The Korea national
health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES) 2008. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 96:643–651. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lips P, Cashman KD, Lamberg-Allardt C,
Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Bianchi ML, Stepan J,
El-Hajj Fuleihan G and Bouillon R: Current vitamin D status in
European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent
vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European
calcified tissue society. Eur J Endocrinol. 180:P23–P54.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ning Z, Song S, Miao L, Zhang P, Wang X,
Liu J, Hu Y, Xu Y, Zhao T, Liang Y, et al: High prevalence of
vitamin D deficiency in urban health checkup population. Clin Nutr.
35:859–863. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang FF, Al Hooti S, Al Zenki S, Alomirah
H, Jamil KM, Rao A, Al Jahmah N, Saltzman E and Ausman LM: Vitamin
D deficiency is associated with high prevalence of diabetes in
Kuwaiti adults: Results from a national survey. BMC Public Health.
16(100)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bachhel R, Singh NR and Sidhu JS:
Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in north-west Punjab population:
A cross-sectional study. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 5:7–11.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kaykhaei MA, Hashemi M, Narouie B,
Shikhzadeh A, Rashidi H, Moulaei N and Ghavami S: High prevalence
of vitamin D deficiency in Zahedan, southeast Iran. Ann Nutr Metab.
58:37–41. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Öztürk ZA, Gol M and Türkbeyler İH:
Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in otherwise healthy individuals
between the ages of 18 and 90 years in southeast Turkey. Wien Klin
Wochenschr. 129:854–855. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Abdulrahman MA, Alkass SY and Mohammed NI:
Total and free vitamin D status among apparently healthy adults
living in Duhok Governorate. Sci Rep. 12(1778)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zargar AH, Ahmad S, Masoodi SR, Wani AI,
Bashir MI, Laway BA and Shah ZA: Vitamin D status in apparently
healthy adults in Kashmir Valley of Indian subcontinent. Postgrad
Med J. 83:713–716. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Atli T, Gullu S, Uysal AR and Erdogan G:
The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and effects of ultraviolet
light on vitamin D levels in elderly Turkish population. Arch
Gerontol Geriatr. 40:53–60. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Goswami R, Kochupillai N, Gupta N, Goswami
D, Singh N and Dudha A: Presence of 25(OH) D deficiency in a rural
North Indian village despite abundant sunshine. J Assoc Physicians
India. 56:755–757. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hussain AN, Alkhenizan AH, El Shaker M,
Raef H and Gabr A: Increasing trends and significance of
hypovitaminosis D: A population-based study in the Kingdom of Saudi
Arabia. Arch Osteoporos. 9(190)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hagenau T, Vest R, Gissel TN, Poulsen CS,
Erlandsen M, Mosekilde L and Vestergaard P: Global vitamin D levels
in relation to age, gender, skin pigmentation and latitude: An
ecologic meta-regression analysis. Osteoporos Int. 20:133–140.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Khan AH, Iqbal R, Naureen G, Dar FJ and
Ahmed FN: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its correlates:
Results of a community-based study conducted in Karachi, Pakistan.
Arch Osteoporos. 7:275–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Al-Daghri NM, Hussain SD, Ansari MGA,
Khattak MNK, Aljohani N, Al-Saleh Y, Al-Harbi MY, Sabico S and
Alokail MS: Decreasing prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the
central region of Saudi Arabia (2008-2017). J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 212(105920)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sadiya A, Ahmed SM, Skaria S and Abusnana
S: Vitamin D status and its relationship with metabolic markers in
persons with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the UAE: A
cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Res. 2014(869307)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Majumdar V, Nagaraja D and Christopher R:
Vitamin D status and metabolic syndrome in Asian Indians. Int J
Obes (Lond). 35:1131–1134. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Oosterwerff MM, Eekhoff EM, Heymans MW,
Lips P and van Schoor NM: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the
metabolic syndrome in older persons: A population-based study. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 75:608–613. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|