Introduction
Salinity is one of the most threatening abiotic
stress factors affecting not only agriculture but also our food
safety. The size of salt-affected areas is >833 million
hectares, and changing climate conditions are responsible for its
increasing incidence worldwide (1). Irrigation with brackish water or
ground water contaminated with salty water also threatens the yield
of salt-sensitive crop plants (2).
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), one of the
primary agricultural crop plants worldwide, is a moderately
salt-tolerant species. As it widely produced in areas affected by
salt stress, it is crucial to develop methods to improve the salt
tolerance of this species. The effect of salinity is pleiotropic;
salinity not only affects growth and development, but also the
reproductive system (3).
In order to enhance the salt stress tolerance of
tomatoes, the exogenous addition of polyamines (PAs) is a widely
used technique in agriculture (4).
The significance of these essential PAs is diverse; for example,
the triamine, spermidine (Spd), may be a substrate for hypusination
(5). Hypusination is the essential
metabolic post-translational modification of eukaryotic translation
factor 5A (eIF5A), which is dependent on the level of Spd (6). The biosynthesis of hypusine, a rare
amino acid essential for the activation of eIF5A, requires two
enzymatic reactions mediated by deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS) and
deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), respectively. This Spd-dependent
eIF5A hypusination is involved in plant growth and development,
such as in flowering and fruit development (7). However, there is a lack of evidence
regarding the role of hypusination during salt stress in tomatoes,
since only plants grown under optimal conditions have been examined
thus far (8).
It was previously found (9) that GC7
(N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane), an inhibitor of exogenously applied
DHS, was effective in alleviating salt stress in Arabidopsis
thaliana seedlings; however, the importance of the first step
of hypusination for the reproductive system of tomatoes during salt
stress is not yet known. The present study thus aimed to confirm
that the exogenously applied DHS inhibitor, GC7, could improve
fruit production by modulating hypusination during salt stress in
tomatoes, affecting PA catabolism. The results obtained in the
present study demonstrate that the modulation of hypusination may
be a promising strategy with which to improve the reproductive
system of tomato plants during conditions of salt stress.
Materials and methods
Plant growth conditions and
treatments
The determinate Solanum lycopersicum cv Manó
from Rédei Kertimag (Budapest, Hungary) was used as a model plant
for plant material. Plants were grown in pots filled with
sand:perlite (ratio, 1:3) in the greenhouse of the Department of
Plant Biology, University of Szeged (Szeged, Hungary). Nutrients
were supplied by irrigation with nutrient solution as previously
described (10). The plants were
divided into four groups as follows: i) The control group without
any treatment; ii) the control + GC7 group which was treated with
GC7, but without NaCl; iii) the NaCl group, which was exposed to
salt stress without GC7; and iv) the NaCl + GC7 group, which was
exposed to salt stress (NaCl) and treated with GC7. The
concentration of GC7 was 1 mM, and moderate NaCl stress was induced
by 100 mM NaCl (Reanal Finechemical Co.) based on the findings of a
previous study by the authors (9).
The application of GC7 (MilliporeSigma) was conducted by leaf cover
with a brush in the third week of the vegetative period of the
tomato. NaCl treatment was applied during the entire growing
period.
Parameters of fruit production and PA
catabolism
Some parameters associated with fruit set were
analyzed, such as the mean fruit weight, Brix index and lycopene
content (11). Pollen viability
was determined as previously described (12). Enzyme activities involved in PA
catabolism, i.e., diamine oxidase (DAO) and PA oxidase (PAO) were
measured using a spectrophotometer (KONTRON), as previously
described (13).
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using GraphPad software Prism
version 8.0.1.244 or Windows (Dotmatics). In the graphs, different
letters on the bars indicate significant differences, based on
one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple range test. A value of
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
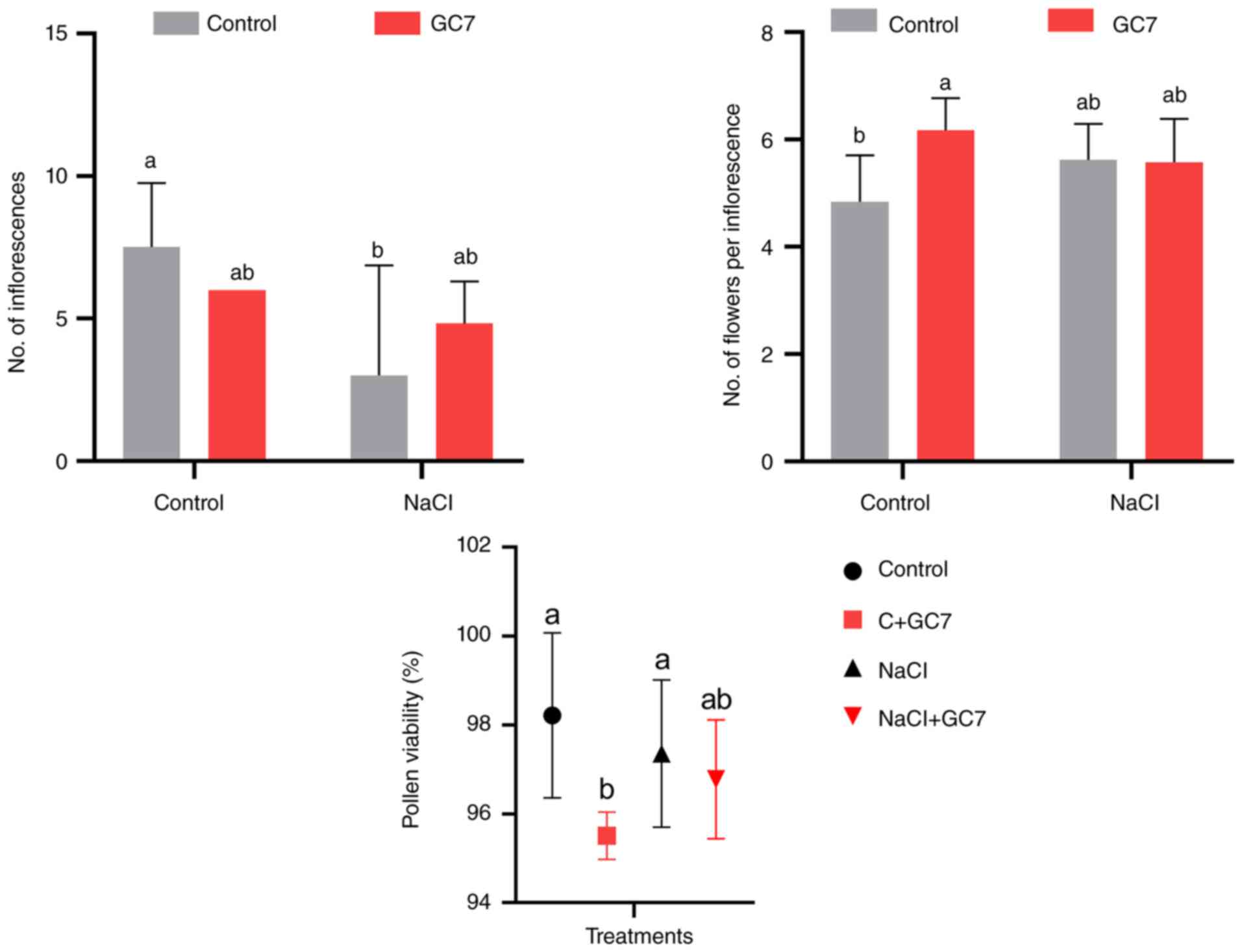
GC7 was applied during the vegetative period on the
tomato leaves. As regards reproductive growth, GC7 treatment
produced more inflorescences in the plants exposed to salt stress
(Fig. 1). Despite the decreased
number of inflorescences in the GC7-treated plants, the flower
numbers were higher compared with the control. When analyzing
pollen viability in the present study samples (Fig. 1), it was found that GC7 was
effective in increasing pollen viability in the salt-stressed
plants, but not in the control plants. It is thus suggested that
precise hypusination is critical for maintaining the viability of
pollen; however, in the case of salt stress, low hypusination may
result in higher viability (Fig.
1).
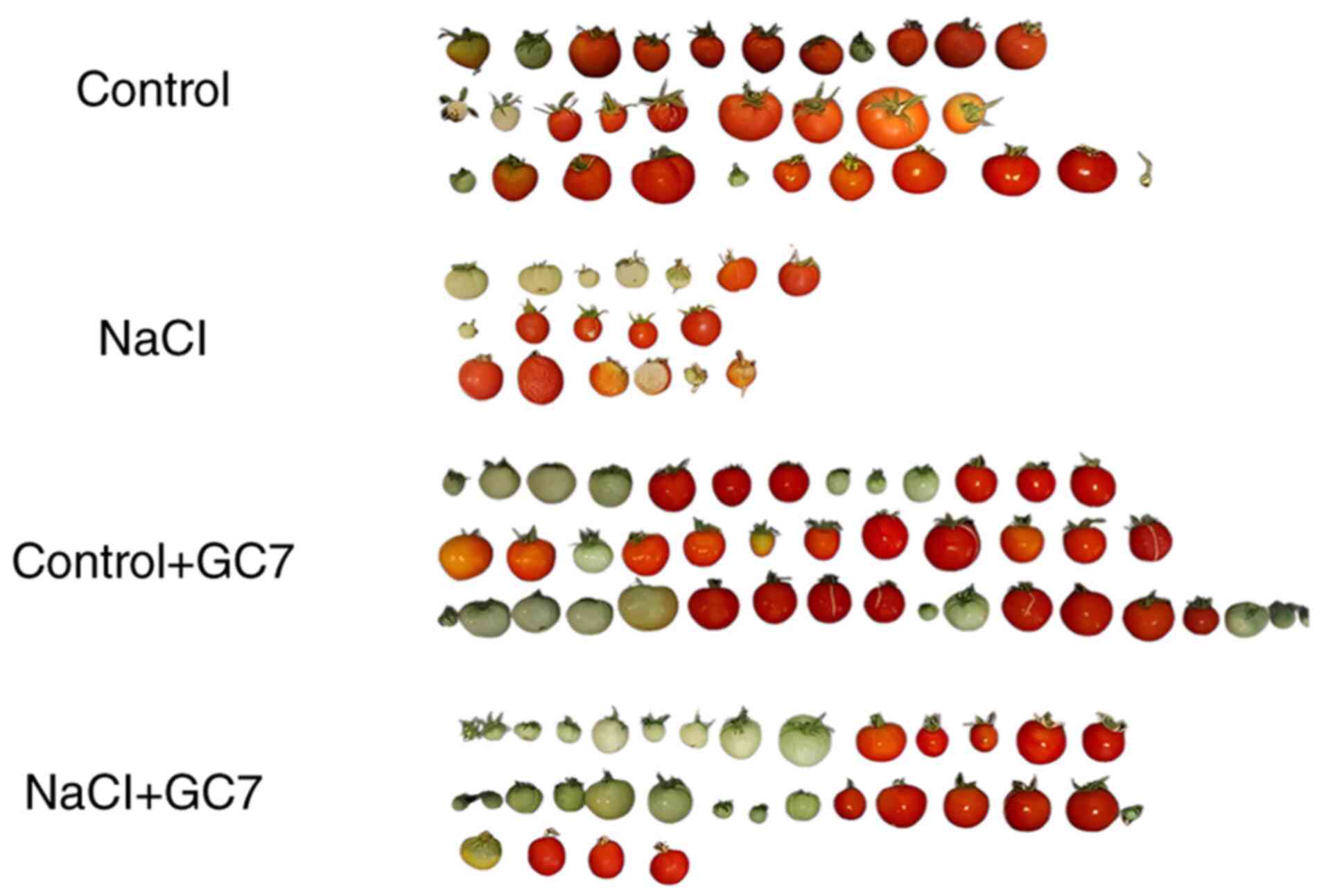
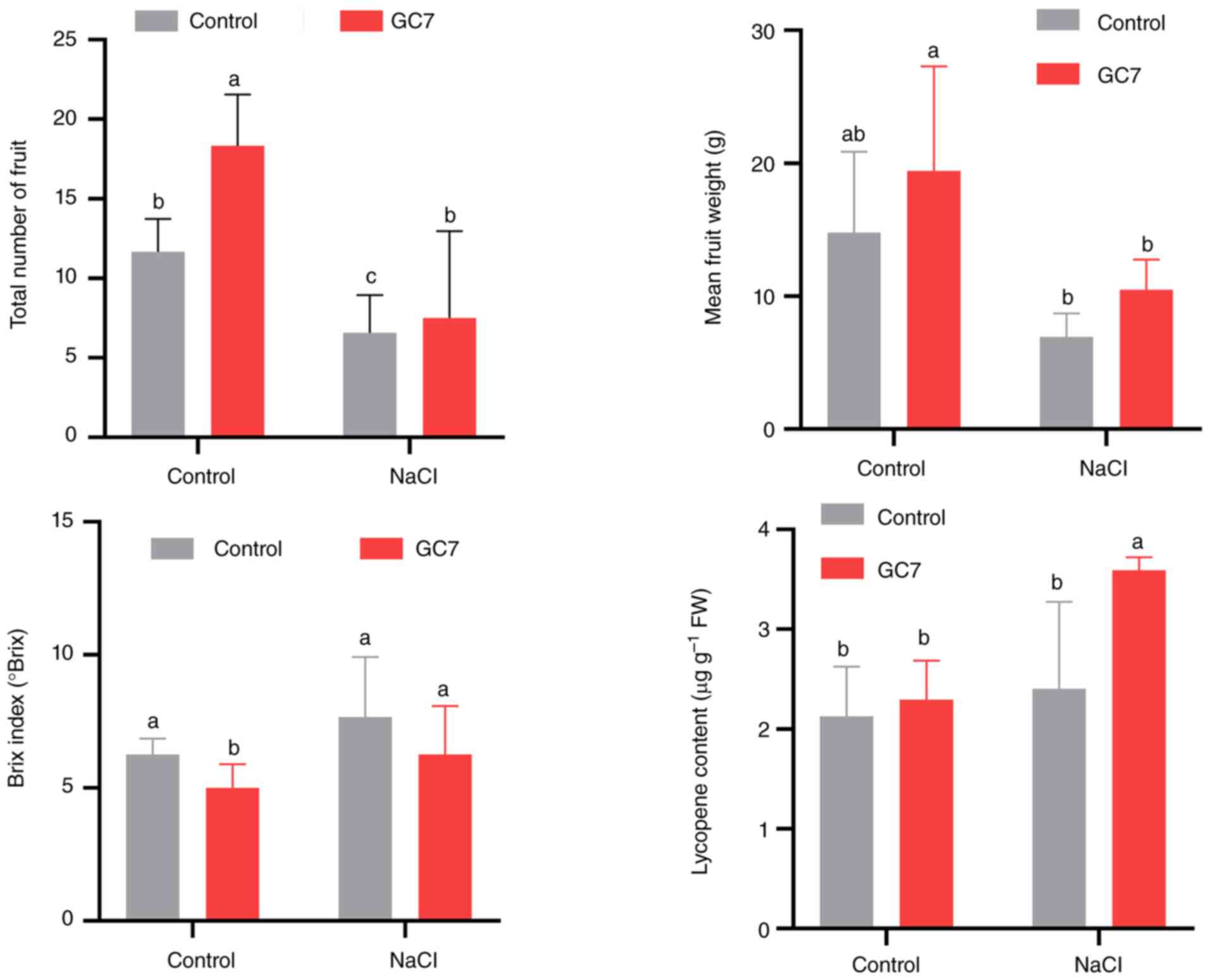
The investigation of tomato fruit production in the
treated plants revealed that GC7 treatment increased the fruit
number (Fig. 2). In addition, the
fruit fresh weight was higher compared with the untreated plants
treated with or without NaCl (Fig.
3). The Brix index decreased in the GC7-treated fruits,
demonstrating that the possible inhibition of DHS caused the
modification of sugar metabolism. In the NaCl-treated plants, a
significantly higher lycopene content was observed following the
application of GC7, suggesting that reduced hypusination may be a
target for inducing lycopene synthesis during conditions of salt
stress (Fig. 3).
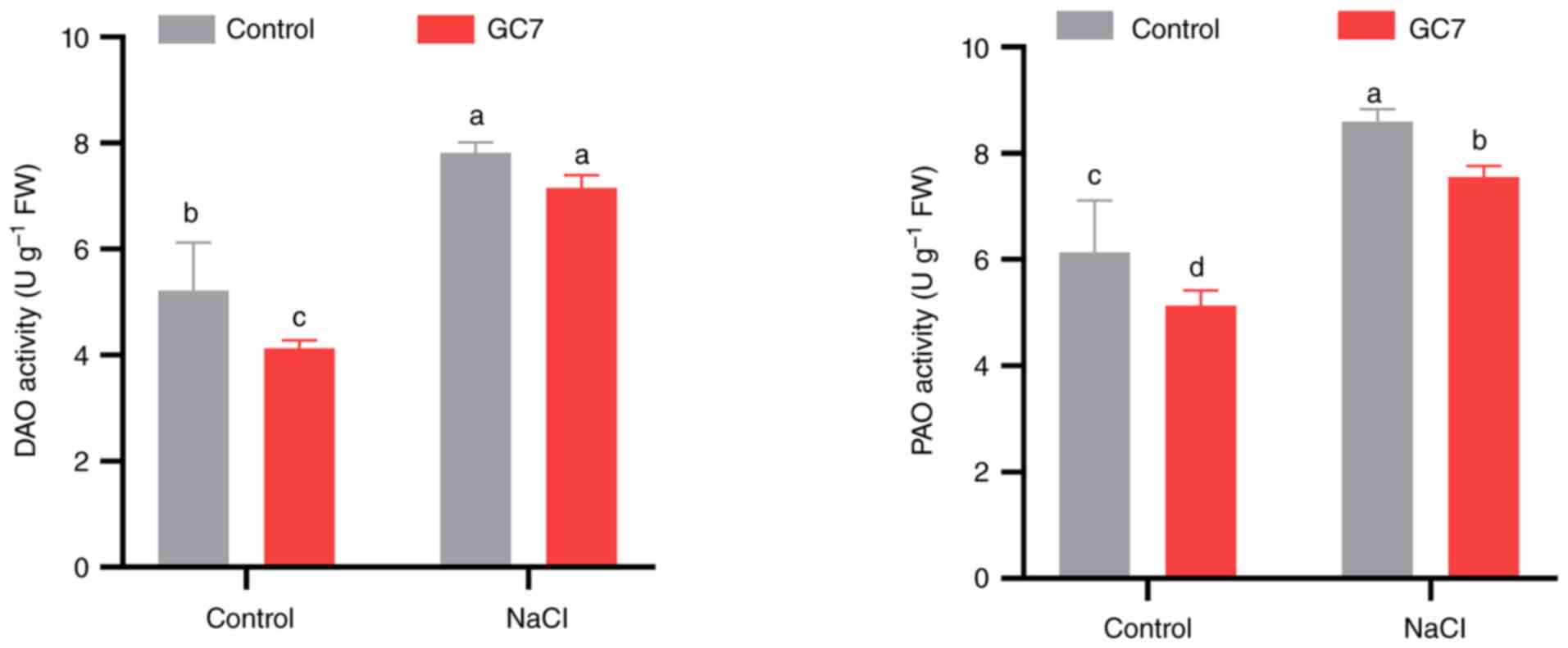
In order to explore potential Spd accumulation in
fruits, the present study investigated PA-catabolic enzyme
activities. GC7 decreased the activation of both enzymes (Fig. 4); however, in the fruits exposed to
salt stress, only the PAO activity decreased, suggesting that more
Spd could accumulate in these samples.
Discussion
The modulation of hypusination, a
metabolite-dependent post-translational modification of eIF5A, can
result in an enhanced tolerance of plants to abiotic stress
(14,15). The role of the first enzyme, DHS,
in hypusination and its effect on tomato growth and development has
been previously investigated (8);
it was found that the antisense suppression of DHS in tomato delays
fruit softening, and alters growth and development. The present
study aimed to elucidate its involvement in the reproductive system
of tomato during salt stress. In order to better elucidate this, a
determinate tomato cultivar was used in conjunction with a
pharmacological approach using GC7, a DHS inhibitor. Using GC7 as
an inhibitor of hypusination by reducing DHS activity is a widely
used method in human and animal experiments. The application of GC7
in plants is very rare; to the best of our knowledge, the present
study is the first to investigate the inhibition of DHS during
conditions of salt stress in tomatoes. The hypothesis was that GC7
could inhibit the first step of hypusination in tomato, resulting
in higher PA levels which can contribute to improved fruit
production and quality in plants exposed to salt stress. Salt
stress decreased the number of inflorescences and the number of
fruits, resulting in a lower yield (4). This finding is in accordance with the
study of Ghanem et al (16), who demonstrated that salt stress
reduced the pollen viability of tomato plants. PAs are essential
for the optimal developmental regulation of pollen production and
viability (17). It has been
proven that Spd synthase downregulation is detrimental to pollen
development (18), suggesting that
a high Spd level is essential for optimal pollen viability.
Furthermore, Song and Tachibana (19) provided evidence that the reduction
in the viability of tomato pollen during long-term dry storage in a
freezer involves a decline in the capacity to enhance gene
translation for PA biosynthetic enzymes upon rehydration. In the
present study, GC7 treatment produced more inflorescences with
higher pollen viability and the fruit set was higher, which
suggests that the modulation of the hypusination process by
altering eIF5A isoforms resulting in a higher Spd level may be
advantageous for breeding and enhanced stress tolerance. Fruit
production is strongly associated with PA metabolism; thus,
hypusination, which is a Spd-related metabolic post-translational
modification of eIF5A plays a crucial role in fruit production
(6). In order to enhance the
current knowledge of hypusination-mediated fruit production in
tomato plants, further studies are required. For example, further
studies are warranted to perform metabolomic assays to elucidate
the role of hypusination in the regulation of nutrient values of
tomato fruits and gene expression studies to decipher the role of
this process in plants.
Another key fruit quality parameter is the Brix
index, which represents the total soluble solids content of the
fruit. The Brix index increases with the higher electric
conductivity of the nutrient solution (20). The Brix index and lycopene content
may be higher during conditions of salt stress and following GC7
treatment, as demonstrated in the present study. Mehta et al
(21) provided evidence that
transgenic tomato plants with higher PA levels enhanced the
nutrient value and juice quality. In addition, Handa and Mattoo
(22) demonstrated that lycopene
levels were positively associated with the Spd and spermine
contents in tomatoes. Based on the findings of the present study,
GC7 affected fruit quality, improving the Brix index and the
lycopene content of tomato plants exposed to salt stress. However,
further research is required to determine the role of hypusination
in fruit sugar metabolism. It is suggested that via the inhibition
of hypusination and DHS activity, GC7 may contribute to the
increased level of Spd, which could improve the nutrient value of
tomato fruits.
The level of PAs, particularly that of Spd, is
crucial for efficient hypusination (6). PA catabolism is one of the main
regulatory processes which can affect the optimal PA level
(5). During the oxidation of PAs,
hydrogen peroxide can be generated as a secondary product, inducing
oxidative stress or the antioxidant defense system, depending on
its concentration. PA catabolism can occur by terminal oxidation,
breaking down the PAs or back-conversion to other PAs. If the
activities of enzymes involved in PA catabolism, namely the DAO and
PAO could be reduced, then these may contribute to the enhanced
level of PAs, such as Spd. The results of the present study
demonstrate that PA catabolism was also reduced following GC7
treatment in the controls and fruits exposed to salt stress,
resulting in higher Spd contents and reduced oxidative stress, by
decreased hydrogen peroxide levels. However, further studies are
required to decipher the eIF5A-dependent effects and the
antioxidant effects of GC7 in plants. Based on animal and
human-related studies, it cannot be disclosed that GC7 may have
effects independent from eIF5A (23); however, in plants, further
experiments are required in the future. A recent study suggested
that GC7 could disrupt the energy metabolism mediated by
mitochondria in cancer cells (24); therefore, further research is
required to reveal the precise mechanisms of GC7 action in plants.
Furthermore, the GC7-induced inhibition of DHS could affect the
translation of certain key proteins involved in tomato fruit
setting (6,25).
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that
reduced DHS activities resulted in higher PA contents and
maintained fruit production, contributing to an improved
reproductive system in tomatoes exposed to salt stress. The
inhibition of hypusination modulated the tomato reproductive system
during conditions of salt stress. GC7, a pharmacological inhibitor
of DHS, promoted flower and fruit production. The application of
GC7 was efficient to increase the lycopene content of tomato
fruits. Furthermore, alleviated polyamine catabolism could enhance
the PA level during conditions of salt stress, resulting in
improved salt tolerance. However, further studies are required to
elucidate the role of the salt-induced hypusination process for
breeding salt stress-resistant tomatoes.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was funded by a grant from the
National Research, Development and Innovation (NRDI) Fund (office
no. FK129061).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
ÁS and LB conceived the study. LS and PP performed
the plant growth experiments. ÁS, LS, PP and LB were involved in
the acquisition of data, in the design of the study, and in the
writing of the manuscript. RS and PP performed the microscopic
analyses. ÁS and LB performed the statistical analyses. ÁS and LB
confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors have read
and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO):
Global Map of Salt Affected Soils Version 1.0. FAO, Rome, 2021.
https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/global-map-of-salt-affected-soils/en/
Accessed May, 2023.
|
|
2
|
Munns R and Tester M: Mechanisms of
salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 59:651–681.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
van Zelm E, Zhang Y and Testerink C: Salt
tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 71:403–433.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guo M, Wang XS, Guo HD, Bai SY, Khan A,
Wang XM, Gao YM and Li JS: Tomato salt tolerance mechanisms and
their potential applications for fighting salinity: A review. Front
Plant Sci. 13(949541)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen D, Shao Q, Yin L, Younis A and Zheng
B: Polyamine function in plants: Metabolism, regulation on
development, and roles in abiotic stress responses. Front. Plant
Sci. 9(1945)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pálfi P, Bakacsy L, Kovács H and Szepesi
Á: Hypusination, a metabolic posttranslational modification of
eIF5A in plants during development and environmental stress
responses. Plants (Basel). 10(1261)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Belda-Palazón B, Almendáriz C, Martí E,
Carbonell J and Ferrando A: Relevance of the axis spermidine/eIF5A
for plant growth and development. Front Plant Sci.
7(245)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang TW, Zhang CG, Wu W, Nowack LM, Madey
E and Thompson JE: Antisense suppression of deoxyhypusine synthase
in tomato delays fruit softening and alters growth and development.
Plant Physiol. 138:1372–1382. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Szepesi Á, Kakas E, Szőllősi R, Molnár Á
and Pálfi P: Application of GC7 to reduce hypusination via
inhibiting deoxyhypusine synthase in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings
exposed salt stress. Plant Stress. 10(100257)2023.
|
|
10
|
Szepesi Á, Csiszár J, Gémes K, Horváth E,
Horváth F, Simon ML and Tari I: Salicylic acid improves acclimation
to salt stress by stimulating abscisic aldehyde oxidase activity
and abscisic acid accumulation, and increases Na+ content in leaves
without toxicity symptoms in Solanum lycopersicum L. Journal of
Plant Physiology. 166:914–925. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ghebbi Si-smail K, Bellal M and Halladj F:
Effect of potassium supply on the behaviour of two processing
tomato cultivars and on the changes of fruit technological
characteristics. Acta Hortic. 758:269–274. 2007.
|
|
12
|
Pline WA, Edmisten KL, Oliver T, Wilcut
JW, Wells R and Allen NS: Use of digital image analysis, viability
stains, and germination assays to estimate conventional and
glyphosate-resistant cotton pollen viability. Crop Sci.
42:2193–2200. 2022.
|
|
13
|
Szepesi Á, Bakacsy L, Kovács H, Szilágyi Á
and Köhler ZM: Inhibiting copper amine oxidase using
L-Aminoguanidine induces cultivar and Age-dependent alterations of
polyamine catabolism in tomato seedlings. Agriculture.
12(274)2022.
|
|
14
|
Xu J, Zhang B, Jiang C and Ming F:
RceIF5A, encoding a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A in
Rosa chinensis, can enhance thermotolerance, oxidative and osmotic
stress resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol.
75:167–178. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Xu C, Wang C and Wag Y:
Characterization of a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A
homolog from Tamarix androssowii involved in plant abiotic stress
tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 12(118)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ghanem ME, van Elteren J, Albacete A,
Quinet M, Martinez-Andujar C, Kinet JM, Pérez-Alfocea F and Lutts
S: Impact of salinity on early reproductive physiology of tomato
(Solanum lycopersicum) in relation to a heterogeneous distribution
of toxic ions in flower organs. Funct Plant Biol. 36:125–136.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Aloisi I, Cai G, Serafini-Fracassini D and
Del Duca S: Polyamines in pollen: From microsporogenesis to
fertilization. Front Plant Sci. 7(155)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Choubey A and Rajam MV: RNAi-mediated
silencing of spermidine synthase gene results in reduced
reproductive potential in tobacco. Physiol Mol Biol Plants.
24:1069–1081. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Song J and Tachibana S: Loss of viability
of tomato pollen during long-term dry storage is associated with
reduced capacity for translating polyamine biosynthetic enzyme
genes after rehydration. J Exp Bot. 58:4235–4244. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu M, Buck JS and Kubota C: Effects of
nutrient solution EC, plant microclimate and cultivars on fruit
quality and yield of hydroponic tomatoes (Lycopersicum esculentum
L.). Acta Hort. 659:541–547. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Mehta RA, Cassol T, Li N, Ali N, Handa AK
and Mattoo AK: Engineered polyamine accumulation in tomato enhances
phytonutrient content, juice quality, and vine life. Nat
Biotechnol. 20:613–618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Handa AK and Mattoo AK: Differential and
functional interactions emphasize the multiple roles of polyamines
in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 48:540–546. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Oliverio S, Corazzari M, Sestito C,
Piredda L, Ippolito G and Piacentini M: The spermidine analogue GC7
(N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineoheptane) induces autophagy through a
mechanism not involving the hypusination of eIF5A. Amino Acids.
46:2767–2776. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cui Q, Ding W, Luo B, Lu W, Huang P and
Wen S: Novel gold-based complex GC7 suppresses cancer cell
proliferation via impacting energy metabolism mediated by
mitochondria. Bioorg Med Chem. 112(117897)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Park MH and Wolff EC: Hypusine, a
polyamine-derived amino acid critical for eukaryotic translation. J
Biol Chem. 293:18710–18718. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|