|
1
|
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO):
Global Map of Salt Affected Soils Version 1.0. FAO, Rome, 2021.
https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/global-map-of-salt-affected-soils/en/
Accessed May, 2023.
|
|
2
|
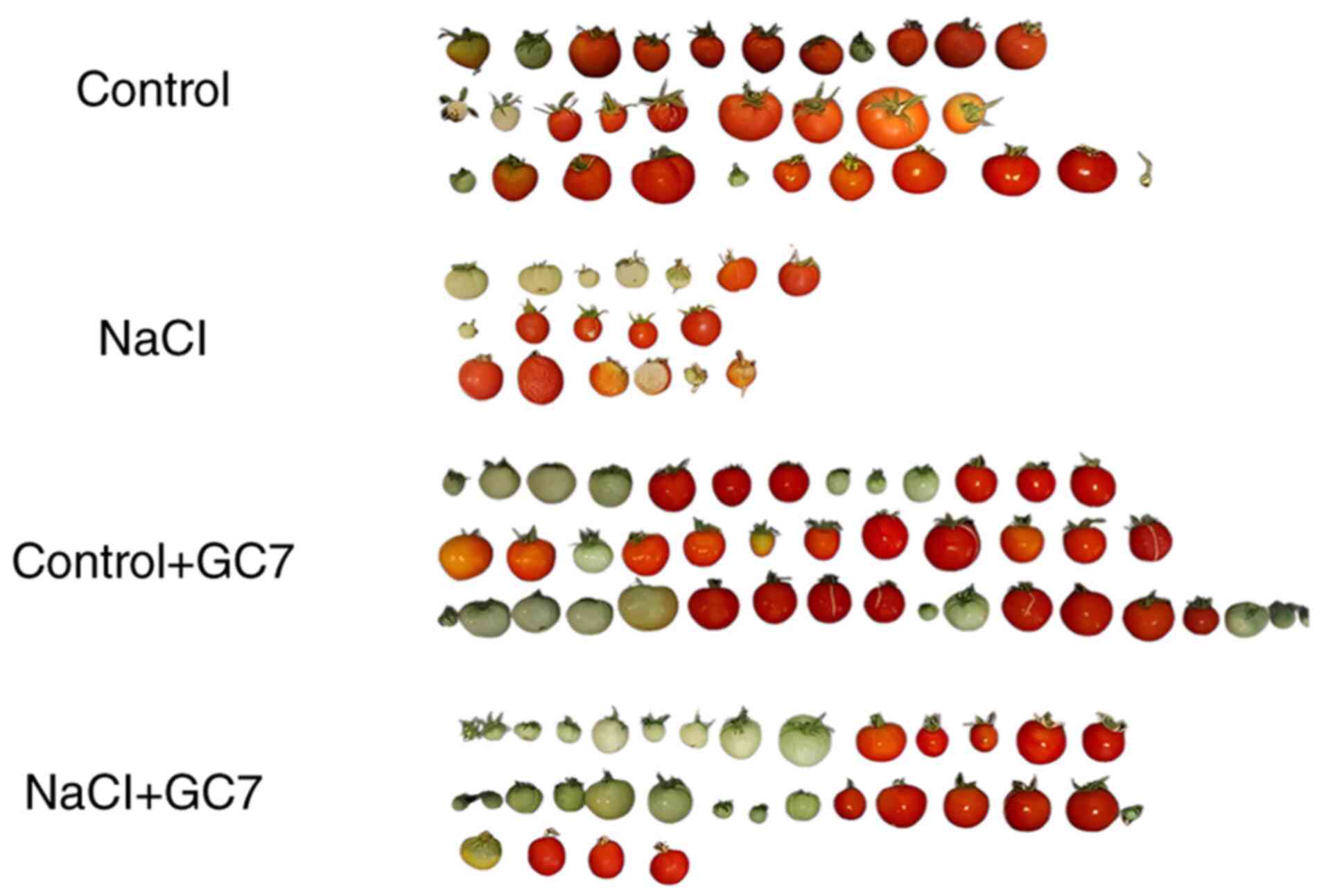
Munns R and Tester M: Mechanisms of
salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 59:651–681.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
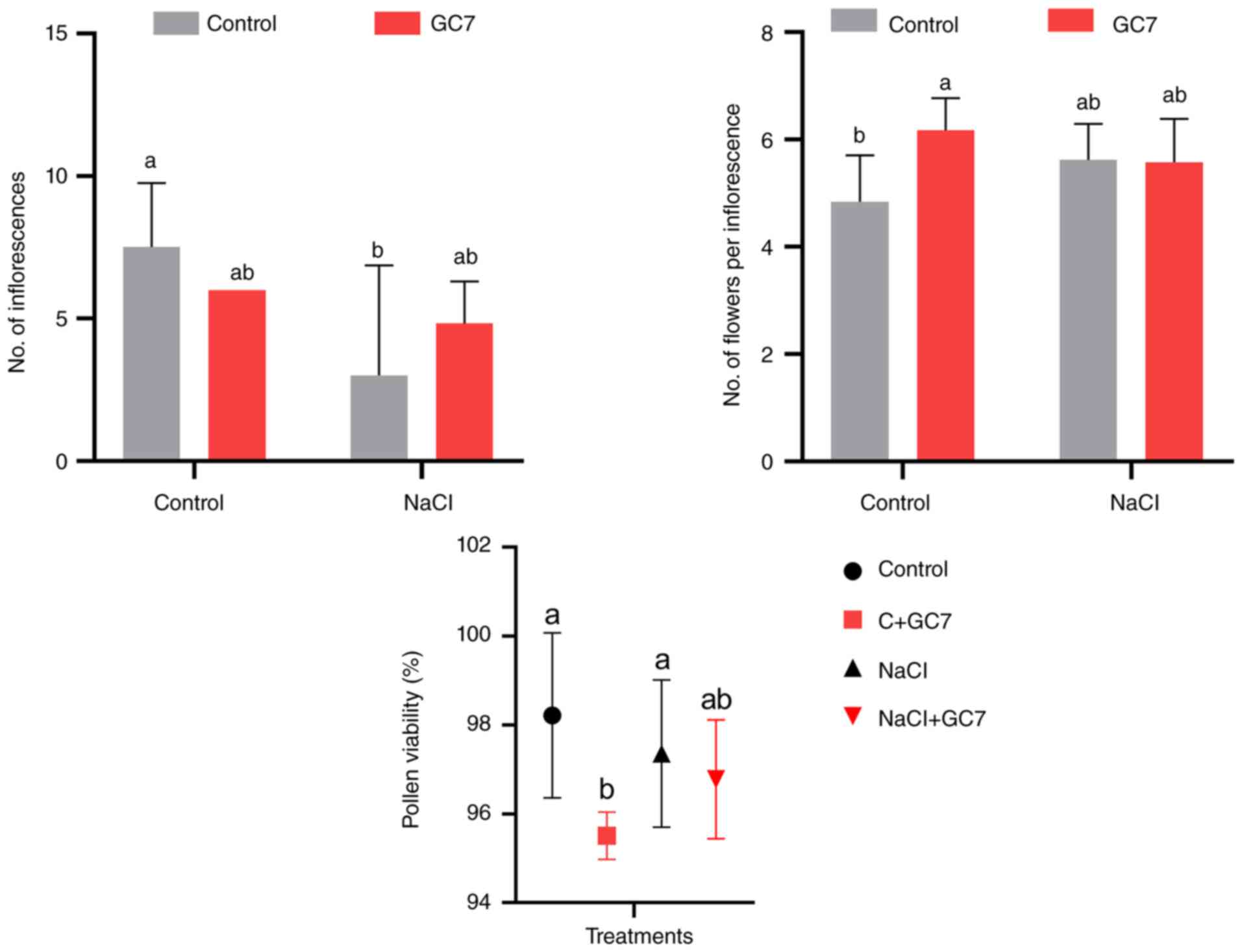
3
|
van Zelm E, Zhang Y and Testerink C: Salt
tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 71:403–433.
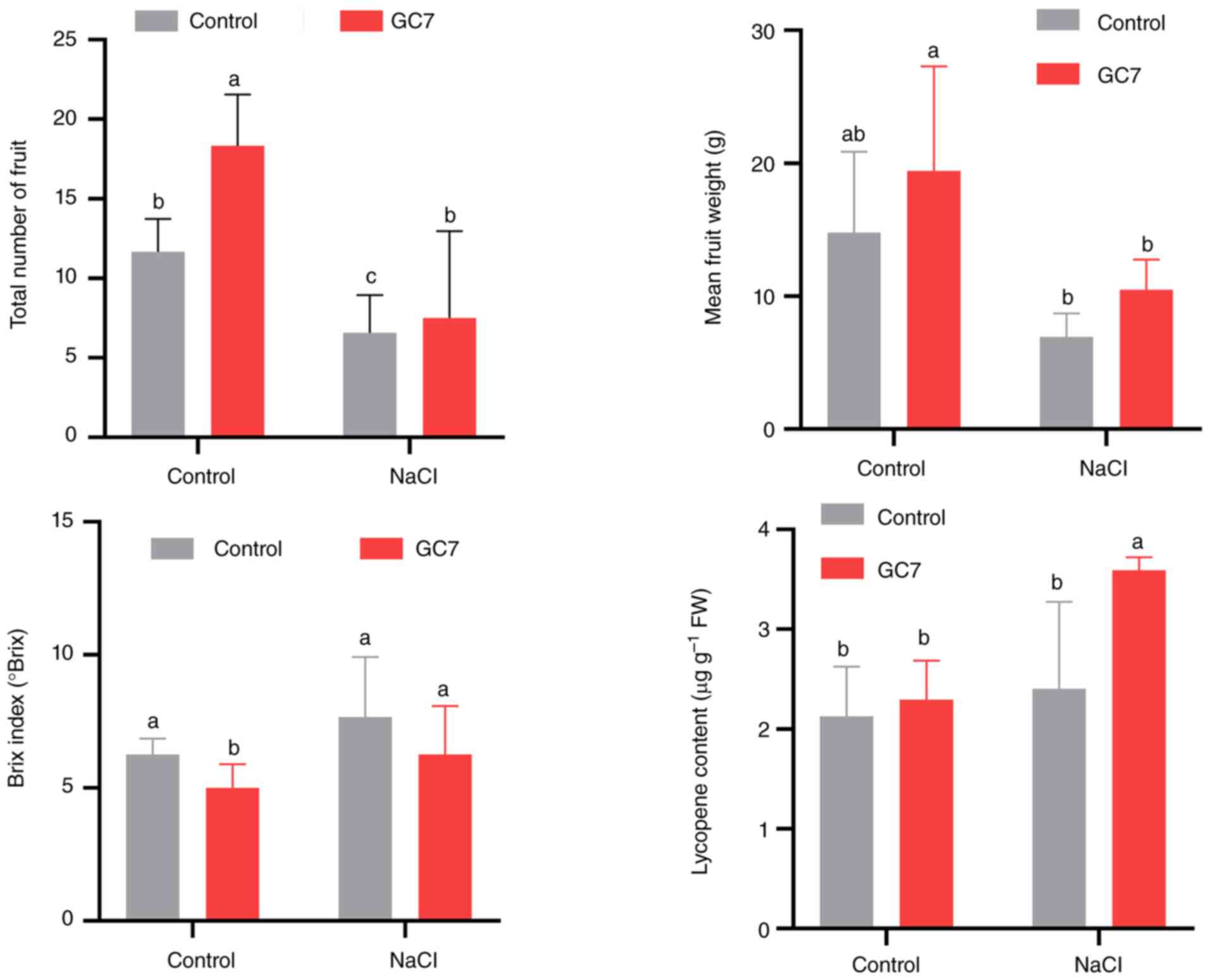
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guo M, Wang XS, Guo HD, Bai SY, Khan A,
Wang XM, Gao YM and Li JS: Tomato salt tolerance mechanisms and
their potential applications for fighting salinity: A review. Front
Plant Sci. 13(949541)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen D, Shao Q, Yin L, Younis A and Zheng
B: Polyamine function in plants: Metabolism, regulation on
development, and roles in abiotic stress responses. Front. Plant
Sci. 9(1945)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pálfi P, Bakacsy L, Kovács H and Szepesi
Á: Hypusination, a metabolic posttranslational modification of
eIF5A in plants during development and environmental stress
responses. Plants (Basel). 10(1261)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Belda-Palazón B, Almendáriz C, Martí E,
Carbonell J and Ferrando A: Relevance of the axis spermidine/eIF5A
for plant growth and development. Front Plant Sci.
7(245)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang TW, Zhang CG, Wu W, Nowack LM, Madey
E and Thompson JE: Antisense suppression of deoxyhypusine synthase
in tomato delays fruit softening and alters growth and development.
Plant Physiol. 138:1372–1382. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Szepesi Á, Kakas E, Szőllősi R, Molnár Á
and Pálfi P: Application of GC7 to reduce hypusination via
inhibiting deoxyhypusine synthase in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings
exposed salt stress. Plant Stress. 10(100257)2023.
|
|
10
|
Szepesi Á, Csiszár J, Gémes K, Horváth E,
Horváth F, Simon ML and Tari I: Salicylic acid improves acclimation
to salt stress by stimulating abscisic aldehyde oxidase activity
and abscisic acid accumulation, and increases Na+ content in leaves
without toxicity symptoms in Solanum lycopersicum L. Journal of
Plant Physiology. 166:914–925. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ghebbi Si-smail K, Bellal M and Halladj F:
Effect of potassium supply on the behaviour of two processing
tomato cultivars and on the changes of fruit technological
characteristics. Acta Hortic. 758:269–274. 2007.
|
|
12
|
Pline WA, Edmisten KL, Oliver T, Wilcut
JW, Wells R and Allen NS: Use of digital image analysis, viability
stains, and germination assays to estimate conventional and
glyphosate-resistant cotton pollen viability. Crop Sci.
42:2193–2200. 2022.
|
|
13
|
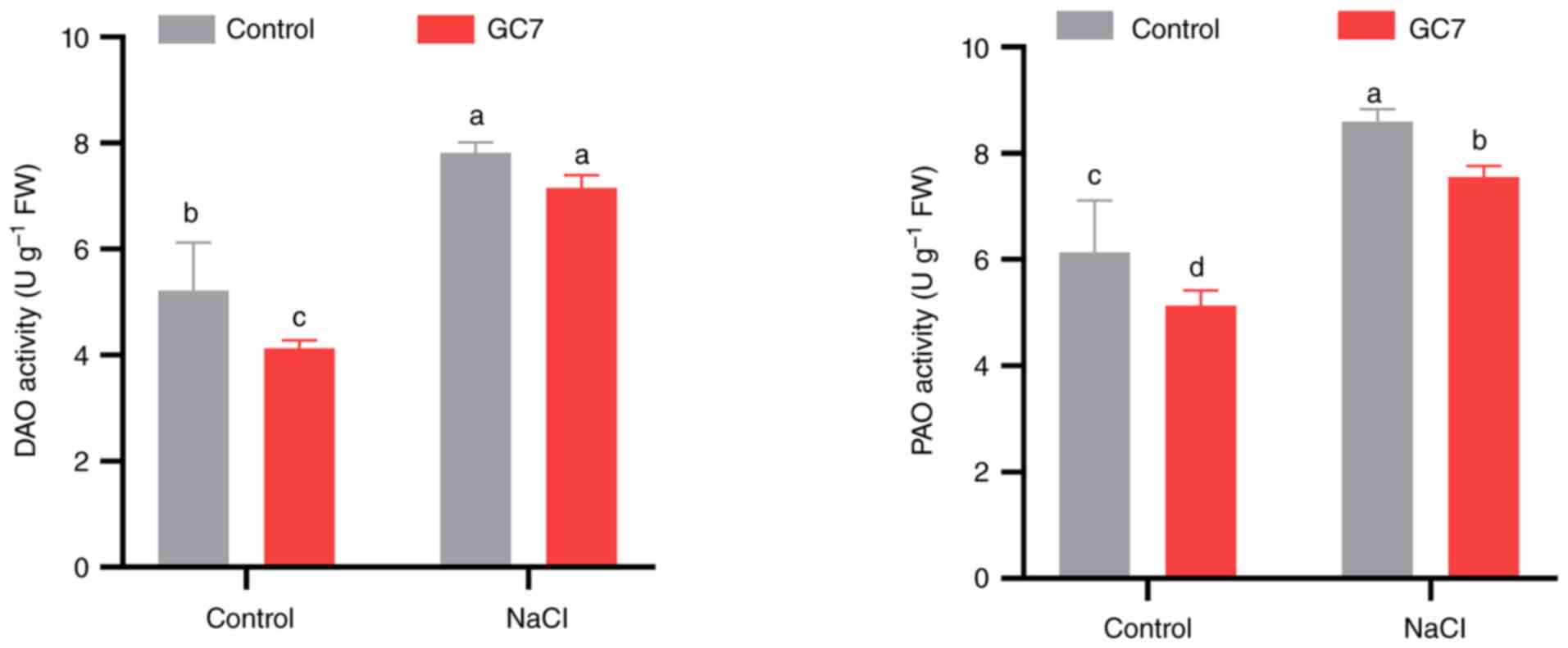
Szepesi Á, Bakacsy L, Kovács H, Szilágyi Á
and Köhler ZM: Inhibiting copper amine oxidase using
L-Aminoguanidine induces cultivar and Age-dependent alterations of
polyamine catabolism in tomato seedlings. Agriculture.
12(274)2022.
|
|
14
|
Xu J, Zhang B, Jiang C and Ming F:
RceIF5A, encoding a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A in
Rosa chinensis, can enhance thermotolerance, oxidative and osmotic
stress resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol.
75:167–178. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Xu C, Wang C and Wag Y:
Characterization of a eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A
homolog from Tamarix androssowii involved in plant abiotic stress
tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 12(118)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ghanem ME, van Elteren J, Albacete A,
Quinet M, Martinez-Andujar C, Kinet JM, Pérez-Alfocea F and Lutts
S: Impact of salinity on early reproductive physiology of tomato
(Solanum lycopersicum) in relation to a heterogeneous distribution
of toxic ions in flower organs. Funct Plant Biol. 36:125–136.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Aloisi I, Cai G, Serafini-Fracassini D and
Del Duca S: Polyamines in pollen: From microsporogenesis to
fertilization. Front Plant Sci. 7(155)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Choubey A and Rajam MV: RNAi-mediated
silencing of spermidine synthase gene results in reduced
reproductive potential in tobacco. Physiol Mol Biol Plants.
24:1069–1081. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Song J and Tachibana S: Loss of viability
of tomato pollen during long-term dry storage is associated with
reduced capacity for translating polyamine biosynthetic enzyme
genes after rehydration. J Exp Bot. 58:4235–4244. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu M, Buck JS and Kubota C: Effects of
nutrient solution EC, plant microclimate and cultivars on fruit
quality and yield of hydroponic tomatoes (Lycopersicum esculentum
L.). Acta Hort. 659:541–547. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Mehta RA, Cassol T, Li N, Ali N, Handa AK
and Mattoo AK: Engineered polyamine accumulation in tomato enhances
phytonutrient content, juice quality, and vine life. Nat
Biotechnol. 20:613–618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Handa AK and Mattoo AK: Differential and
functional interactions emphasize the multiple roles of polyamines
in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem. 48:540–546. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Oliverio S, Corazzari M, Sestito C,
Piredda L, Ippolito G and Piacentini M: The spermidine analogue GC7
(N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineoheptane) induces autophagy through a
mechanism not involving the hypusination of eIF5A. Amino Acids.
46:2767–2776. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cui Q, Ding W, Luo B, Lu W, Huang P and
Wen S: Novel gold-based complex GC7 suppresses cancer cell
proliferation via impacting energy metabolism mediated by
mitochondria. Bioorg Med Chem. 112(117897)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Park MH and Wolff EC: Hypusine, a
polyamine-derived amino acid critical for eukaryotic translation. J
Biol Chem. 293:18710–18718. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|