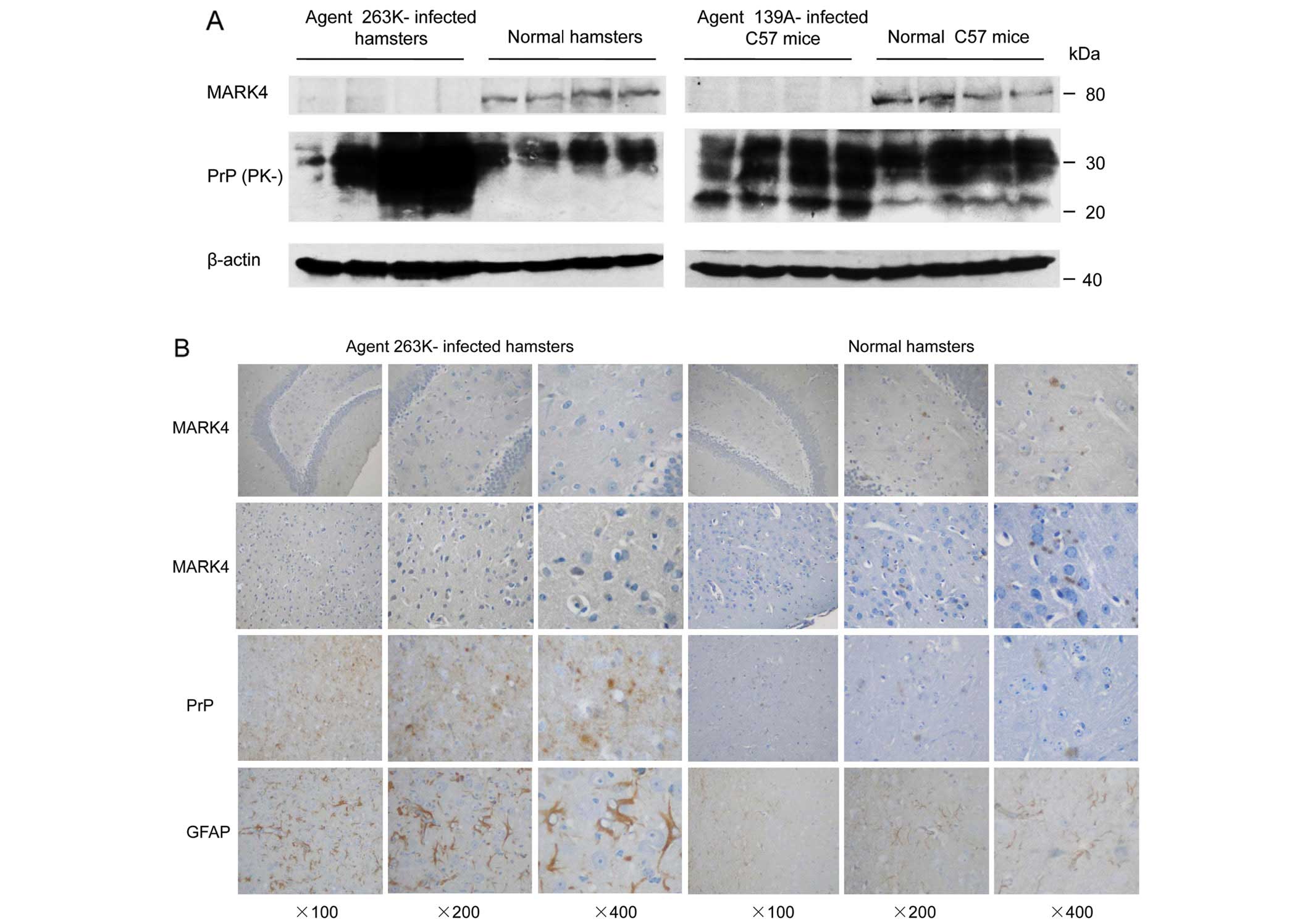
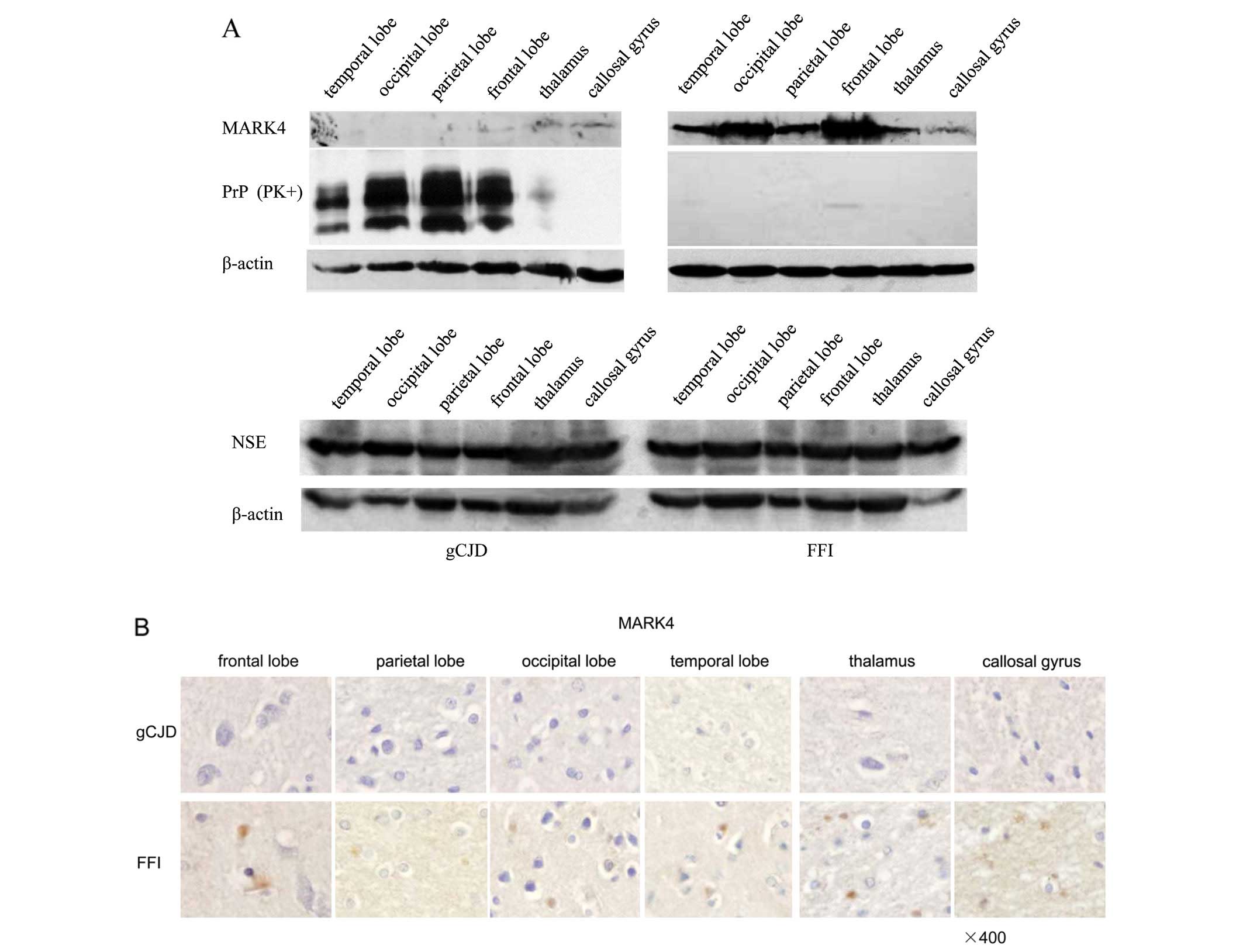
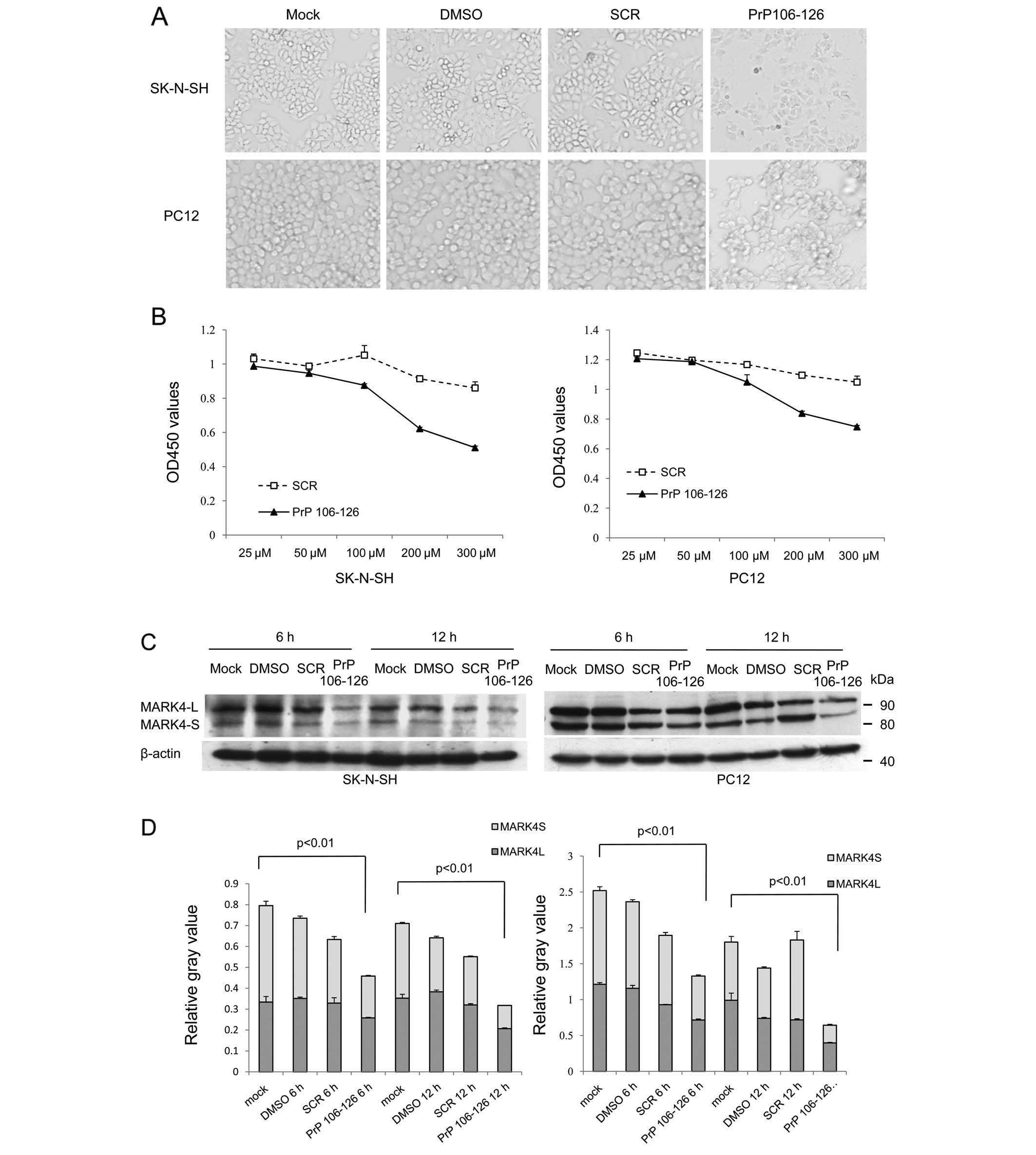
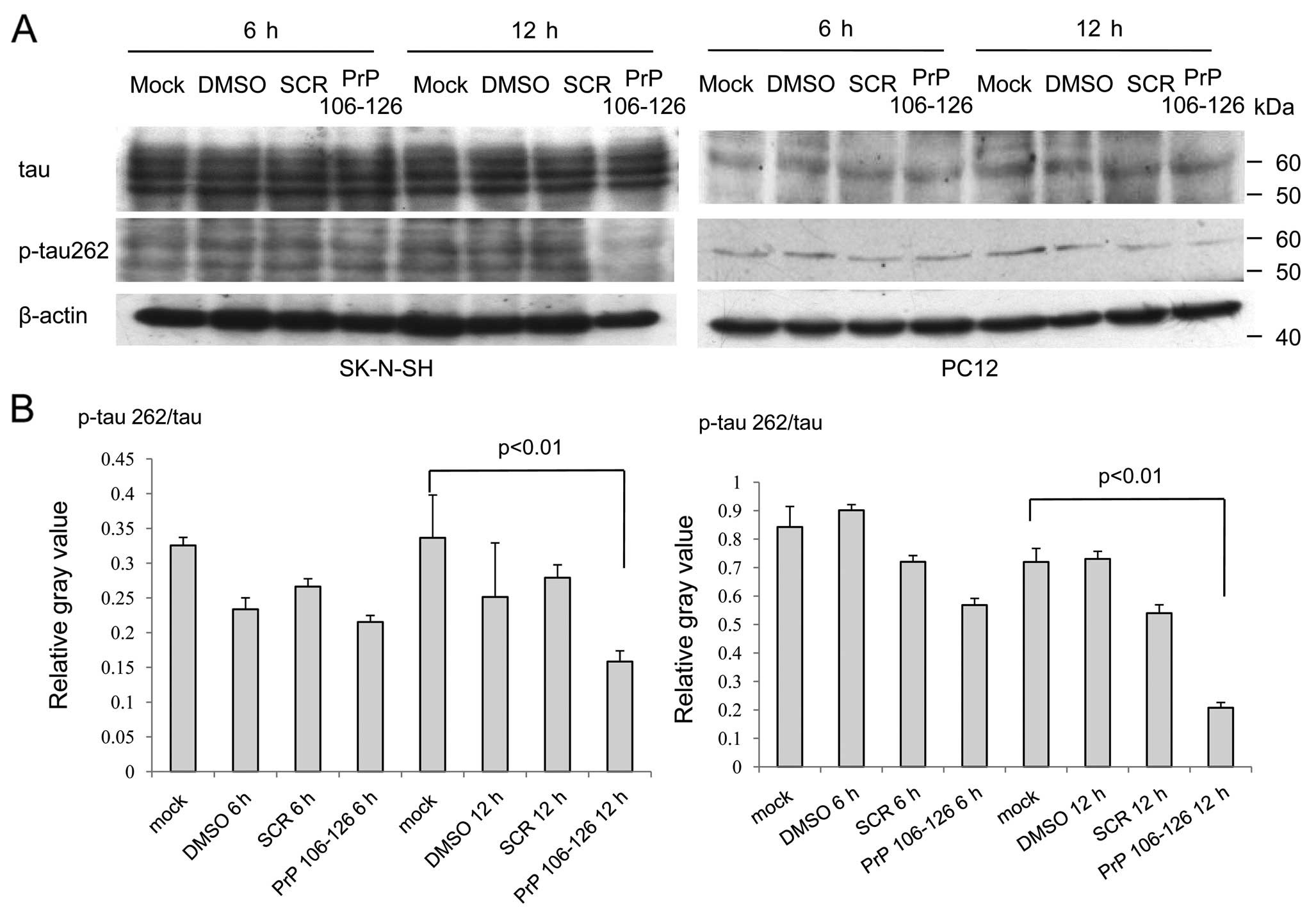
Spandidos Publications style
Gong H, Guo Y, Tian C, Xie W, Shi Q, Zhang J, Xu Y, Wang S, Zhang B, Chen C, Chen C, et al: Reduction of protein kinase MARK4 in the brains of experimental scrapie rodents and human prion disease correlates with deposits of PrPSc. Int J Mol Med 30: 569-578, 2012.
APA
Gong, H., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Xie, W., Shi, Q., Zhang, J. ... Dong, X. (2012). Reduction of protein kinase MARK4 in the brains of experimental scrapie rodents and human prion disease correlates with deposits of PrPSc. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 30, 569-578. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1025
MLA
Gong, H., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Xie, W., Shi, Q., Zhang, J., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, B., Chen, C., Liu, Y., Dong, X."Reduction of protein kinase MARK4 in the brains of experimental scrapie rodents and human prion disease correlates with deposits of PrPSc". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30.3 (2012): 569-578.
Chicago
Gong, H., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Xie, W., Shi, Q., Zhang, J., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, B., Chen, C., Liu, Y., Dong, X."Reduction of protein kinase MARK4 in the brains of experimental scrapie rodents and human prion disease correlates with deposits of PrPSc". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30, no. 3 (2012): 569-578. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1025