Spandidos Publications style
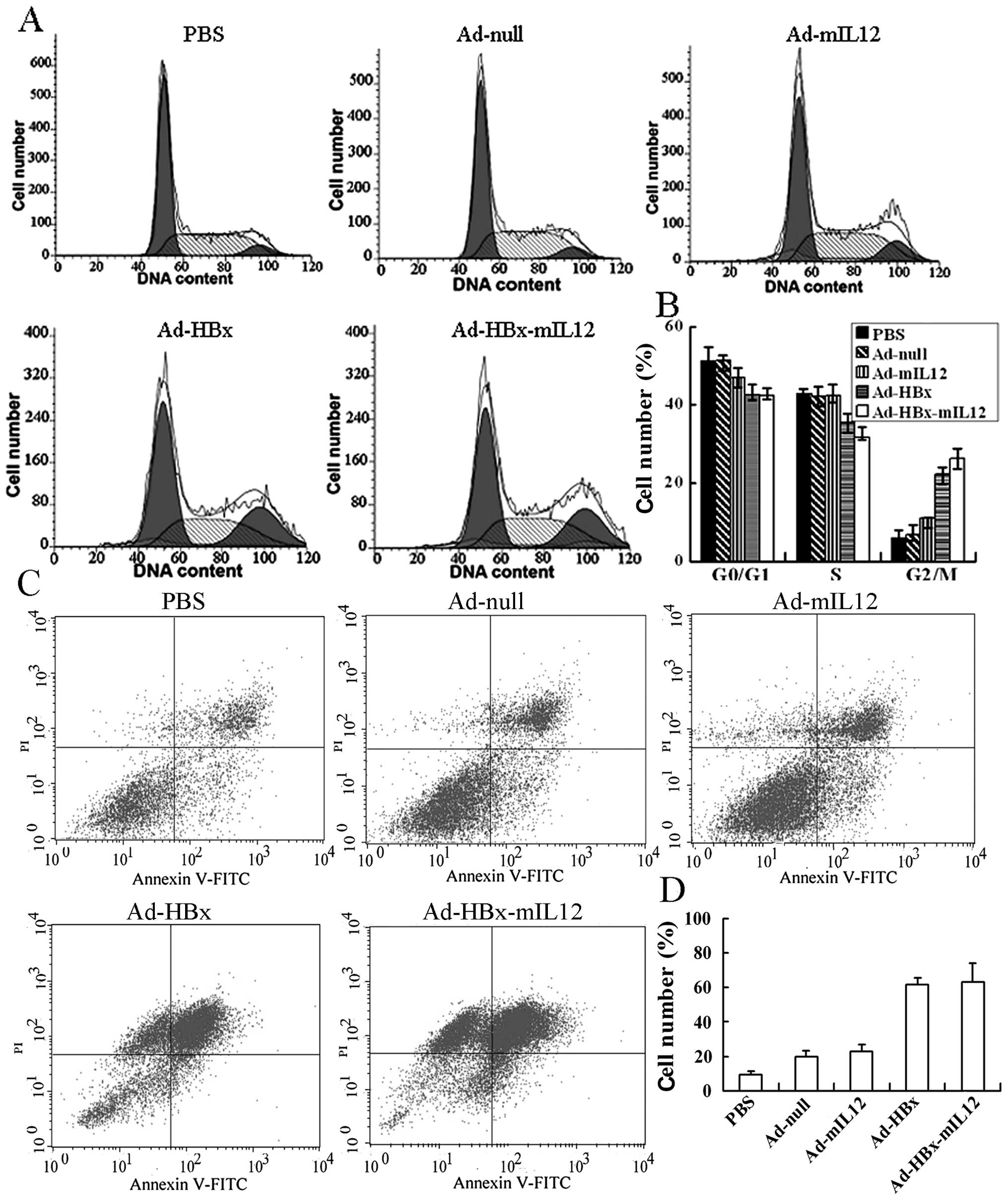
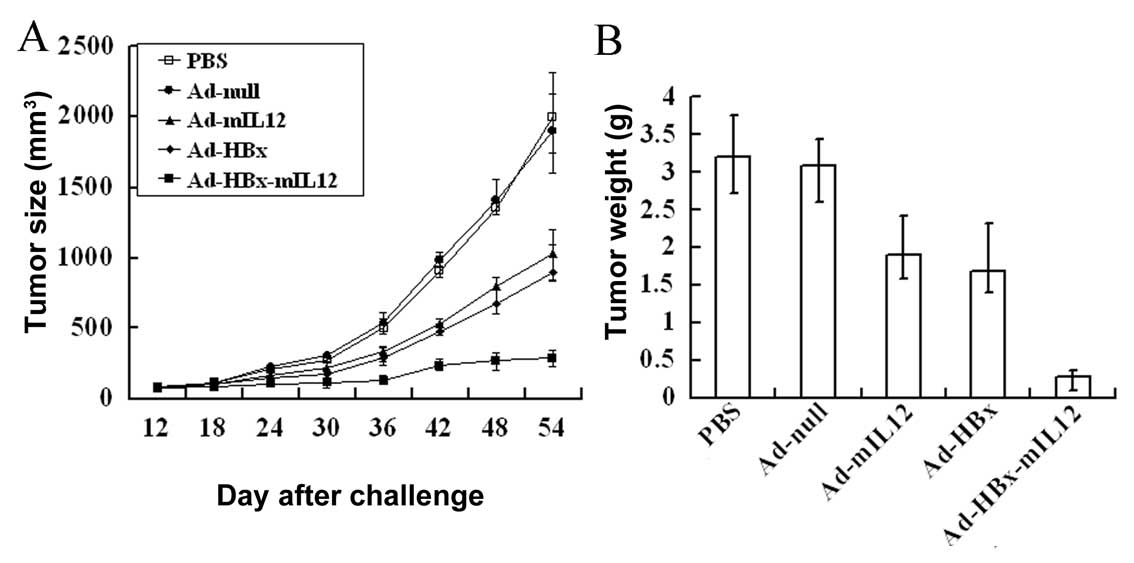
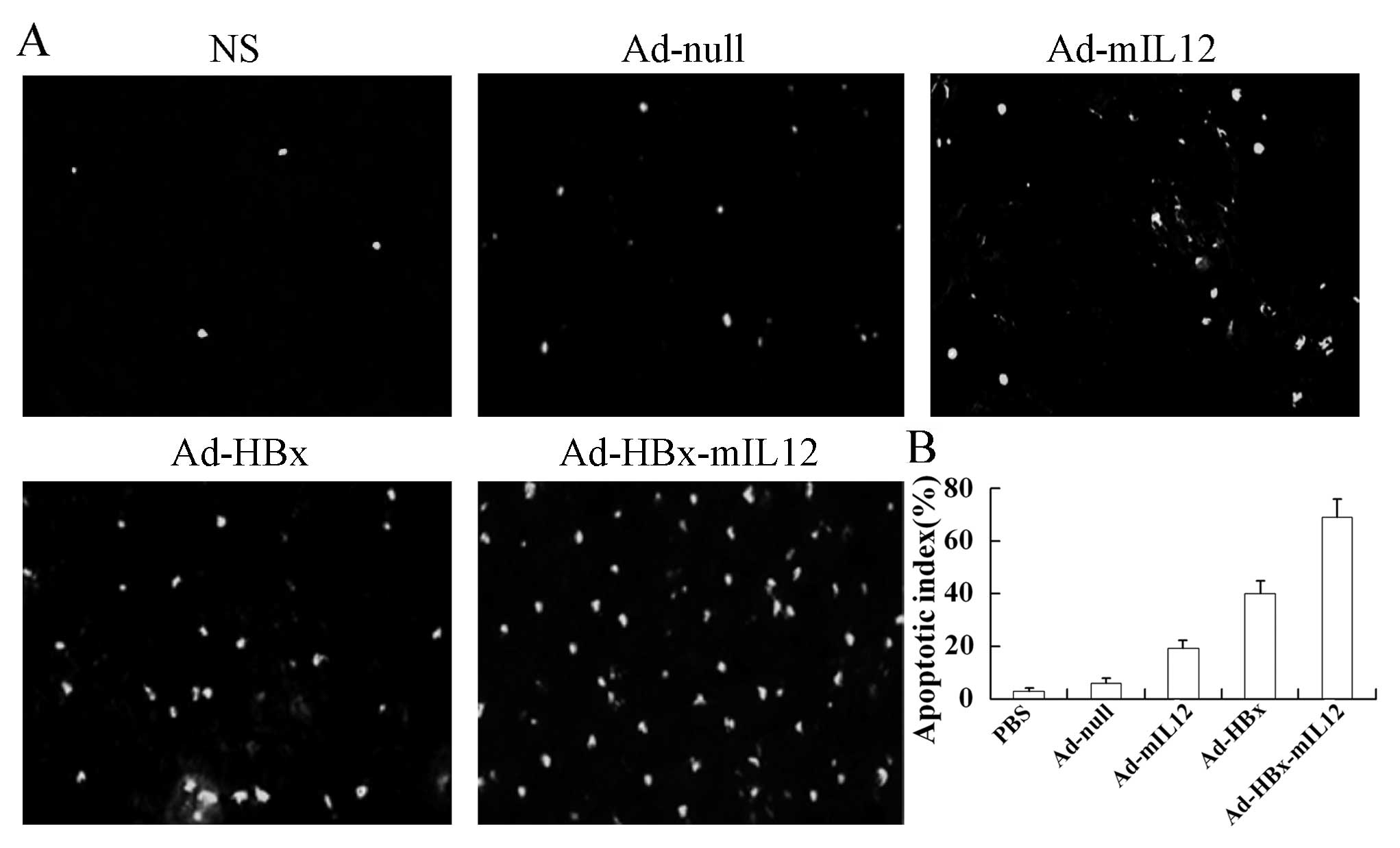
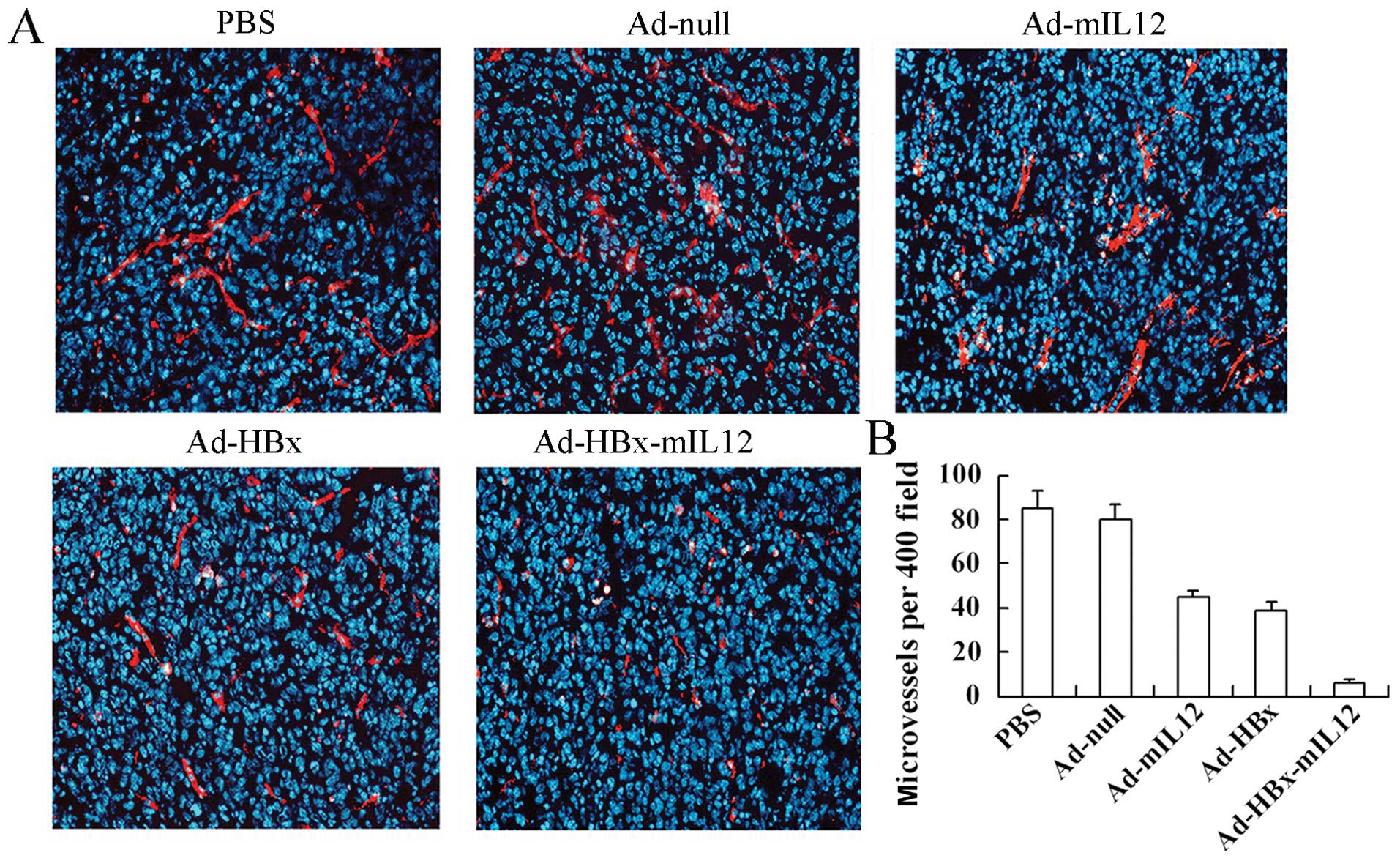
He H, Fan P, Yin T, Chen Q, Shi H, Liu S, Li H, Jing Q, Yan Y, Zhang H, Zhang H, et al: Local delivery of recombinant adenovirus expressing hepatitis B virus X protein and interleukin-12 results in antitumor effects via inhibition of hepatoma cell growth and intervention of tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Med 30: 599-605, 2012.
APA
He, H., Fan, P., Yin, T., Chen, Q., Shi, H., Liu, S. ... Cheng, P. (2012). Local delivery of recombinant adenovirus expressing hepatitis B virus X protein and interleukin-12 results in antitumor effects via inhibition of hepatoma cell growth and intervention of tumor microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 30, 599-605. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1027
MLA
He, H., Fan, P., Yin, T., Chen, Q., Shi, H., Liu, S., Li, H., Jing, Q., Yan, Y., Zhang, H., Yang, L., Wen, Y., Li, Y., Cheng, P."Local delivery of recombinant adenovirus expressing hepatitis B virus X protein and interleukin-12 results in antitumor effects via inhibition of hepatoma cell growth and intervention of tumor microenvironment". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30.3 (2012): 599-605.
Chicago
He, H., Fan, P., Yin, T., Chen, Q., Shi, H., Liu, S., Li, H., Jing, Q., Yan, Y., Zhang, H., Yang, L., Wen, Y., Li, Y., Cheng, P."Local delivery of recombinant adenovirus expressing hepatitis B virus X protein and interleukin-12 results in antitumor effects via inhibition of hepatoma cell growth and intervention of tumor microenvironment". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30, no. 3 (2012): 599-605. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1027