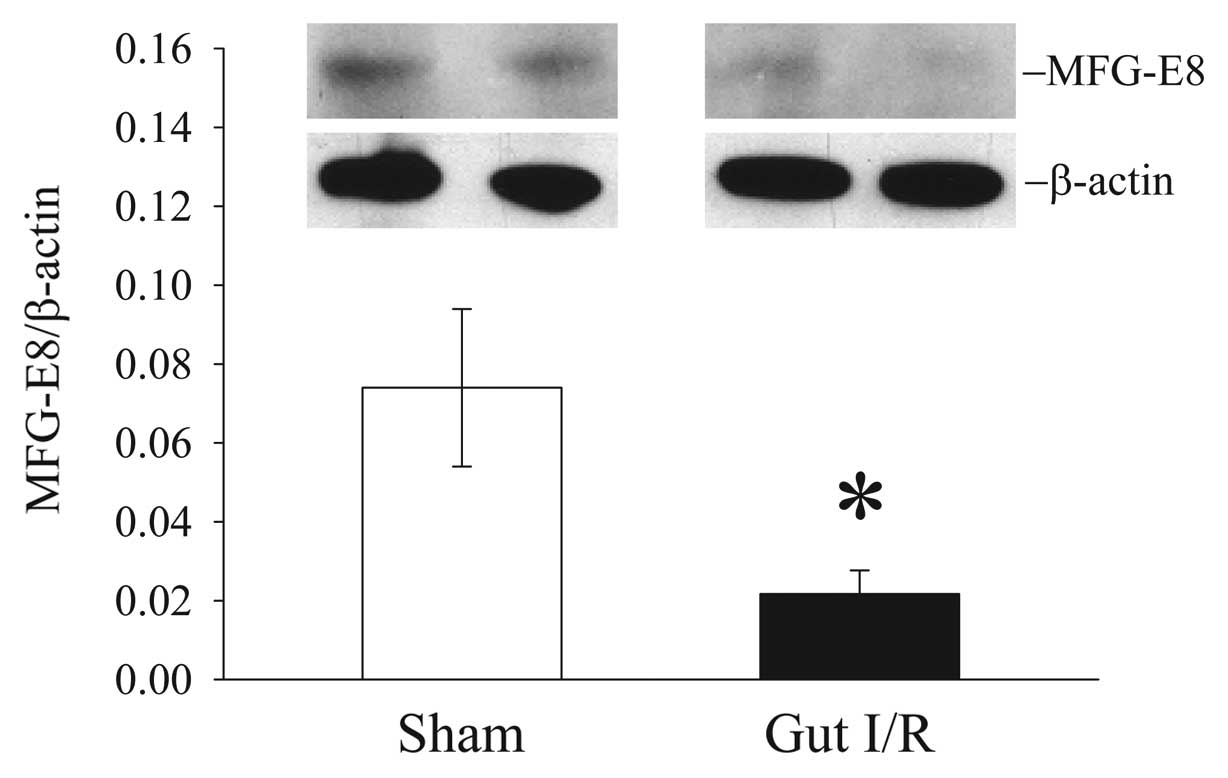
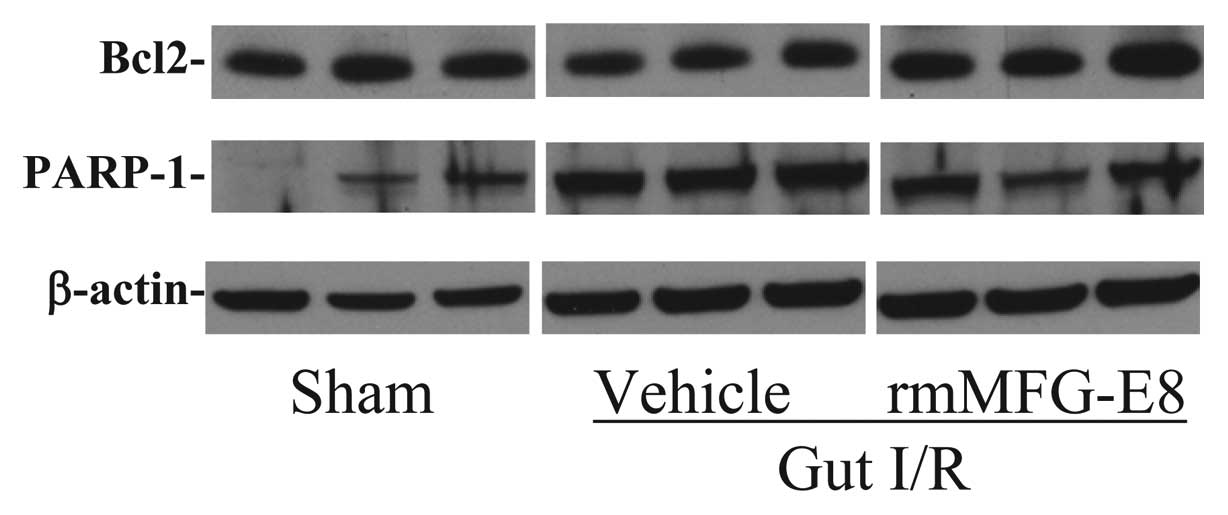
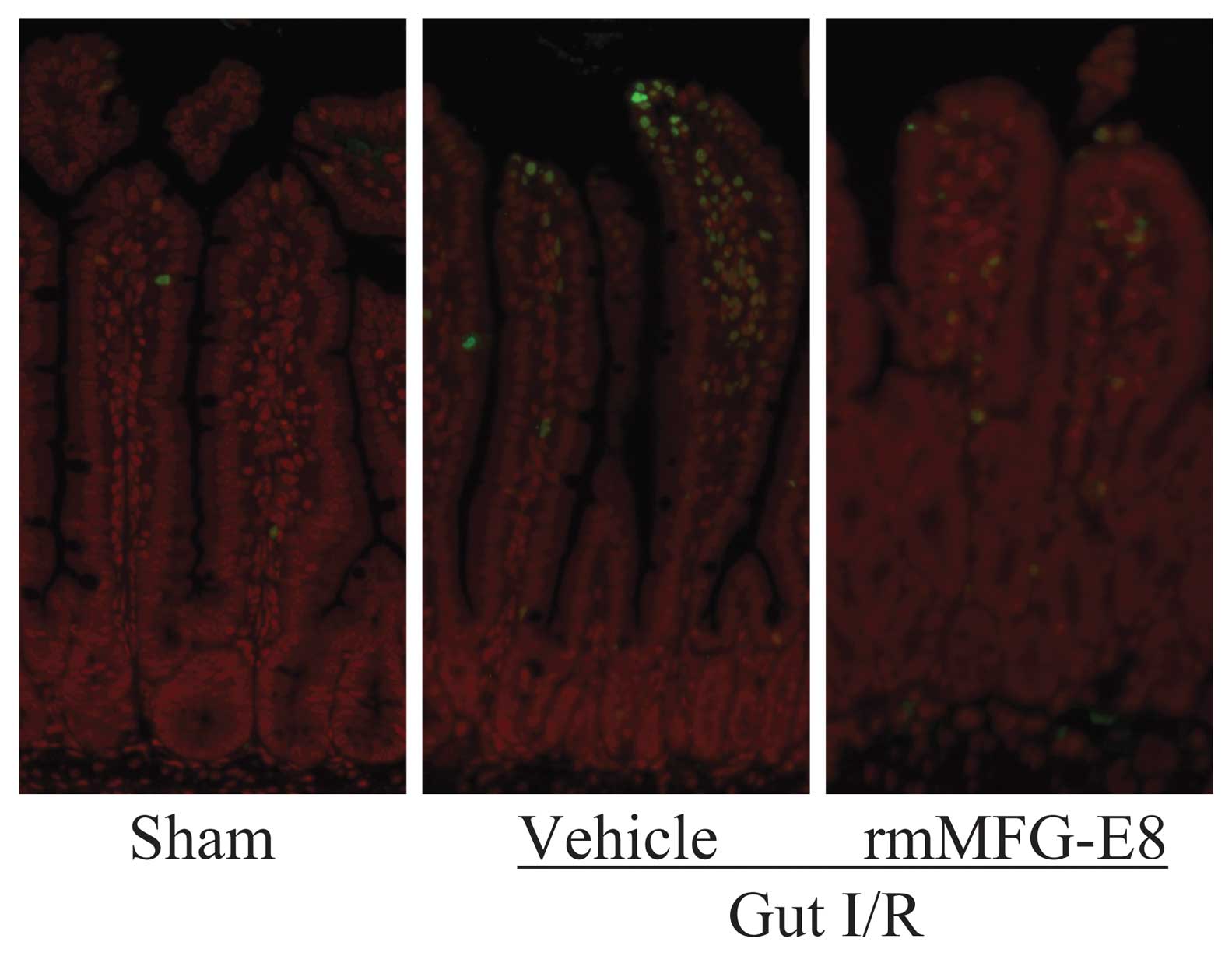
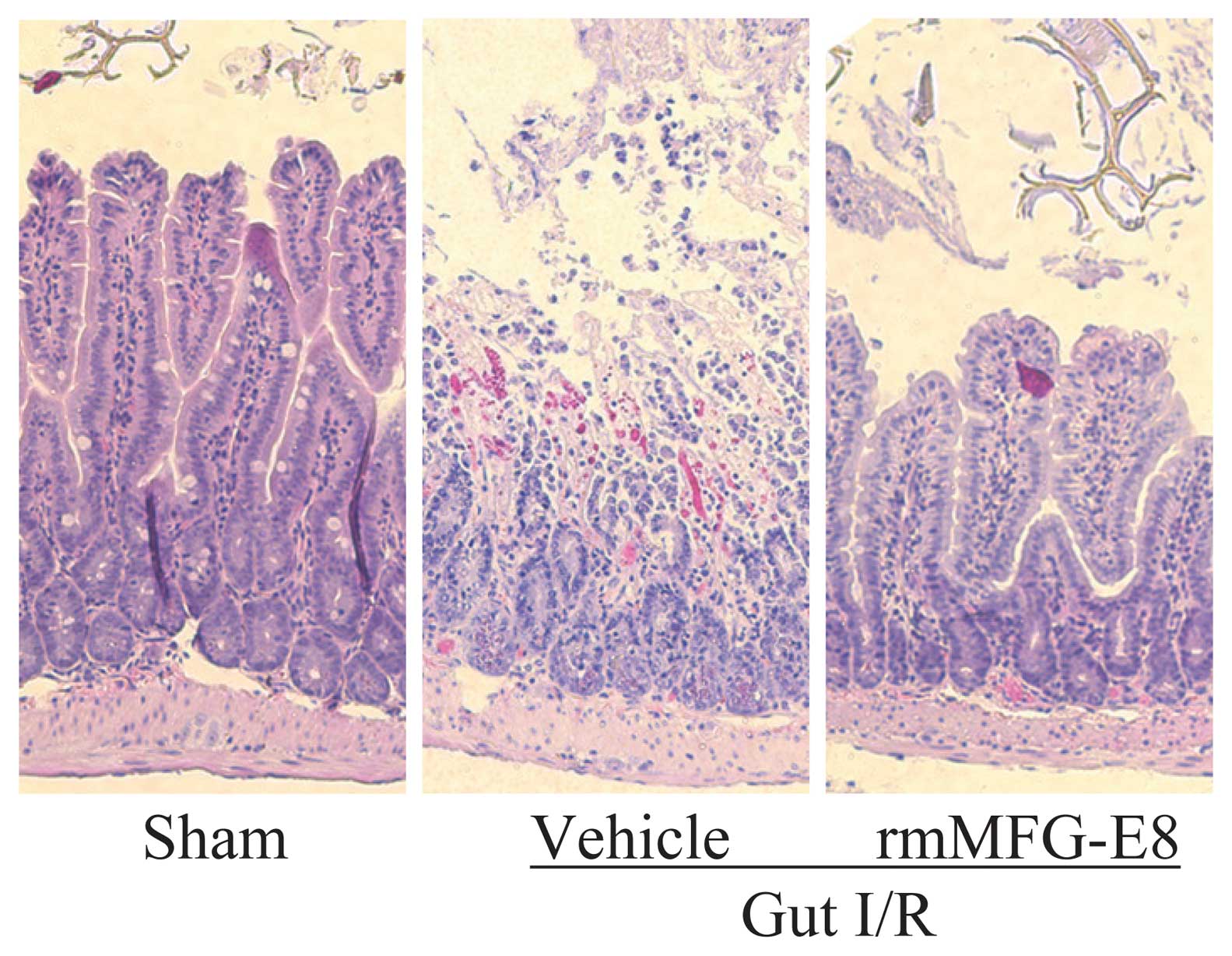
|
1.
|
WA OldenburgLL LauTJ RodenbergHJ EdmondsCD
BurgerAcute mesenteric ischemia: a clinical reviewArch Intern
Med16410541062200410.1001/archinte.164.10.105415159262
|
|
2.
|
J BerlangaP PratsD RemirezR GonzalezP
Lopez-SauraJ AguiarM OjedaJJ BoyleAJ FitzgeraldRJ
PlayfordProphylactic use of epidermal growth factor reduces
ischemia/reperfusion intestinal damageAm J
Pathol161373379200210.1016/S0002-9440(10)64192-212163361
|
|
3.
|
LJ BrandtSJ BoleyAGA technical review on
intestinal ischemia. American Gastrointestinal
AssociationGastroenterology118954968200010.1016/S0016-5085(00)70183-110784596
|
|
4.
|
DV RocourtVB MehtaGE BesnerHeparin-binding
EGF-like growth factor decreases inflammatory cytokine expression
after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injuryJ Surg
Res139269273200710.1016/j.jss.2006.10.047
|
|
5.
|
HT HassounBC KoneDW MercerFG MoodyNW
WeisbrodtFA MoorePost-injury multiple organ failure: the role of
the gutShock15110200110.1097/00024382-200115010-0000111198350
|
|
6.
|
MP FinkEffect of critical illness on
microbial translocation and gastrointestinal mucosa
permeabilitySemin Respir Infect925626019947886323
|
|
7.
|
RA MatthijsenJP DerikxD KuipersRM van
DamCH DejongWA BuurmanEnterocyte shedding and epithelial lining
repair following ischemia of the human small intestine attenuate
inflammationPLoS ONE4e7045200910.1371/journal.pone.0007045
|
|
8.
|
CY HuangJK HsiaoYZ LuTC LeeLC
YuAnti-apoptotic PI3K/Akt signaling by sodium/glucose transporter 1
reduces epithelial barrier damage and bacterial translocation in
intestinal ischemiaLab
Invest91294309201110.1038/labinvest.2010.17720975661
|
|
9.
|
PR DiE EspositoE MazzonI PaternitiM
GaluppoS CuzzocreaGW0742, a selective PPAR-beta/delta agonist,
contributes to the resolution of inflammation after gut
ischemia/reperfusion injuryJ Leukoc
Biol88291301201010.1189/jlb.011005320430778
|
|
10.
|
A OberholzerC OberholzerRM MinterLL
MoldawerConsidering immunomodulatory therapies in the septic
patient: should apoptosis be a potential therapeutic target?Immunol
Lett75221224200110.1016/S0165-2478(00)00307-211166379
|
|
11.
|
PA EfronK TinsleyDJ MinnichV MonterrosoJ
WagnerP LaineeK LorrePE SwansonR HotchkissLL MoldawerIncreased
lymphoid tissue apoptosis in baboons with bacteremic
shockShock21566571200410.1097/01.shk.0000126648.58732.8c15167687
|
|
12.
|
RS HotchkissPE SwansonBD FreemanKW
TinsleyJP CobbGM MatuschakTG BuchmanIE KarlApoptotic cell death in
patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunctionCrit
Care Med2712301251199910.1097/00003246-199907000-0000210446814
|
|
13.
|
RS HotchkissCM CoopersmithIE
KarlPrevention of lymphocyte apoptosis - a potential treatment of
sepsis?Clin Infect Dis41Suppl
7S465S469200510.1086/43199816237649
|
|
14.
|
RS HotchkissSB OsmonKC ChangTH WagnerCM
CoopersmithIE KarlAccelerated lymphocyte death in sepsis occurs by
both the death receptor and mitochondrial pathwaysJ
Immunol17451105118200510.4049/jimmunol.174.8.511015814742
|
|
15.
|
R MahidharaTR BilliarApoptosis in
sepsisCrit Care
Med28N105N113200010.1097/00003246-200004001-00013
|
|
16.
|
A AyalaXY XinCA AyalaDE SonefeldSM KarrTA
EvansIH ChaudryIncreased mucosal B-lymphocyte apoptosis during
polymicrobial sepsis is a Fas ligand but not an endotoxin-mediated
processBlood911362137219989454767
|
|
17.
|
DE WescheJL Lomas-NeiraM PerlCS ChungA
AyalaLeukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis and shockJ
Leukoc Biol78325337200510.1189/jlb.010501715817707
|
|
18.
|
DE Wesche-SoldatoCS ChungJ Lomas-NeiraLA
DoughtySH GregoryA AyalaIn vivo delivery of caspase-8 or Fas siRNA
improves the survival of septic
miceBlood10622952301200510.1182/blood-2004-10-408615941915
|
|
19.
|
R HanayamaK MiyasakaM NakayaS
NagataMFG-E8-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells, and
autoimmunity caused by its failureCurr Dir
Autoimmun9162172200616394660
|
|
20.
|
R HanayamaM TanakaK MiwaA ShinoharaA
IwamatsuS NagataIdentification of a factor that links apoptotic
cells to phagocytesNature417182187200210.1038/417182a12000961
|
|
21.
|
R HanayamaM TanakaK MiyasakaK AozasaM
KoikeY UchiyamaS NagataAutoimmune disease and impaired uptake of
apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-deficient
miceScience30411471150200410.1126/science.109435915155946
|
|
22.
|
M MiksaR WuW DongP DasD YangP
WangDendritic cell-derived exosomes containing milk fat globule
epidermal growth factor-factor VIII attenuate proinflammatory
responses in
sepsisShock25586593200610.1097/01.shk.0000209533.22941.d016721266
|
|
23.
|
M MiksaR WuW DongH KomuraD AminY JiZ WangH
WangTS RavikumarKJ TraceyP WangImmature dendritic cell-derived
exosomes rescue septic animals via milk fat globule epidermal
growth factor VIIIJ
Immunol18359835990200910.4049/jimmunol.080299419812188
|
|
24.
|
T CuiM MiksaR WuH KomuraM ZhouW DongZ
WangS HiguchiW ChaungSA BlauMilk fat globule epidermal growth
factor 8 attenuates acute lung injury in mice after intestinal
ischemia and reperfusionAm J Respir Crit Care
Med181238246201010.1164/rccm.200804-625OC19892861
|
|
25.
|
S AkakuraS SinghM SpataroR AkakuraJI KimML
AlbertRB BirgeThe opsonin MFG-E8 is a ligand for the alphavbeta5
integrin and triggers DOCK180-dependent Rac1 activation for the
phagocytosis of apoptotic cellsExp Cell
Res292403416200410.1016/j.yexcr.2003.09.01114697347
|
|
26.
|
K OshimaN AokiM NegiM KishiK KitajimaT
MatsudaLactation-dependent expression of an mRNA splice variant
with an exon for a multiply O-glycosylated domain of mouse milk fat
globule glycoprotein MFG-E8Biochem Biophys Res
Commun254522528199910.1006/bbrc.1998.01079920772
|
|
27.
|
MR TaylorJR CoutoCD ScallanRL CerianiJA
PetersonLactadherin (formerly BA46), a membrane-associated
glycoprotein expressed in human milk and breast carcinomas,
promotes Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-dependent cell adhesionDNA Cell
Biol16861869199710.1089/dna.1997.16.861
|
|
28.
|
DS NewburgJA PetersonGM Ruiz-PalaciosDO
MatsonAL MorrowJ ShultsML GuerreroP ChaturvediSO NewburgCD
ScallanRole of human-milk lactadherin in protection against
symptomatic rotavirus
infectionLancet35111601164199810.1016/S0140-6736(97)10322-19643686
|
|
29.
|
K MiyasakaR HanayamaM TanakaS
NagataExpression of milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 in
immature dendritic cells for engulfment of apoptotic cellsEur J
Immunol3414141422200410.1002/eji.20042493015114675
|
|
30.
|
C TheryA RegnaultJ GarinJ WolfersL
ZitvogelP Ricciardi-CastagnoliG RaposoS AmigorenaMolecular
characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective
accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73J Cell
Biol147599610199910.1083/jcb.147.3.59910545503
|
|
31.
|
K OshimaN AokiT KatoK KitajimaT
MatsudaSecretion of a peripheral membrane protein, MFG-E8, as a
complex with membrane vesiclesEur J
Biochem26912091218200210.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02758.x11856354
|
|
32.
|
P VeronE SeguraG SuganoS AmigorenaC
TheryAccumulation of MFG-E8/lactadherin on exosomes from immature
dendritic cellsBlood Cells Mol
Dis358188200510.1016/j.bcmd.2005.05.00115982908
|
|
33.
|
GM SwankEA DeitchRole of the gut in
multiple organ failure: bacterial translocation and permeability
changesWorld J Surg20411417199610.1007/s0026899000658662128
|
|
34.
|
WW SoubaRJ SmithDW WilmoreGlutamine
metabolism by the intestinal tractJPEN J Parenter Enteral
Nutr9608617198510.1177/01486071850090056083900455
|
|
35.
|
ML MarinAJ GreensteinSA GellerRE GordonAH
Aufses JrA freeze fracture study of Crohn’s disease of the terminal
ileum: changes in epithelial tight junction organizationAm J
Gastroenterol785375471983
|
|
36.
|
BJ AmmoriPC LeederRF KingGR BarclayIG
MartinM LarvinMJ McMahonEarly increase in intestinal permeability
in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: correlation with
endotoxemia, organ failure, and mortalityJ Gastrointest
Surg3252262199910.1016/S1091-255X(99)80067-5
|
|
37.
|
PL FariesRJ SimonAT MartellaMJ LeeGW
MachiedoIntestinal permeability correlates with severity of injury
in trauma patientsJ
Trauma4410311035199810.1097/00005373-199806000-000169637159
|
|
38.
|
CJ DoigLR SutherlandJD SandhamGH FickM
VerhoefJB MeddingsIncreased intestinal permeability is associated
with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in
critically ill ICU patientsAm J Respir Crit Care
Med158444451199810.1164/ajrccm.158.2.97100929700119
|
|
39.
|
RH YolkenJA PetersonSL VonderfechtET
FoutsK MidthunDS NewburgHuman milk mucin inhibits rotavirus
replication and prevents experimental gastroenteritisJ Clin
Invest9019841991199210.1172/JCI1160781331178
|
|
40.
|
HF BuXL ZuoX WangMA EnsslinV KotiW HsuehAS
RaymondBD ShurXD TanMilk fat globule-EGF factor 8/lactadherin plays
a crucial role in maintenance and repair of murine intestinal
epitheliumJ Clin Invest11736733683200718008006
|
|
41.
|
JS SilvestreC TheryG HamardJ BoddaertB
AguilarA DelcayreC HoubronR TamaratO Blanc-BrudeS
HeenemanLactadherin promotes VEGF-dependent neovascularizationNat
Med11499506200510.1038/nm1233
|
|
42.
|
Y WangHK HaiderN AhmadM XuR GeM
AshrafCombining pharmacological mobilization with intramyocardial
delivery of bone marrow cells over-expressing VEGF is more
effective for cardiac repairJ Mol Cell
Cardiol40736745200610.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.02.00416603183
|
|
43.
|
DE VonS MeyerD ThornD MarmeUT HoptO
ThomuschTargeting vascular endothelial growth factor pathway offers
new possibilities to counteract microvascular disturbances during
ischemia/reperfusion of the
pancreasTransplantation82543549200610.1097/01.tp.0000229434.92523.99
|
|
44.
|
T GrigaA TrommW SchmiegelO PfistererKM
MullerF BraschCollagenous colitis: implications for the role of
vascular endothelial growth factor in repair mechanismsEur J
Gastroenterol
Hepatol16397402200410.1097/00042737-200404000-0000515028972
|
|
45.
|
R ScaliaG BoothDJ LeferVascular
endothelial growth factor attenuates leukocyte-endothelium
interaction during acute endothelial dysfunction: essential role of
endothelium-derived nitric oxideFASEB J13103910461999
|