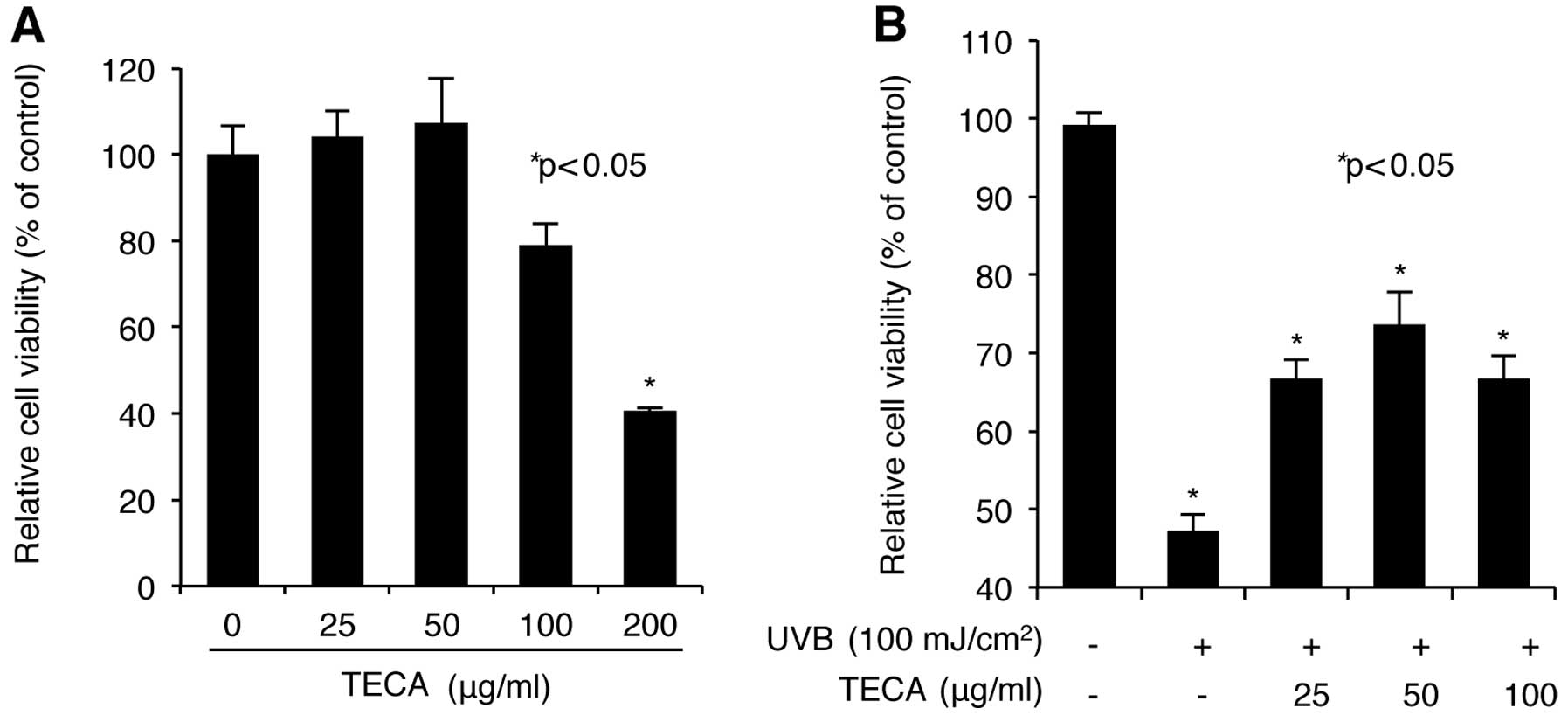
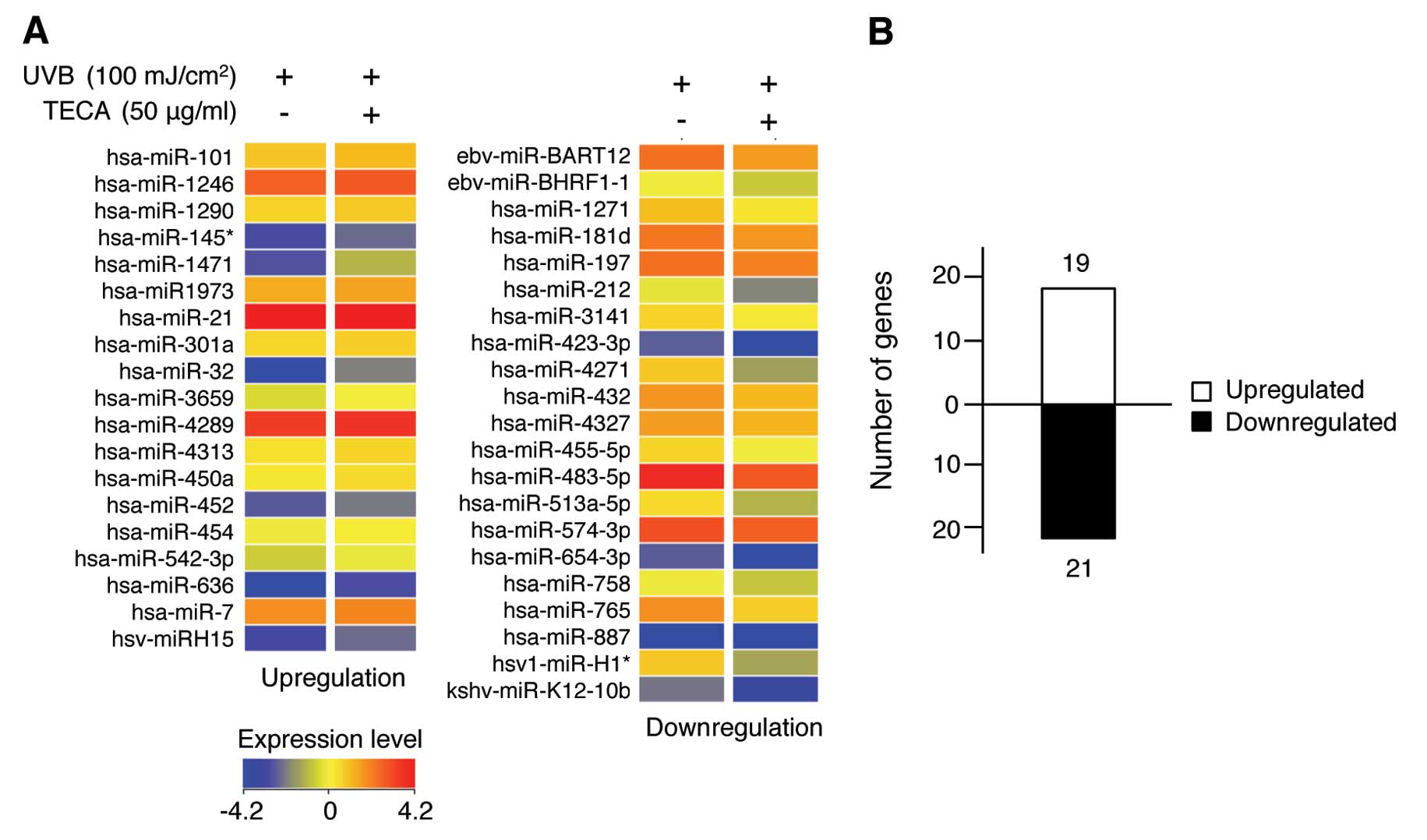
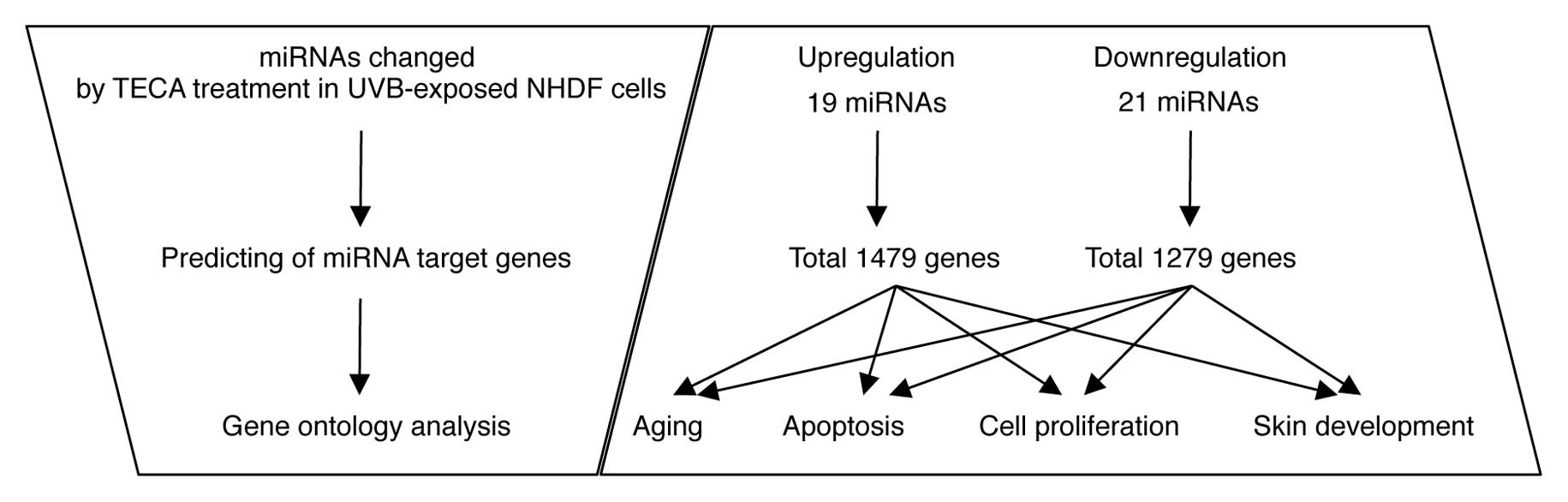
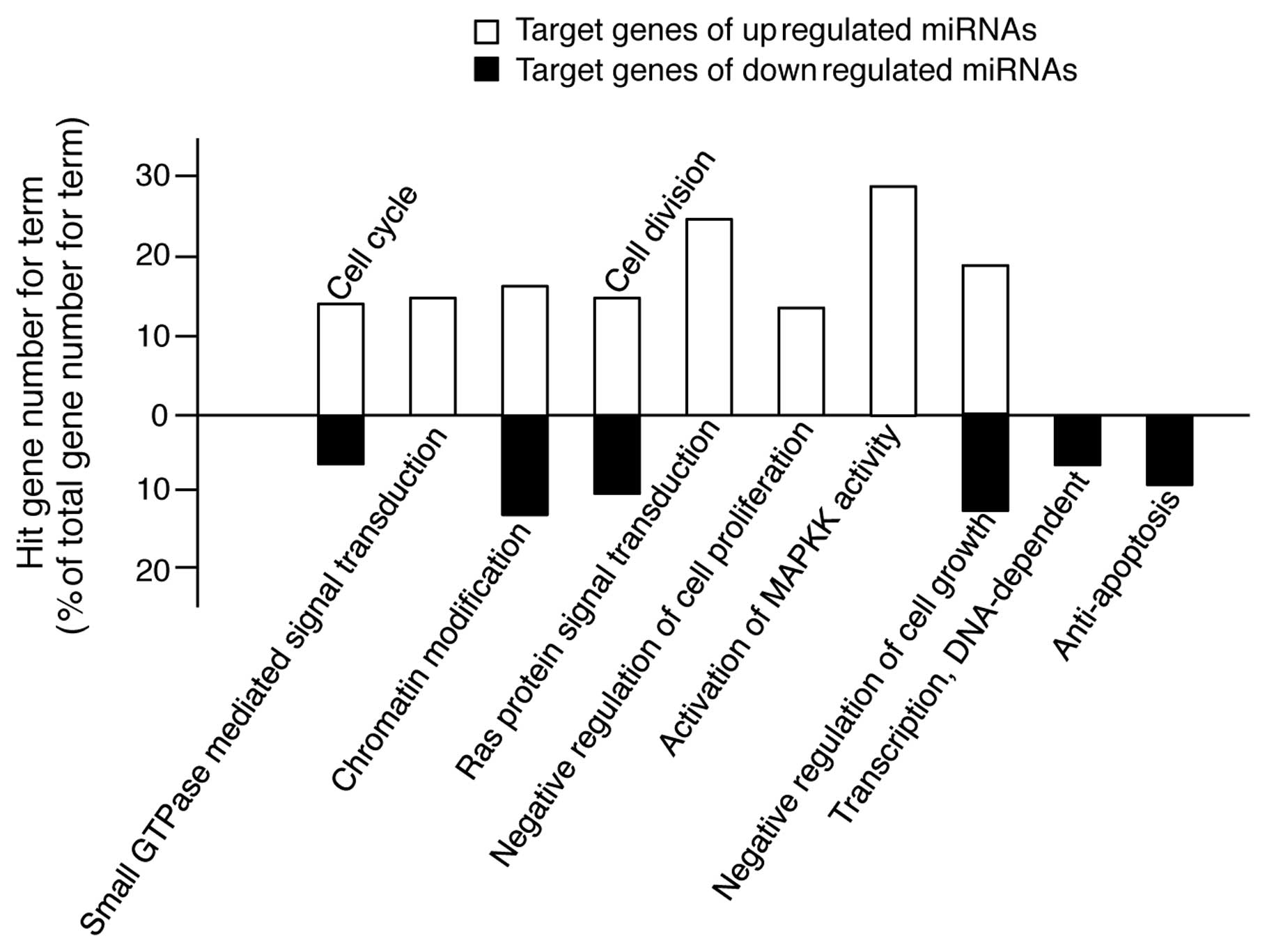
|
1.
|
CD ColdrenP HashimJM AliSK OhAJ SinskeyC
RhaGene expression changes in the human fibroblast induced by
Centella asiatica triterpenoidsPlanta
Med69725732200310.1055/s-2003-4279114531023
|
|
2.
|
B BrinkhausM LindnerD SchuppanEG
HahnChemical, pharmacological and clinical profile of the East
Asian medical plant Centella
asiaticaPhytomedicine7427448200010.1016/S0944-7113(00)80065-311081995
|
|
3.
|
JT JamesIA DuberyPentacyclic triterpenoids
from the medicinal herb, Centella asiatica (L.)
UrbanMolecules1439223941200910.3390/molecules1410392219924039
|
|
4.
|
G JayashreeG Kurup MuraleedharaS
SudarslalVB JacobAnti-oxidant activity of Centella asiatica
on lymphoma-bearing miceFitoterapia744314342003
|
|
5.
|
TD BabuG KuttanJ PadikkalaCytotoxic and
anti-tumour properties of certain taxa of Umbelliferae with special
reference to Centella asiatica (L.) UrbanJ
Ethnopharmacol485357199510.1016/0378-8741(95)01284-K8569247
|
|
6.
|
FX MaquartF ChastangA SimeonP BirembautP
GilleryY WegrowskiTriterpenes from Centella asiatica
stimulate extracellular matrix accumulation in rat experimental
woundsEur J Dermatol92892961999
|
|
7.
|
F BonteM DumasC ChaudagneA
MeybeckInfluence of asiatic acid, madecassic acid, and asiaticoside
on human collagen I synthesisPlanta
Med60133135199410.1055/s-2006-9594348202564
|
|
8.
|
MR CesaroneG BelcaroMT De SanctisEffects
of the total triterpenic fraction of Centella asiatica in
venous hypertensive microangiopathy: a prospective,
placebo-controlled, randomized trialAngiology52Suppl 215182001
|
|
9.
|
L IncandelaMR CesaroneM CacchioTotal
triterpenic fraction of Centella asiatica in chronic venous
insufficiency and in high-perfusion microangiopathyAngiology52Suppl
29132001
|
|
10.
|
F BonteM DumasC ChaudagneA
MeybeckComparative activity of asiaticoside and madecassoside on
type I and III collagen synthesis by cultured human fibroblastsAnn
Pharm Fr5338421995(In French).
|
|
11.
|
R TenniG ZanaboniMP De AgostiniA RossiC
BendottiG CettaEffect of the triterpenoid fraction of Centella
asiatica on macromolecules of the connective matrix in human
skin fibroblast culturesItal J Biochem3769771988
|
|
12.
|
FX MaquartG BellonP GilleryY WegrowskiJP
BorelStimulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblast cultures by a
triterpene extracted from Centella asiaticaConnect Tissue
Res24107120199010.3109/030082090091524272354631
|
|
13.
|
T OttE FritzA PolleA
SchutzendubelCharacterisation of antioxidative systems in the
ectomycorrhiza-building basidiomycete Paxillus involutus
(Bartsch) Fr. and its reaction to cadmiumFEMS Microbiol
Ecol42359366200210.1111/j.1574-6941.2002.tb01025.x19709295
|
|
14.
|
RA MustafaA Abdul HamidS MohamedFA
BakarTotal phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and radical scavenging
activity of 21 selected tropical plantsJ Food
Sci75C28C35201010.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01401.x20492146
|
|
15.
|
YJ KimHJ ChaKH NamY YoonH LeeS
AnCentella asiatica extracts modulate hydrogen
peroxide-induced senescence in human dermal fibroblastsExp
Dermatol209981003201110.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01388.x
|
|
16.
|
GJ ClydesdaleGW DandieHK MullerUltraviolet
light induced injury: immunological and inflammatory effectsImmunol
Cell Biol79547568200110.1046/j.1440-1711.2001.01047.x11903614
|
|
17.
|
A HennessyC OhJ ReesB DiffeyThe
photoadaptive response to ultraviolet exposure in human skin using
ultraviolet spectrophotometryPhotodermatol Photoimmunol
Photomed21229233200510.1111/j.1600-0781.2005.00170.x16149934
|
|
18.
|
Y MatsumuraHN AnanthaswamyToxic effects of
ultraviolet radiation on the skinToxicol Appl
Pharmacol195298308200410.1016/j.taap.2003.08.01915020192
|
|
19.
|
V MuthusamyTJ PivaThe UV response of the
skin: a review of the MAPK, NFkappaB and TNFalpha signal
transduction pathwaysArch Dermatol
Res302517201010.1007/s00403-009-0994-y19756672
|
|
20.
|
P HashimH SidekMH HelanA SaberyUD
PalanisamyM IlhamTriterpene composition and bioactivities of
Centella
asiaticaMolecules1613101322201110.3390/molecules1602131021278681
|
|
21.
|
JH YangJH LiP ShaoH ZhouYQ ChenLH
QustarBase: a database for exploring microRNA-mRNA interaction maps
from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq dataNucleic Acids
Res39D202D209201110.1093/nar/gkq105621037263
|
|
22.
|
V AmbrosRC LeeIdentification of microRNAs
and other tiny noncoding RNAs by cDNA cloningMethods Mol
Biol265131158200415103073
|
|
23.
|
AM ChengMW ByromJ SheltonLP FordAntisense
inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of
miRNA in cell growth and apoptosisNucleic Acids
Res3312901297200510.1093/nar/gki20015741182
|
|
24.
|
JF ChenEM MandelJM ThomsonThe role of
microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and
differentiationNat Genet38228233200610.1038/ng172516380711
|
|
25.
|
WJ ChoJM ShinJS KimmiR-372 regulates cell
cycle and apoptosis of ags human gastric cancer cell line through
direct regulation of LATS2Mol
Cells28521527200910.1007/s10059-009-0158-019937137
|
|
26.
|
AS O’TooleS MillerN HainesMC ZinkMJ
SerraComprehensive thermodynamic analysis of 3’ double-nucleotide
overhangs neighboring Watson-Crick terminal base pairsNucleic Acids
Res34333833442006
|
|
27.
|
L GuoZ LuThe fate of miRNA*
strand through evolutionary analysis: implication for degradation
as merely carrier strand or potential regulatory molecule?PLoS
One5e11387201020613982
|
|
28.
|
RS PillaiSN BhattacharyyaW
FilipowiczRepression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many
mechanisms?Trends Cell
Biol17118126200710.1016/j.tcb.2006.12.00717197185
|
|
29.
|
B JohnAJ EnrightA AravinT TuschlC SanderDS
MarksHuman MicroRNA targetsPLoS
Biol2e363200410.1371/journal.pbio.0020363
|
|
30.
|
AB JaffeA HallRho GTPases: biochemistry
and biologyAnnu Rev Cell Dev
Biol21247269200510.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.020604.15072116212495
|
|
31.
|
L WangY ZhengCell type-specific functions
of Rho GTPases revealed by gene targeting in miceTrends Cell
Biol175864200710.1016/j.tcb.2006.11.00917161947
|
|
32.
|
E NikolovaV MitevN ZhelevCF DeroanneY
PoumayThe small Rho GTPase Rac1 controls normal human dermal
fibroblasts proliferation with phosphorylation of the oncoprotein
c-mycBiochem Biophys Res
Commun359834839200710.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.21417568564
|
|
33.
|
S JinRM RayLR JohnsonRac1 mediates
intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via JNKAm J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver
Physiol291G1137G1147200610.1152/ajpgi.00031.200616798728
|
|
34.
|
E RudolfM CervinkaTrivalent chromium
activates Rac-1 and Src and induces switch in the cell death mode
in human dermal fibroblastsToxicol
Lett188236242200910.1016/j.toxlet.2009.04.01919406221
|
|
35.
|
YW EomMH YooCH WooImplication of the small
GTPase Rac1 in the apoptosis induced by UV in Rat-2
fibroblastsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun285825829200110.1006/bbrc.2001.523311453667
|
|
36.
|
Y DevaryRA GottliebT SmealM KarinThe
mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src
tyrosine
kinasesCell7110811091199210.1016/S0092-8674(05)80058-31473146
|
|
37.
|
MT RamirezVP SahXL ZhaoJJ HunterKR ChienJH
BrownThe MEKK-JNK pathway is stimulated by alpha1-adrenergic
receptor and ras activation and is associated with in vitro and in
vivo cardiac hypertrophyJ Biol
Chem2721405714061199710.1074/jbc.272.22.140579162028
|
|
38.
|
I SanchezRT HughesBJ MayerRole of SAPK/ERK
kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription
factor c-JunNature372794798199410.1038/372794a07997269
|
|
39.
|
M YanT DaiJC DeakActivation of
stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its
activator SEK1Nature372798800199410.1038/372798a07997270
|
|
40.
|
N ChouinardK ValerieM RouabhiaJ
HuotUVB-mediated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
enhances resistance of normal human keratinocytes to apoptosis by
stabilizing cytoplasmic p53Biochem
J365133145200210.1042/BJ2002007212071847
|
|
41.
|
J HildesheimRT AwwadAJ Fornace Jrp38
Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor protects the epidermis
against the acute damaging effects of ultraviolet irradiation by
blocking apoptosis and inflammatory responsesJ Invest
Dermatol122497502200410.1111/j.1523-1747.2004.22229.x
|
|
42.
|
YR ChenX WangD TempletonRJ DavisTH TanThe
role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in apoptosis induced by
ultraviolet C and gamma radiation. Duration of JNK activation may
determine cell death and proliferationJ Biol
Chem2713192931936199610.1074/jbc.271.50.319298943238
|
|
43.
|
R WisdomRS JohnsonC Moorec-Jun regulates
cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct mechanismsEMBO
J18188197199910.1093/emboj/18.1.1889878062
|
|
44.
|
YY HeJL HuangCF ChignellDelayed and
sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in
human keratinocytes by UVA: implications in carcinogenesisJ Biol
Chem2795386753874200410.1074/jbc.M40578120015471881
|
|
45.
|
JW ChoK ParkGR KweonCurcumin inhibits the
expression of COX-2 in UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes (HaCaT)
by inhibiting activation of AP-1: p38 MAP kinase and JNK as
potential upstream targetsExp Mol
Med37186192200510.1038/emm.2005.2516000872
|
|
46.
|
AL KimJM LabasiY ZhuRole of p38 MAPK in
UVB-induced inflammatory responses in the skin of SKH-1 hairless
miceJ Invest
Dermatol12413181325200510.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23747.x15955110
|