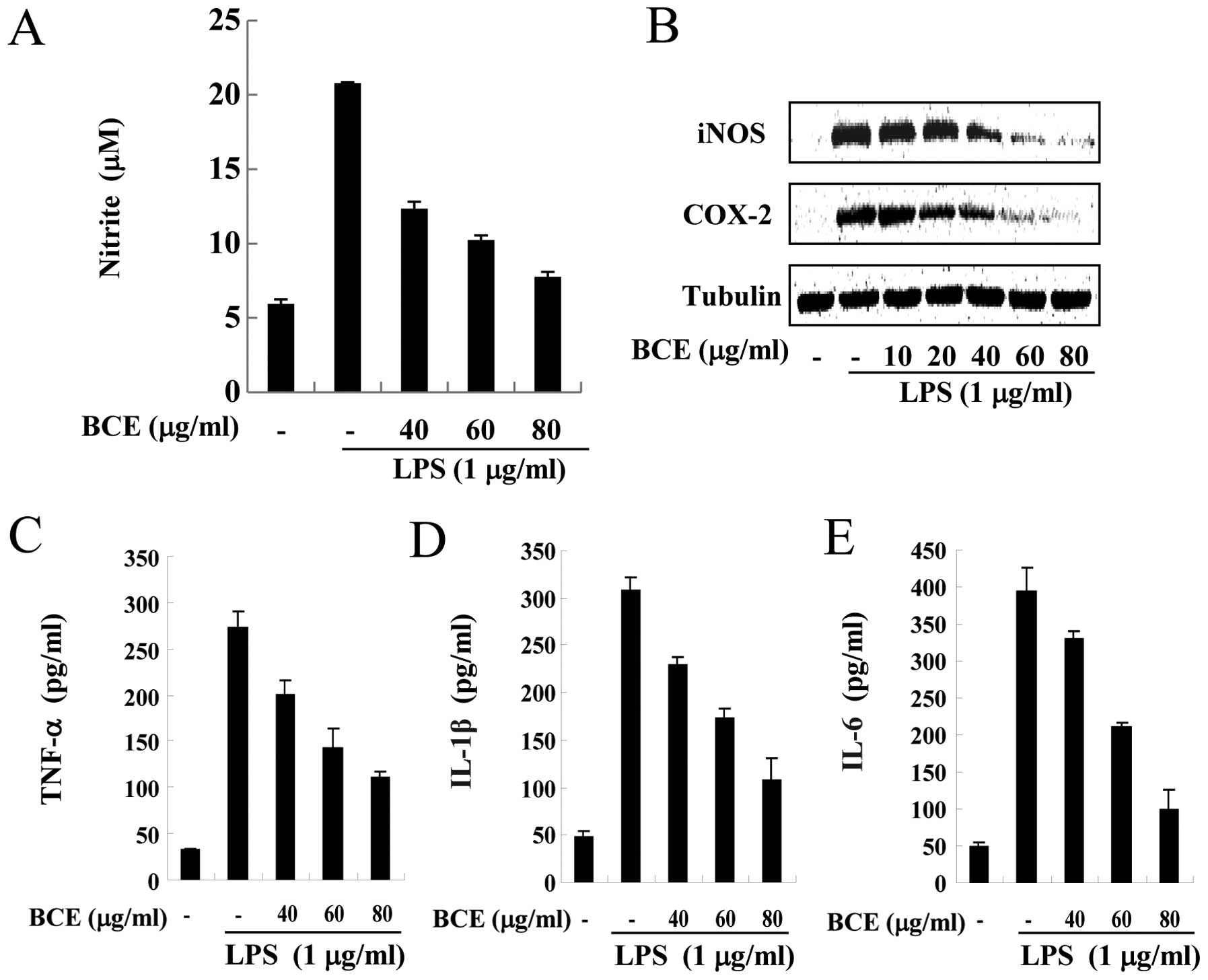
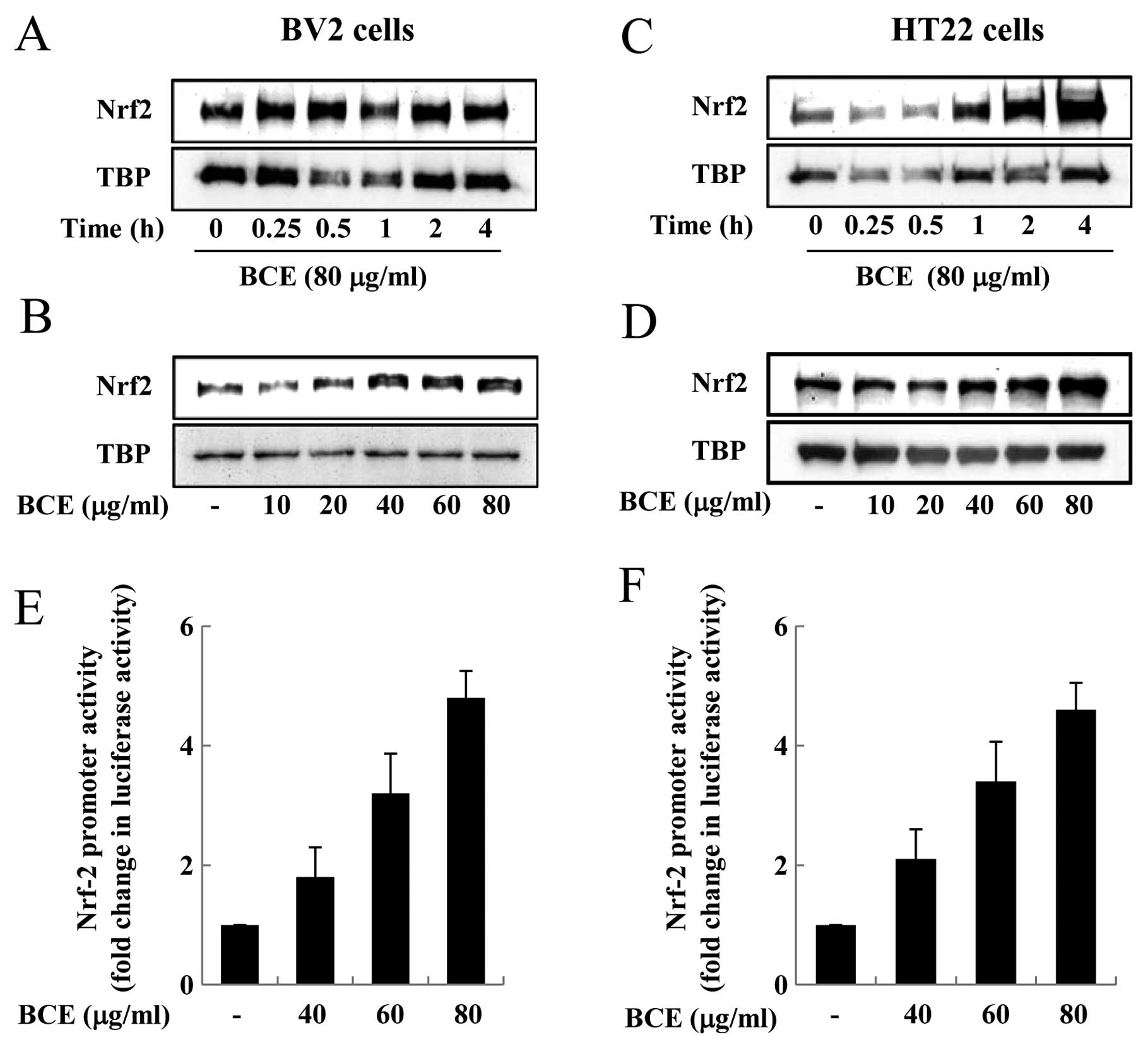
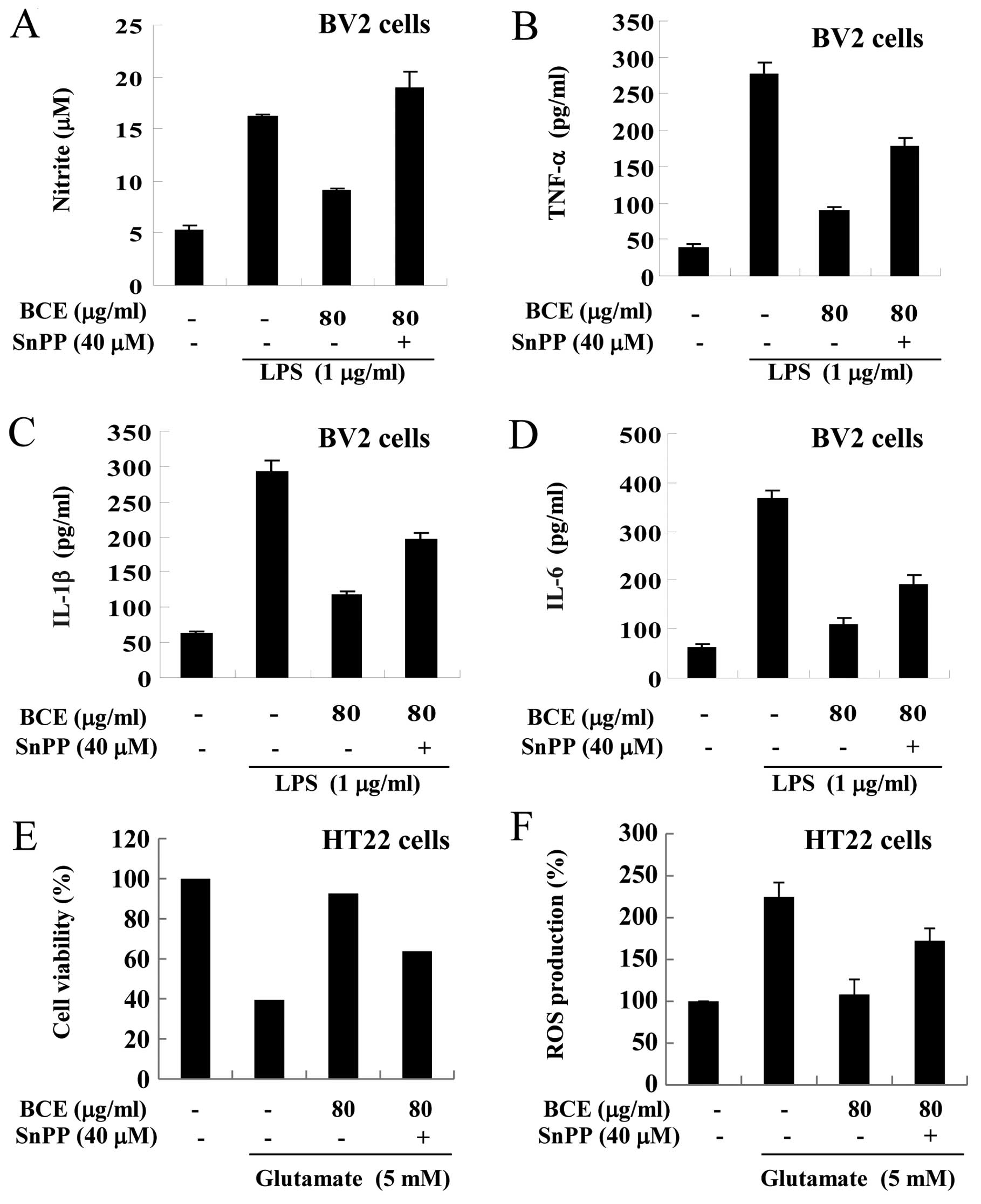
Spandidos Publications style
Eom HW, Park SY, Kim YH, Seong SJ, Jin ML, Ryu EY, Kim MJ and Lee SJ: Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam modulates neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in hippocampal and microglial cells via HO-1- and Nrf-2-mediated pathways. Int J Mol Med 30: 1512-1520, 2012.
APA
Eom, H.W., Park, S.Y., Kim, Y.H., Seong, S.J., Jin, M.L., Ryu, E.Y. ... Lee, S.J. (2012). Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam modulates neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in hippocampal and microglial cells via HO-1- and Nrf-2-mediated pathways. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 30, 1512-1520. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1128
MLA
Eom, H. W., Park, S. Y., Kim, Y. H., Seong, S. J., Jin, M. L., Ryu, E. Y., Kim, M. J., Lee, S. J."Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam modulates neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in hippocampal and microglial cells via HO-1- and Nrf-2-mediated pathways". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30.6 (2012): 1512-1520.
Chicago
Eom, H. W., Park, S. Y., Kim, Y. H., Seong, S. J., Jin, M. L., Ryu, E. Y., Kim, M. J., Lee, S. J."Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam modulates neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in hippocampal and microglial cells via HO-1- and Nrf-2-mediated pathways". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 30, no. 6 (2012): 1512-1520. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1128