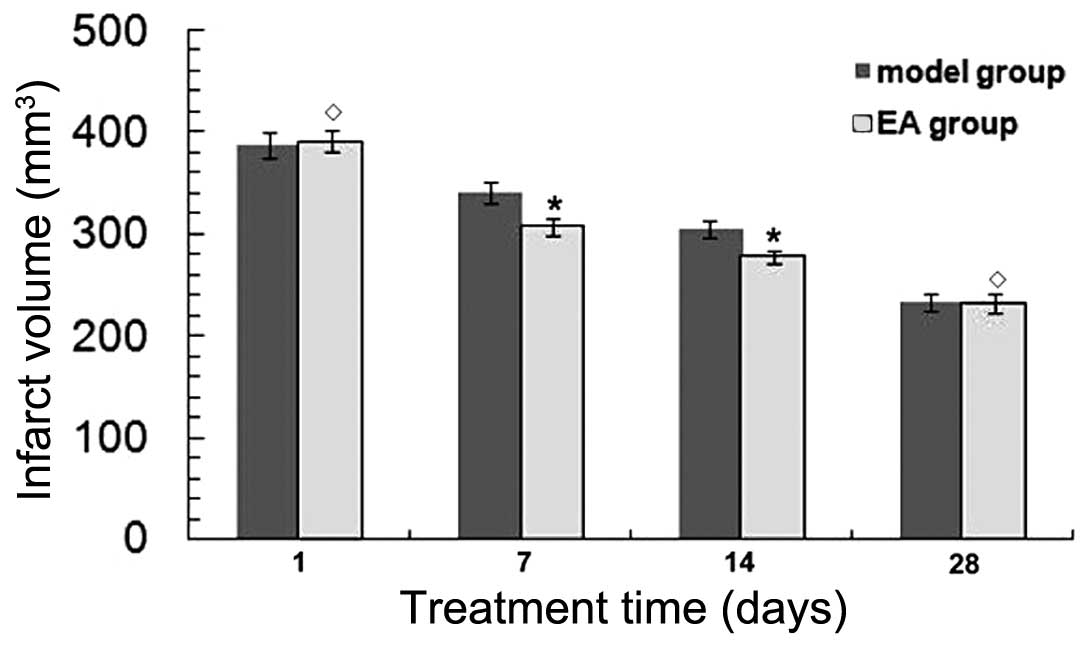
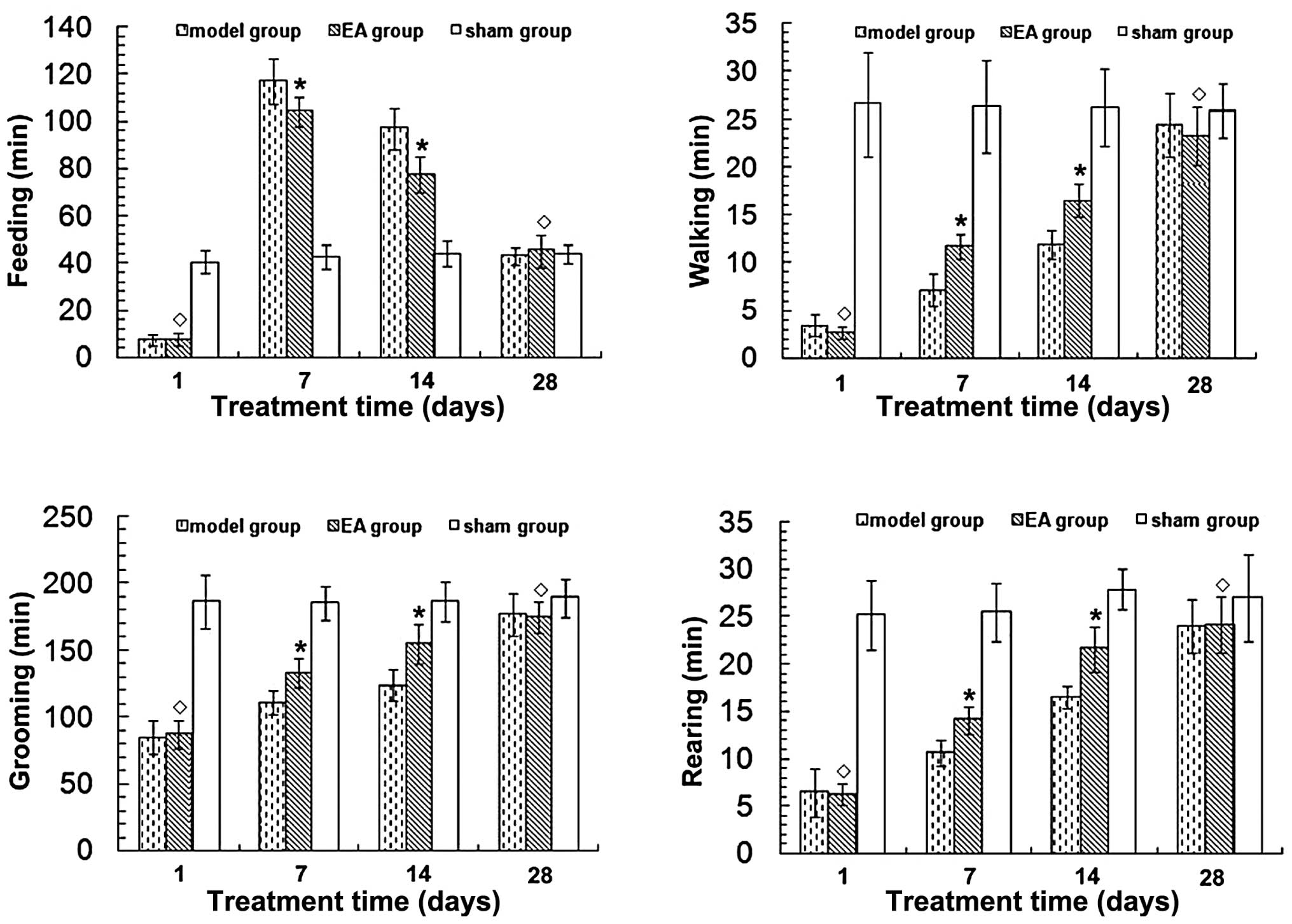
|
1
|
Lo EH, Dalkara T and Moskowitz MA:
Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 4:399–415. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Madden K: Optimal timing of thrombolytic
therapy in acute ischaemic stroke. CNS Drugs. 16:213–218. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Willaime-Morawek S and van der Kooy D:
Cortex- and striatum-derived neural stem cells produce distinct
progeny in the olfactory bulb and striatum. Eur J Neurosci.
27:2354–2362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakagomi T, Taguchi A, Fujimori Y, Saino
O, Nakano-Doi A, Kubo S, Gotoh A, Soma T, Yoshikawa H, Nishizaki T,
Nakagomi N, Stern DM and Matsuyama T: Isolation and
characterization of neural stem/progenitor cells from post-stroke
cerebral cortex in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 29:1842–1852. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jin K, Wang X, Xie L, Mao XO, Zhu W, Wang
Y, Shen J, Mao Y, Banwait S and Greenberg DA: Evidence for
stroke-induced neurogenesis in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:13198–13202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macas J, Nern C, Plate KH and Momma S:
Increased generation of neuronal progenitors after ischemic injury
in the aged adult human forebrain. J Neurosci. 26:13114–13119.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Minger SL, Ekonomou A, Carta EM, Chinoy A,
Perry RH and Ballard CG: Endogenous neurogenesis in the human brain
following cerebral infarction. Regen Med. 2:69–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Landgren H and Curtis MA: Locating and
labeling neural stem cells in the brain. J Cell Physiol. 226:1–7.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hodge RD and Hevner RF: Expression and
actions of transcription factors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
Dev Neurobiol. 71:680–689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ross SA, McCaffery PJ, Drager UC and De
Luca LM: Retinoids in embryonal development. Physiol Rev.
80:1021–1054. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCaffery P, Zhang J and Crandall JE:
Retinoic acid signaling and function in the adult hippocampus. J
Neurobiol. 66:780–791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Werner EA and Deluca HF: Retinoic acid is
detected at relatively high levels in the CNS of adult rats. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 282:E672–E678. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calza L, Giuliani A, Fernandez M, Pirondi
S, D’Intino G, Aloe L and Giardino L: Neural stem cells and
cholinergic neurons: regulation by immunolesion and treatment with
mitogens, retinoic acid, and nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:7325–7330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haskell GT and LaMantia AS: Retinoic acid
signaling identifies a distinct precursor population in the
developing and adult forebrain. J Neurosci. 25:7636–7647. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang TW, Zhang H and Parent JM: Retinoic
acid regulates postnatal neurogenesis in the murine subventricular
zone-olfactory bulb pathway. Development. 132:2721–2732. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jacobs S, Lie DC, DeCicco KL, Shi Y,
DeLuca LM, Gage FH and Evans RM: Retinoic acid is required early
during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:3902–3907. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mey J and McCaffery P: Retinoic acid
signaling in the nervous system of adult vertebrates.
Neuroscientist. 10:409–421. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Plane JM, Whitney JT, Schallert T and
Parent JM: Retinoic acid and environmental enrichment alter
subventricular zone and striatal neurogenesis after stroke. Exp
Neurol. 214:125–134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ikeda R, Kurokawa MS, Chiba S, Yoshikawa
H, Ide M, Tadokoro M, Nito S, Nakatsuji N, Kondoh Y, Nagata K,
Hashimoto T and Suzuki N: Transplantation of neural cells derived
from retinoic acid-treated cynomolgus monkey embryonic stem cells
successfully improved motor function of hemiplegic mice with
experimental brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 20:38–48. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim EH, Jang MH, Shin MC, Lim BV, Kim HB,
Kim YJ, Chung JH and Kim CJ: Acupuncture increases cell
proliferation and neuropeptide Y expression in dentate gyrus of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett. 327:33–36.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim EH, Kim YJ, Lee HJ, Huh Y, Chung JH,
Seo JC, Kang JE, Lee HJ, Yim SV and Kim CJ: Acupuncture increases
cell proliferation in dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia
in gerbils. Neurosci Lett. 297:21–24. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu Q, Yu J, Mi WL, Mao-Ying QL, Yang R,
Wang YQ and Wu GC: Electroacupuncture attenuates the decrease of
hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rats exposed
to chronic unpredictable stress. Life Sci. 81:1489–1495. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng H, Yu J, Jiang Z, Zhang X, Liu C,
Peng Y, Chen F, Qu Y, Jia Y, Tian Q, Xiao C, Chu Q, Nie K, Kan B,
Hu X and Han J: Acupuncture improves cognitive deficits and
regulates the brain cell proliferation of SAMP8 mice. Neurosci
Lett. 432:111–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Naylor AS, Bull C, Nilsson MK, Zhu C,
Bjork-Eriksson T, Eriksson PS, Blomgren K and Kuhn HG: Voluntary
running rescues adult hippocampal neurogenesis after irradiation of
the young mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:14632–14637.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yun SJ, Park HJ, Yeom MJ, Hahm DH, Lee HJ
and Lee EH: Effect of electroacupuncture on the stress-induced
changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rat
hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 318:85–88. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao J, Wang S, Wang X and Zhu C:
Electroacupuncture enhances cell proliferation and neuronal
differentiation in young rat brains. Neurol Sci. 32:369–374. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang MH, Shin MC, Lee TH, Lim BV, Shin MS,
Min BI, Kim H, Cho S, Kim EH and Kim CJ: Acupuncture suppresses
ischemia-induced increase in c-Fos expression and apoptosis in the
hippocampal CA1 region in gerbils. Neurosci Lett. 347:5–8. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
The Ministry of Science and Technology of
the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care
and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006 09 30
|
|
29
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z
and Lindvall O: Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in
the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 8:963–970. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goings GE, Sahni V and Szele FG: Migration
patterns of subventricular zone cells in adult mice change after
cerebral cortex injury. Brain Res. 996:213–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lichtenwalner RJ and Parent JM: Adult
neurogenesis and the ischemic forebrain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
26:1–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Parent JM, Valentin VV and Lowenstein DH:
Prolonged seizures increase proliferating neuroblasts in the adult
rat subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway. J Neurosci.
22:3174–3188. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N
and Ferriero DM: Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron
replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol. 52:802–813. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind
DH, Sloviter RS and Lowenstein DH: Dentate granule cell
neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant
network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci.
17:3727–3738. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L and Chopp M:
Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex
and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral
ischemia. Neuroscience. 105:33–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liden M and Eriksson U: Understanding
retinol metabolism: structure and function of retinol
dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 281:13001–13004. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Chiang YH, Su TP, Hayashi T,
Morales M, Hoffer BJ and Lin SZ: Vitamin D(3) attenuates cortical
infarction induced by middle cerebral arterial ligation in rats.
Neuropharmacology. 39:873–880. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Doyle KP, Suchland KL, Ciesielski TM,
Lessov NS, Grandy DK, Scanlan TS and Stenzel-Poore MP: Novel
thyroxine derivatives, thyronamine and 3-iodothyronamine, induce
transient hypothermia and marked neuroprotection against stroke
injury. Stroke. 38:2569–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sato Y, Meller R, Yang T, Taki W and Simon
RP: Stereo-selective neuroprotection against stroke with vitamin A
derivatives. Brain Res. 1241:188–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Harvey BK, Shen H, Chen GJ, Yoshida Y and
Wang Y: Midkine and retinoic acid reduce cerebral infarction
induced by middle cerebral artery ligation in rats. Neurosci Lett.
369:138–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
McCaffery P and Drager UC: Regulation of
retinoic acid signaling in the embryonic nervous system: a master
differentiation factor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:233–249.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Steele AD, Jackson WS, King OD and
Lindquist S: The power of automated high-resolution behavior
analysis revealed by its application to mouse models of
Huntington’s and prion diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:1983–1988. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Otero L, Zurita M, Aguayo C, Bonilla C,
Rodríguez A and Vaquero J: Video-Tracking-Box linked to Smart
software as a tool for evaluation of locomotor activity and
orientation in brain injured rats. J Neurosci Methods. 188:53–57.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Roedel A, Storch C, Holsboer F and Ohl F:
Effects of light or dark phase testing on behavioural and cognitive
performance in DBA mice. Lab Anim. 40:371–381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Spruijt BM and DeVisser L: Advanced
behavioural screening: automated home cage ethology. Drug Discov
Today Technol. 3:231–237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen L, Zhang X, Chen-Roetling J and Regan
RF: Increased striatal injury and behavioral deficits after
intracerebral hemorrhage in hemopexin knockout mice. J Neurosurg.
114:1159–1167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Stichel CC and Muller HW: Experimental
strategies to promote axonal regeneration after traumatic central
nervous system injury. Prog Neurobiol. 56:119–148. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gao P, Shen F, Gabriel RA, Law D, Yang E,
Yang GY, Young WL and SU H: Attenuation of brain response to
vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis and
neurogenesis in aged mice. Stroke. 40:3596–3600. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Leasure JL and Grider M: The effect of
mild post-stroke exercise on reactive neurogenesis and recovery of
somatosensation in aged rats. Exp Neurol. 226:58–67. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|