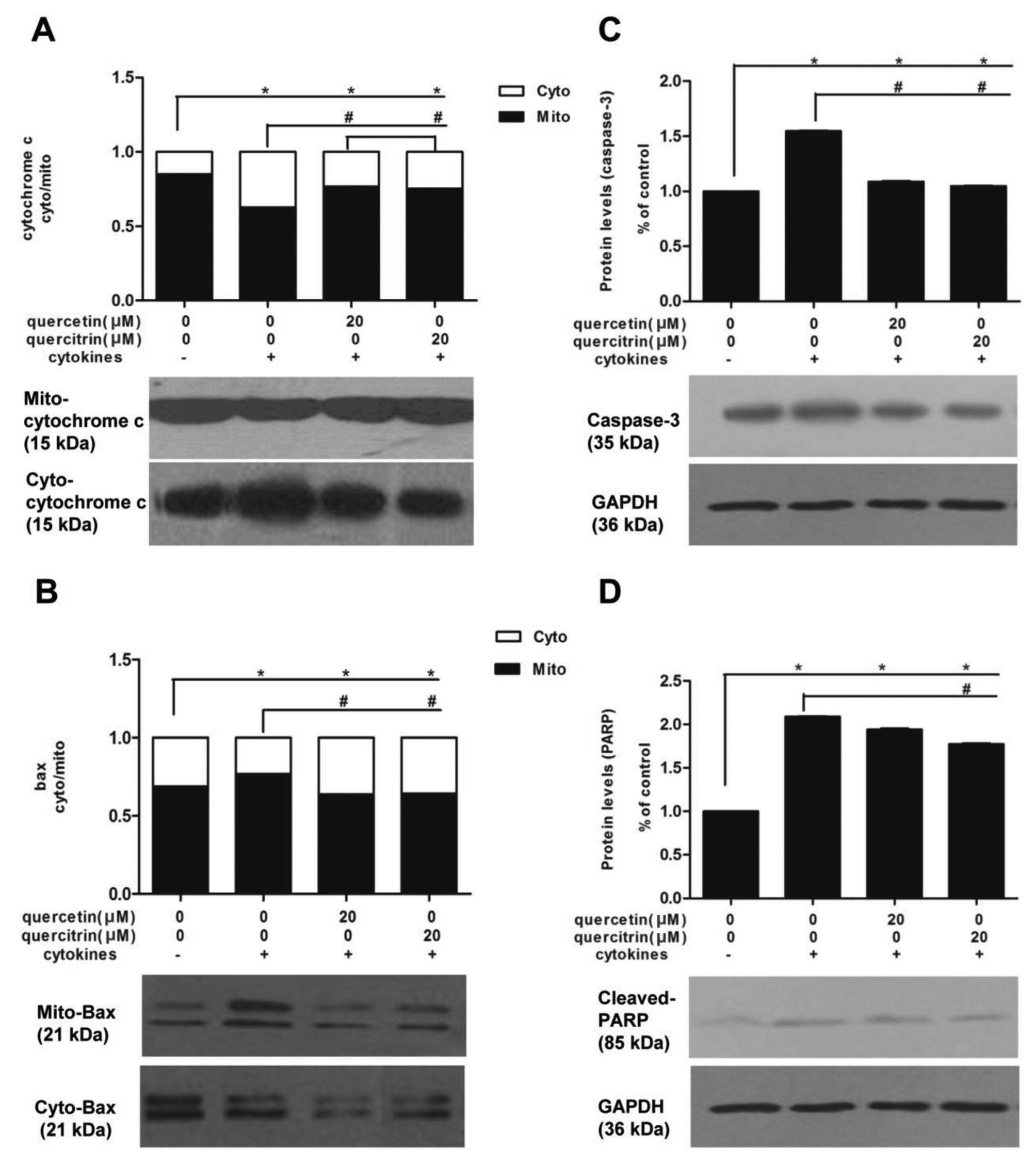
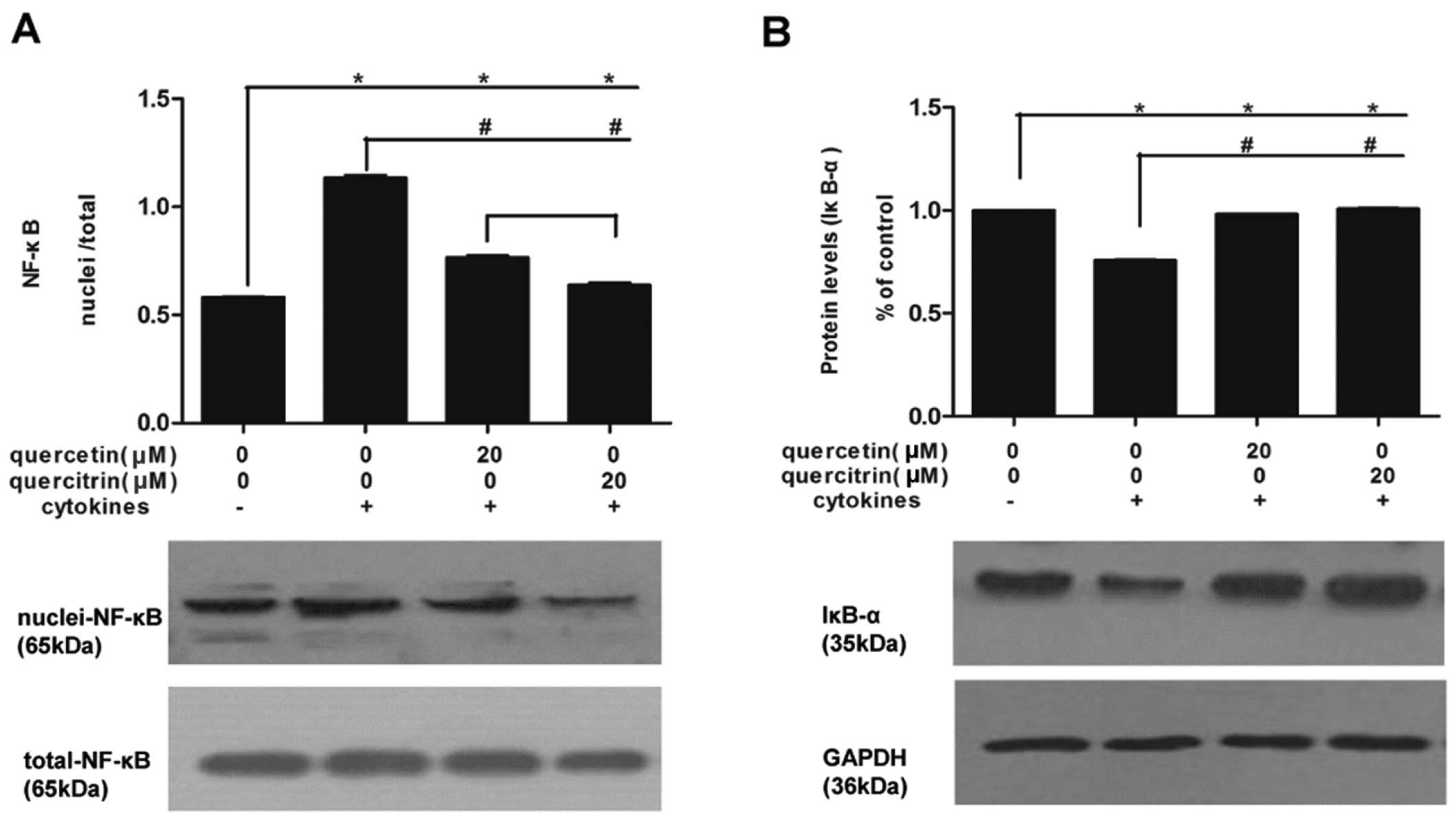
|
1
|
Wagner C, Vargas AP, Roos DH, et al:
Comparative study of quercetin and its two glycoside derivatives
quercitrin and rutin against methylmercury (MeHg)-induced ROS
production in rat brain slices. Arch Toxicol. 84:89–97. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan
MB and Kromhout D: Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of
coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet.
342:1007–1011. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babujanarthanam R, Kavitha P, Mahadeva Rao
US and Pandian MR: Quercitrin a bioflavonoid improves the
antioxidant status in streptozotocin: induced diabetic rat tissues.
Mol Cell Biochem. 358:121–129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coskun O, Kanter M, Korkmaz A and Oter S:
Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects
streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat
pancreas. Pharmacol Res. 51:117–123. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mathis D, Vence L and Benoist C: beta-Cell
death during progression to diabetes. Nature. 414:792–798. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mandrup-Poulsen T: Apoptotic signal
transduction pathways in diabetes. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1433–1440.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saldeen J: Cytokines induce both necrosis
and apoptosis via a common Bcl-2-inhibitable pathway in rat
insulin-producing cells. Endocrinology. 141:2003–2010.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cnop M, Welsh N, Jonas JC, Jorns A, Lenzen
S and Eizirik DL: Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type
1 and type 2 diabetes: many differences, few similarities.
Diabetes. 54(Suppl 2): S97–S107. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsujimoto Y: Cell death regulation by the
Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J Cell Physiol.
195:158–167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Menegazzi M, Novelli M, Beffy P, et al:
Protective effects of St. John’s wort extract and its component
hyperforin against cytokine-induced cytotoxicity in a pancreatic
beta-cell line. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1509–1521. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Adewole SO, Caxton-Martins EA and Ojewole
JA: Protective effect of quercetin on the morphology of pancreatic
beta-cells of streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Afr J Tradit
Complement Altern Med. 4:64–74. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Youl E, Bardy G, Magous R, et al:
Quercetin potentiates insulin secretion and protects INS-1
pancreatic beta-cells against oxidative damage via the ERK1/2
pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 161:799–814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cho JM, Chang SY, Kim DB, Needs PW, Jo YH
and Kim MJ: Effects of physiological quercetin metabolites on
interleukin-1beta-induced inducible NOS expression. J Nutr Biochem.
Jan 3–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
14
|
Babujanarthanam R, Kavitha P and Pandian
MR: Quercitrin, a bioflavonoid improves glucose homeostasis in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic tissues by altering glycolytic and
gluconeogenic enzymes. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 24:357–364. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hollman PC, de Vries JH, van Leeuwen SD,
Mengelers MJ and Katan MB: Absorption of dietary quercetin
glycosides and quercetin in healthy ileostomy volunteers. Am J Clin
Nutr. 62:1276–1282. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rattanajarasroj S and Unchern S:
Comparable attenuation of Abeta(25–35)-induced neurotoxicity by
quercitrin and 17beta-estradiol in cultured rat hippocampal
neurons. Neurochem Res. 35:1196–1205. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chow JM, Shen SC, Huan SK, Lin HY and Chen
YC: Quercetin, but not rutin and quercitrin, prevention of
H2O2-induced apoptosis via anti-oxidant
activity and heme oxygenase 1 gene expression in macrophages.
Biochem Pharmacol. 69:1839–1851. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y and
Kang YJ: Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium:
mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway.
Diabetes. 51:1938–1948. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Veluthakal R, Jangati GR and Kowluru A:
IL-1beta-induced iNOS expression, NO release and loss in metabolic
cell viability are resistant to inhibitors of ceramide synthase and
sphingomyelinase in INS 832/13 cells. JOP. 7:593–601.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Denis MC, Mahmood U, Benoist C, Mathis D
and Weissleder R: Imaging inflammation of the pancreatic islets in
type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:12634–12639. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Michalska M, Wolf G, Walther R and
Newsholme P: Effects of pharmacological inhibition of NADPH oxidase
or iNOS on pro-inflammatory cytokine, palmitic acid or
H2O2-induced mouse islet or clonal pancreatic
beta-cell dysfunction. Biosci Rep. 30:445–453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pi J, Bai Y, Zhang Q, et al: Reactive
oxygen species as a signal in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
Diabetes. 56:1783–1791. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cumaoglu A, Ari N, Kartal M and Karasu C:
Polyphenolic extracts from Olea europea L. protect against
cytokine-induced beta-cell damage through maintenance of redox
homeostasis. Rejuvenation Res. 14:325–334. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Burkle A: Physiology and pathophysiology
of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Bioessays. 23:795–806. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Allagnat F, Cunha D, Moore F, Vanderwinden
JM, Eizirik DL and Cardozo AK: Mcl-1 downregulation by
pro-inflammatory cytokines and palmitate is an early event
contributing to beta-cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 18:328–337.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barbu A, Welsh N and Saldeen J:
Cytokine-induced apoptosis and necrosis are preceded by disruption
of the mitochondrial membrane potential (Deltapsi(m)) in pancreatic
RINm5F cells: prevention by Bcl-2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 190:75–82.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mehmeti I, Lenzen S and Lortz S:
Modulation of Bcl-2-related protein expression in pancreatic beta
cells by pro-inflammatory cytokines and its dependence on the
antioxidative defense status. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 332:88–96. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, et al:
Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of
apoptosis. Science. 311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Muranyi M, Fujioka M, He Q, et al:
Diabetes activates cell death pathway after transient focal
cerebral ischemia. Diabetes. 52:481–486. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Virag L, Marmer DJ and Szabo C: Crucial
role of apopain in the peroxynitrite-induced apoptotic DNA
fragmentation. Free Radic Biol Med. 25:1075–1082. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roeske-Nielsen A, Dalgaard LT, Mansson JE
and Buschard K: The glycolipid sulfatide protects insulin-producing
cells against cytokine-induced apoptosis, a possible role in
diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 26:631–638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang ZJ, Cheang LC, Wang MW and Lee SM:
Quercetin exerts a neuroprotective effect through inhibition of the
iNOS/NO system and pro-inflammation gene expression in PC12 cells
and in zebrafish. Int J Mol Med. 27:195–203. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hirst DG and Robson T: Nitrosative stress
as a mediator of apoptosis: implications for cancer therapy. Curr
Pharm Des. 16:45–55. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Melloul D: Role of NF-kappaB in beta-cell
death. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:334–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109(Suppl): S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamaguchi M and Weitzmann MN: Quercetin, a
potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts. Int
J Mol Med. 28:521–525. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morand C, Manach C, Crespy V and Remesy C:
Quercetin 3-O-beta-glucoside is better absorbed than other
quercetin forms and is not present in rat plasma. Free Radic Res.
33:667–676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|