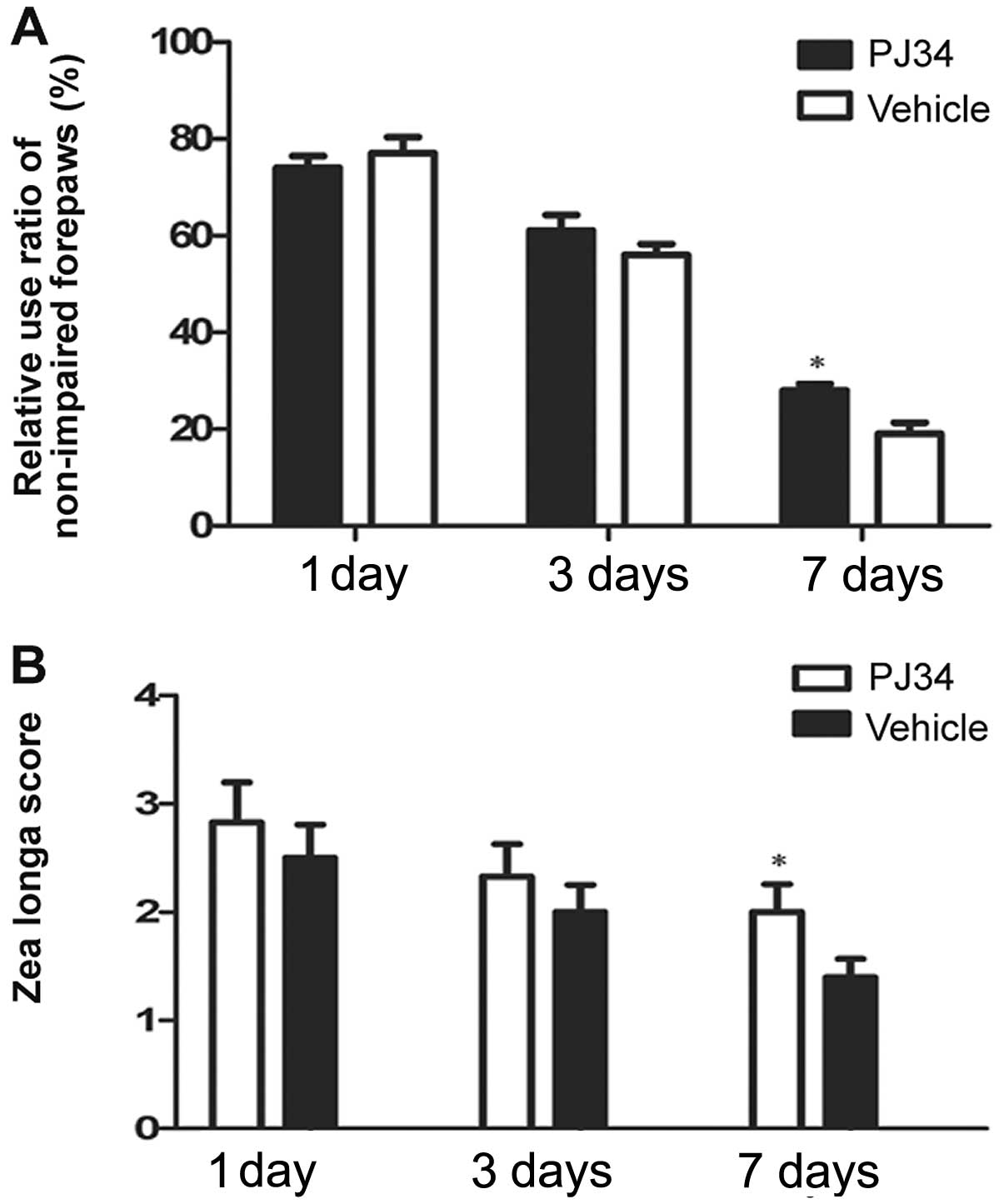
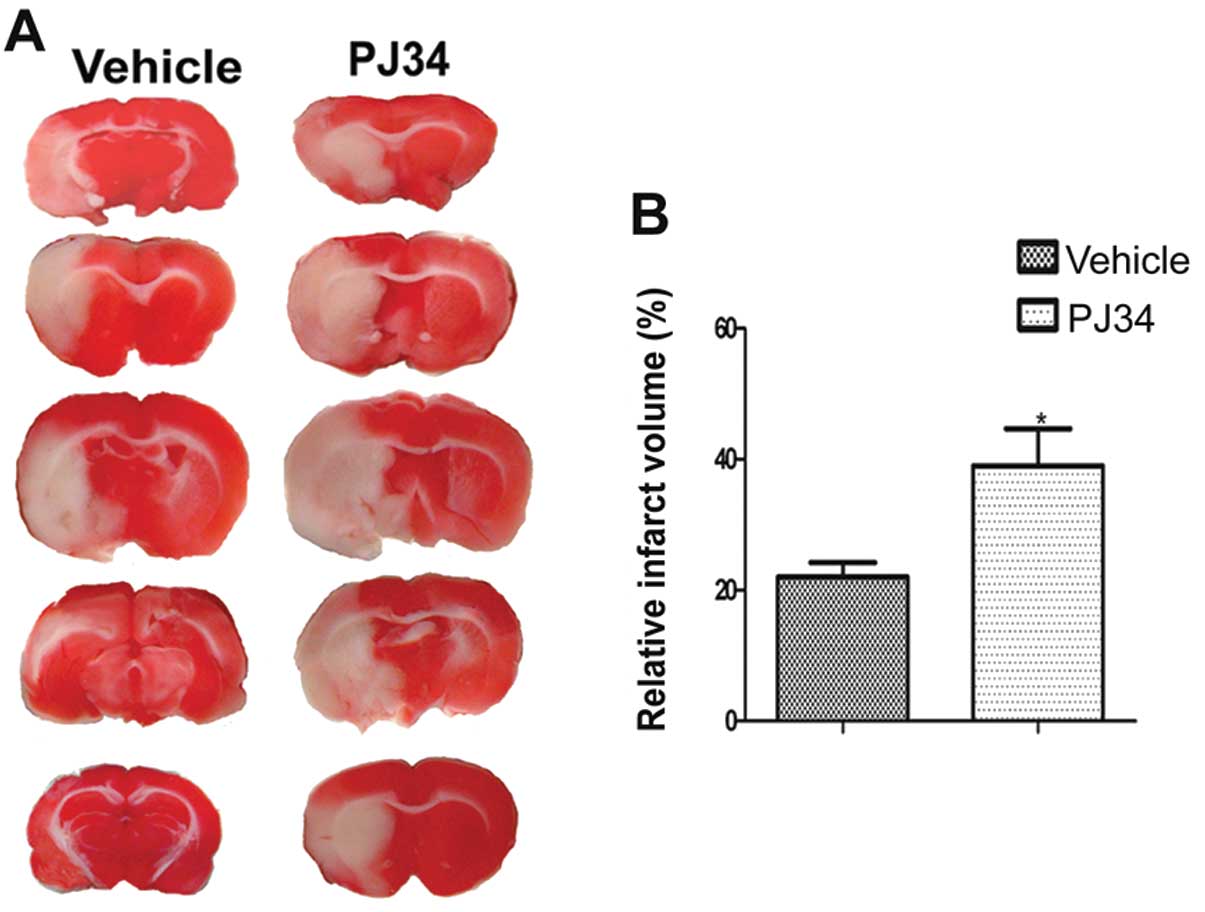
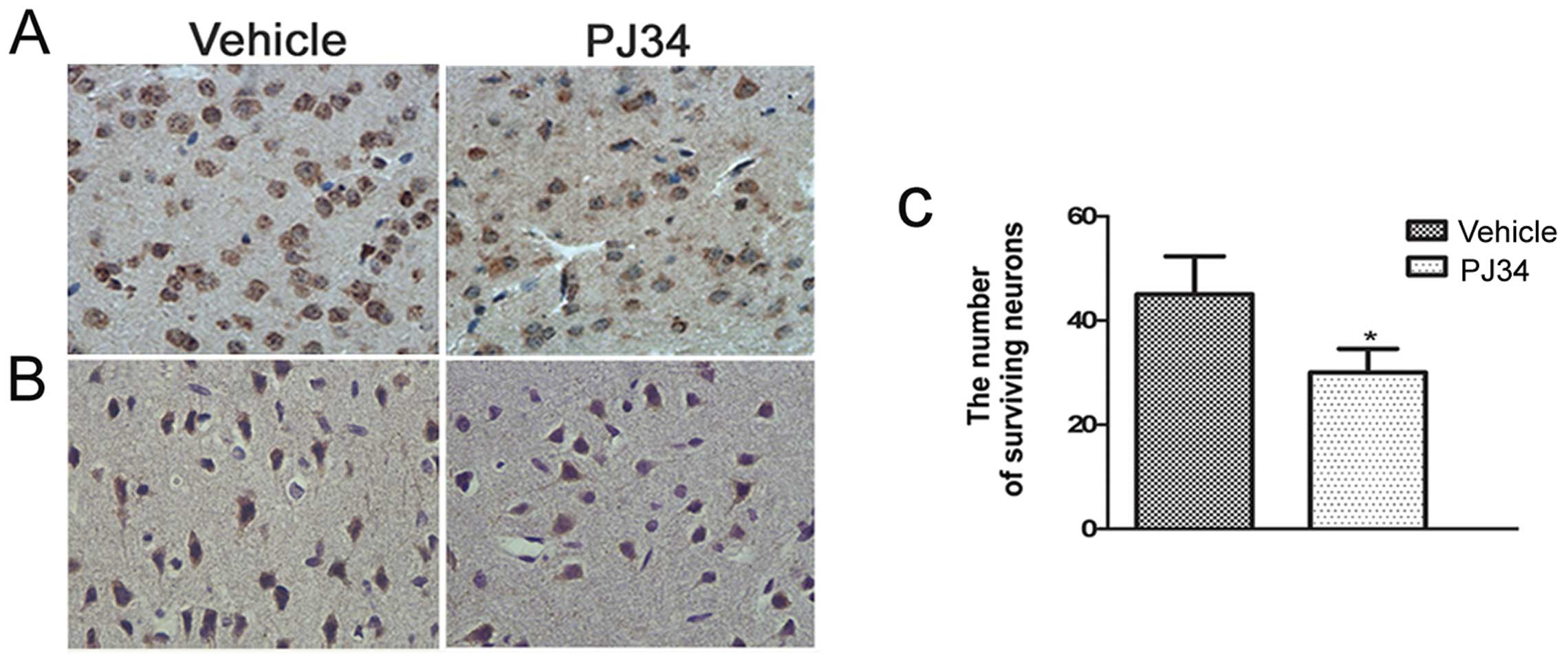
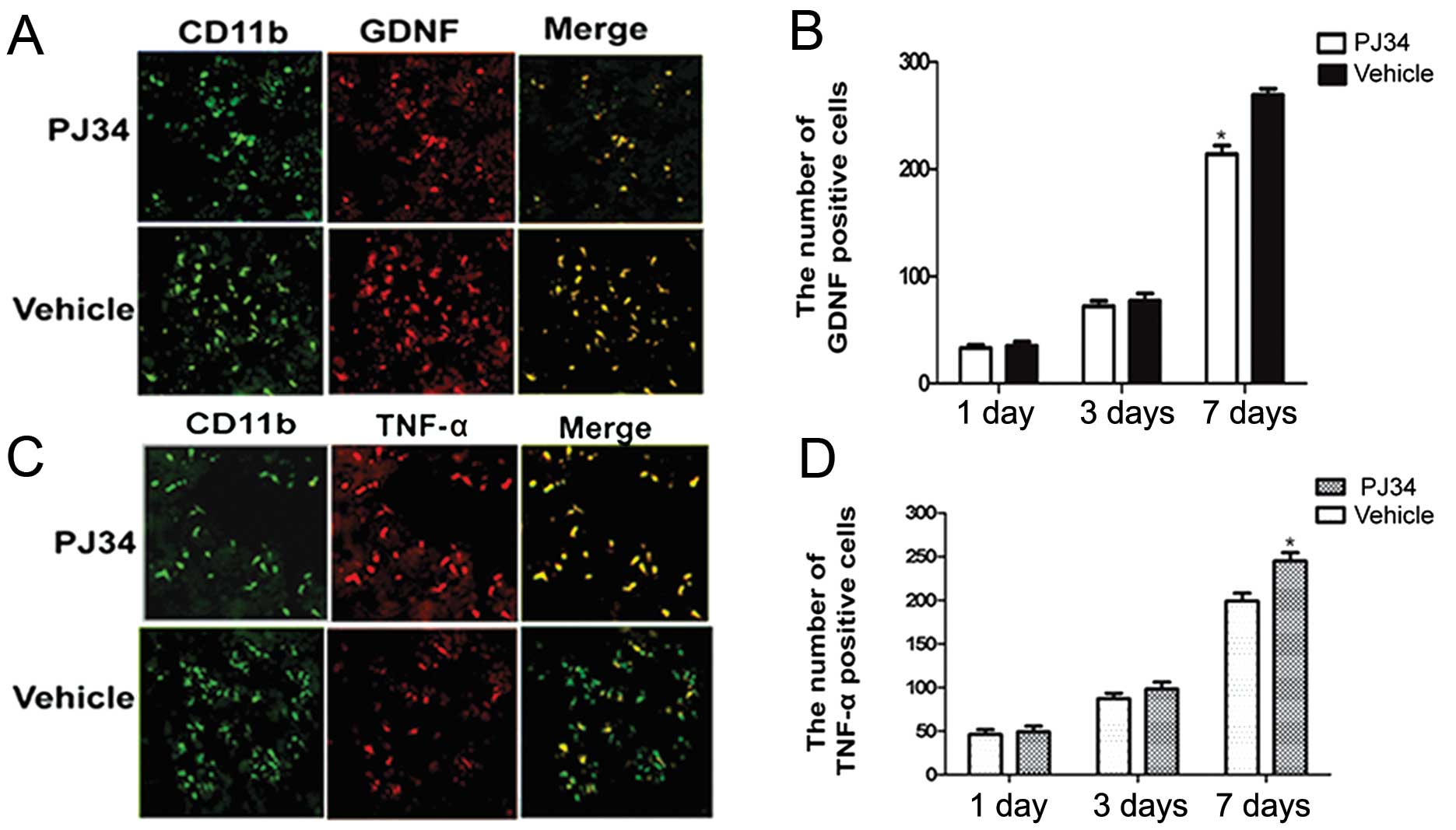
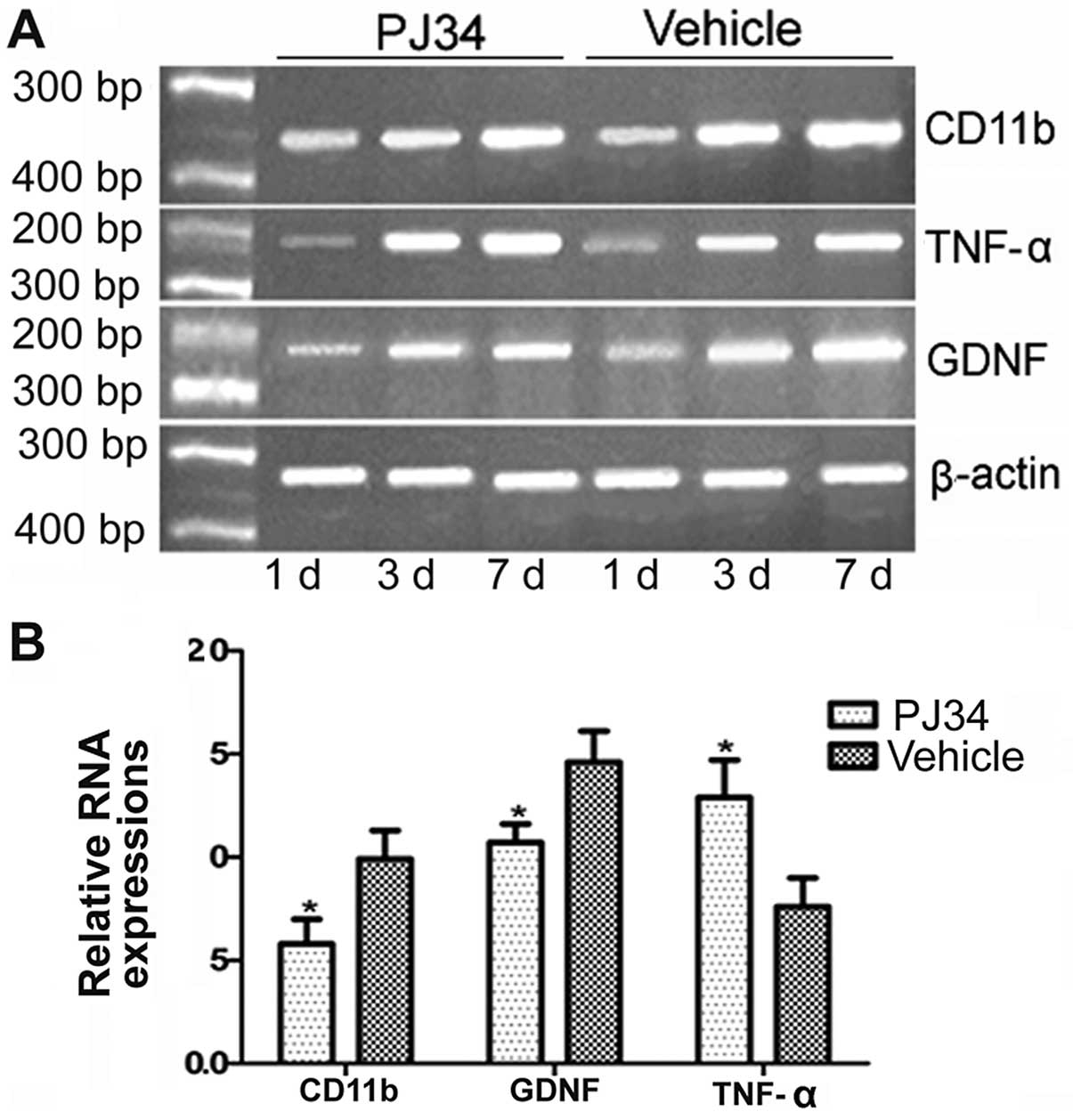
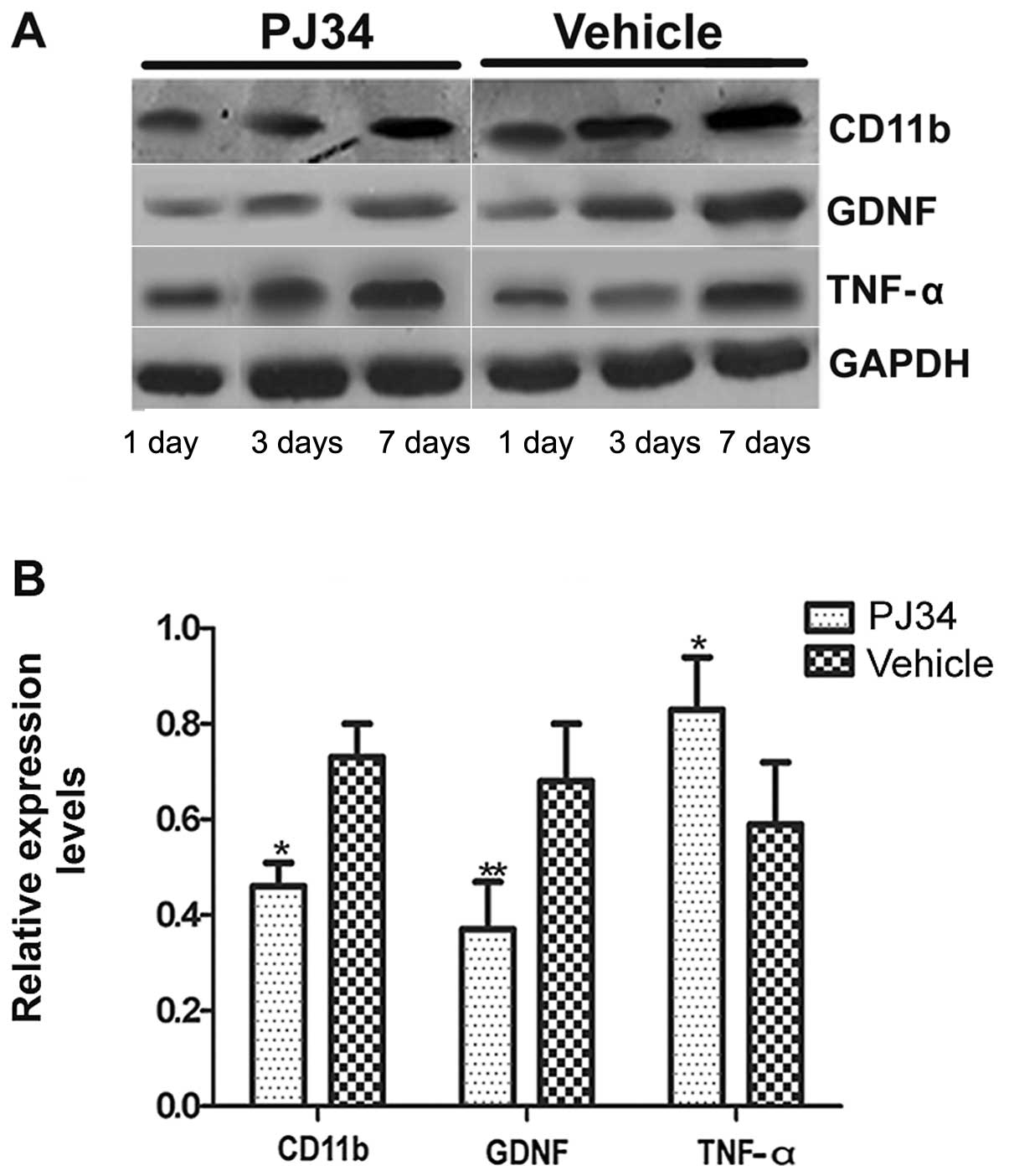
|
1
|
Lv M, Liu Y, Zhang J, et al: Roles of
inflammation response in microglia cell through Toll-like receptors
2/interleukin-23/interleukin-17 pathway in cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neuroscience. 176:162–172. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Block ML and Hong JS: Microglia and
inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a
common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol. 76:77–98. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu B, Du L and Hong JS: Naloxone protects
rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through
inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 293:607–617. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Napoli I and Neumann H: Protective effects
of microglia in multiple sclerosis. Exp Neurol. 225:24–28. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Petersen MA and Dailey ME: Diverse
microglial motility behaviors during clearance of dead cells in
hippocampal slices. Glia. 46:195–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lalancette-Hebert M, Gowing G, Simard A,
Weng YC and Kriz J: Selective ablation of proliferating microglial
cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. J Neurosci.
27:2596–2605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Figueiredo C, Pais TF, Gomes JR and
Chatterjee S: Neuron-microglia crosstalk up-regulates neuronal
FGF-2 expression which mediates neuroprotection against
excitotoxicity via JNK1/2. J Neurochem. 107:73–85. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamby AM, Suh SW, Kauppinen TM and Swanson
RA: Use of a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor to suppress
inflammation and neuronal death after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion. Stroke. 38:632–636. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xi GM, Wang HQ, He GH, Huang CF and Wei
GY: Evaluation of murine models of permanent focal cerebral
ischemia. Chin Med J (Engl). 117:389–394. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van der Kooij MA, Ohl F, Arndt SS,
Kavelaars A, van Bel F and Heijnen CJ: Mild neonatal
hypoxia-ischemia induces long-term motor- and cognitive impairments
in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 24:850–856. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brooks SP and Dunnett SB: Tests to assess
motor phenotype in mice: a user's guide. Nat Rev Neurosci.
10:519–529. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura
MC, Davis RL and Bartkowski H: Rat middle cerebral artery
occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic
examination. Stroke. 17:472–476. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
d'Avila JC, Lam TI, Bingham D, et al:
Microglial activation induced by brain trauma is suppressed by
post-injury treatment with a PARP inhibitor. J Neuroinflammation.
9:312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanisch UK and Kettenmann H: Microglia:
active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and
pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 10:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frank-Cannon TC, Alto LT, McAlpine FE and
Tansey MG: Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in
neurodegenerative diseases? Mol Neurodegener. 4:472009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Polazzi E and Monti B: Microglia and
neuroprotection: from in vitro studies to therapeutic applications.
Prog Neurobiol. 92:293–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaushal V and Schlichter LC: Mechanisms of
microglia-mediated neurotoxicity in a new model of the stroke
penumbra. J Neurosci. 28:2221–2230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hassa PO and Hottiger MO: The functional
role of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase 1 as novel coactivator of
NF-kappaB in inflammatory disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci.
59:1534–1553. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hassa PO, Buerki C, Lombardi C, Imhof R
and Hottiger MO: Transcriptional coactivation of nuclear
factor-kappaB-dependent gene expression by p300 is regulated by
poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase-1. J Biol Chem. 278:45145–45153. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kauppinen TM and Swanson RA:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 promotes microglial activation,
proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated neuron
death. J Immunol. 174:2288–2296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kauppinen TM, Higashi Y, Suh SW, Escartin
C, Nagasawa K and Swanson RA: Zinc triggers microglial activation.
J Neurosci. 28:5827–5835. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ullrich O, Diestel A, Eyupoglu IY and
Nitsch R: Regulation of microglial expression of integrins by
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1035–1042. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yrjanheikki J, Keinanen R, Pellikka M,
Hokfelt T and Koistinaho J: Tetracyclines inhibit microglial
activation and are neuroprotective in global brain ischemia. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:15769–15774. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fan R, Xu F, Previti ML, et al:
Minocycline reduces microglial activation and improves behavioral
deficits in a transgenic model of cerebral microvascular amyloid. J
Neurosci. 27:3057–3063. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mabley JG, Jagtap P, Perretti M, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of a novel, potent inhibitor of poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Inflamm Res. 50:561–569. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mabley JG, Horvath EM, Murthy KG, et al:
Gender differences in the endotoxin-induced inflammatory and
vascular responses: potential role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 315:812–820. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gash DM, Zhang Z, Ovadia A, et al:
Functional recovery in parkinsonian monkeys treated with GDNF.
Nature. 380:252–255. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li L, Wu W, Lin LF, Lei M, Oppenheim RW
and Houenou LJ: Rescue of adult mouse motoneurons from
injury-induced cell death by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic
factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9771–9775. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Lin SZ, Chiou AL, Williams LR and
Hoffer BJ: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor protects
against ischemia-induced injury in the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci.
17:4341–4348. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boscia F, Esposito CL, Di Crisci A, de
Franciscis V, Annunziato L and Cerchia L: GDNF selectively induces
microglial activation and neuronal survival in CA1/CA3 hippocampal
regions exposed to NMDA insult through Ret/ERK signalling. PLoS
One. 4:e64862009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hung SY, Liou HC and Fu WM: The mechanism
of heme oxygenase-1 action involved in the enhancement of
neurotrophic factor expression. Neuropharmacology. 58:321–329.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarit BS, Lajos G, Abraham D, Ron A and
Sigal FB: Inhibitory role of kinins on microglial nitric oxide and
tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Peptides. 35:172–181. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boucsein C, Zacharias R, Farber K,
Pavlovic S, Hanisch UK and Kettenmann H: Purinergic receptors on
microglial cells: functional expression in acute brain slices and
modulation of microglial activation in vitro. Eur J Neurosci.
17:2267–2276. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nodin C, Zhu C, Blomgren K, Nilsson M and
Blomstrand F: Decreased oxidative stress during glycolytic
inhibition enables maintenance of ATP production and astrocytic
survival. Neurochem Int. 61:291–301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee GA, Lin CH, Jiang HH, Chao HJ, Wu CL
and Hsueh CM: Microglia-derived glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor could protect Sprague-Dawley rat astrocyte from
in vitro ischemia-induced damage. Neurosci Lett. 356:111–114. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beers DR, Henkel JS, Zhao W, Wang J and
Appel SH: CD4+ T cells support glial neuroprotection,
slow disease progression, and modify glial morphology in an animal
model of inherited ALS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15558–15563.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|