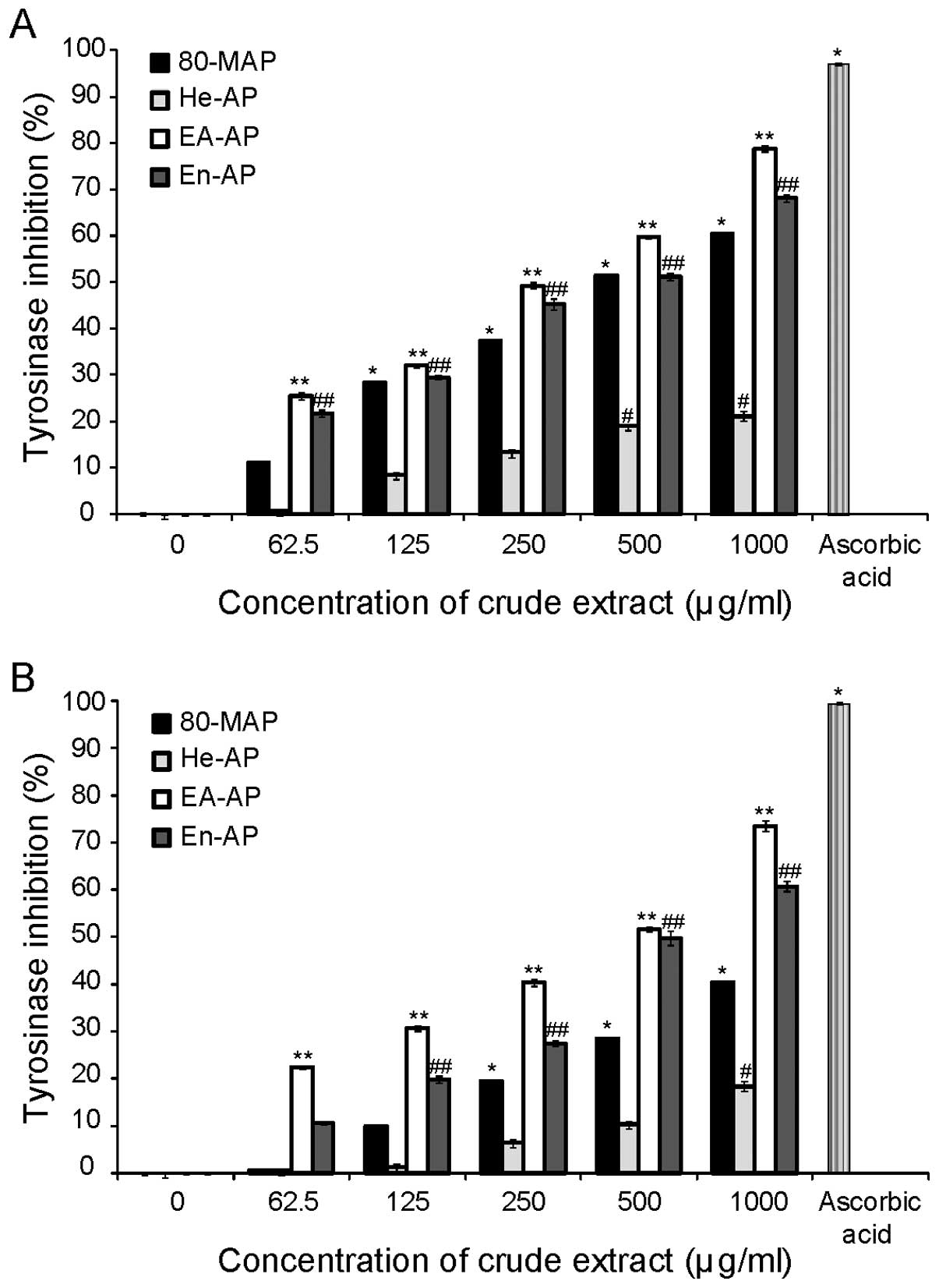
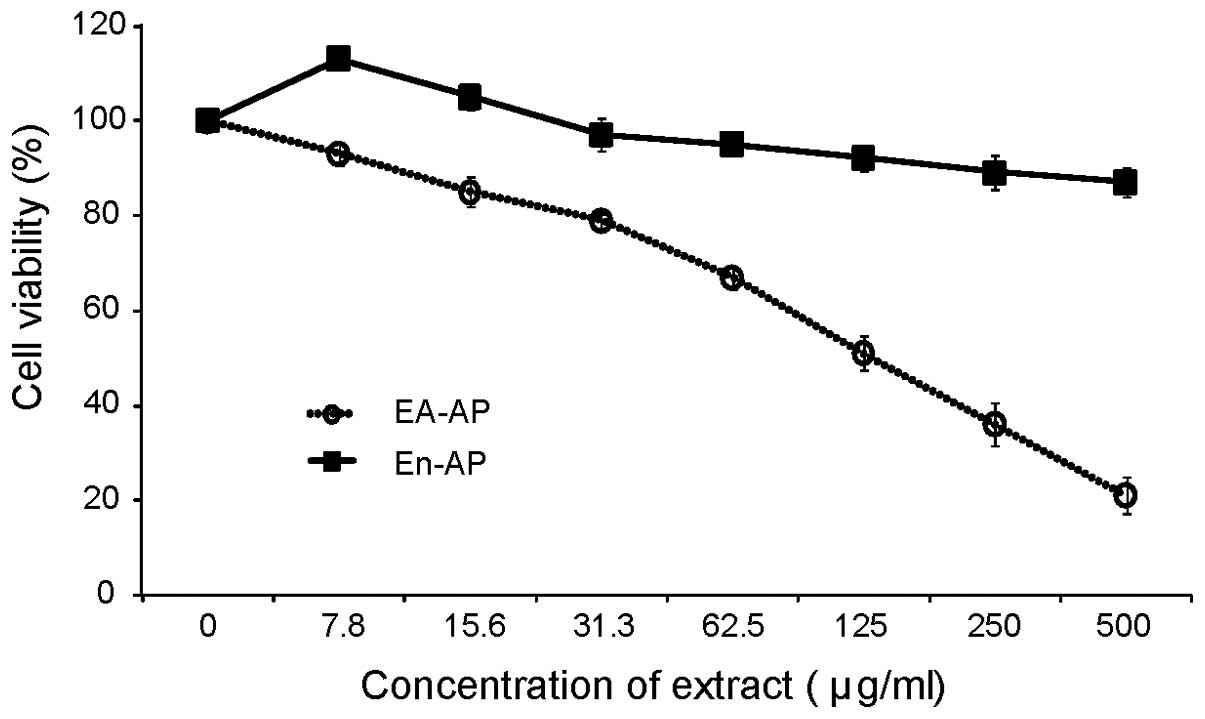
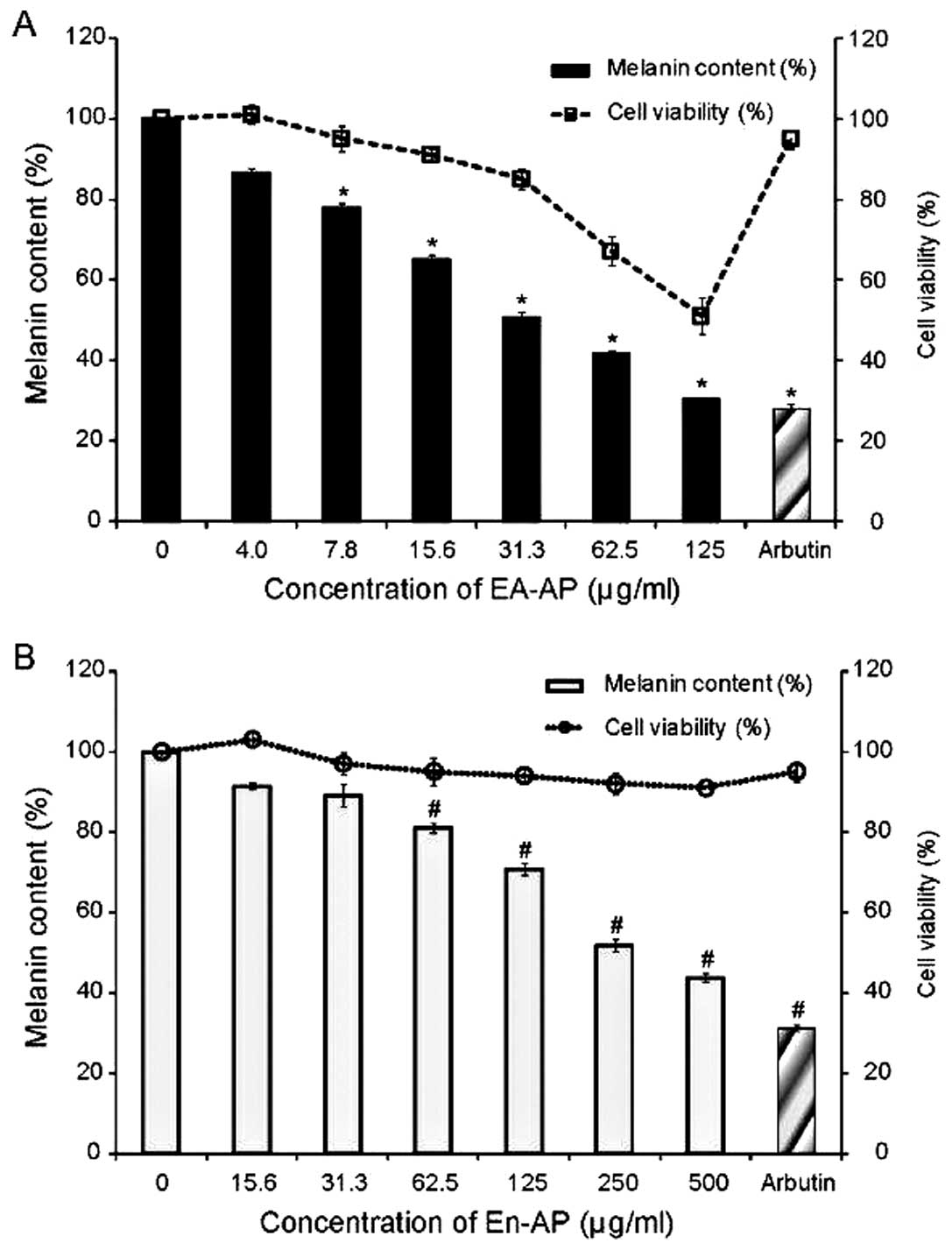
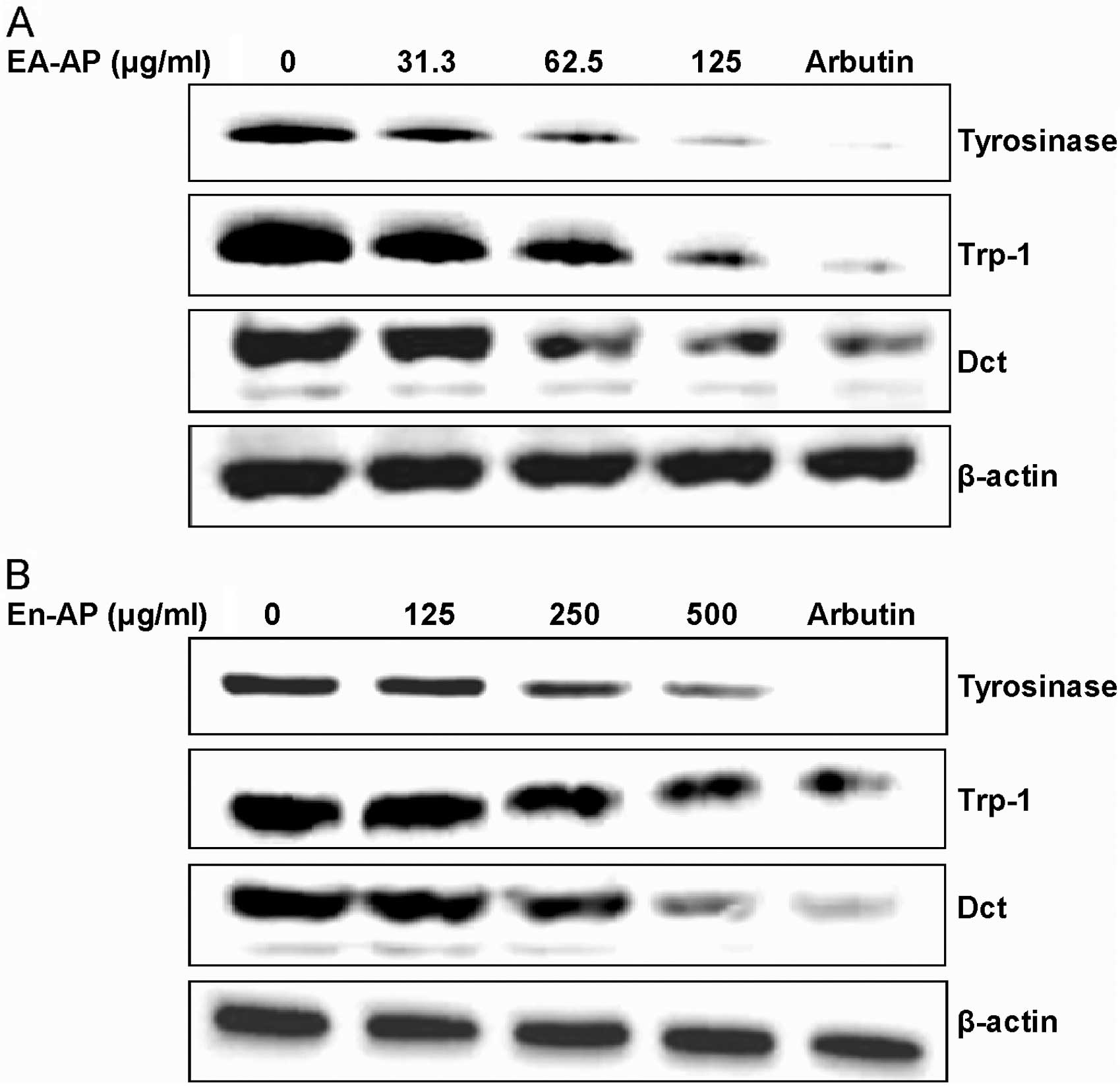
|
1
|
Pawelek JM, Chakraborty AK, Osber MP and
Bolognia JL: Ultraviolet light and pigmentation of the skin.
Cosmetics & Toiletries Magazine. 107:61–68. 1992.
|
|
2
|
Briganti S, Camera E and Picardo M:
Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpigmentation.
Pigment Cell Res. 16:101–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kobayashi T, Urabe K, Winder A, et al:
Tyrosinase related protein 1 (TRP1) functions as a DHICA oxidase in
melanin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 13:5818–5825. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
del Marmol V and Beermann F: Tyrosinase
and related proteins in mammalian pigmentation. FEBS Lett.
381:165–168. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lerner AB, Fitzpatrick TB, Calkins E and
Summerson WH: Mammalian tyrosinase; preparation and properties. J
Biol Chem. 178:185–195. 1949.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slominski A, Tobin DJ, Shibahara S and
Wortsman J: Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal
regulation. Physiol Rev. 84:1155–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones K, Hughes J, Hong M, Jia Q and
Orndorff S: Modulation of melanogenesis by aloesin: a competitive
inhibitor of tyrosinase. Pigment Cell Res. 15:335–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maeda K and Fukuda M: In vitro
effectiveness of several whitening cosmetic components in human
Melanocyte. J Soc Cosmet Chem. 4:361–368. 1991.
|
|
9
|
Shiino M, Watanabe Y and Umezawa K:
Synthesis of N-substituted N-nitrosohydroxylamines as inhibitors of
mashroom tyrosinase. Bioorg Med Chem. 9:1233–1240. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shimogaki H, Tanaka Y, Tamai H and Masuda
M: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ellagic acid on melanogenesis
inhibition. Int J Cosmetic Sci. 22:291–303. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim DS, Kim SY, Chung JH, Kim KH, Eun HC
and Park KC: Delayed ERK activation by ceramide reduces melanin
synthesis in human melanocytes. Cell Signal. 14:779–785. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimizu K, Kondo R, Sakai K, Lee SH and
Sato H: The inhibitory components from Artocarpus incisus on
melanin biosynthesis. Planta Med. 64:408–412. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Komthong P, Igura N and Shimoda M: Effect
of ascorbic acid on the odours of cloudy apple juice. Food Chem.
100:1342–1349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cha SH, Ko SC, Kim D and Jeon YJ:
Screening of marine algae for potential tyrosinase inhibitor: those
inhibitors reduced tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in
zebrafish. J Dermatol. 38:354–363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park MS and Kim BY: Feeding behaviour of
the starfish, Asterias amurensis (LUTKEN). Bull Fish Res Dev
Agency. 34:1–174. 1985.
|
|
16
|
Park SW, Kim TH and Oh HK: A study on the
development of the extermination gear for starfish, Asterias
amurensis and its efficiency. J Korean Soc Fish Technol.
33:166–172. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Seo JK: Conformation and biological
activity of Mastoparan B and its analogs: isolation and
characterization of the biological substances from Inshore Hagfish
(Eptatretus burgeri) skin and starfish (Asterina
pectinifera). Thesis. Pukyong National University; 1997
|
|
18
|
Cho SY, Kang HJ, Joo DS, Jeon JK, Oh MH
and Kim JS: Seperation and identification of nature antimicrobial
agent from starfish. In: 47th Conference of Korean Society; J Food
Science Nutr. pp. 695–701. 2000
|
|
19
|
Cho SY, You BJ, Chang MH, Lee SJ, Sung NJ
and Lee EH: Screening for antimicrobial compounds in unused marine
resources by the paper disk method. Korean J Food Sci Technol.
26:261–265. 1994.(In Korean).
|
|
20
|
Jo WS, Choi YJ, Kim HJ, Nam BH, Lee GA,
Seo SY, Lee SW and Jeong MH: Methanolic extract of Asterina
pectinifera inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory mediators in
murine macrophage. Toxicol Res. 6:1–82. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Chang TS, Ding HY, Tai SSK and Wu CY:
Mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory effects of isoflavones isolated from
soygerm koji fermented with Aspergillus oryzae BCRC 32288.
Food Chem. 105:1430–1438. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Masamoto Y, Ando H, Murata Y, Shimoishi
YTM and Takahata K: Mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory activity of
esculetin isolated from seeds of Euphorbia lathyris L. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 67:631–634. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hosoi J, Abe E, Suda T and Kuroki T:
Regulation of melanin synthesis of B16 mouse melanoma cells by 1α,
25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and retinoic acid. Cancer Res.
45:1474–1478. 1985.
|
|
24
|
Pomerantz HS: Tyrosine hydroxylation
catalyzed by mammalian tyrosinase: an improved method of assay.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 16:188–194. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li EPH, Min HJ, Belk RW, Kimura J and Bahl
S: Skin lightening and beauty in four Asian cultures. Adv Consum
Res. 35:444–449. 2008.
|
|
26
|
Oh EY, Jang JY, Choi YH, Choi YW and Choi
BT: Inhibitory effects of 1-O-methyl-fructofuranose from
Schisandra chinensis fruit on melanogenesis in B16F0
melanoma cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 132:219–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Virador VM, Kobayashi N, Matsunaga J and
Hearing VJ: A standardized protocol for assessing regulators of
pigmentation. Anal Biochem. 270:207–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hearing VJ and Tsukamoto K: Enzymatic
control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 5:2902–2909.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Busca R and Ballotti R: Cyclic AMP a key
messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res.
13:60–69. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Momtaz S, Mapunya BM, Houghton PJ, Edgerly
C, Hussein A, Naidoo S and Lall N: Tyrosinase inhibition by
extracts and constituents of Sideroxylon inerme L. stem
bark, used in South Africa for skin lightening. J Ethnopharmacol.
119:507–517. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dooley TP: Topical skin depigmenting
agents: current products and discovery of novel inhibitors of
melanogenesis. J Dermatol Treat. 7:188–200. 1997.
|
|
32
|
Levy C, Khaled M and Fisher DE: MITF:
master regulator of melanocyte development and melanoma oncogene.
Trends Mol Med. 12:406–414. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sturm RA, O’ Sullivan BJ, Box NF, et al:
Chromosomal structure of the human TYRP1 and TYRP2 loci and
comparison of the tyrosinase-related protein gene family. Genomics.
29:24–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kobayashi T, Imokawa G, Bennett DC and
Hearing VJ: Tyrosinase stabilization by Tyrp1 (the brown locus
protein). J Biol Chem. 273:31801–31805. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Setaluri V: The melanosome: dark pigment
granule shines bright light on vesicle biogenesis and more. J
Invest Dermatol. 121:650–660. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu H and Park HY: Protein kinase
C-beta-mediated complex formation between tyrosinase and TRP-1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 311:948–953. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pawelek JM and Chakraborty AK: The
enzymology of melanogenesis. The Pigmentary System: Physiology and
Pathophysiology. Nordlund JJ, Boissy RE, Hearing VJ, King RA and
Ortonne JP: Oxford University Press; New York: pp. 391–400.
1998
|
|
38
|
Manga P, Sato K, Ye L, Beermann F, Amoreux
ML and Orlow SJ: Mutational analysis of the modulation of
tyrosinase by tyrosinase-related proteins 1 and 2 in vitro. Pigment
Cell Res. 13:364–374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hamid MA, Sarmidi MR and Park CS:
Mangosteen leaf extract increases melanogenesis in B16F1 melanoma
cells by stimulating tyrosinase activity in vitro and by
up-regulating tyrosinase gene expression. Int J Mol Med.
29:209–217. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim DS, Jeong YM, Park IK, et al: A new
2-imino-1,3-thiazoline derivative, KHG22394, inhibits melanin
synthesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:180–183.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|