Spandidos Publications style
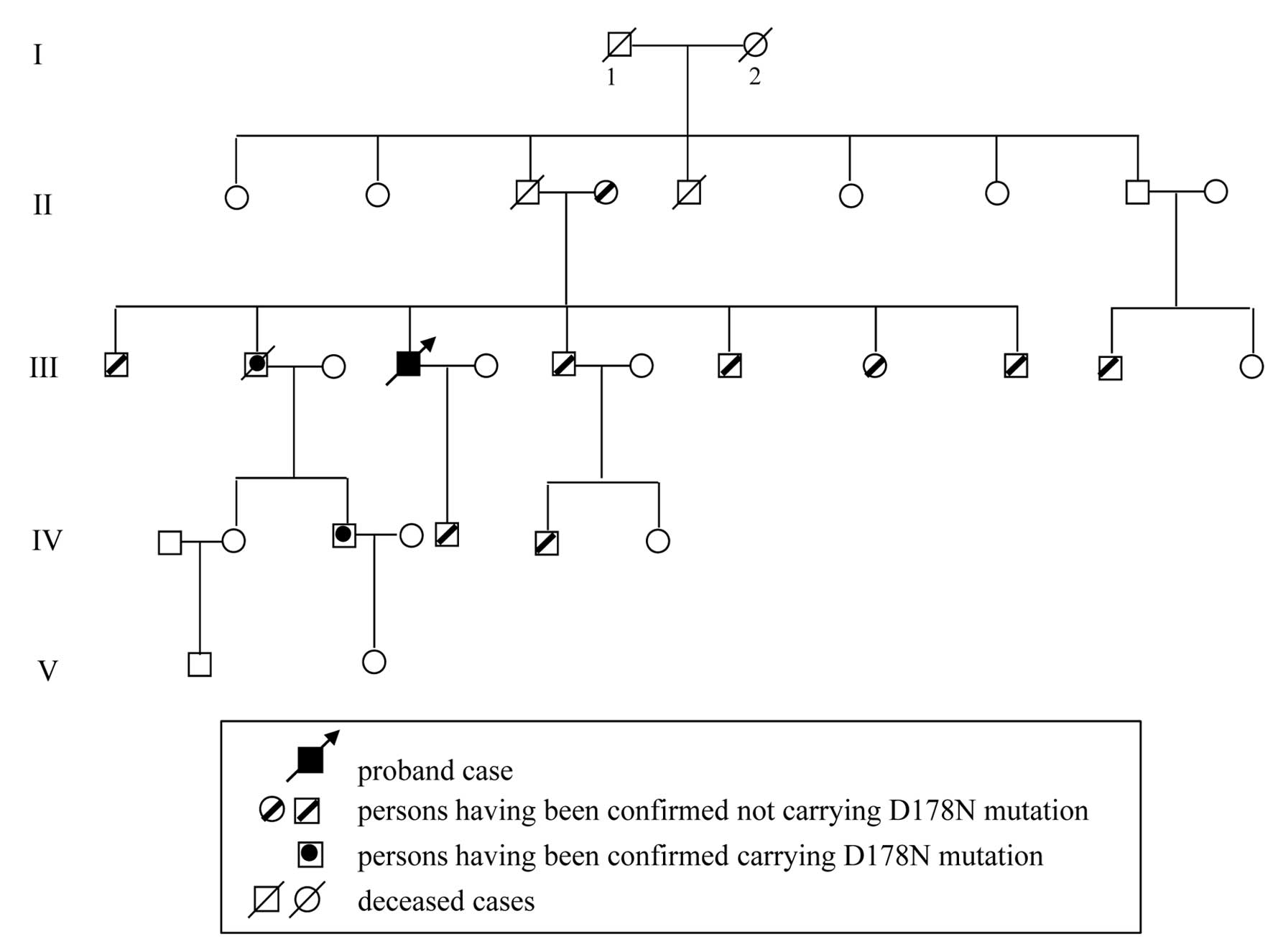
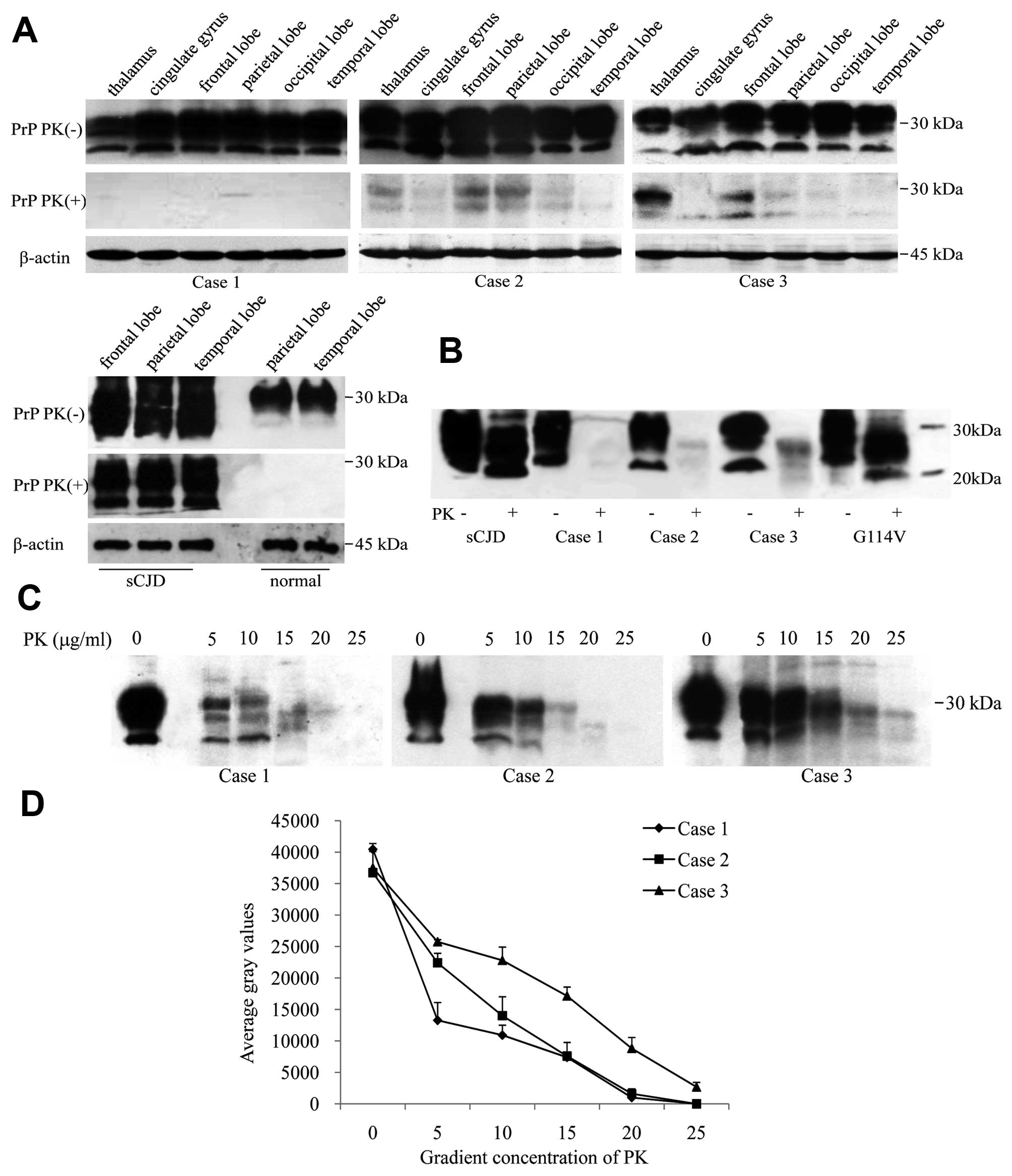
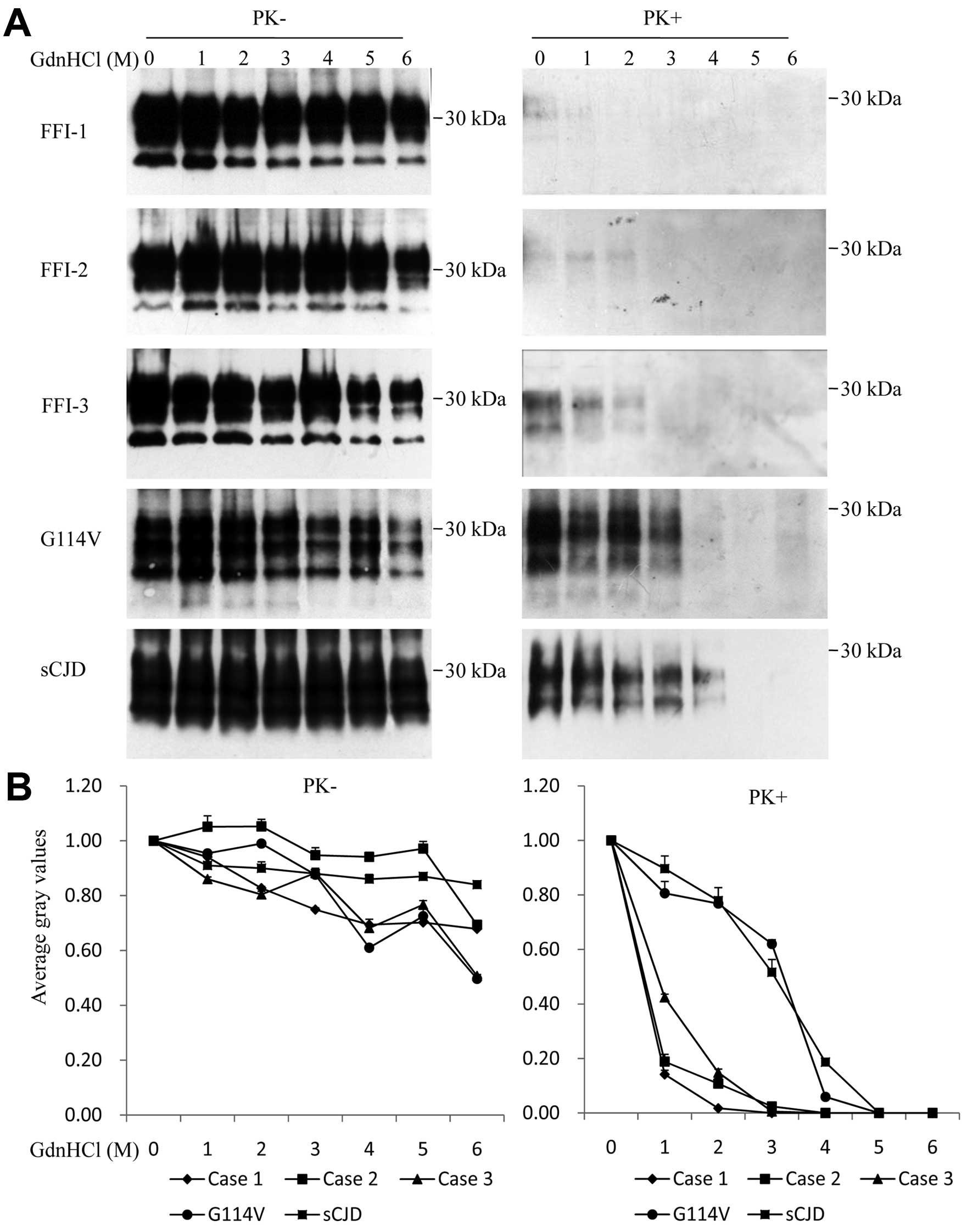
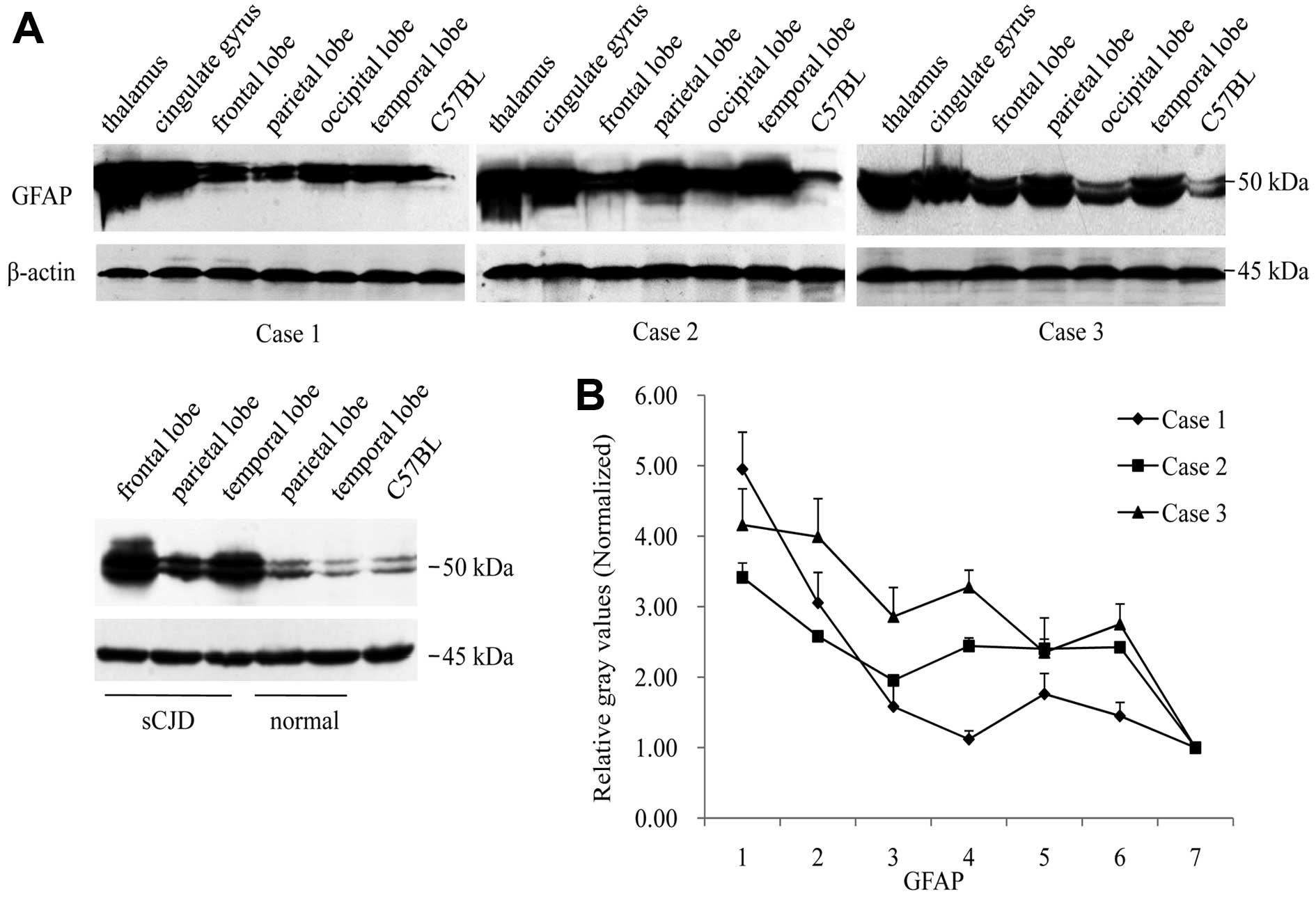
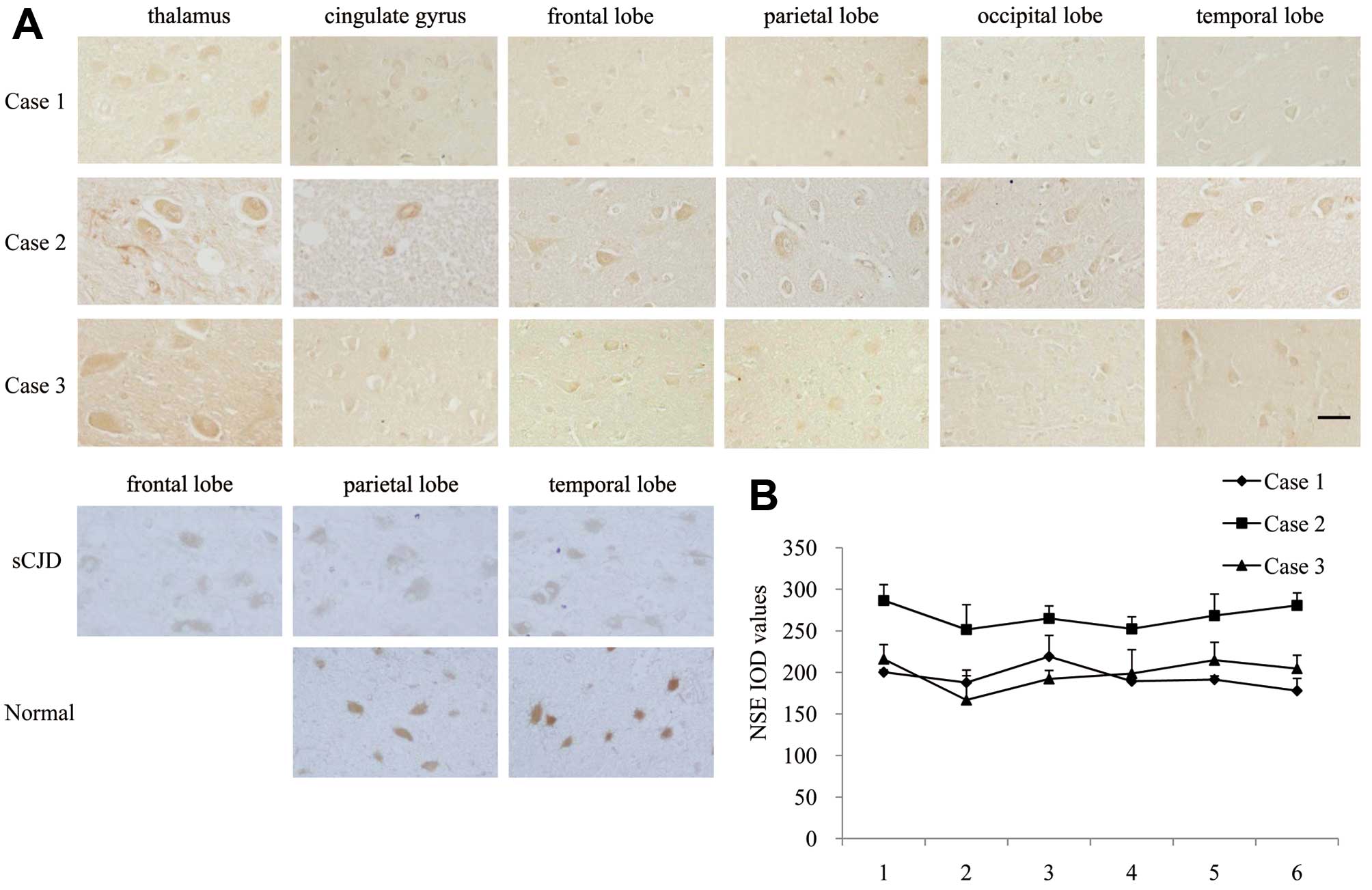
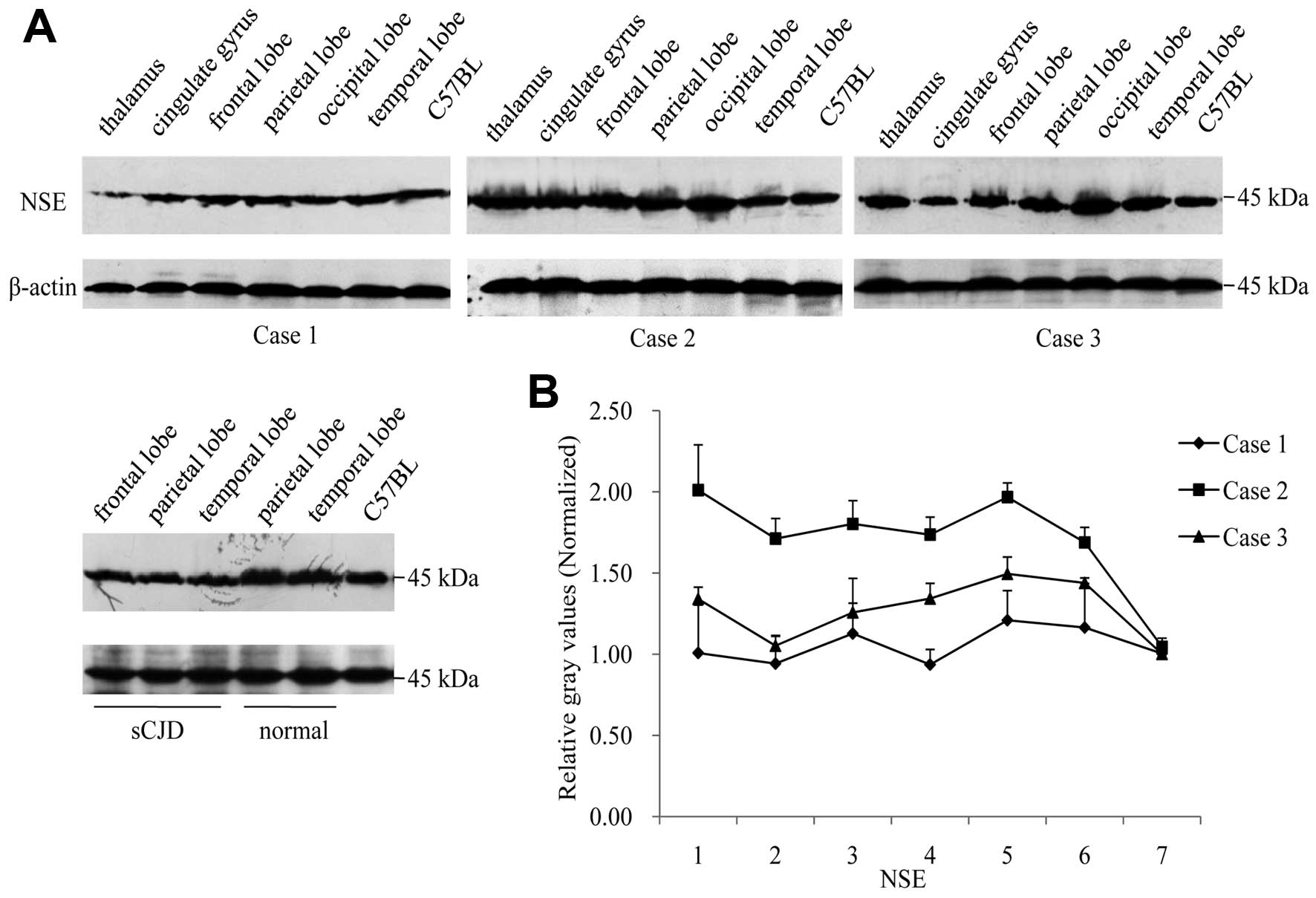
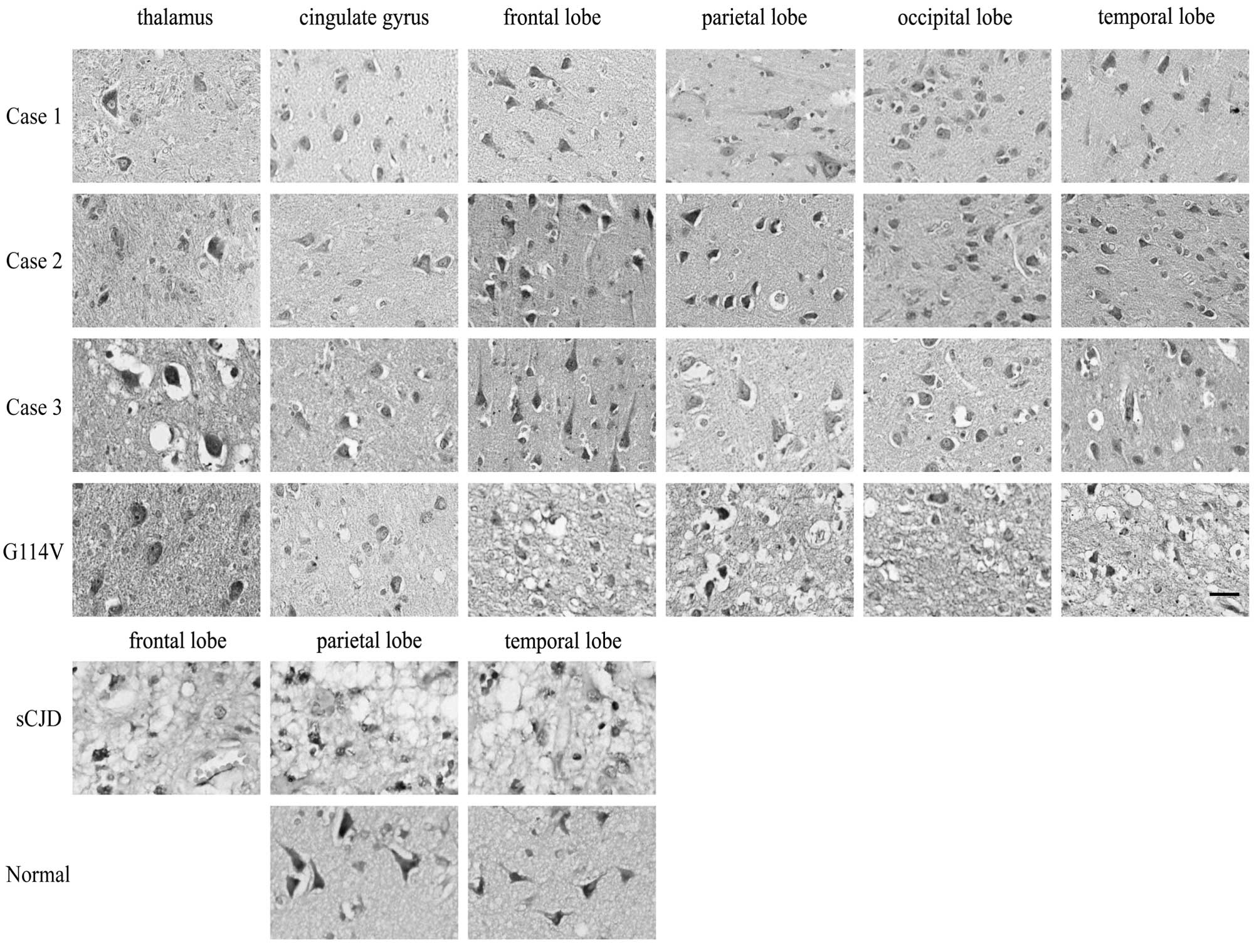
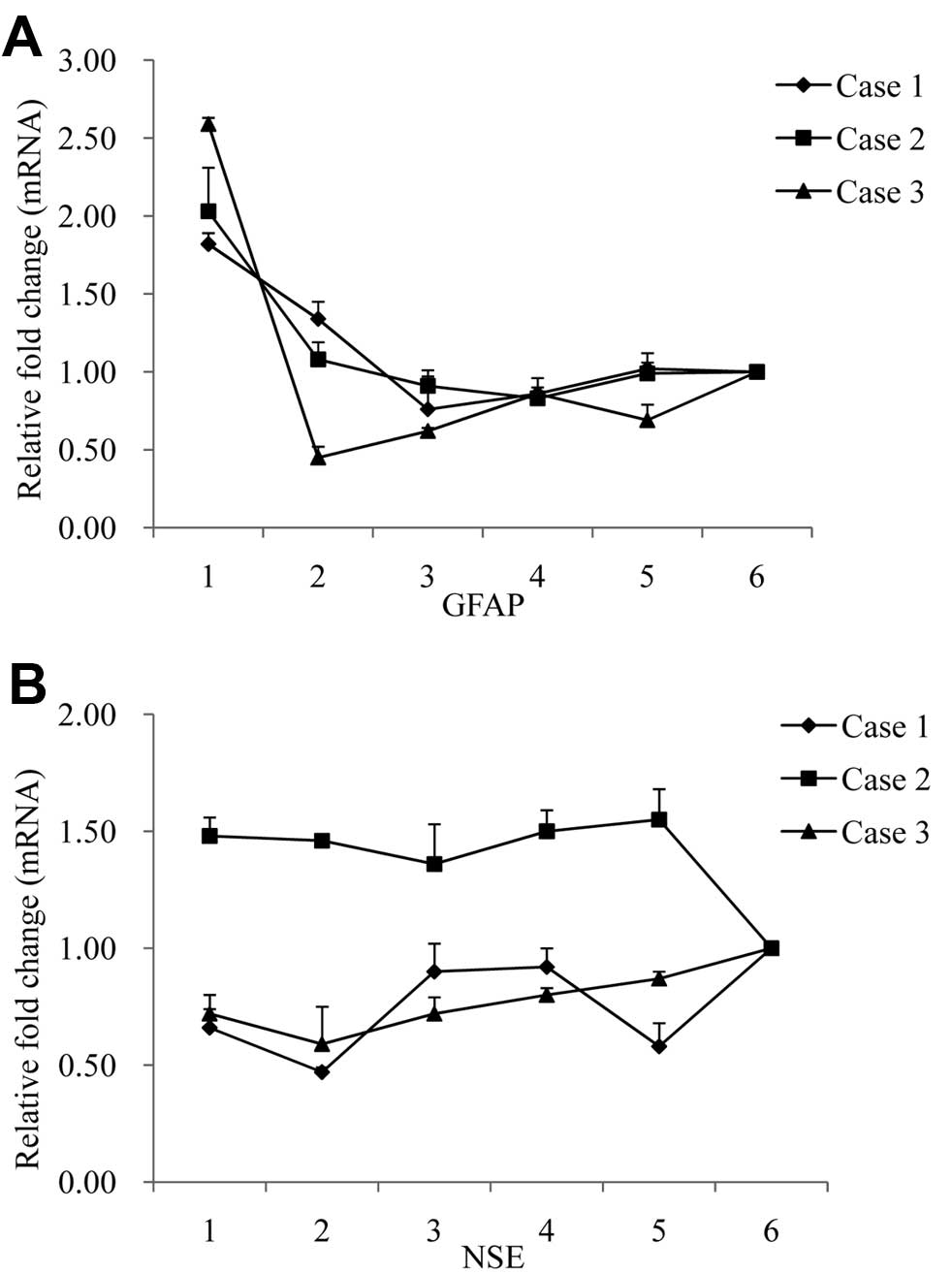
Xie W, Shi Q, Xia S, Zhang B, Gong H, Wang S, Xu Y, Guo Y, Tian C, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al: Comparison of the pathologic and pathogenic features in six different regions of postmortem brains of three patients with fatal familial insomnia. Int J Mol Med 31: 81-90, 2013.
APA
Xie, W., Shi, Q., Xia, S., Zhang, B., Gong, H., Wang, S. ... Dong, X. (2013). Comparison of the pathologic and pathogenic features in six different regions of postmortem brains of three patients with fatal familial insomnia. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 31, 81-90. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1194
MLA
Xie, W., Shi, Q., Xia, S., Zhang, B., Gong, H., Wang, S., Xu, Y., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Zhang, J., Xu, B., Liu, Y., Dong, X."Comparison of the pathologic and pathogenic features in six different regions of postmortem brains of three patients with fatal familial insomnia". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 31.1 (2013): 81-90.
Chicago
Xie, W., Shi, Q., Xia, S., Zhang, B., Gong, H., Wang, S., Xu, Y., Guo, Y., Tian, C., Zhang, J., Xu, B., Liu, Y., Dong, X."Comparison of the pathologic and pathogenic features in six different regions of postmortem brains of three patients with fatal familial insomnia". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 31, no. 1 (2013): 81-90. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1194