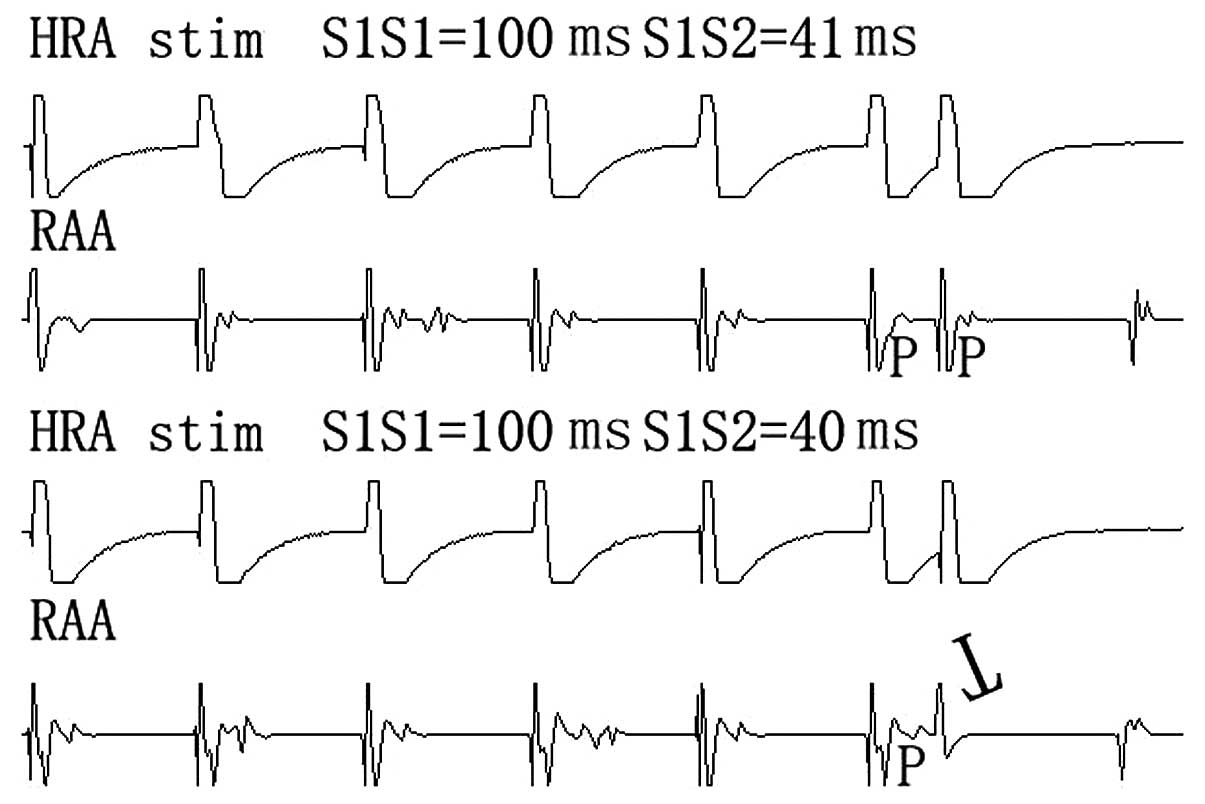
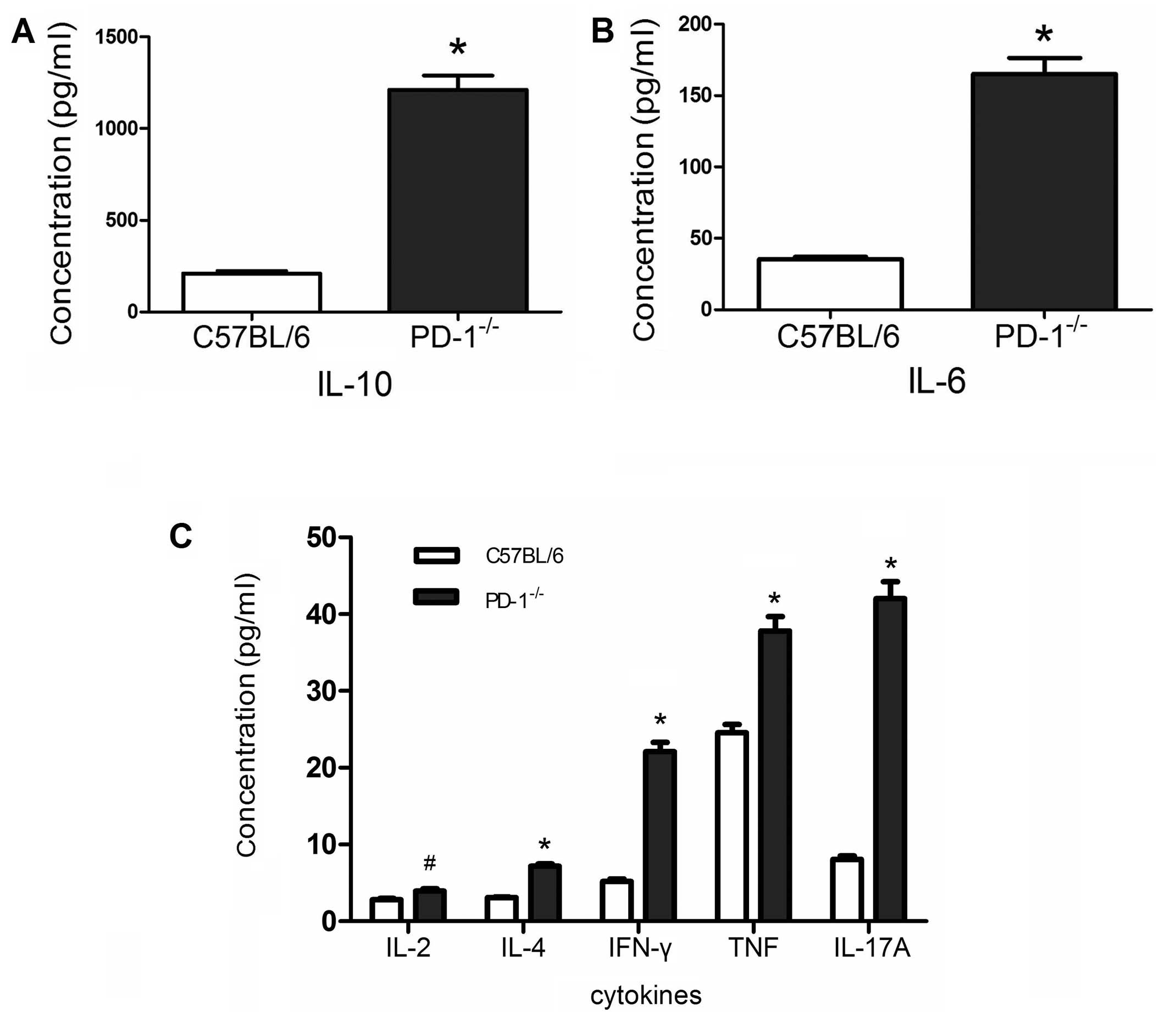
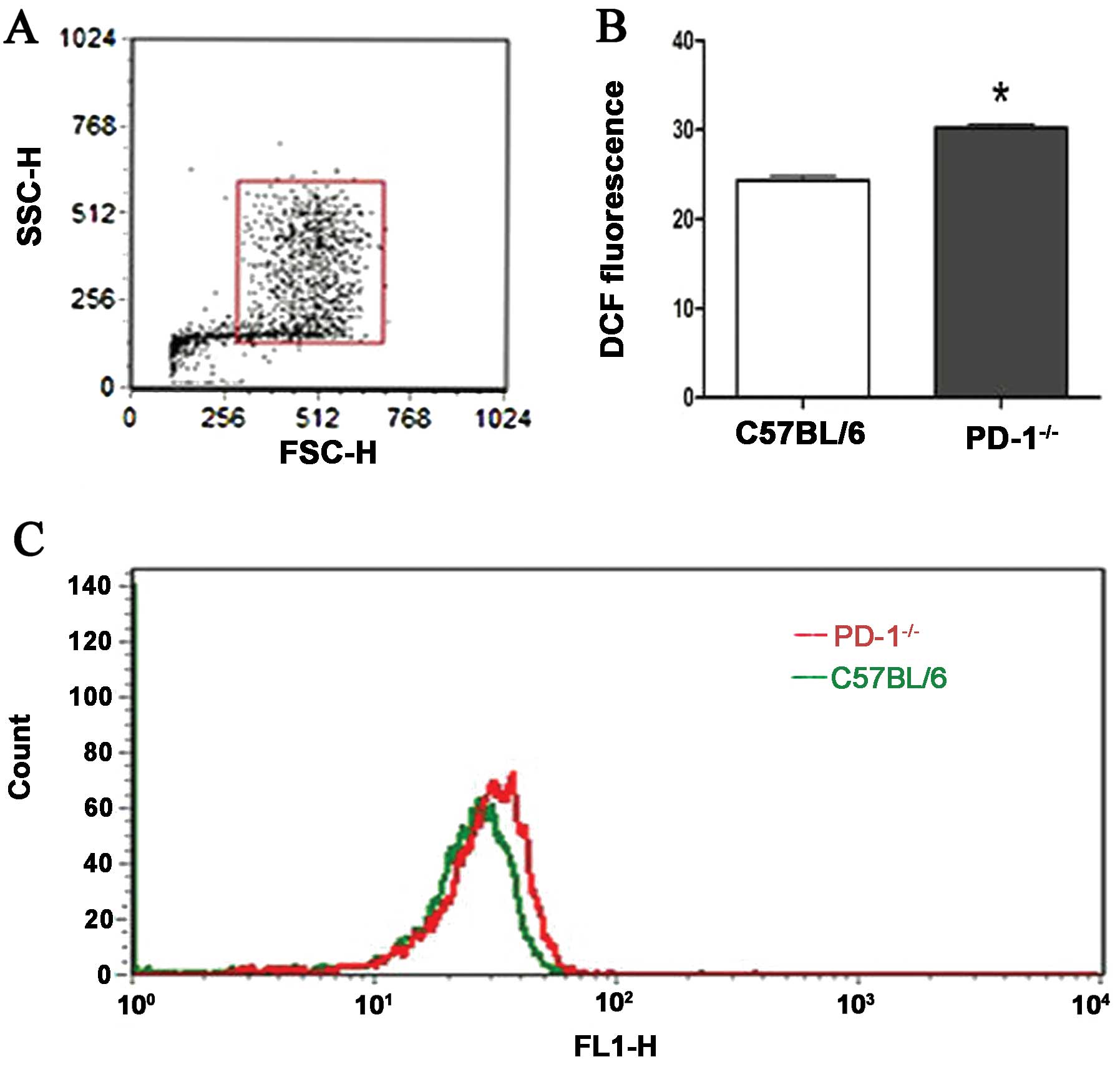
|
1.
|
Page RL: Clinical practice. Newly
diagnosed atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 351:2408–2416. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB,
Silbershatz H, Kannel WB and Levy D: Impact of atrial fibrillation
on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation.
946–952. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Nattel S, Burstein B and Dobrev D: Atrial
remodeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and implications.
Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 1:62–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sharma D, Li G, Xu G, Liu Y and Xu Y:
Atrial remodeling in atrial fibrillation and some related
microRNAs. Cardiology. 120:111–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bruins P, te Velthuis H, Yazdanbakhsh AP,
et al: Activation of the complement system during and after
cardiopulmonary bypass surgery: postsurgery activation involves
C-reactive protein and is associated with postoperative arrhythmia.
Circulation. 96:3542–3548. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ommen SR, Odell JA and Stanton MS: Atrial
arrhythmias after cardiothoracic surgery. N Engl J Med.
336:1429–1434. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Engelmann MD and Svendsen JH: Inflammation
in the genesis and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart
J. 26:2083–2092. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH:
The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:515–548. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: The PD-1-PD-L
pathway in immunological tolerance. Trends Immunol. 27:195–201.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Iwai Y, Terawaki S, Ikegawa M, Okazaki T
and Honjo T: PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase
in the liver. J Exp Med. 198:39–50. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Carter LL, Leach MW, Azoitei ML, et al:
PD-1/PD-L1, but not PD-1/PD-L2, interactions regulate the severity
of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol.
182:124–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Cho H, Nam GB, Lee SH, Earm YE and Ho WK:
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate is acting as a signal
molecule in alpha(1)-adrenergic pathway via the modulation of
acetylcholine-activated K(+) channels in mouse atrial myocytes. J
Biol Chem. 276:159–164. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Golan O, Issan Y, Isak A, Leipziger J,
Robaye B and Shainberg A: Extracellular nucleotide derivatives
protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxic stress. Biochem Pharmacol.
81:1219–1227. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Etzion Y, Mor M, Shalev A, et al: New
insights into the atrial electrophysiology of rodents using a novel
modality: the miniature-bipolar hook electrode. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 295:H1460–H1469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chen L: Co-inhibitory molecules of the
B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol.
4:336–347. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Nishimura H, Minato N, Nakano T and Honjo
T: Immunological studies on PD-1 deficient mice: implication of
PD-1 as a negative regulator for B cell responses. Int Immunol.
10:1563–1572. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N and
Honjo T: Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by
disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying
immunoreceptor. Immunity. 11:141–151. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, et al:
Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice.
Science. 291:319–322. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: Pathogenic roles of
cardiac autoantibodies in dilated cardiomyopathy. Trends Mol Med.
11:322–326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nishio R, et al:
Autoantibodies against cardiac troponin I are responsible for
dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1-deficient mice. Nat Med.
9:1477–1483. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Wang J, Okazaki IM, Yoshida T, et al: PD-1
deficiency results in the development of fatal myocarditis in MRL
mice. Int Immunol. 22:443–452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Falk RH: Atrial fibrillation. N Engl J
Med. 344:1067–1078. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Aviles RJ, Martin DO, Apperson-Hansen C,
et al: Inflammation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation.
Circulation. 108:3006–3010. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Korantzopoulos P, Kolettis T, Siogas K and
Goudevenos J: Atrial fibrillation and electrical remodeling: the
potential role of inflammation and oxidative stress. Med Sci Monit.
9:225–229. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Kunkel SL, Joshi BH,
Puri RK and Hogaboam CM: Impact of interleukin-13 responsiveness on
the synthetic and proliferative properties of Th1- and Th2-type
pulmonary granuloma fibroblasts. Am J Pathol. 162:1475–1486. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Liu W, Feng W, Wang F, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated ICOSIg gene transfer alleviates cardiac
remodeling in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Immunol Cell
Biol. 86:659–665. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yu Q, Horak K and Larson DF: Role of T
lymphocytes in hypertension-induced cardiac extracellular matrix
remodeling. Hypertension. 48:98–104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Cortez DM, Feldman MD, Mummidi S, et al:
IL-17 stimulates MMP-1 expression in primary human cardiac
fibroblasts via p38 MAPK- and ERK1/2-dependent C/EBP-beta,
NF-kappaB, and AP-1 activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
293:H3356–H3365. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Feng W, Li W, Liu W, Wang F, Li Y and Yan
W: IL-17 induces myocardial fibrosis and enhances RANKL/OPG and
MMP/TIMP signaling in isoproterenol-induced heart failure. Exp Mol
Pathol. 87:212–218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Ishii Y, Schuessler RB, Gaynor SL, et al:
Inflammation of atrium after cardiac surgery is associated with
inhomogeneity of atrial conduction and atrial fibrillation.
Circulation. 111:2881–2888. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Sawaya SE, Rajawat YS, Rami TG, et al:
Downregulation of connexin40 and increased prevalence of atrial
arrhythmias in transgenic mice with cardiac-restricted
overexpression of tumor necrosis factor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 292:1561–1567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kawada H, Niwano S, Niwano H, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha downregulates the voltage gated outward
K+ current in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes: a
possible cause of electrical remodeling in diseased hearts. Circ J.
70:605–609. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Petkova-Kirova PS, Gursoy E, Mehdi H,
McTiernan CF, London B and Salama G: Electrical remodeling of
cardiac myocytes from mice with heart failure due to the
overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 290:2098–2107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Carnes CA, Chung MK, Nakayama T, et al:
Ascorbate attenuates atrial pacing-induced peroxynitrite formation
and electrical remodeling and decreases the incidence of
postoperative atrial fibrillation. Circ Res. 89:e32–e38. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Galaris D and Korantzopoulos P: On the
molecular mechanism of metmyoglobin-catalyzed reduction of hydrogen
peroxide by ascorbate. Free Radic Biol Med. 22:657–667. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Wu S, Gao J, Ohlemeyer C, et al:
Activation of AP-1 through reactive oxygen species by angiotensin
II in rat cardiomyocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:1601–1610. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Korantzopoulos P, Galaris D, Papaioannides
D and Kokkoris S: C-reactive protein and oxidative stress in atrial
fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 88:103–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Sata N, Hamada N, Horinouchi T, et al:
C-reactive protein and atrial fibrillation. Is inflammation a
consequence or a cause of atrial fibrillation? Jpn Heart J.
45:441–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Tang RB, Dong JZ, Liu XP and Ma CS:
Inflammation and atrial fibrillation: is Chlamydia
pneumoniae a candidate pathogen of atrial fibrillation. Med
Hypotheses. 67:462–466. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|