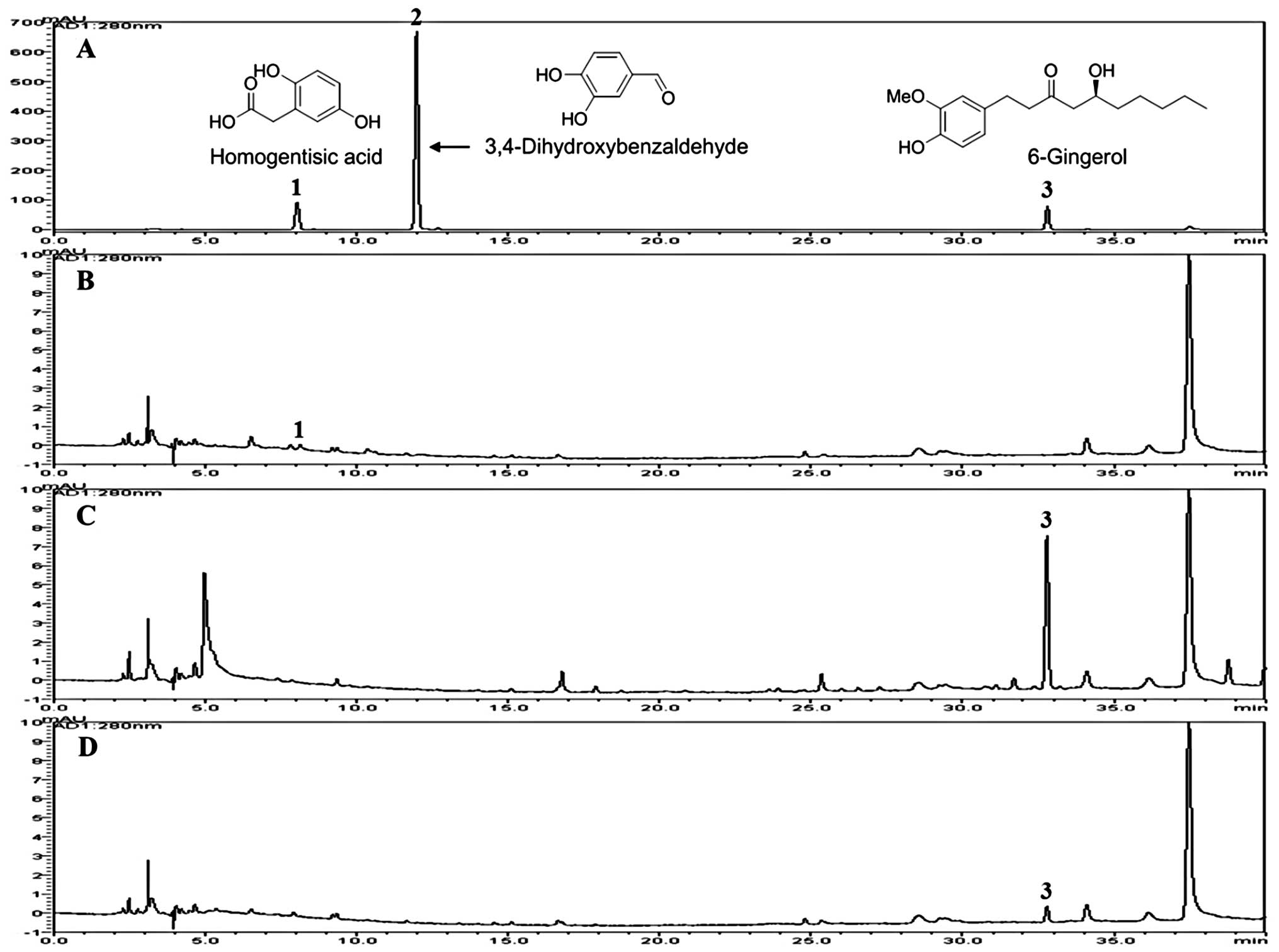
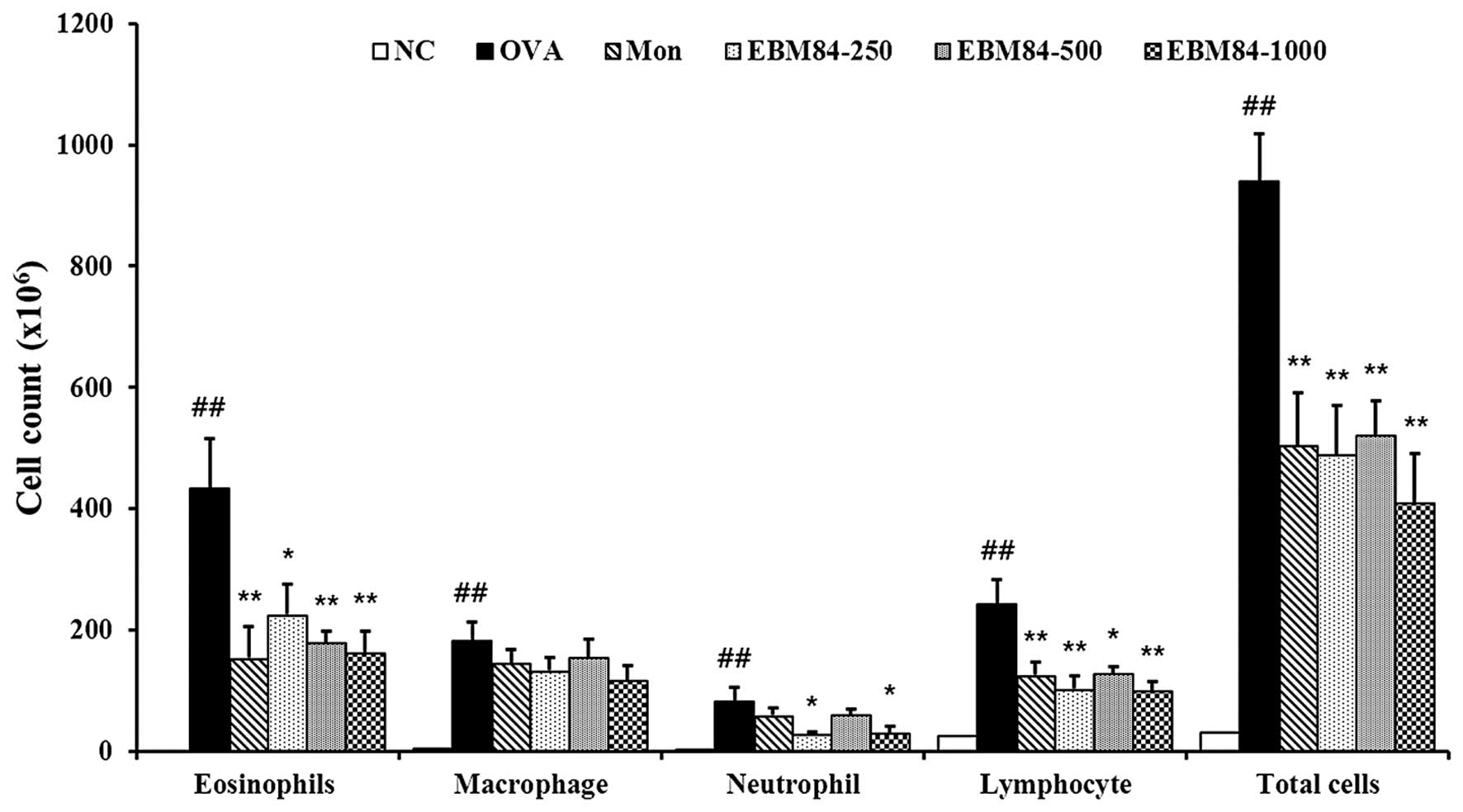
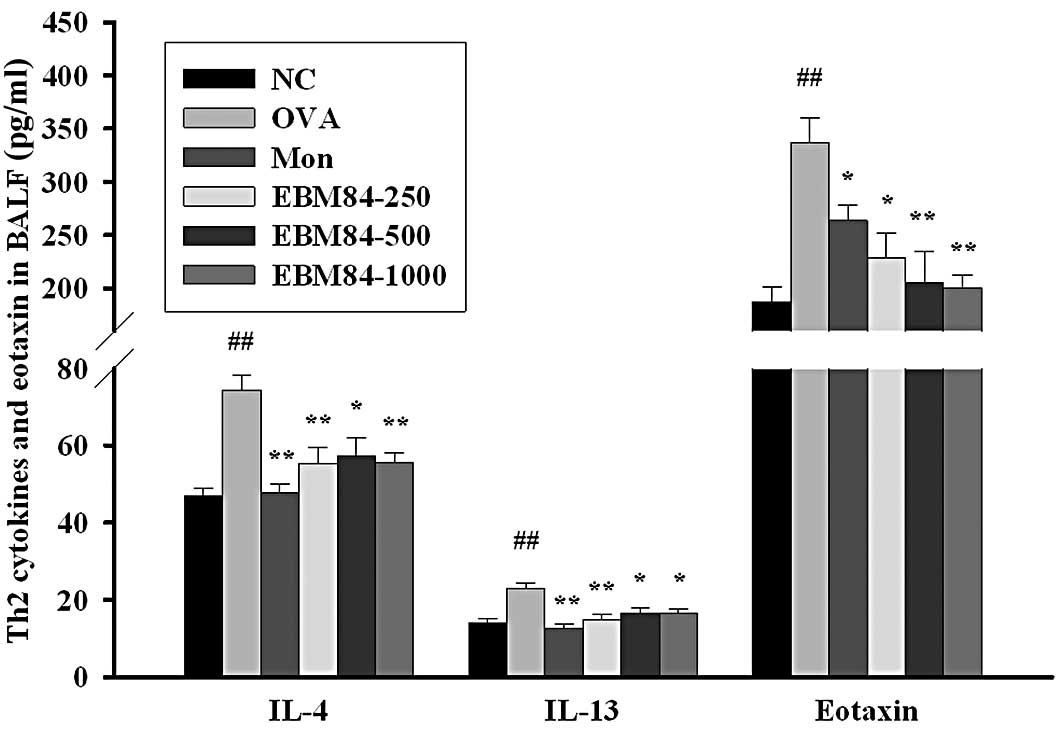
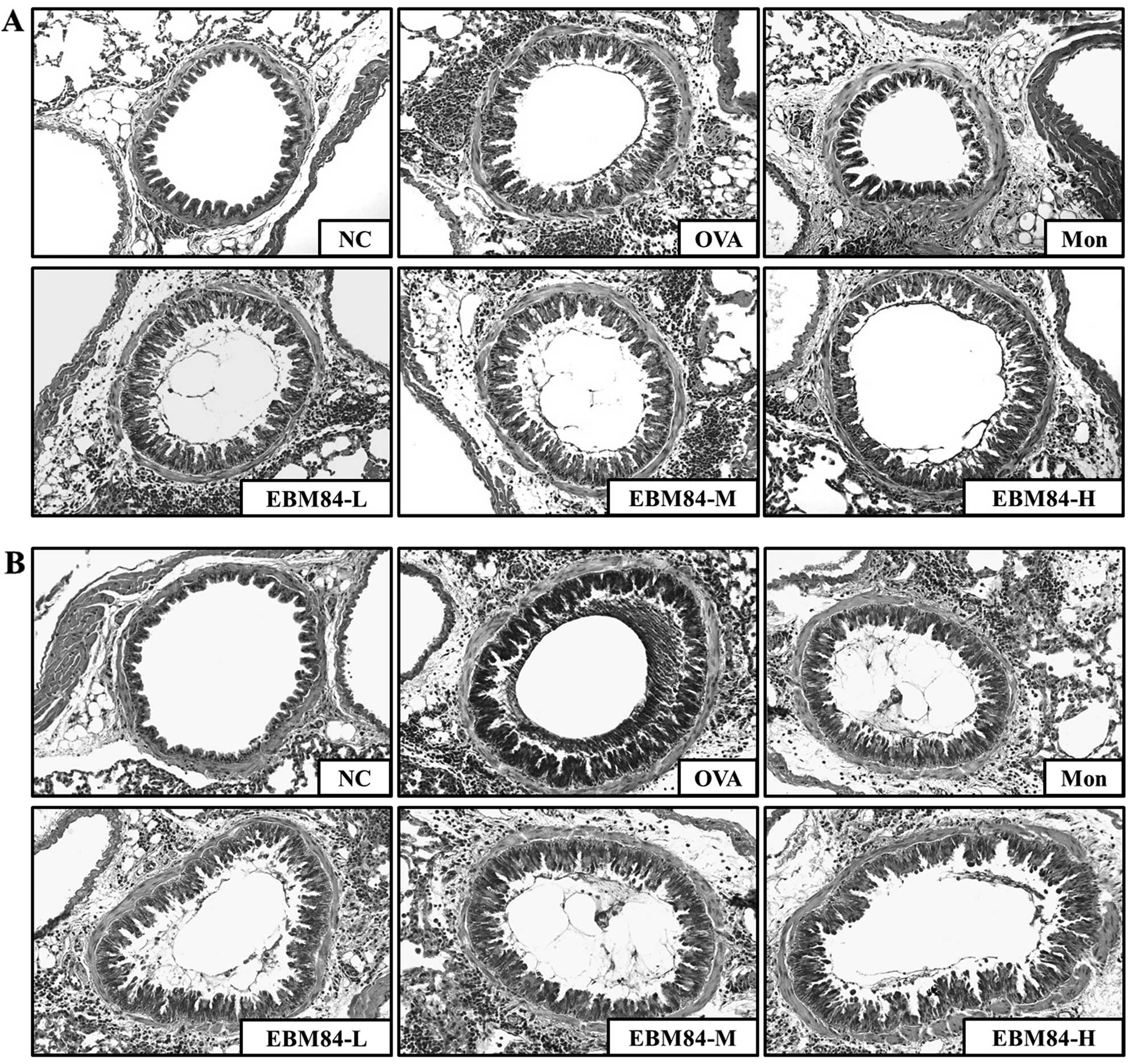
|
1
|
Liu LY, Coe CL, Swenson CA, Kelly EA, Kita
H and Busse WW: School examinations enhance airway inflammation to
antigen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 165:1062–1067. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Selgrade MK, Plopper CG, Gilmoour MI,
Conolly RB and Foos BS: Assessing the health effects of risks
associated with children’s inhalation exposures - asthma and
allergy. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 71:196–207. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Lee MY, Lee JA, Seo CS, Ha H, Lee NH and
Shin HK: Protective effects of Mentha haplocalyx ethanol
extract (MH) in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Phytother Res.
25:863–869. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Yuk JE, Lee MY, Kwon OK, Cai XF, Jang HY,
Oh SR, Lee HK and Ahn KS: Effects of astilbic acid on airway
hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a mouse model of allergic
asthma. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:266–273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim DY and Yang WM: Panax ginseng
ameliorates airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-sensitized mouse
allergic asthma model. J Ethnopharmacol. 136:230–235. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou DY, Du Q, Li RR, Huang M, Zhang Q and
Wei GZ: Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract attenuates airway
inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma by
downregulating inducible nitric oxide synthase. Plant Med.
77:1575–1581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shao MX, Nakanaga T and Nadel JA:
Cigarette smoke induces MUC5AC mucin overproduction via tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme in human airway epithelium
(NCI-H292) cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 287:420–427.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inoue D, Kubo H, Sasaki T, Yasuda H,
Numasaki M, Sasaki H and Yamaya M: Erythromycin attenuates MUC5AC
synthesis and secretion in cultured human tracheal cells infected
with RV14. Respirology. 13:215–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li R, Meng Z and Xie J: Effects of sulfur
dioxide on the expressions of MUC5AC and ICAM-1 in airway of
asthmatic rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 48:284–291. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanoh S, Tanabe T and Rubin BK:
IL-13-induced MUC5AC production and goblet cell differentiation is
steroid resistant in human airway cells. Clin Exp Allergy.
41:1747–1756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim YJ, Shin YO, Ha YW, Lee S, Oh JK and
Kim YS: Anti-obesity effect of Pinellia ternata extract in
Zucker rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1278–1281. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Li XH, McGrath KC, Nammi S, Heather AK and
Roufogalis BD: Attenuation of liver pro-inflammatory responses by
Zingiber officinale via inhibition of NF-kappa B activation
in high-fat diet-fed rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
110:238–244. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oboh G, Akinyemi AJ and Ademiluyi AO:
Antioxidant and inhibitory effect of red ginger (Zingiber
officinale var. Rubra) and white ginger (Zingiber
officinale Roscoe) on Fe(2+) induced lipid peroxidation in rat
brain in vitro. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 64:31–36. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ok IS, Kim SH, Kim BK, Lee JC and Lee YC:
Pinellia ternata, Citrus reticulata, and their
combinational prescription inhibit eosinophil infiltration and
airway hyperresponsiveness by suppressing CCR3+ and Th2
cytokines production in the ovalbumin-induced asthma model.
Mediators Inflamm. 2009:4132702009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Huang MS, Tsai MJ and Ko
YC: Ginger suppresses phthalate ester-induced airway remodeling. J
Agric Food Chem. 59:3429–3438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Wu H and Zhu T: Study on
processing for Rhizoma Pinelliae Praeparatum by
comprehensive evaluation of multiple mark. Zhong Yao Cai. 31:20–23.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Lynch KR, O’Neill GP, Liu Q, Im DS, Sawyer
N, Metters KM, Coulombe N, Abramovitz M, Figueroa DJ, Zeng Z,
Connolly BM, Bai C, Austin CP, Chateauneuf A, Stocco R, Greig GM,
Kargman S, Hooks SB, Hosfield E, Williams DL Jr, Ford-Hutchinson
AW, Caskey CT and Evans JF: Characterization of the human cysteinyl
leukotriene CysLT1 receptor. Nature. 399:789–793. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Korenblat PE; Antileukotriene Working
Group. The role of antileukotrienes in the treatment of asthma. Ann
Allergy Asthma Immunol. 86(Suppl 1): S31–S39. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Lee HJ, Choi YH, Park YM,
Heo MS and Kim GY: Curcumin attenuates ovalbumin-induced airway
inflammation by regulating nitric oxide. Biochem Biophy Res Commun.
375:275–279. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bloemen K, Verstraelen S, Van Den Heuvel
R, Witters H, Nelissen I and Schoeters G: The allergic cascade:
review of the most important molecules in the asthmatic lung.
Immunol Lett. 113:6–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pascual RM and Peters SP: Airway
remodeling contributes to the progressive loss of lung function in
asthma: an overview. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 116:477–486. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang D, Li Q, Kolosov VP and Zhou X: The
inhibition of aldose reductase on mucus production induced by
interleukin-13 in the human bronchial epithelial cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:588–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang DP, Perelman JM, Kolosov VP and Zhou
XD: Effects of scutellarin on MUC5AC mucin production induced by
human neutrophil elastase or interleukin 13 on airway epithelial
cells. J Korean Med Sci. 26:778–784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
World Health Oraganization (WHO).
Medicinal Plants in the Republic of Korea. Western Pacific Series
no. 21. Western Pacific; Manila: pp. 2071998
|
|
25
|
Chen Q, Chen KL, Yang M and Yang CX:
Effect of original processing method on sterol compounds of rhizoma
Pinelliae. Zhong Yao Cai. 33:1701–1703. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Huang CF, Yang RS, Liu SH, Hsieh PC and
Lin-Shiau SY: Evidence for improved neuropharmacological efficacy
and decreased neurotoxicity in mice with traditional processing of
Rhizoma Arisaematis. Am J Chin Med. 39:981–998. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|