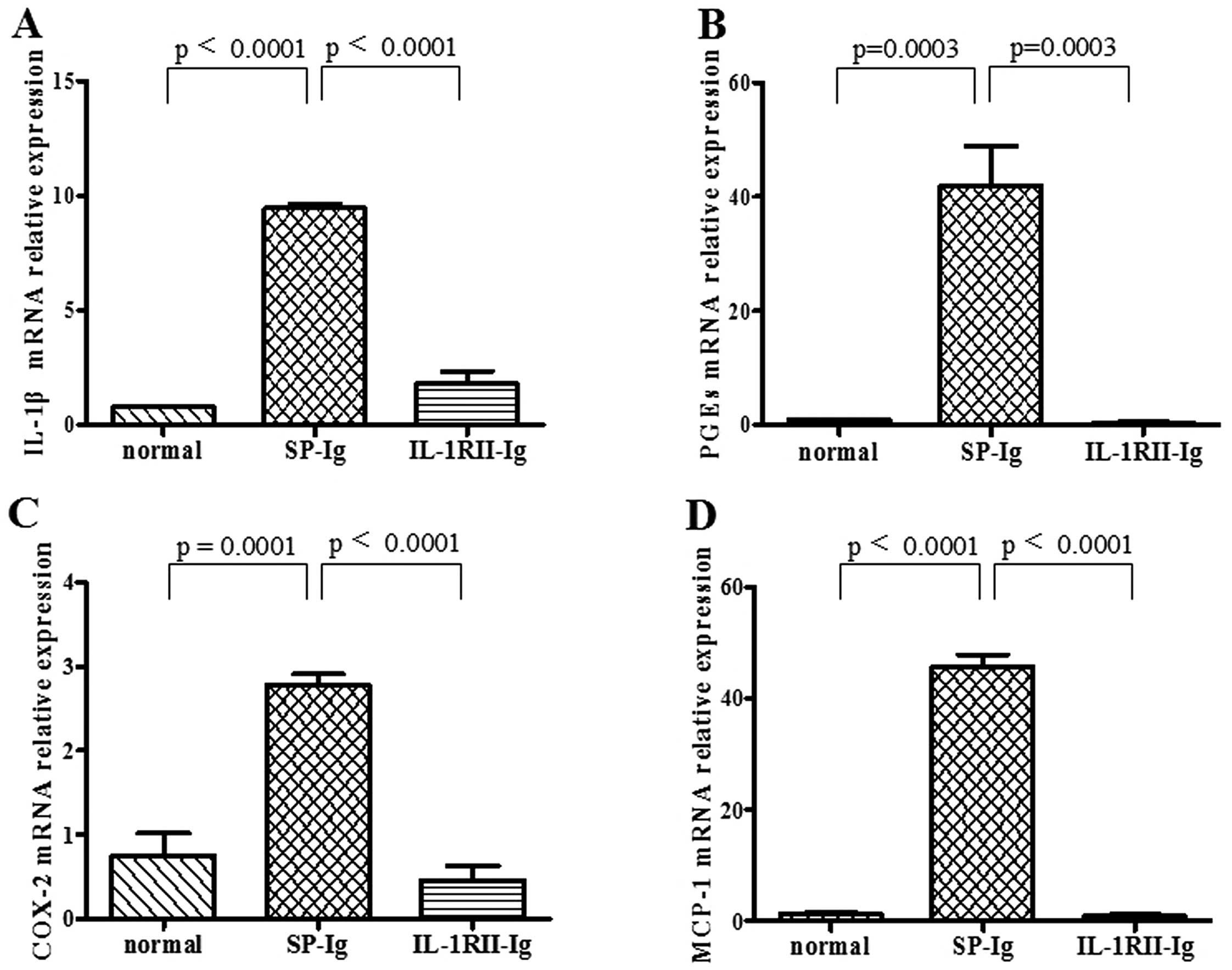
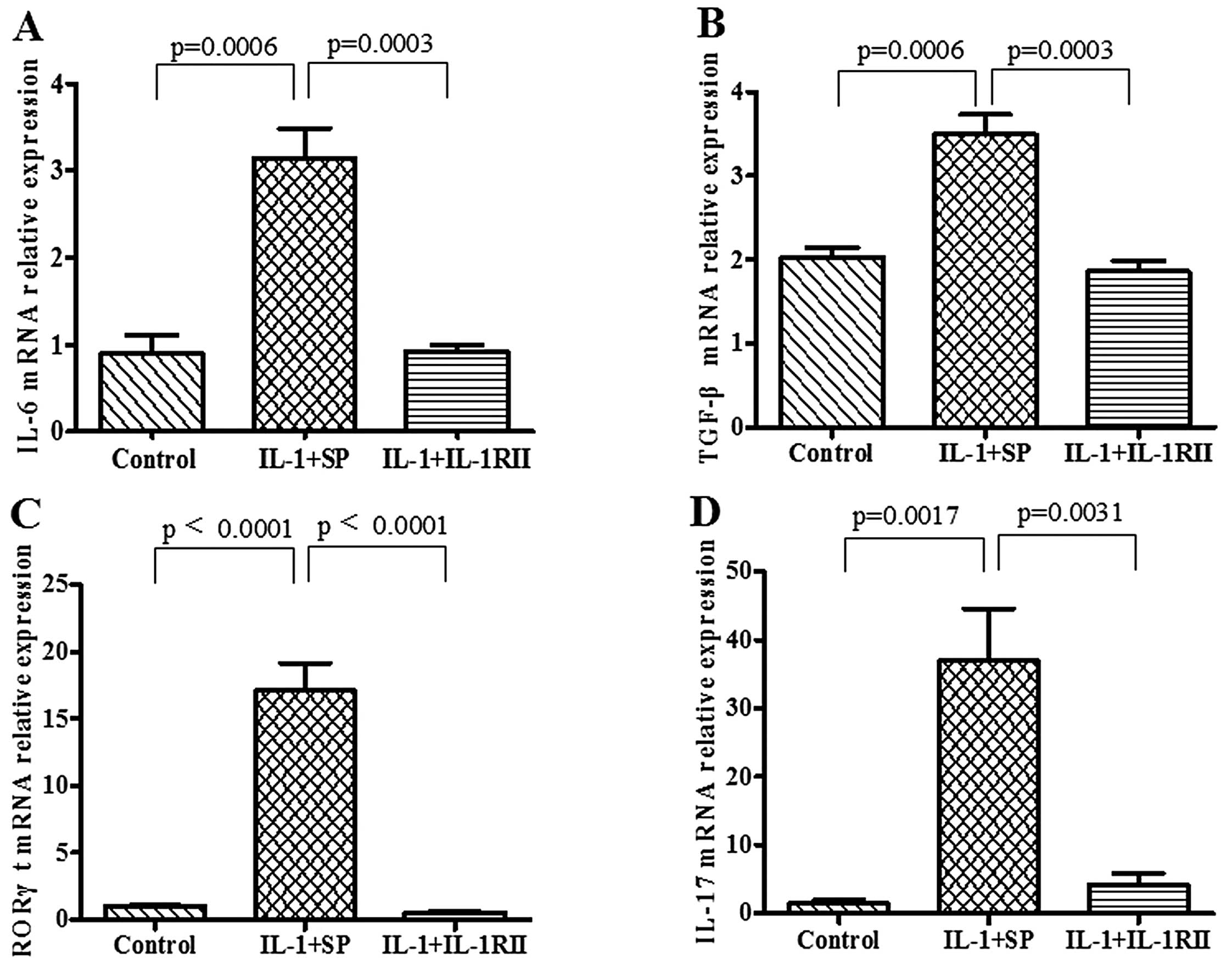
|
1
|
Blauwet LA and Cooper LT: Myocarditis.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 52:274–288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Leuschner F, Katus HA and Kaya Z:
Autoimmune myocarditis: past, present and future. J Autoimmun.
33:282–289. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kodama M, Matsumoto Y, Fujiwara M, Masani
F, Izumi T and Shibata A: A novel experimental model of giant cell
myocarditis induced in rats by immunization with cardiac myosin
fraction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 57:250–262. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arend WP and Dayer JM: Inhibition of the
production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor
alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 38:151–160. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vicenová B, Vopálenský V, Burýsek L and
Pospísek M: Emerging role of Interleukin-1 in cardiovascular
diseases. Physiol Res. 58:481–498. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Scala G, Allavena P, Djeu JY, Kasahara T,
Ortaldo JR, Herberman RB and Oppenheim JJ: Human large granular
lymphocytes are potent producers of interleukin-1. Nature.
309:56–59. 1984. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
March CJ, Mosley B, Larsen A, et al:
Cloning sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1
complementary DNAs. Nature. 315:641–647. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dinarello CA, Donath MY and
Mandrup-Poulsen T: Role of IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin
Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 17:314–321. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bujak M and Frangogiannis NG: The role of
IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp.
57:165–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dinarello CA: IL-1: discoveries,
controversies and future directions. Eur J Immunol. 40:599–606.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Colotta F, Re F, Muzio M, et al:
Interleukin-1 type II receptor: a decoy target for IL-1 that is
regulated by IL-4. Science. 261:472–475. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Greenfeder SA, Nunes P, Kwee L, Labow M,
Chizzonite RA and Ju G: Molecular cloning and characterization of a
second subunit of the interleukin 1 receptor complex. J Biol Chem.
270:13757–13765. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith DE, Hanna R, Friend Della, et al:
The soluble form of IL-1 receptor accessory protein enhances the
ability of soluble type II IL-1 receptor to inhibit IL-1 action.
Immunity. 18:87–96. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sims JE and Smith DE: The IL-1 family:
regulators of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:89–102. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, et al:
Interleukin-1-receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N
Engl J Med. 356:1517–1526. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
El-Osta H, Janku F and Kurzrock R:
Successful treatment of Castle-man's disease with interleukin-1
receptor antagonist (Anakinra). Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1485–1488.
2010.
|
|
17
|
Mertens M and Singh JA: Anakinra for
rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol.
36:1118–1125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Hanawa H, Yoshida T, et al: Effect
of hydrodynamics-based gene delivery of plasmid DNA encoding
interleukin-1 receptor antagonist-Ig for treatment of rat
autoimmune myocarditis: possible mechanism for lymphocytes and
noncardiac cells. Circulation. 111:1593–1600. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Maruyama H, Higuchi N, Nishikawa Y, et al:
High-level expression of naked DNA delivered to rat liver via tail
vein injection. J Gene Med. 4:333–341. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abe S, Hanawa H, Hayashi M, et al:
Prevention of experimental autoimmune myocarditis by
hydrodynamics-based naked plasmid DNA encoding CTLA4-Ig gene
delivery. J Card Fail. 11:557–564. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang H, Hanawa H, Yoshida T, et al:
Alteration of IL-17 related protein expressions in experimental
autoimmune myocarditis and inhibition of IL-17 by IL-10-Ig fusion
gene transfer. Circ J. 72:813–819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Attur MG, Dave M, Cipolletta C, et al:
Reversal of autocrine and paracrine effects of interleukin 1 (IL-1)
in human arthritis by type II IL-1 decoy receptor. Potential for
pharmacological intervention. J Biol Chem. 275:40307–40315. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu F, Song Y and Liu D:
Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic
administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 6:1258–1266. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang G, Budker V and Wolff JA: High
levels of foreign gene expression in hepatocytes after tail vein
injections of naked plasmid DNA. Hum Gene Ther. 10:1735–1737. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang H, Hanawa H, Liu H, et al:
Hydrodynamic-based delivery of an interleukin-22-Ig fusion gene
ameliorates experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats. J Immunol.
177:3635–3643. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Higuchi N, Maruyama H, Kuroda T, et al:
Hydrodynamics-based delivery of the viral interleukin-10 gene
suppresses experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis in
Wistar-Kyoto rats. Gene Ther. 10:1297–1310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang J, Yamato E and Miyazaki J:
Sustained expression of Fc-fusion cytokine following in vivo
electroporation and mouse strain differences in expression levels.
J Biochem. 133:423–427. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Elnaggar R, Hanawa H, Liu H, et al: The
effect of hydrodynamics-based delivery of an IL-13-Ig fusion gene
for experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats and its possible
mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 35:1995–2005. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dinarello CA: Immunological and
inflammatory functions of the interleukin 1 family. Annu Rev
Immunol. 27:519–550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boraschi D and Tagliabue A: The
interleukin-1 receptor family. Vitam Horm. 74:229–254. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chung Y, Chang SH, Martinez GJ, et al:
Critical regulation of early Th17 cell differentiation by
interleukin-1 signaling. Immunity. 30:576–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Aranami T and Yamamura T: Th17 cells and
autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE/MS). Allergol Int. 57:115–120.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|