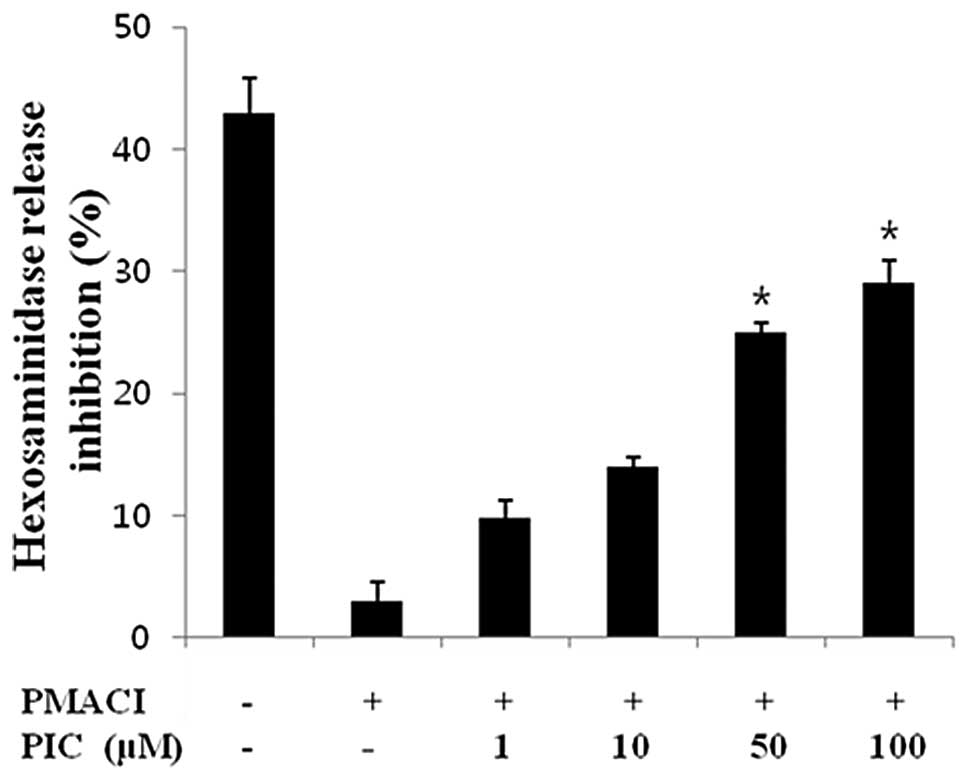
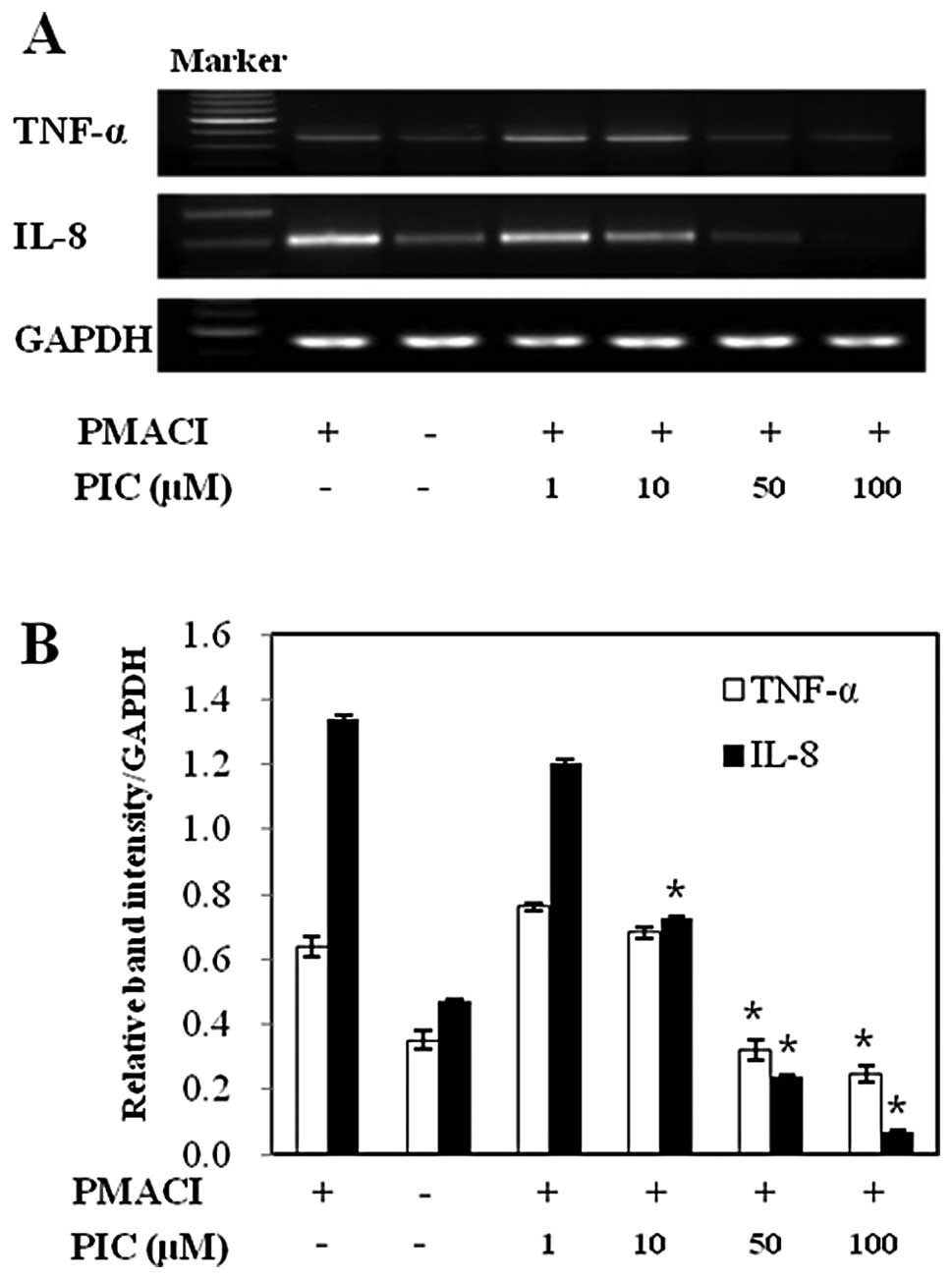
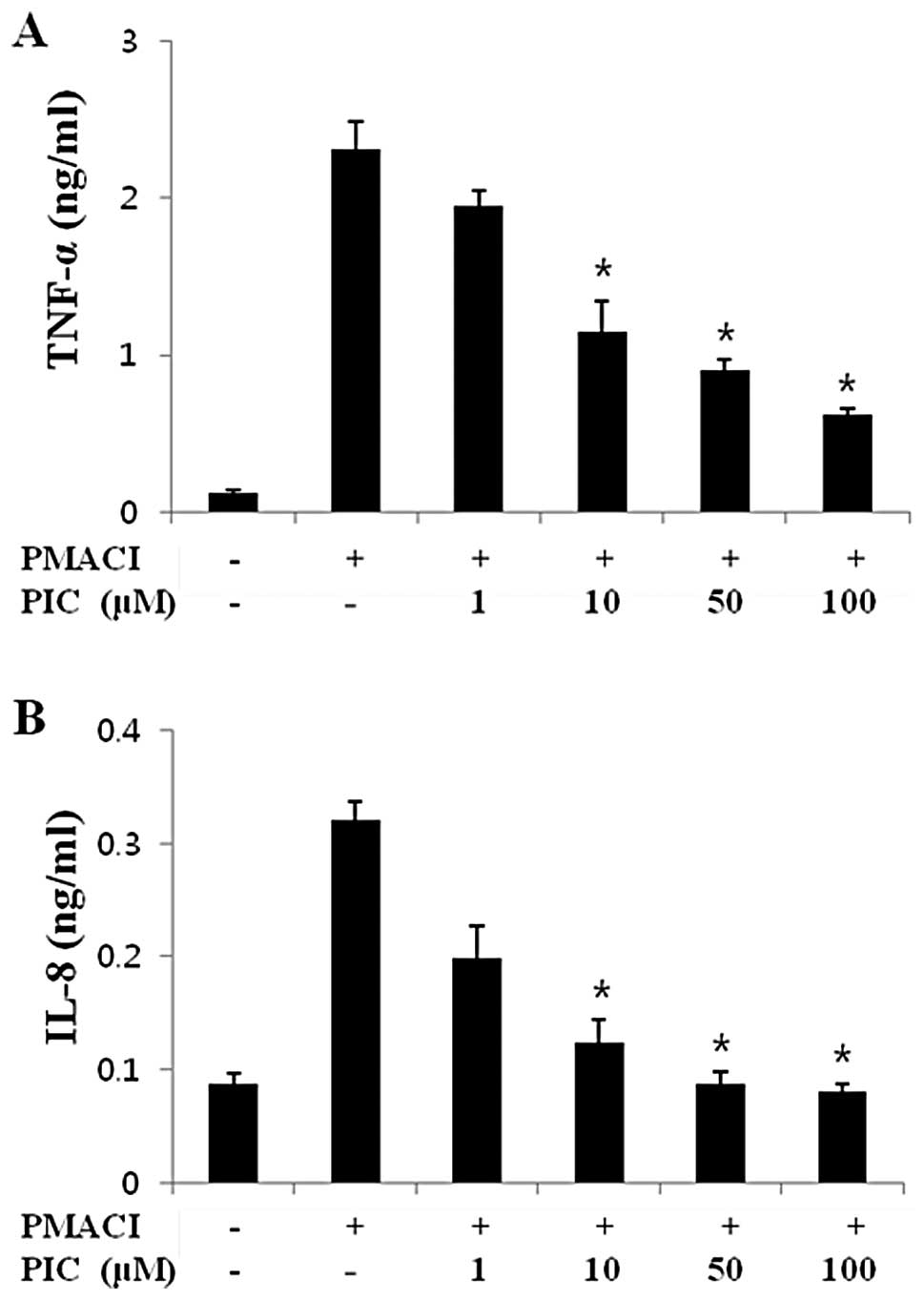
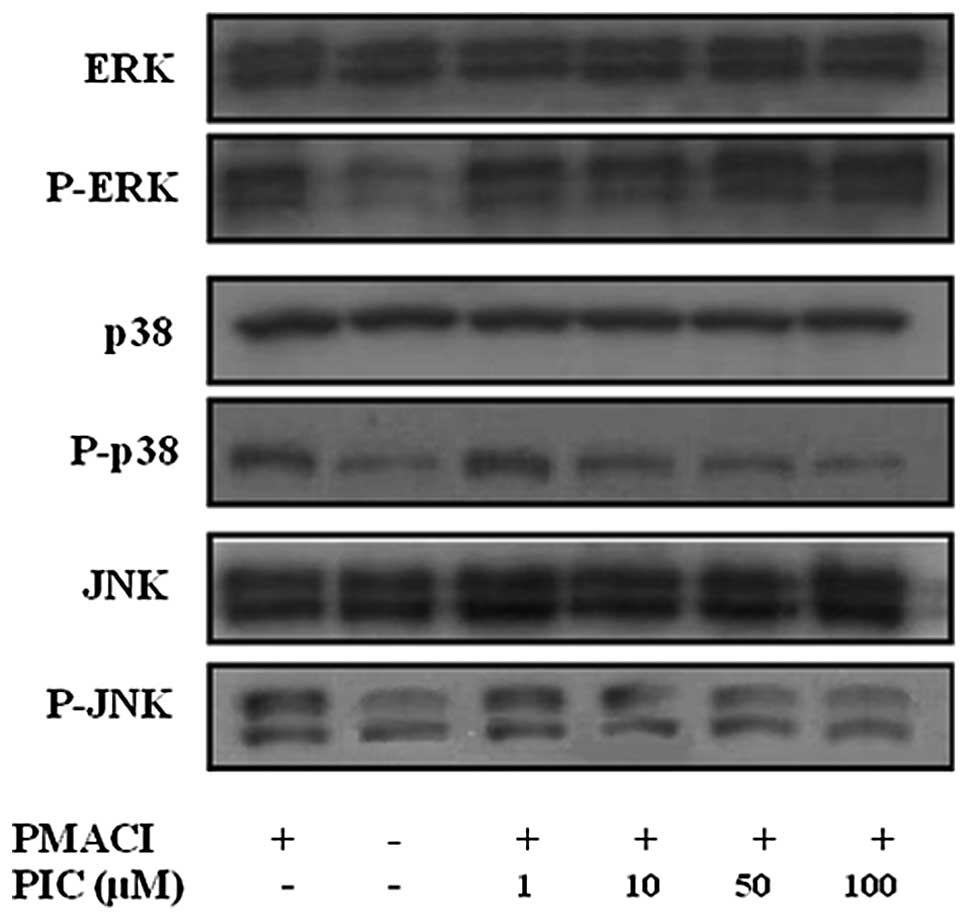
|
1
|
Bhat KPL, Kosmeder JW II and Pezzuto JM:
Biological effects of resveratrol. Antiox Redox Signal.
3:1041–1064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
ElAttar TM and Virji AS: Modulating effect
of resveratrol and quercetin on oral cancer cell growth and
proliferation. Anticancer Drugs. 10:187–193. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kawada N, Seki S, Inoue M and Kuroki T:
Effect of antioxidants, resverarol, quercetin, and
N-acetylcysteine, on the functions of cultured rat hepatic stellate
cells and Kupffer cells. J Hepatol. 27:1265–1274. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wadsworth TL and Koop DR: Effect of wine
polyphenolic quercetin and resveratrol on pro-inflammatory cytokine
expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 57:941–949.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martinez J and Moreno JJ: Effect of
resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on reactive oxygen
species and prostaglandin production. Biochem Pharmacol.
59:865–870. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferrigni NR, McLaughlin JL, Powell RG and
Smith CR Jr: Use of potato disc and brine shrimp bioassays to
detect activity and isolate piceatannol as the antileukemic
principle from the seeds of Euphorbia lagascae. J Nat Prod.
47:347–352. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wieder T, Prokop A, Bagci B, et al:
Piceatannol, a hydroxylated analog of the chemopreventive agent
resveratrol, is a potent inducer of apoptosis in the lymphoma cell
line BJAB and in primary, leukemic lymphoblasts. Leukemia.
15:1735–1742. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Geahlen RL and McLaughlin JL: Piceatannol
(3,4,3′,5′-tetrahydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a naturally
occurring protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 165:241–245. 1989.
|
|
9
|
Cheong H, Ryu SY and Kim KM: Anti-allergic
action of resveratrol and related hydroxystilbenes. Planta Med.
65:266–274. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB activation: a question of life or death. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 35:28–40. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thakkar K, Geahlen RL and Cushman M:
Synthesis and protein tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity of
polyhydroxylated stilbene analogues of piceatannol. J Med Chem.
36:2950–2955. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang BH, Lu ZX and Polya GM: Inhibition of
eukaryote serine/threonine-specific protein kinases by piceatannol.
Planta Med. 64:195–159. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oliver JM, Burg DL, Wilson BS, McLaughlin
JL and Geahlen RL: Inhibition of mast cell FcR1-mediated signaling
and effector function by the syk selective inhibitor, Piceatannol.
J Biol Chem. 269:296–297. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsai SK, Hung LM, Fu YT, et al:
Resveratrol neuroprotective effects during focal cerebral ischemia
injury via nitric oxide mechanism in rats. J Vasc Surg. 46:346–353.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rocha-Gronzălez HI, Ambriz-Tututi M and
Granados-Soto V: Resveratrol: A natural compound with
pharmacological potential in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS
Neurosci Ther. 14:234–247. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, et al: Pulmonary
expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus
hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities,
and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest. 103:779–788. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Royer B, Varadaradjalou S, Saas P, et al:
Autocrine regulation of cord blood-derived human mast cell
activation by IL-10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 108:80–86. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stassen M, Müller C, Arnold M, et al: IL-9
and IL-13 production by activation mast cells is strongly enhanced
in the presence of lipopolysaccharide: NF-kappa B is decisively
involved in the expression of IL-9. J Immunol. 166:4391–4398. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barmes PJ and Adcock I: Anti-inflammatory
actions of steroids: molecular mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
14:436–441. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mukaida N: Interleukin-8: an expanding
universe beyond neutrophil chemotaxis and activation. Int J
Hematol. 72:391–398. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rasmussen H and Goodman DB: Relationships
between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol
Rev. 57:421–509. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
White JR, Pluznik DH, Ishizaka K and
Ishizaka T: Antigen-induced increase in protein kinase C activity
in plasma membranes of mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
82:8193–8197. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim MS, Lim WK, Park RK, et al:
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB
activation in Ca2+ induced IL-8 production in human mast
cells. Cytokine. 32:226–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SH, Kwon TK and Shin TY: Antiallergic
effects of Vitis amurensis on mast cell-mediated allergy
model. Exp Biol Med. 233:192–199. 2008.
|
|
25
|
Kim SH, Park SB, Kang SM, et al:
Anti-allergic effects of Teucrium japonicum on mast
cell-mediated allergy model. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:398–403.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim SH, Lee S, Kim IK, et al: Suppression
of mast cell-mediated allergic reaction by Amomum
xanthiodes. Food Chem Toxicol. 45:2138–2144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang OH, Jang HJ, Chae HS, et al:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of resveratrol in activated HMC-1
cells: pivotal roles of NF-κB and MAPK. Pharmacol Res. 59:330–337.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seow CJ, Chue SC and Wong WS: Piceatannol,
a syk-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, attenuated antigen
challenge of guinea pig airway in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol.
443:189–196. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park HH, Lee SY, Son HY, et al: Flavonoids
inhibit histamine release and expression of proinflammatory
cytokine in mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:1303–1311. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kemp SF and Lockey RF: Anaphylaxis: a
review of causes and mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
110:341–348. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jutel M, Blaser K and Akdis CA: Histamine
in allergic inflammation and immune modulation. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 137:82–92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jutel M, Watanabe T, Akdis M, Blaser K and
Akdis CA: Immune regulation by histamine. Curr Opin Immunol.
14:735–740. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsuda H, Tewtrakul S, Morikawa T and
Yoshikawa M: Anti-allergic activity of stilbenes from Korean
rhubarb (Rheum undulatum L.): structure requirements for
inhibition of antigen-induced degranulation and their effects on
the release of TNF-alpha and IL-4 in RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med
Chem. 12:4871–4876. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu ZQ, Zhao WH and Shimamura T: Regulation
of mast cell development by inflammatory factors. Curr Med Chem.
14:3044–3050. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA,
Piliponsky AM, Williams CM and Tsai M: Mast cells as ‘tunable’
effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:749–786. 2005.
|
|
36
|
Hu ZQ, Kobayashi K, Zenda N and Shimamura
T: Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 triggered mast
cell development from mouse spleen cells. Blood. 89:526–533.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burd PR, Rogers HW, Gordon JR, et al:
Interleukin 3-dependent and independent mast cells stimulated with
IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines. J Exp Med. 170:245–257.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arbabi S and Maier RV: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases. Crit Care Med. 30:S74–S79. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ashikawa K, Majumdar S, Banerjee S, Bharti
AC, Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Piceatannol inhibits TNF-induced
NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-mediated gene expression through
suppression of IkappaBalpha kinase and p65 phosphorylation. J
Immunol. 169:6490–6497. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|