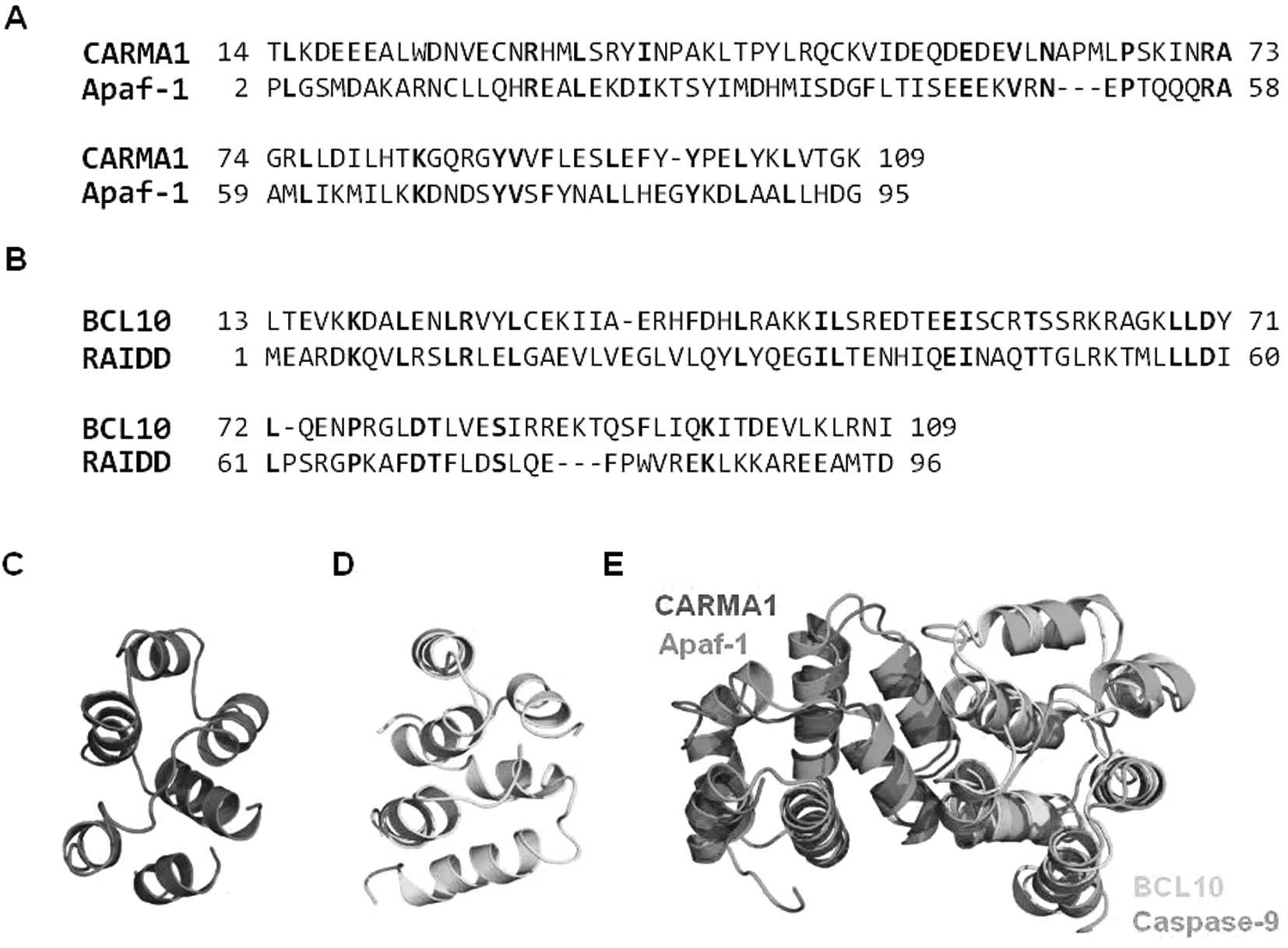
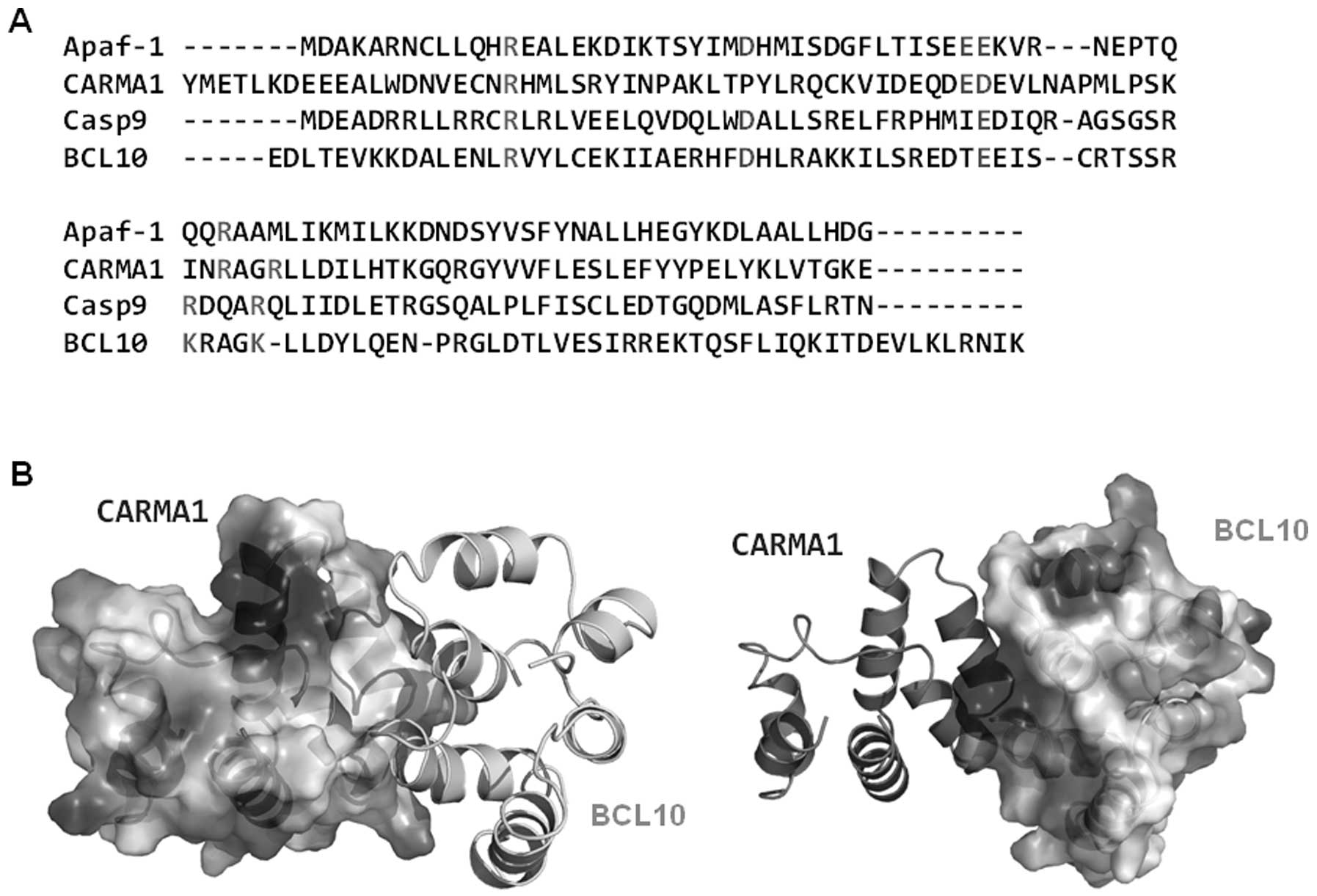
|
1
|
Li Q and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thome M: CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in
lymphocyte development and activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:348–359.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bertin J, Wang L, Guo Y, et al: CARD11 and
CARD14 are novel caspase recruitment domain
(CARD)/membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family members
that interact with BCL10 and activate NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem.
276:11877–11882. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gaide O, Martinon F, Micheau O, Bonnet D,
Thome M and Tschopp J: Carma1, a CARD-containing binding partner of
Bcl10, induces Bcl10 phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. FEBS
Lett. 496:121–127. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park HH, Lo YC, Lin SC, Wang L, Yang JK
and Wu H: The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling
of apoptosis and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:561–586. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weber CH and Vincenz C: The death domain
superfamily: a tale of two interfaces? Trends Biochem Sci.
26:475–481. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reed JC, Doctor KS and Godzik A: The
domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE.
2004:re92004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park HH, Logette E, Rauser S, et al: Death
domain assembly mechanism revealed by crystal structure of the
oligomeric PIDDosome core complex. Cell. 128:533–546. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou H, Wertz I, O’Rourke K, et al: Bcl10
activates the NF-kappaB pathway through ubiquitination of NEMO.
Nature. 427:167–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oeckinghaus A, Wegener E, Welteke V, et
al: Malt1 ubiquitination triggers NF-kappaB signaling upon T-cell
activation. EMBO J. 26:4634–4645. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rebeaud F, Hailfinger S, Posevitz-Fejfar
A, et al: The proteolytic activity of the paracaspase MALT1 is key
in T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 9:272–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Coornaert B, Baens M, Heyninck K, et al: T
cell antigen receptor stimulation induces MALT1
paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor A20. Nat
Immunol. 9:263–271. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uren AG, O’Rourke K, Aravind LA, et al:
Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient
families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in
MALT lymphoma. Mol Cell. 6:961–967. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lucas PC, Yonezumi M, Inohara N, et al:
Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation
in malt lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-kappa B signaling
pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:19012–19019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Z, Arendt CW, Ellmeier W, et al:
PKC-theta is required for TCR-induced NF-kappaB activation in
mature but not immature T lymphocytes. Nature. 404:402–407. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsumoto R, Wang D, Blonska M, et al:
Phosphorylation of CARMA1 plays a critical role in T cell
receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Immunity. 23:575–585. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang B, Eberstadt M, Olejniczak ET,
Meadows RP and Fesik SW: NMR structure and mutagenesis of the Fas
(APO-1/CD95) death domain. Nature. 384:638–641. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jang TH and Park HH: Purification,
crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of
RAIDD Death-Domain (DD). Int J Mol Sci. 10:2501–2509. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeong EJ, Bang S, Lee TH, Park YI, Sim WS
and Kim KS: The solution structure of FADD death domain. Structural
basis of death domain interactions of Fas and FADD. J Biol Chem.
274:16337–16342. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jang TH and Park HH: Generalized
semi-refolding methods for purification of the functional death
domain superfamily. J Biotechnol. 151:335–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YH, Yang JT and Martinez HM:
Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular
dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry.
11:4120–4131. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N and Peitsch MC:
SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic
Acids Res. 31:3381–3385. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW,
Kaptein R and Thornton JM: AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for
checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol
NMR. 8:477–486. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bae JY and Park HH: Crystal structure of
NALP3 protein pyrin domain (PYD) and its implications in
inflammasome assembly. J Biol Chem. 286:39528–39536. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bae JY and Park HH: Crystallization and
preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the PYD domain of
human NALP3. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun.
67:1421–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park HH: Structural analyses of death
domains and their interactions. Apoptosis. 16:209–220. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wegener E and Krappmann D:
CARD-Bcl10-Malt1 signalosomes: missing link to NF-kappaB. Sci STKE.
2007:pe212007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu Y, Song R, Gao Y, et al: Protein
kinase C-delta negatively regulates T cell receptor-induced
NF-kappaB activation by inhibiting the assembly of CARMA1
signalosome. J Biol Chem. 287:20081–20087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park HH: Structural features of
caspase-activating complexes. Int J Mol Sci. 13:4807–4818. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferrao R and Wu H: Helical assembly in the
death domain (DD) superfamily. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 22:241–247.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|