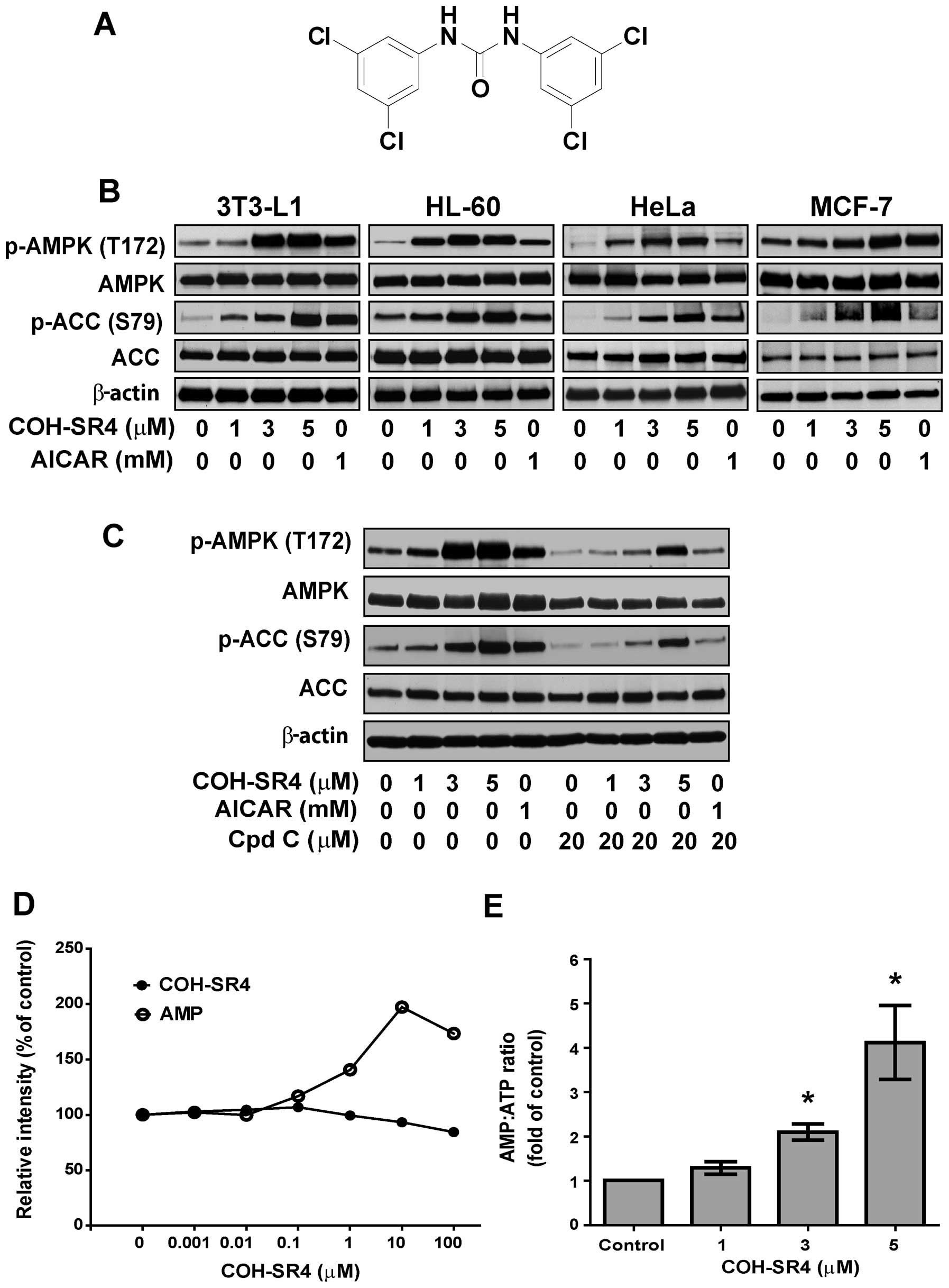
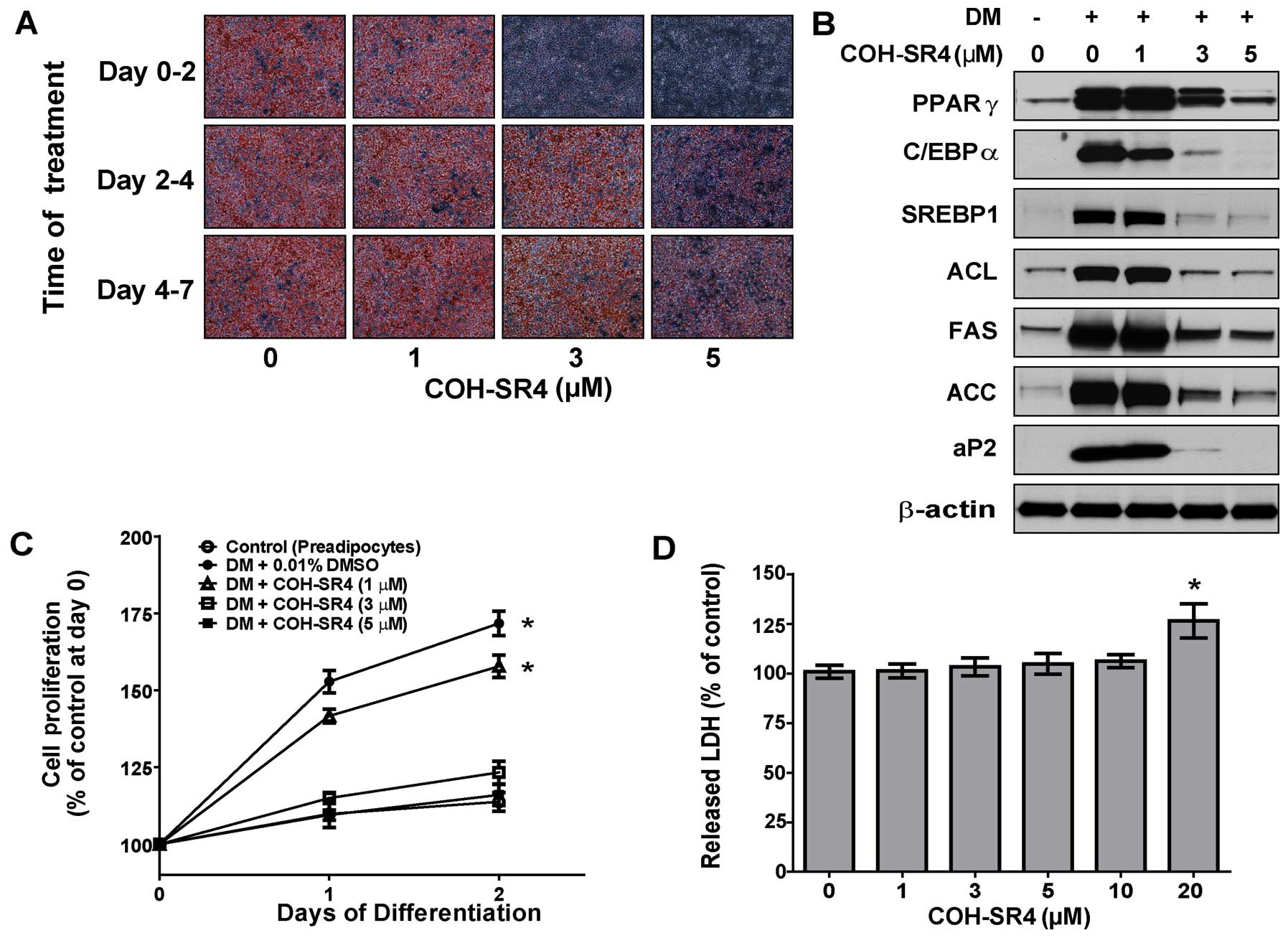
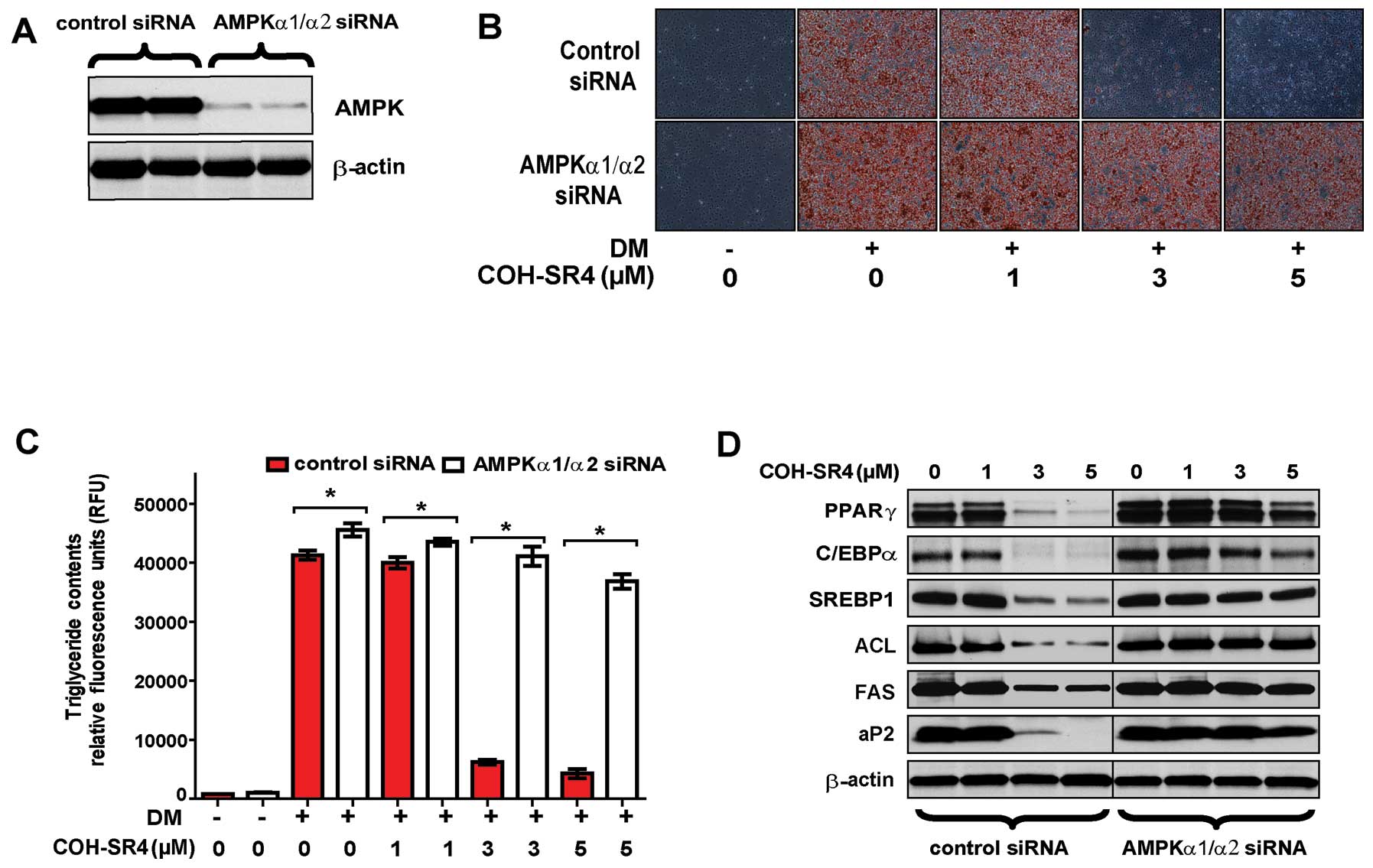
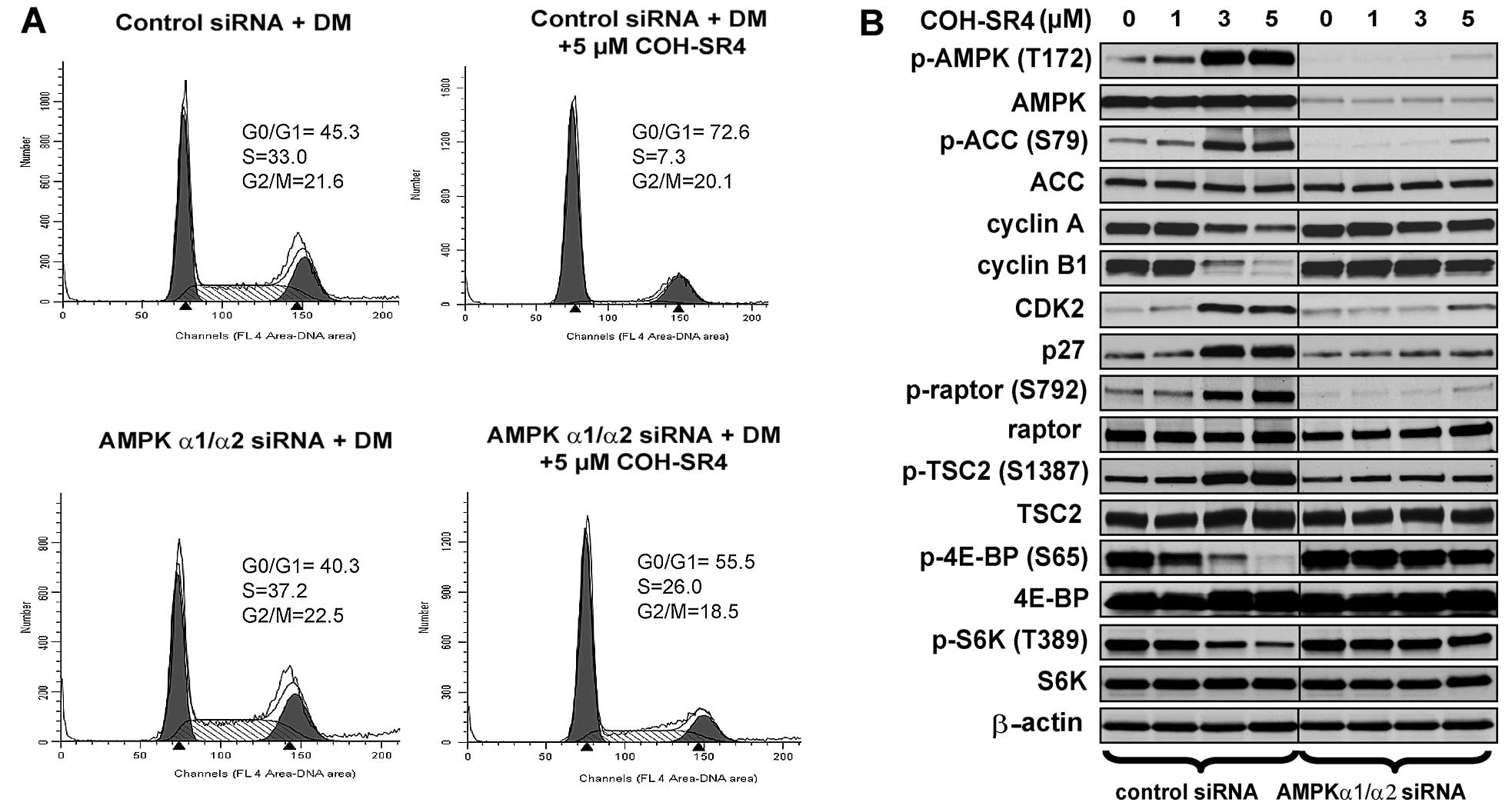
|
1
|
Grundy SM: Obesity, metabolic syndrome,
and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:2595–2600.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khandekar MJ, Cohen P and Spiegelman BM:
Molecular mechanisms of cancer development in obesity. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:886–895. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jo J, Gavrilova O, Pack S, Jou W, Mullen
S, Sumner AE, Cushman SW and Periwal V: Hypertrophy and/or
hyperplasia: dynamics of adipose tissue growth. PLoS Comput Biol.
5:e10003242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pilch PF and Bergenhem N: Pharmacological
targeting of adipocytes/fat metabolism for treatment of obesity and
diabetes. Mol Pharmacol. 70:779–785. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosen ED and MacDougald OA: Adipocyte
differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
7:885–896. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lowe CE, O’Rahilly S and Rochford JJ:
Adipogenesis at a glance. J Cell Sci. 124:2681–2686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang QQ, Otto TC and Lane MD: Mitotic
clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:44–49. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fajas L: Adipogenesis: a cross-talk
between cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Ann Med.
35:79–85. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farmer SR: Transcriptional control of
adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 4:263–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated protein kinase:
an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes
Dev. 25:1895–1908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carling D, Mayer FV, Sanders MJ and
Gamblin SJ: AMP-activated protein kinase: nature’s energy sensor.
Nat Chem Biol. 7:512–518. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Villena JA, Viollet B, Andreelli F, Kahn
A, Vaulont S and Sul HS: Induced adiposity and adipocyte
hypertrophy in mice lacking the AMP-activated protein kinase-alpha2
subunit. Diabetes. 53:2242–2249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang W, Zhang X, Wang H, et al:
AMP-activated protein kinase α1 protects against diet-induced
insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes. 61:3114–3125. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Habinowski SA and Witters LA: The effects
of AICAR on adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 286:852–856. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Giri S, Rattan R, Haq E, Khan M, Yasmin R,
Won JS, Key L, Singh AK and Singh I: AICAR inhibits adipocyte
differentiation in 3T3L1 and restores metabolic alterations in
diet-induced obesity mice model. Nutr Metab. 3:312006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Y, Wang D, Zhu Q, Gao X, Yang S, Xu A
and Wu D: Inhibitory effects of A-769662, a novel activator of
AMP-activated protein kinase, on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 32:993–998. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vingtdeux V, Chandakkar P, Zhao H, Davies
P and Marambaud P: Small-molecule activators of AMP-activated
protein kinase (AMPK), RSVA314 and RSVA405, inhibit adipogenesis.
Mol Med. 17:1022–1030. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Figarola JL, Weng Y, Lincoln C, Horne D
and Rahbar S: Novel dichlorophenyl urea compounds inhibit
proliferation of human leukemia HL-60 cells by inducing cell cycle
arrest, differentiation and apoptosis. Invest New Drugs.
30:1413–1425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Singhal SS, Figarola J, Singhal J, et al:
1,3-Bis(3,5-dichlorophenyl) urea compound ‘COH-SR4′ inhibits
proliferation and activates apoptosis in melanoma. Biochem
Pharmacol. 84:1419–1427. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fingar DC, Richardson CJ, Tee AR, Cheatham
L, Tsou C and Blenis J: mTOR controls cell cycle progression
through its cell growth effectors S6K1 and 4E-BP1/eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biol. 24:200–216. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zoncu R, Efeyan A and Sabatini DM: mTOR:
from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:21–35. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF,
Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, Turk BE and Shaw RJ: AMPK
phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol
Cell. 30:214–226. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inoki K, Zhu T and Guan KL: TSC2 mediates
cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell.
115:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fogarty S and Hardie DG: Development of
protein kinase activators: AMPK as a target in metabolic disorders
and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:581–591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:763–777. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hardie DG: Sensing of energy and nutrients
by AMP-activated protein kinase. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:891S–896S.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qiu BY, Turner N, Li YY, et al:
High-throughput assay for modulators of mitochondrial membrane
potential identifies a novel compound with beneficial effects on
db/db mice. Diabetes. 59:256–265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Li Z, Li W, Shan Z and Zhu W:
Resveratrol inhibits cell differentiation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via
activation of AMPK. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 89:793–799.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, et al: Berberine,
a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase
with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant
states. Diabetes. 55:2256–2264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Singh AK and Singh I:
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside inhibits
cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via AMP-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:39582–39593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Inoki K, Kim J and Guan KL: AMPK and mTOR
in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 52:381–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: An emerging
role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr Biol. 19:R1046–R1052.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Polak P, Cybulski N, Feige JN, Auwerx J,
Rüegg MA and Hall MN: Adipose-specific knockout of raptor results
in lean mice with enhanced mitochondrial respiration. Cell Metab.
8:399–410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang HH, Huang J, Düvel K, et al: Insulin
stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS
One. 4:e61892009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dowling RJ, Topisirovic I, Alain T, et al:
mTORC1-mediated cell proliferation, but not cell growth, controlled
by the 4E-BPs. Science. 328:1172–1176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Skrabanek L,
Ruiz-Gutierrez M and Borden KL: eIF4E is a central node of an RNA
regulon that governs cellular proliferation. J Cell Biol.
175:415–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Calkhoven CF, Muller C and Leutz A:
Translational control of C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta isoform
expression. Genes Dev. 14:1920–1932. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rosen ED, Hsu C-H, Wang X, Sakai S,
Freeman MW, Gonzalez FJ and Spiegelman BM: C/EBPalpha induces
adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway. Genes Dev.
16:22–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yeh WC, Bierer BE and McKnight SL:
Rapamycin inhibits clonal expansion and adipogenic differentiation
of 3T3-L1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:11086–11090. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hashemolhosseini S, Nagamine Y, Morley SJ,
Desrivières S, Mercep L and Ferrari S: Rapamycin inhibition of the
G1 to S transition is mediated by effects on cyclin D1 mRNA and
protein stability. J Biol Chem. 273:14424–14429. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cho HJ, Park J, Lee HW, Lee YS and Kim JB:
Regulation of adipocyte differentiation and insulin action with
rapamycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 321:942–948. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
El-Chaar D, Gagnon A and Sorisky A:
Inhibition of insulin signaling and adipogenesis by rapamycin:
effect on phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase vs eIF4E-BP1. Int J Obes
Relat Metab Disord. 28:191–198. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kimura N, Tokunaga C, Dalal S, et al: A
possible linkage between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway. Genes
Cells. 8:65–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chiang PC, Lin SC, Pan SL, Kuo CH, et al:
Antroquinonol displays anticancer potential against human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: a crucial role of AMPK and mTOR
pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:162–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kalender A, Selvaraj A, Kim SY, et al:
Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag
GTPase-dependent manner. Cell Metab. 11:390–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|