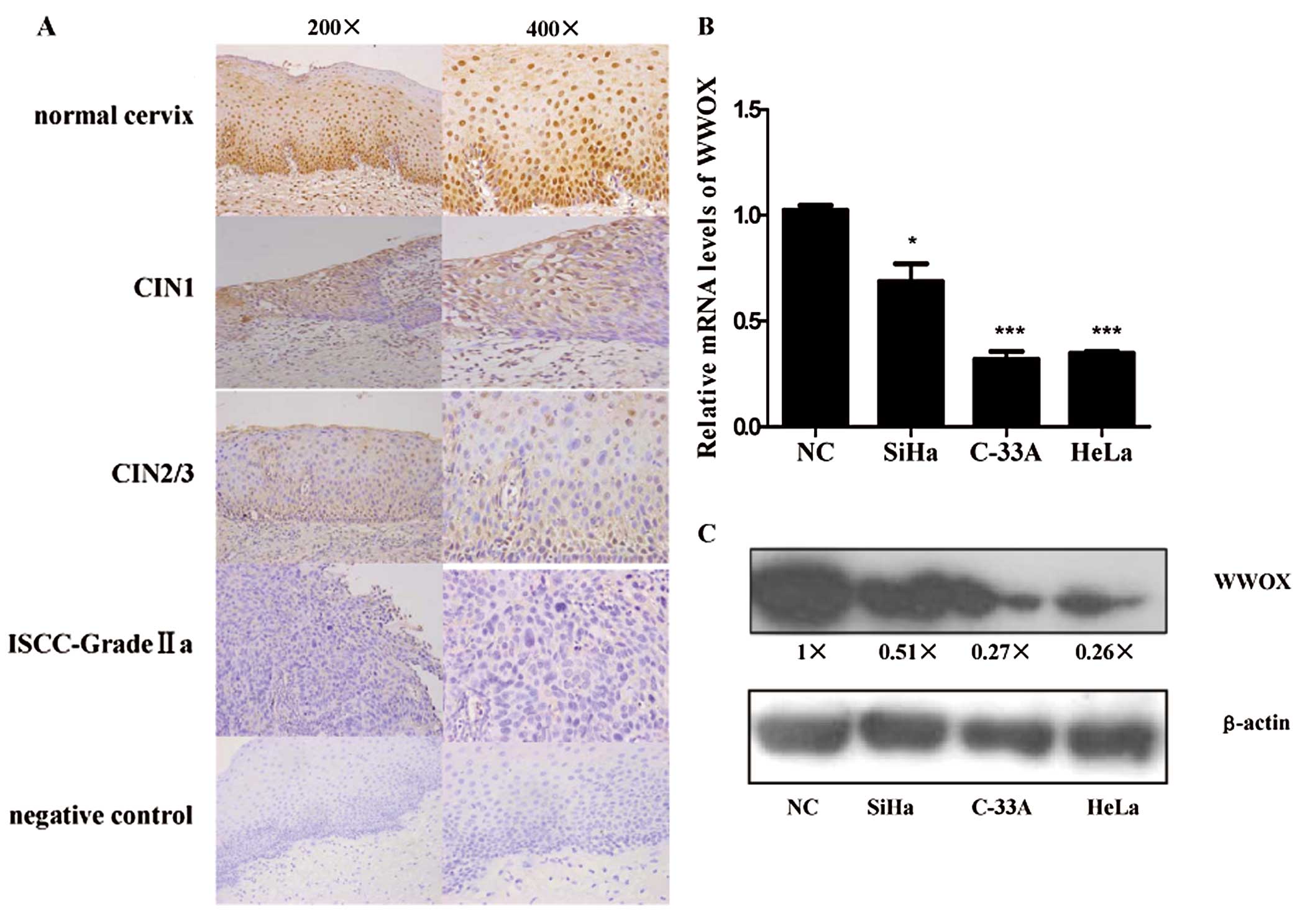
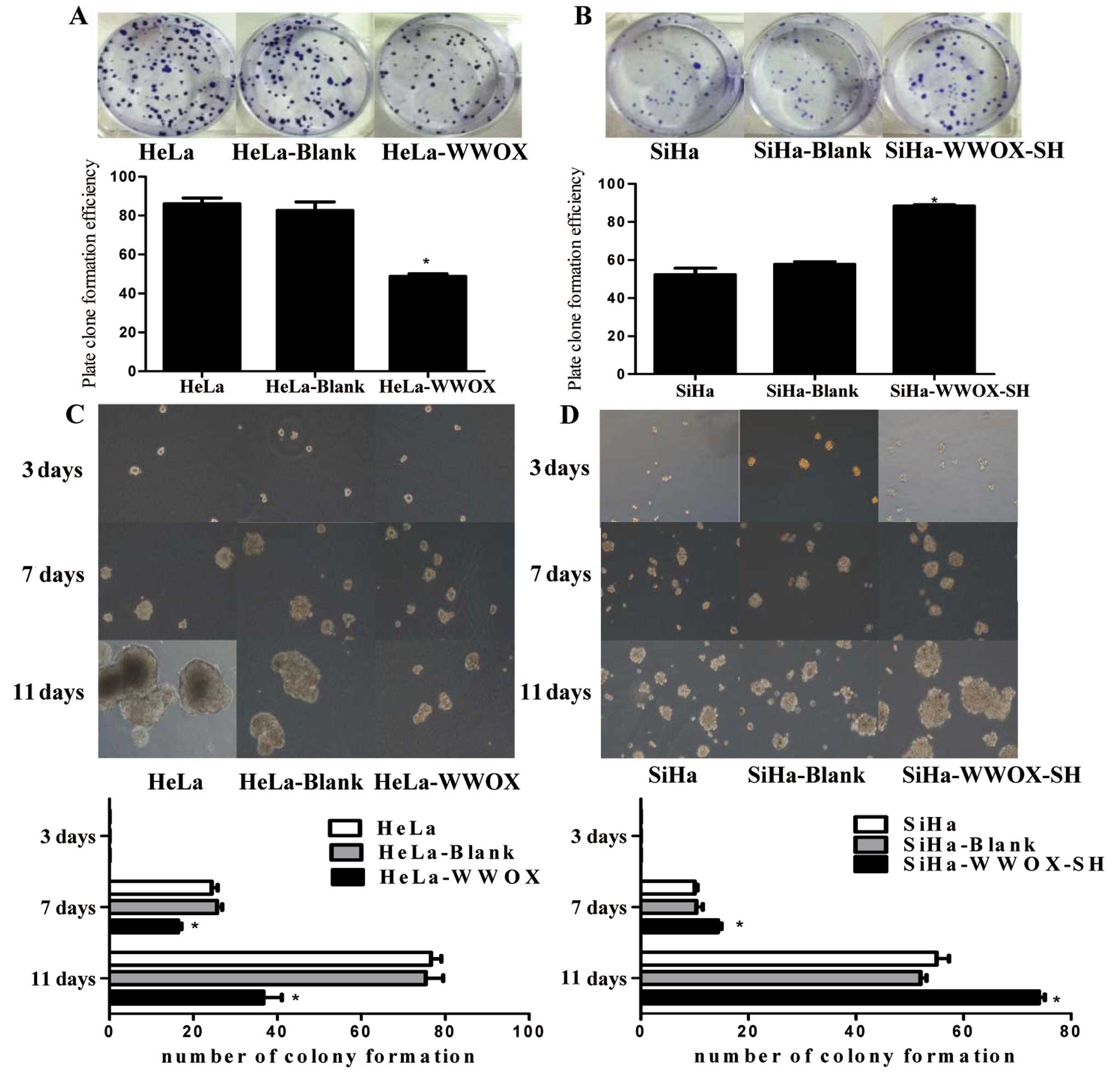
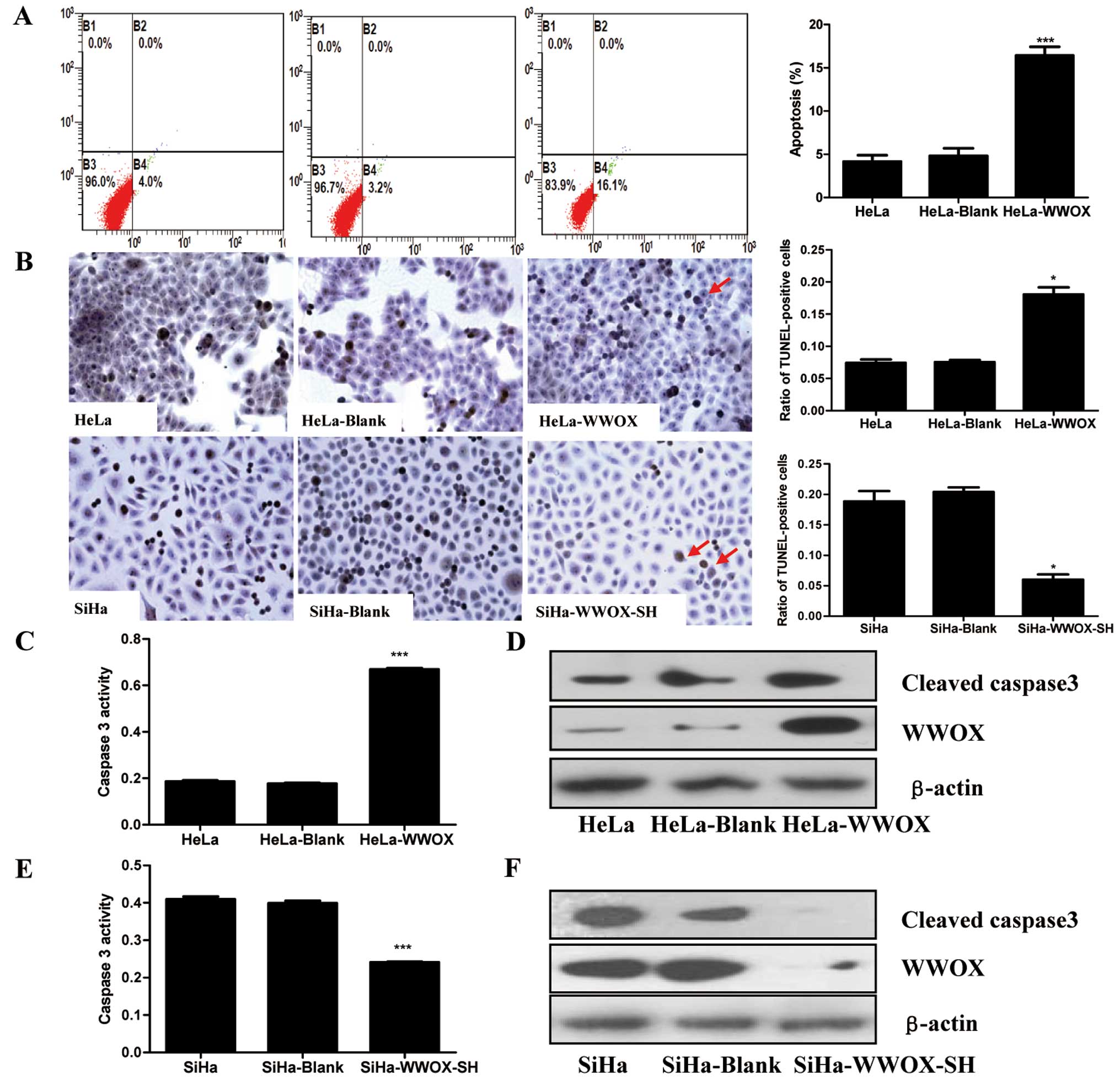
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mayrand MH, Duarte-Franco E, Rodrigues I,
et al: Human papillomavirus DNA versus Papanicolaou screening tests
for cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 357:1579–1588. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kent A: HPV vaccination and testing. Rev
Obstet Gynecol. 3:33–34. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Chen J, Zhang W, Hong W and Yu F:
Study of the prevalence of human Papillomavirus infection in
Chinese women with cervical cancer. Afr J Microbiol Res.
6:1048–1053. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Aleyamma M and Preethi SG: Trends in
incidence and mortality rates of squamous cell carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma of cervix - worldwide. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
10:645–650. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Misson DR, Abdalla DR, Borges AM, et al:
Cytokine serum levels in patients with cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia grade II-III treated with intralesional interferon-α 2b.
Tumori. 97:578–584. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bednarek AK, Laflin KJ, Daniel RL, Liao Q,
Hawkins KA and Aldaz CM: WWOX, a novel WW domain-containing protein
mapping to human chromosome 16q23.3-24.1, a region frequently
affected in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 60:2140–2145. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Del Mare S, Salah Z and Aqeilan RI: WWOX:
its genomics, partners, and functions. J Cell Biochem. 108:737–745.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aqeilan RI, Hagan JP, de Bruin A, et al:
Targeted ablation of the WW domain-containing oxidoreductase tumor
suppressor leads to impaired steroidogenesis. Endocrinology.
150:1530–1535. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hsu LJ, Schultz L, Hong Q, et al:
Transforming growth factor beta1 signaling via interaction with
cell surface Hyal-2 and recruitment of WWOX/WOX1. J Biol Chem.
284:16049–16059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aqeilan RI, Pekarsky Y, Herrero JJ, et al:
Functional association between Wwox tumor suppressor protein and
p73, a p53 homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4401–4406. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gaudio E, Palamarchuk A, Palumbo T, et al:
Physical association with WWOX suppresses c-Jun transcriptional
activity. Cancer Res. 66:11585–11589. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li MY, Lai FJ, Hsu LJ, et al: Dramatic
co-activation of WWOX/WOX1 with CREB and NF-kappaB in delayed loss
of small dorsal root ganglion neurons upon sciatic nerve
transection in rats. PLoS One. 4:e78202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo W, Wang G, Dong Y, Guo Y, Kuang G and
Dong Z: Decreased expression of WWOX in the development of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. Dec 27–2011.(Epub
ahead of print). View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Maeda N, Semba S, Nakayama S, Yanagihara K
and Yokozaki H: Loss of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase
expression in the progression and development of gastric carcinoma:
clinical and histopathologic correlations. Virchows Arch.
457:423–432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kuroki T, Yendamuri S, Trapasso F, et al:
The tumor suppressor gene WWOX at FRA16D is involved in pancreatic
carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2459–2465. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Donati V, Fontanini G, Dell’Omodarme M, et
al: WWOX expression in different histologic types and subtypes of
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:884–891. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Giarnieri E, Zanesi N, Bottoni A, et al:
Oncosuppressor proteins of fragile sites are reduced in cervical
cancer. Cancer Lett. 289:40–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guler G, Uner A, Guler N, et al: The
fragile genes FHIT and WWOX are inactivated coordinately in
invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 100:1605–1614. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kurek KC, Del Mare S, Salah Z, et al:
Frequent attenuation of the WWOX tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma
is associated with increased tumorigenicity and aberrant RUNX2
expression. Cancer Res. 70:5577–5586. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Evan G and Littlewood T: A matter of life
and cell death. Science. 281:1317–1322. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arnoult D, Gaume B, Karbowski M, Sharpe
JC, Cecconi F and Youle RJ: Mitochondrial release of AIF and EndoG
requires caspase activation downstream of Bax/Bak-mediated
permeabilization. EMBO J. 22:4385–4399. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R and
Wang X: Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts:
requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 86:147–157. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A and
Wang X: Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans
CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of
caspase-3. Cell. 90:405–413. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu BS, Tan JW, Zhu GH, Wang DF, Zhou X and
Sun ZQ: WWOX induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of human
hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721. World J Gastroenterol. 18:3020–3026.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang P, Jia R, Ying L, et al:
WWOX-mediated apoptosis in A549 cells mainly involves the
mitochondrial pathway. Mol Med Rep. 6:121–124. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chiang MF, Yeh ST, Liao HF, Chang NS and
Chen YJ: Overexpression of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase WOX1
preferentially induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells
harboring mutant p53. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:433–438. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Finnis M, Dayan S, Hobson L, et al: Common
chromosomal fragile site FRA16D mutation in cancer cells. Hum Mol
Genet. 14:1341–1349. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jee KJ, Kim YT, Kim KR, Aalto Y and
Knuutila S: Amplification at 9p in cervical carcinoma by
comparative genomic hybridization. Anal Cell Pathol. 22:159–163.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tsuda H, Takarabe T, Okada S, et al:
Different pattern of loss of heterozygosity among endocervical-type
adenocarcinoma, endometrioid-type adenocarcinoma and adenoma
malignum of the uterine cervix. Int J Cancer. 98:713–717. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cullen AP, Reid R, Campion M and Lörincz
AT: Analysis of the physical state of different human
papillomavirus DNAs in intraepithelial and invasive cervical
neoplasm. J Virol. 65:606–612. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hopman AH, Smedts F, Dignef W, et al:
Transition of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia to
micro-invasive carcinoma is characterized by integration of HPV
16/18 and numerical chromosome abnormalities. J Pathol. 202:23–33.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Crook T, Wrede D, Tidy JA, Mason WP, Evans
DJ and Vousden KH: Clonal p53 mutation in primary cervical cancer:
association with human-papillomavirus-negative tumours. Lancet.
339:1070–1073. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|