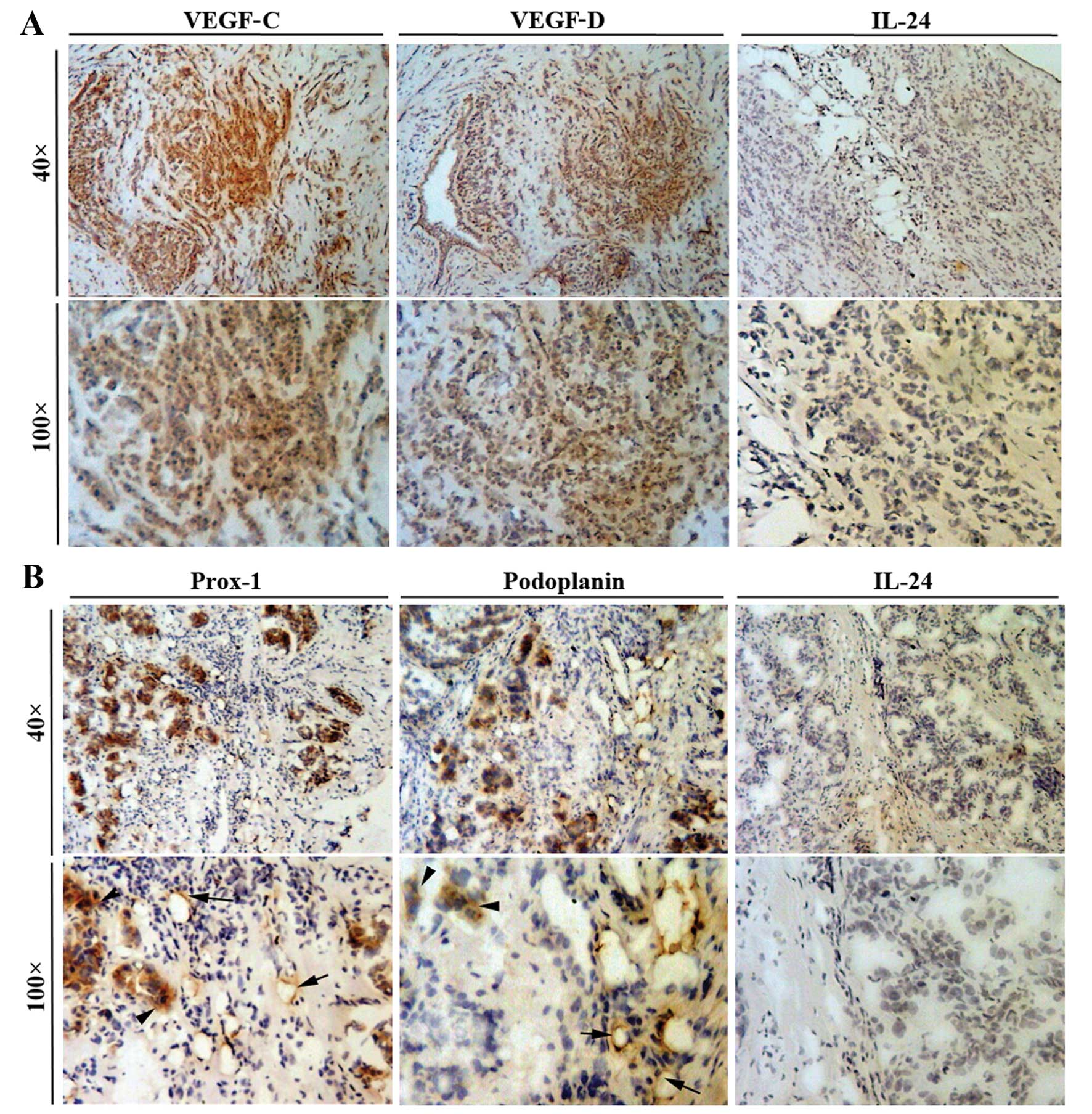
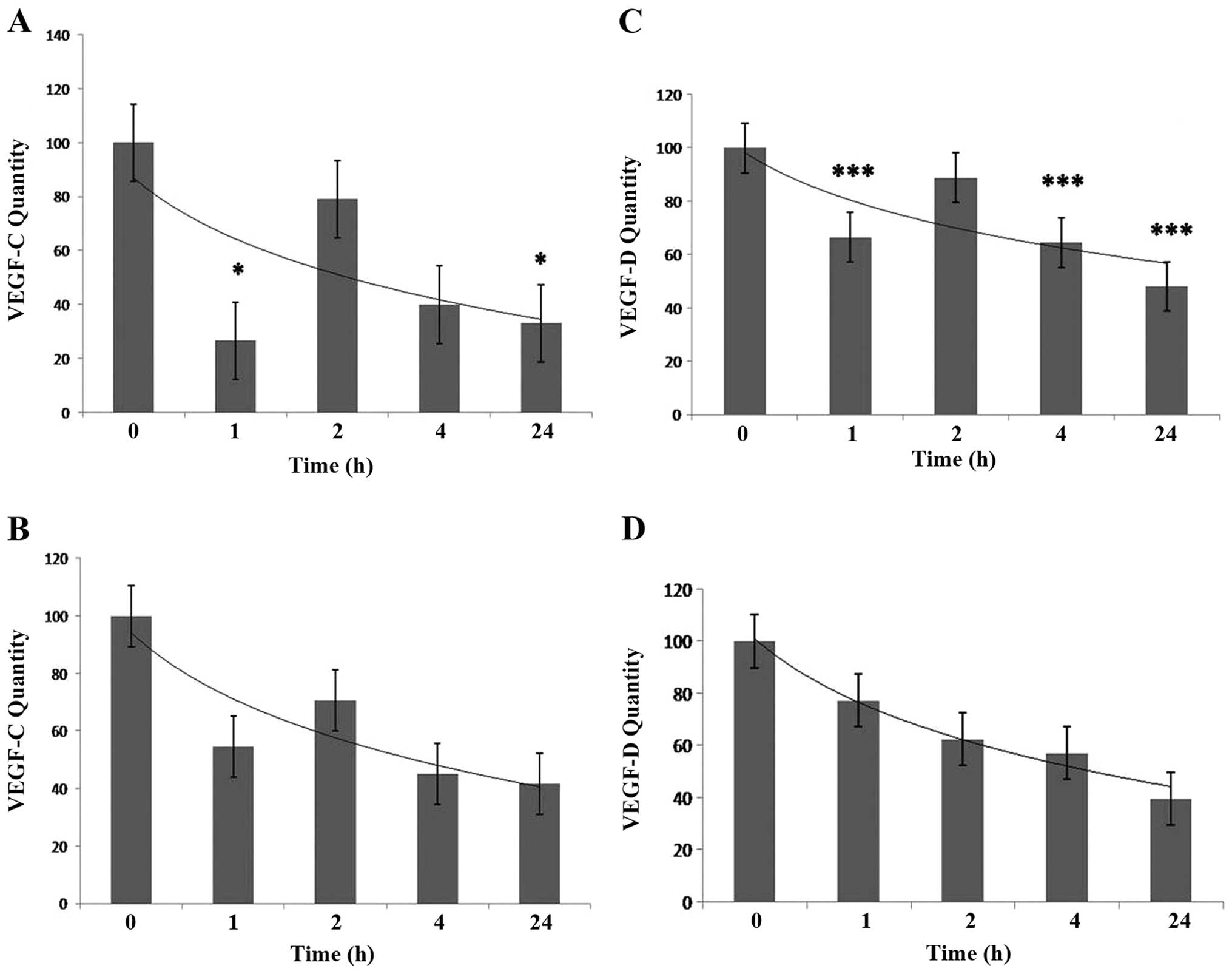
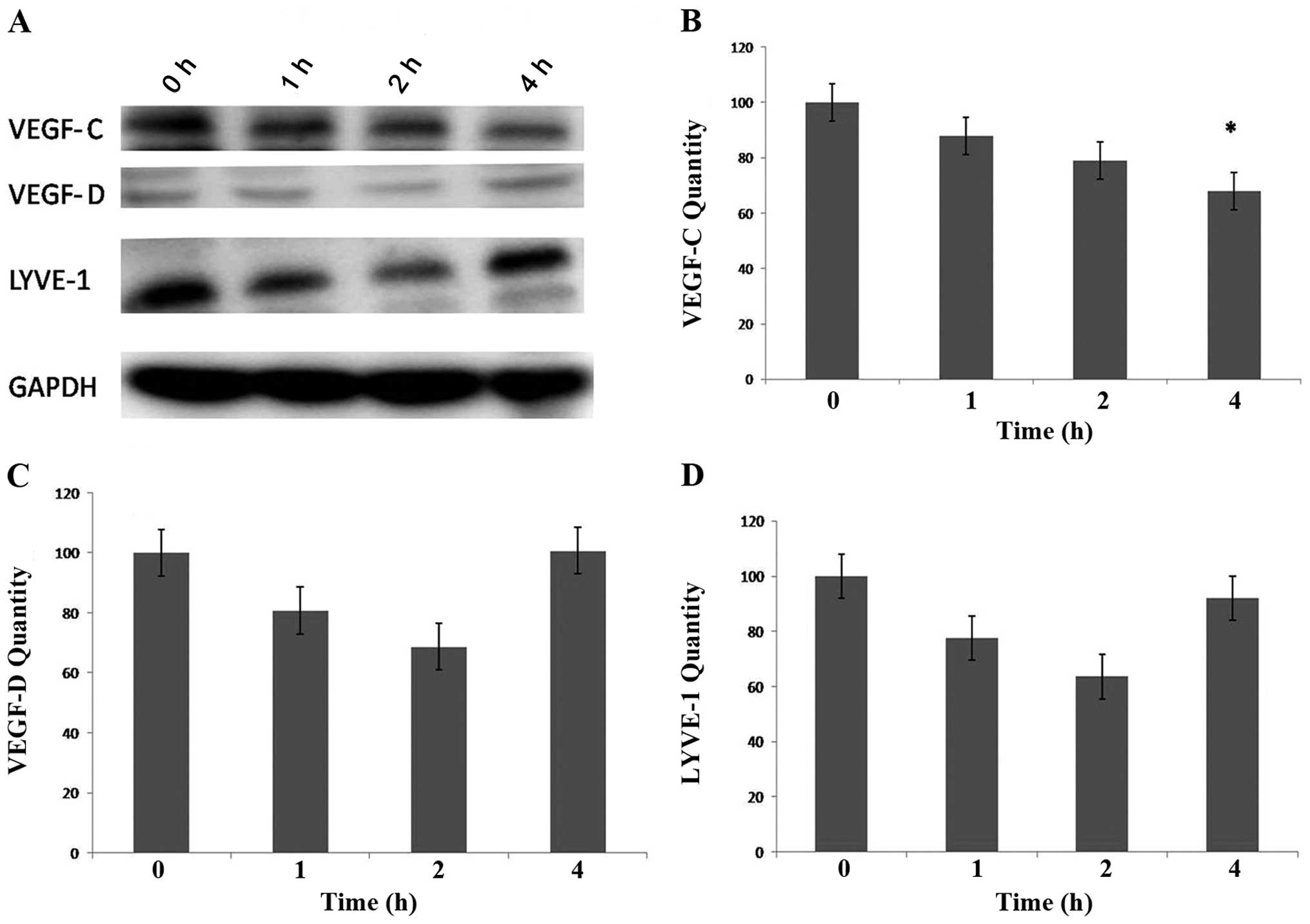
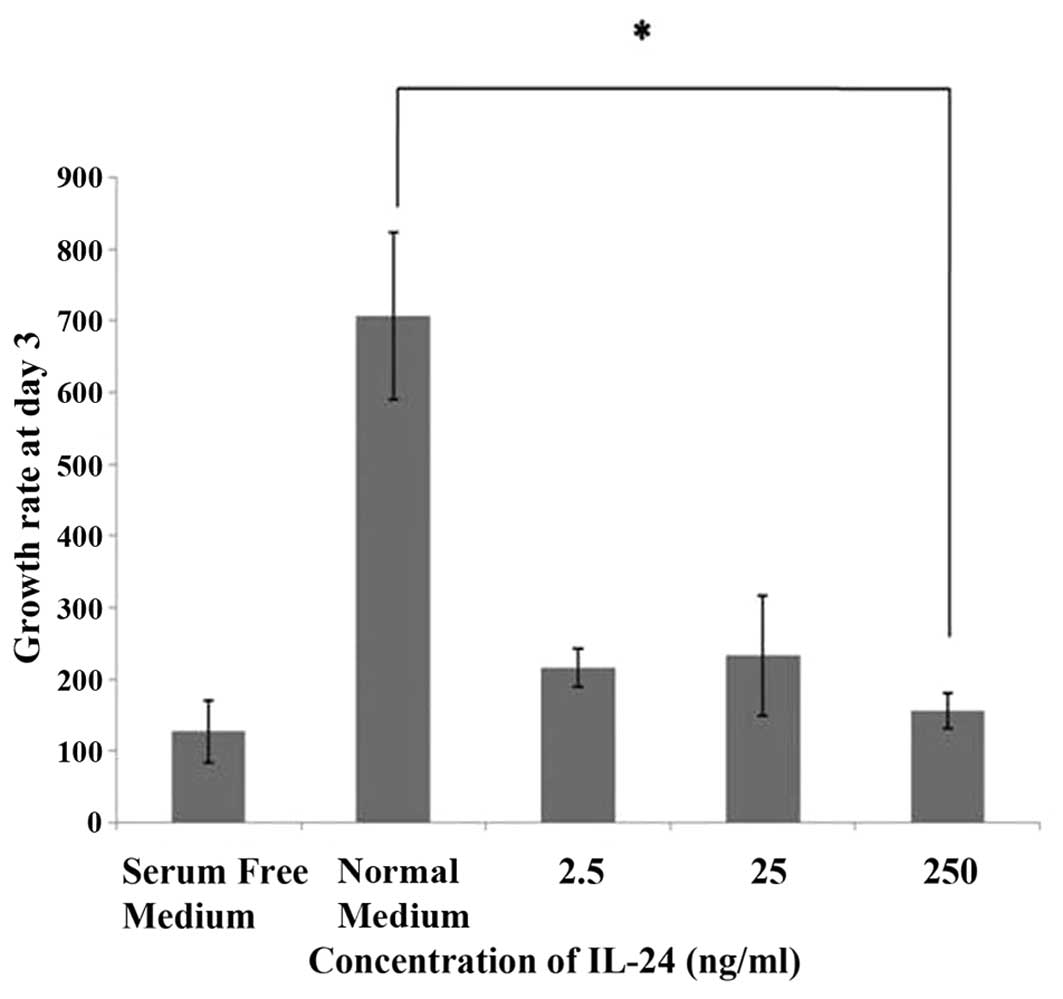
|
1
|
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo
R, Janes L, Velasco P, Riccardi L, Alitalo K, Claffey K and Detmar
M: Induction of tumour lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast
cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 7:192–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Rawi MA and Jiang WG: Lymphangiogenesis
and cancer metastasis. Front Biosci. 16:723–739. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weninger W, Partanen TA,
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Mayer C, Kowalski H, Mildner M, Pammer J,
Stürzl M, Kerjaschki D, Alitalo K and Tschachler E: Expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and podoplanin
suggests a lymphatic endothelial cell origin of Kaposi’s sarcoma
tumor cells. Lab Invest. 79:243–251. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wigle JT and Oliver G: Prox1 function is
required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell.
98:769–778. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M,
Compagni A, Baetens D, Prevo R, Banerji S, Huarte J, Montesano R,
Jackson DJ, Orc L, Alitalo K, Christofori G and Pepper MS: Vascular
endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes
tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 20:672–682. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi WW, Lewis MM, Lawson D, Yin-Goen Q,
Birdsong GG, Cotsonis GA, Cohen C and Young AN: Angiogenic and
lymphangiogenic microvessel density in breast carcinoma:
correlation with clinicopathologic parameters and VEGF-family gene
expression. Mod Pathol. 18:143–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lee SK, Cho EY, Kim WW, Kim S, Hur SM, Kim
S, Choe JH, Kim JH, Kim JS, Lee JE, Nam SJ and Yang JH: The
prediction of lymph node metastasis in ductal carcinoma in situ
with microinvasion by assessing lymphangiogenesis. J Surg Oncol.
102:225–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bono P, Wasenius VM, Heikkilä P, Lundin J,
Jackson DG and Joensuu H: High LYVE-1-positive lymphatic vessel
numbers are associated with poor outcome in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:7144–7149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Imabun
S, Nakahara M, Nakao K, Nakamura M, Mori I and Kakudo K: Lymph
vessel density correlates with nodal status, VEGF-C expression, and
prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 91:125–132.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stacker SA, Achen MG, Jussila L, Baldwin
ME and Alitalo K: Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:573–583. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kinoshita J, Kitamura K, Kabashima A,
Saeki H, Tanaka S and Sugimachi K: Clinical significance of
vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 66:159–164. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cunnick GH, Jiang WG, Douglas-Jones T,
Watkins G, Gomez KF, Morgan MJ, Subramanian A, Mokbel K and Mansel
RE: Lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.
Mol Cancer. 7:232008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weidner N: Tumour vascularity and
proliferation: clear evidence of a close relationship. J Pathol.
189:297–299. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Van den Eynden GG, Van der Auwera I, Van
Laere SJ, Huygelen V, Colpaert CG, van Dam P, Dirix LY, Vermeulen
PB and Van Marck EA: Induction of lymphangiogenesis in and around
axillary lymph node metastases of patients with breast cancer. Br J
Cancer. 95:1362–1366. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang EY, Madireddi MT, Gopalkrishnan RV,
Leszczyniecka M, Su Z, Lebedeva IV, Kang D, Jiang H, Lin JJ,
Alexandre D, Chen Y, Vozhilla N, Mei MX, Christiansen KA, Sivo F,
Goldstein NI, Mhashikar AB, Chada S, Huberman E, Pestka S and
Fisher PB: Genomic structure, chromosomal localisation and
expression profile of a novel melanoma differentiation associated
(mda-7) gene with cancer specific growth suppressing and apoptosis
inducing properties. Oncogene. 20:7051–7063. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dash R, Bhutia SK, Azab B, Su ZZ, Quinn
BA, Kegelmen TP, Das SK, Kim K, Lee SG, Park MA, Yacoub A, Rahmani
M, Emdad L, Dmitriev IP, Wang XY, Sarkar D, Grant S, Dent P, Curiel
DT and Fisher PB: mda-7/IL/24: a unique member of the IL-10 gene
family promoting cancer-targeted toxicity. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 21:381–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramesh R, Mhashilkar AM, Tanaka F, Saito
Y, Branch CD, Sieger K, Mumm JB, Stewart AL, Boquoi A, Dumoutier L,
Grimm EA, Renauld JC, Kotenko S and Chada S: Melanoma
differentiation-associated gene7/interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel
ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer
Res. 63:5105–5113. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI and
Fisher PB: Subtract ion hybridization identifies a novel melanoma
differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human
melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene.
11:2477–2486. 1995.
|
|
19
|
Patani N, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel R, Jiang
W and Mokbel K: Tumour suppressor function of MDA-7/IL-24 in human
breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 10:292010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang WG, Douglas-Jones A and Mansel RE:
Expression of peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor-gamma
(PPARgamma) and the PPARgamma co-activator, PGC-1, in human breast
cancer correlates with clinical outcomes. Int J Cancer.
106:752–757. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Al-Rawi MA, Watkins G, Mansel RE and Jiang
WG: The effects of interleukin-7 on the lymphangiogenic properties
of human endothelial cells. Int J Oncol. 27:721–730.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox SE, Parr C, Martin TA,
Matsumoto K, Nakamura T and Mansel RE: Antagonistic effect of NK4,
a novel hepatocyte growth factor variant, on in vitro angiogenesis
of human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Cancer Res. 5:3695–3703.
1999.
|
|
23
|
Sanders AJ, Ye L, Mason MD and Jiang WG:
The impact of EPLINα (epithelial protein lost in neoplasm) on
endothelial cells, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Angiogenesis.
13:317–326. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Hallett MB, Horrobin
DF, Scott C and Puntis MCA: Inhibition of hepatocyte growth
factor-induced motility and in vitro invasion of human colon cancer
cells by gamma-linolenic acid. Br J Cancer. 71:744–752. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|