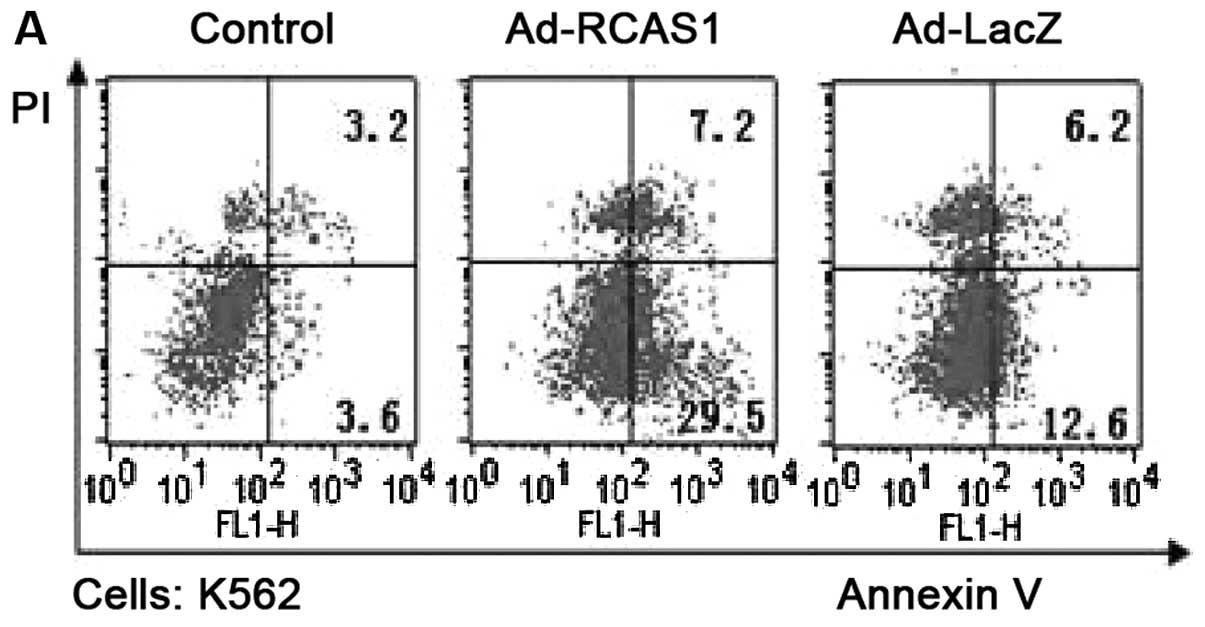
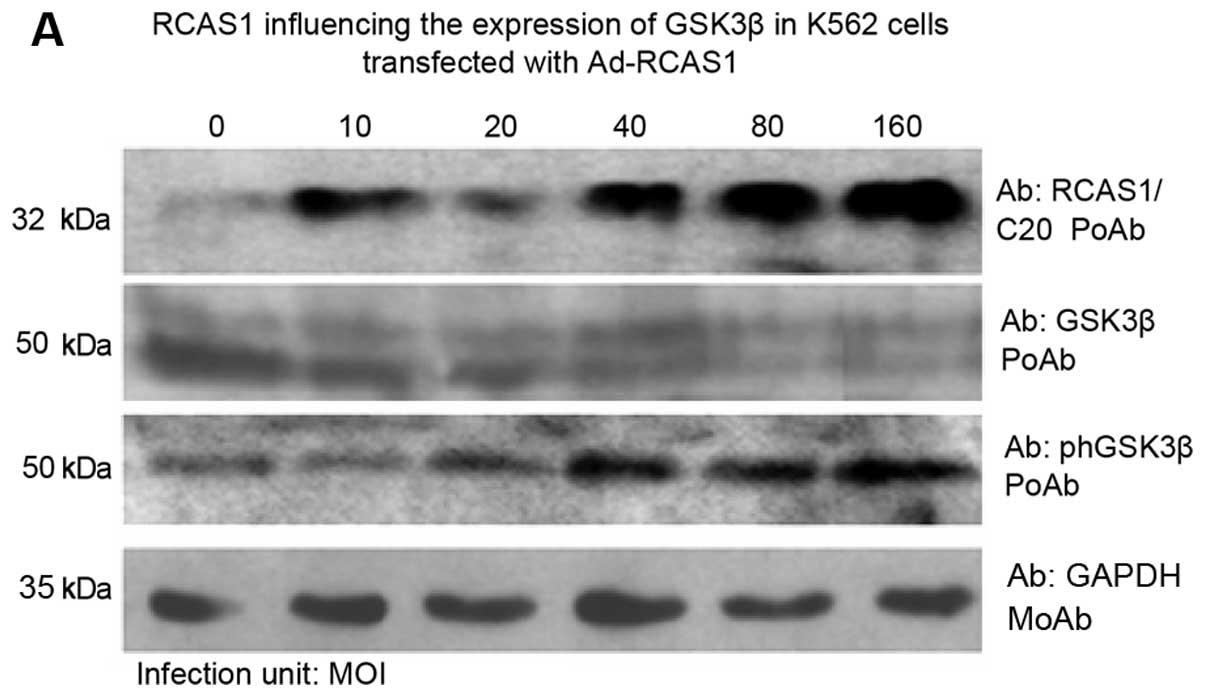
|
1
|
Tsuchiya F, Ikeda K, Tsutsumi O, et al:
Molecular cloning and characterization of mouse EBAG9, homolog of a
human cancer associated surface antigen: expression and regulation
by estrogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 284:2–10. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Suzuki T, Inoue S, Kawabata W, et al:
EBAG9/RCAS1 in human breast carcinoma: a possible factor in
endocrine-immune interactions. Br J Cancer. 85:1731–1737. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akahira JI, Aoki M, Suzuki T, et al:
Expression of EBAG9/RCAS1 is associated with advanced disease in
human epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 90:2197–2202. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takahashi S, Urano T, Tsuchiya F, et al:
EBAG9/RCAS1 expression and its prognostic significance in prostatic
cancer. Int J Cancer. 106:310–315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aoki T, Inoue S, Imamura H, et al:
EBAG9/RCAS1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation
with tumour dedifferentiation and proliferation. Eur J Cancer.
39:1552–1561. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakashima M, Sonoda K and Watanabe T:
Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptotic cell death by
the human tumor-associated antigen RCAS1. Nat Med. 5:938–942. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsushima T, Nakashima M, Oshima K, et
al: Receptor binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells, a
novel regulator of apoptosis of erythroid progenitor cells. Blood.
98:313–321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sonoda K, Miyamoto S, Yamazaki A,
Kobayashi H, Nakashima M, Mekada E and Wake N: Biologic
significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo
cells (RCAS1) as a pivotal regulator of tumor growth through
angiogenesis in human uterine cancer. Cancer. 110:1979–1990. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Oshikiri T, Miyamoto M, Morita T, et al:
Tumor-associated antigen recognized by the 22-1-1 monoclonal
antibody encourages colorectal cancer progression under the scanty
CD8+ T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:411–416. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chatterjee M, Mohapatra S, Ionan A, et al:
Diagnostic markers of ovarian cancer by high-throughput antigen
cloning and detection on arrays. Cancer Res. 66:1181–1190. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong XJ, Shen FP and Wang QQ: Construction
of recombinant GST-RCAS1 fusion gene and its expression in E.
Coli. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 35:377–383. 2006.(In
Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Hong X, Liu Y, Hu G, et al: EBAG9 inducing
hyporesponsiveness of T cells promotes tumor growth and metastasis
in 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:961–969. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reed LJ and Muench HA: A simple method for
estimating fifty percent endpoint. Am J Hyg. 27:493–497. 1938.
|
|
14
|
Engelsberg A, Hermosilla R, Karsten U,
Schülein R, Dörken B and Rehm A: The Golgi protein RCAS1 controls
cell surface expression of tumor-associated O-linked glycan
antigens. J Biol Chem. 278:22998–23007. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reimer TA, Anagnostopoulos I, Erdmann B,
et al: Reevaluation of the 22-1-1 antibody and its putative
antigen, EBAG9/RCAS1, as a tumor marker. BMC Cancer. 5:472005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Embi N, Rylatt DB and Cohen P: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from
cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J
Biochem. 107:519–527. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Woodgett JR and Cohen P: Multisite
phosphorylation of glycogen synthase. Molecular basis for the
substrate specificity of glycogen synthase kinase-3 and casein
kinase-II (glycogen synthase kinase-5). Biochim Biophys Acta.
788:339–347. 1984.
|
|
18
|
Jope RS and Johnson GV: The glamour and
gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 29:95–102.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin
O and Woodgett JR: Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta
in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 406:86–90. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS and Michalek
SM: Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is
differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat
Immunol. 6:777–784. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dutsch-Wicherek M and Wicherek L: The
association of RCAS1 serum concentration with the reversibility or
irreversibility of the process of immune cytotoxic activity
restriction during normal menstrual cycle, cancer relapse, and
surgical treatment for various types of squamous cell carcinomas
and adenocarcinomas. Am J Reprod Immunol. 59:266–275. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Dutsch-Wicherek M, Tomaszewska R, Lazar A,
Wicherek L and Skladzien J: The association between RCAS1
expression in laryngeal and pharyngeal cancer and its healthy
stroma with cancer relapse. BMC Cancer. 28:9–35. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|