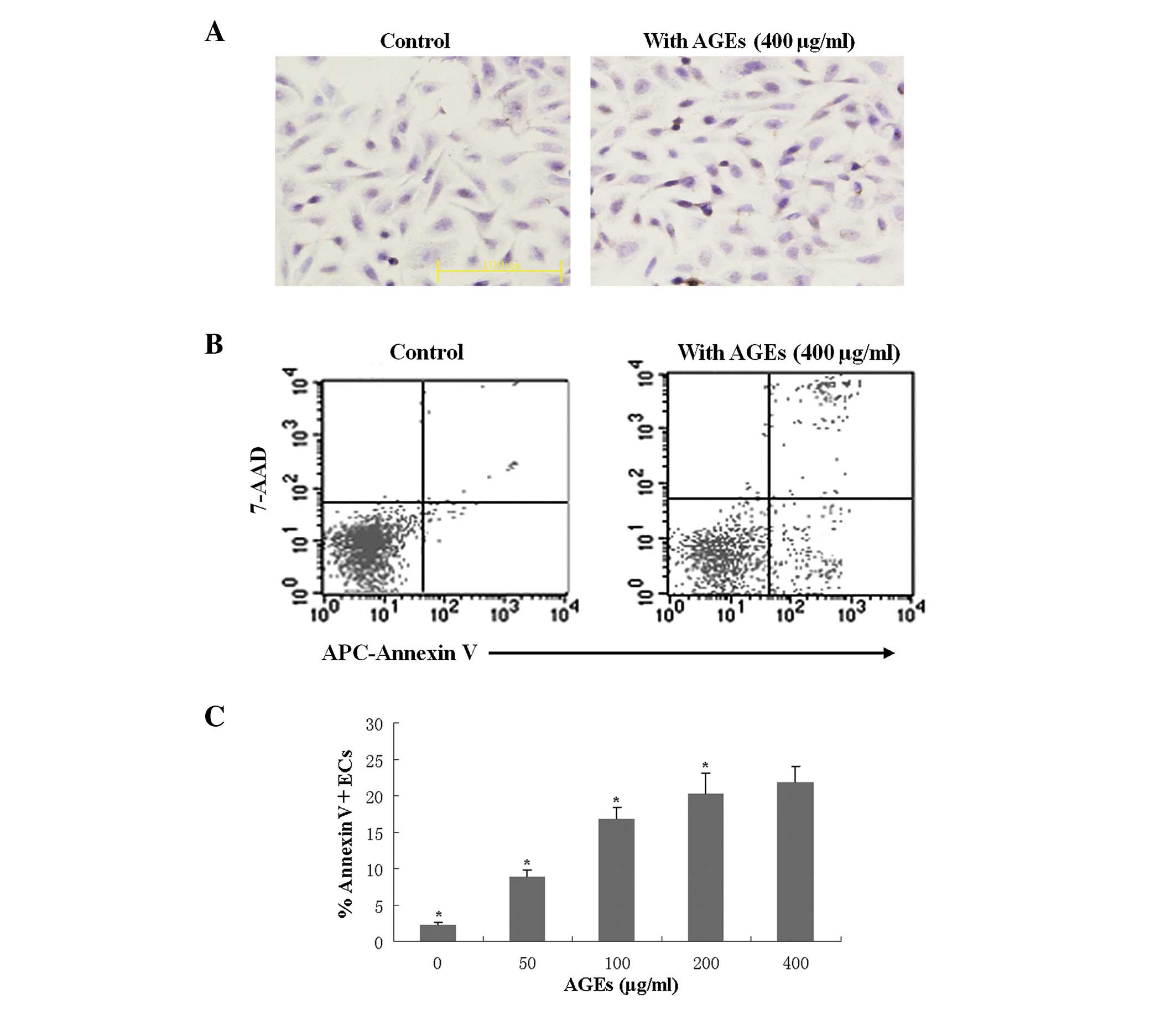
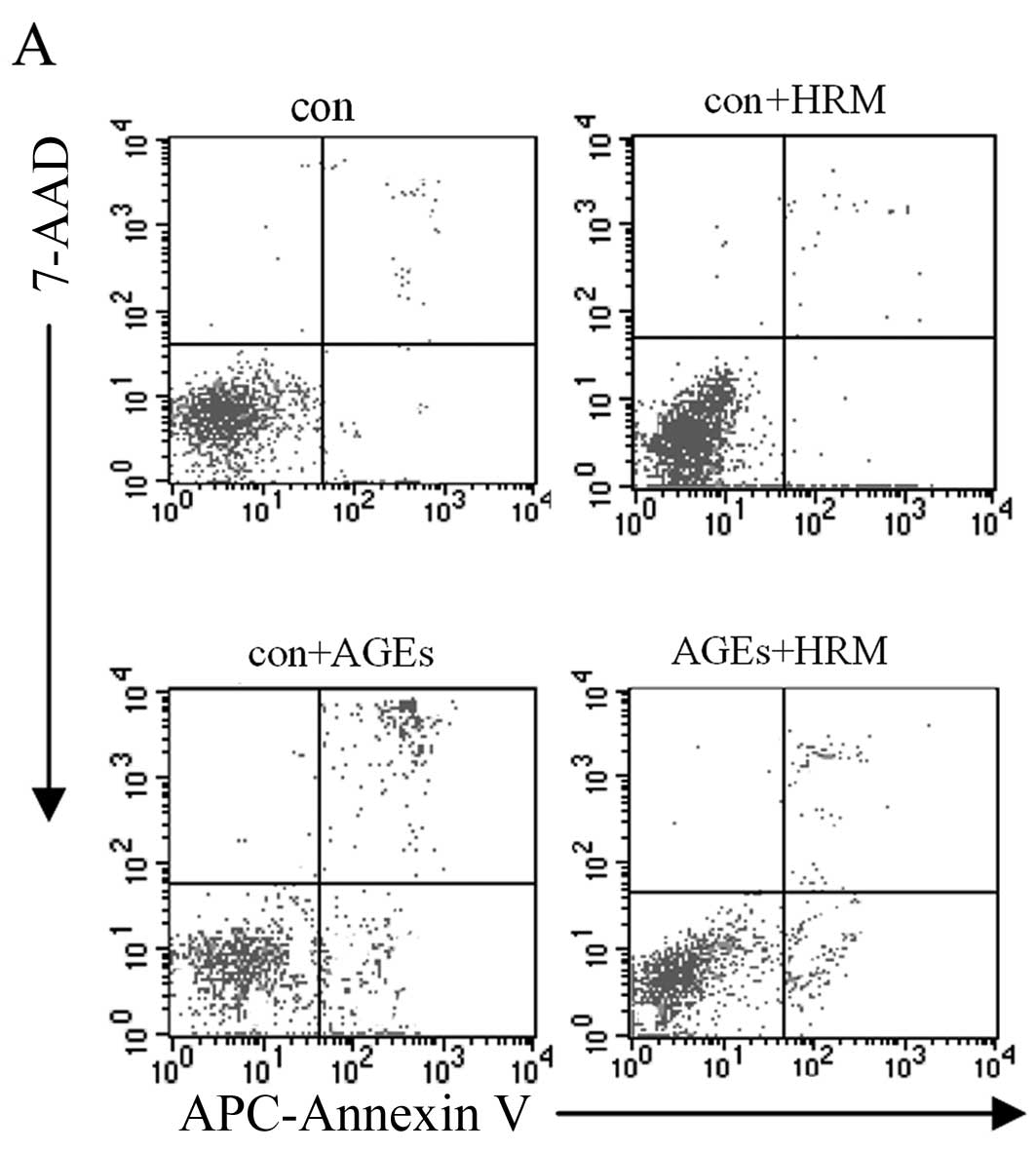
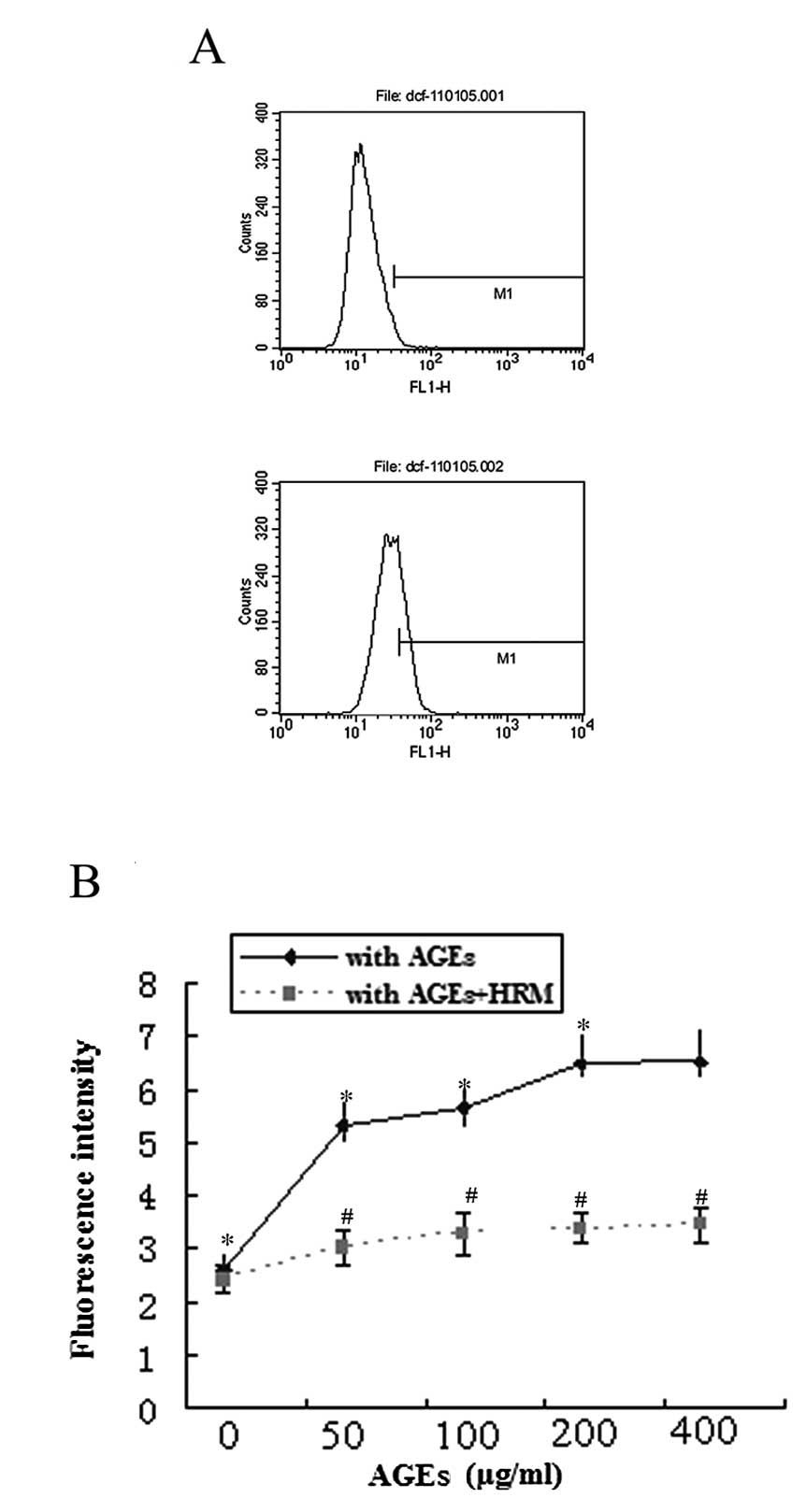
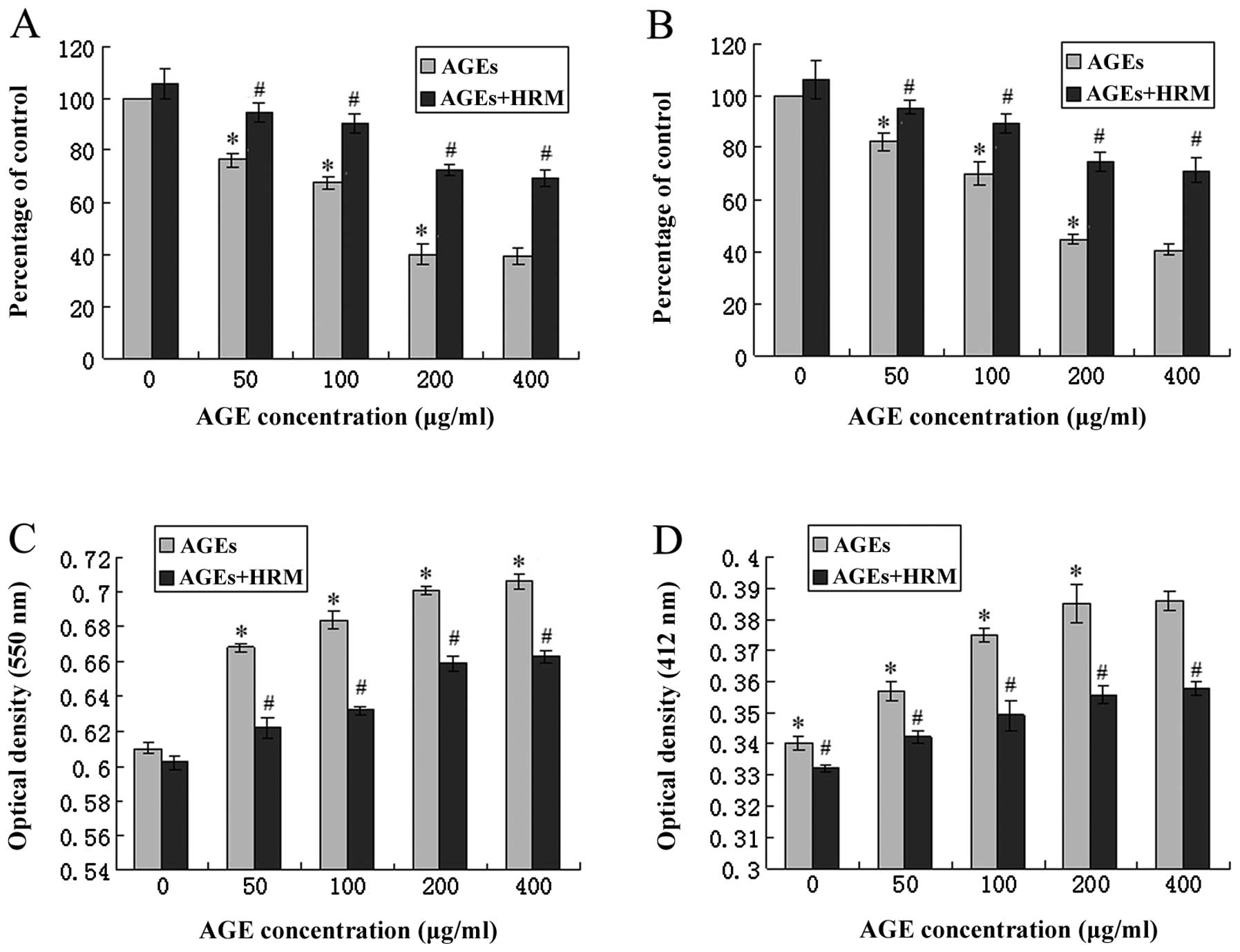
|
1
|
Faria AM, Papadimitriou A, Silva KC, Lopes
de Faria JM and Lopes de Faria JB: Uncoupling endothelial nitric
oxide synthase is ameliorated by green tea in experimental diabetes
by re-establishing tetrahydrobiopterin levels. Diabetes.
61:1838–1847. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Caporali A, Pani E, Horrevoets AJ, et al:
Neurotrophin p75 receptor (p75NTR) promotes endothelial cell
apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis: implications for
diabetes-induced impaired neovascularization in ischemic limb
muscles. Circ Res. 103:e15–e26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Csiszar A and Ungvari Z: Endothelial
dysfunction and vascular inflammation in type 2 diabetes:
interaction of AGE/RAGE and TNF-alpha signaling. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 295:H475–H476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goldin A, Beckman JA, Schmidt AM and
Creager MA: Advanced glycation end products: sparking the
development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation. 114:597–605.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiang M, Yang M, Zhou C, Liu J, Li W and
Qian Z: Crocetin prevents AGEs-induced vascular endothelial cell
apoptosis. Pharmacol Res. 54:268–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen J, Huang L, Song M, Yu S, Gao P and
Jing J: C-reactive protein upregulates receptor for advanced
glycation end products expression and alters antioxidant defenses
in rat endothelial progenitor cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
53:359–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tan AL, Forbes JM and Cooper ME: AGE,
RAGE, and ROS in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 27:130–143.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al:
Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing
cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 13:688–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xie K, Yu Y, Huang Y, et al: Molecular
hydrogen ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
in mice through reducing inflammation and apoptosis. Shock.
37:548–555. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu K, et al:
Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen saline in neonatal
hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Brain Res. 1256:129–137. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen H, Sun YP, Li Y, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline ameliorates the severity of l-arginine-induced acute
pancreatitis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:308–313.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Q, Shen WF, Sun HY, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline protects against liver injury in rats with
obstructive jaundice. Liver Int. 30:958–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. Exp Biol Med. 234:1212–1219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Wang C, Zhang JH, Cai JM, Cao YP and
Sun XJ: Hydrogen-rich saline improves memory function in a rat
model of amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer’s disease by reduction of
oxidative stress. Brain Res. 1328:152–161. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Q, Cai J, Zhou J, Tao H, Zhang JH,
Zhang W and Sun XJ: Hydrogen-rich saline reduces delayed neurologic
sequelae in experimental carbon monoxide toxicity. Crit Care Med.
39:765–769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun H, Chen L, Zhou W, et al: The
protective role of hydrogen-rich saline in experimental liver
injury in mice. J Hepatol. 54:471–480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Terasaki Y, Ohsawa I, Terasaki M, et al:
Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by
reducing oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
301:L415–L426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohsawa I, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K,
Ishikawa M and Ohta S: Consumption of hydrogen water prevents
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 377:1195–1198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qin ZX, Yu P, Qian DH, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline prevents neointima formation after carotid
balloon injury by suppressing ROS and the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway.
Atherosclerosis. 220:343–350. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu X, Zhou Q, Huang L, Sun A, Wang K, Zou
Y and Ge J: Ageing-exaggerated proliferation of vascular smooth
muscle cells is related to attenuation of Jagged1 expression in
endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 77:800–808. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang X, Guo Y, Nakamura K, et al:
Nitroalkenes induce rat aortic smooth muscle cell apoptosis via
activation of caspase-dependent pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 397:239–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Song M, Yu S, Gao P, Yu Y, Wang H
and Huang L: Advanced glycation endproducts alter functions and
promote apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells through receptor
for advanced glycation endproducts mediate overpression of cell
oxidant stress. Mol Cell Biochem. 335:137–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Marsh SA, Laursen PB, Pat BK, Gobe GC and
Coombes JS: Bcl-2 in endothelial cells is increased by vitamin E
and alpha-lipoic acid supplementation but not exercise training. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 38:445–451. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jandeleit-Dahm K, Watson A and
Soro-Paavonen A: The AGE/RAGE axis in diabetes-accelerated
atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 35:329–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kajiyama S, Hasegawa G, Asano M, et al:
Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose
metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose
tolerance. Nutr Res. 28:137–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qian L, Li B, Cao F, Huang Y, Liu S, Cai J
and Gao F: Hydrogen-rich PBS protects cultured human cells from
ionizing radiation-induced cellular damage. Nucl Technol Radiat
Prot. 25:23–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yu P, Wang Z, Sun X, Chen X, Zeng S, Chen
L and Li S: Hydrogen-rich medium protects human skin fibroblasts
from high glucose or mannitol induced oxidative damage. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 409:350–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu Ys and Zheng H: Chronic hydrogen-rich
saline treatment reduces oxidative stress and attenuates left
ventricular hypertrophy in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 365:233–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Sun Q, He B, Xiao J, Wang Z and
Sun X: Anti-inflammatory effect of hydrogen-rich saline in a rat
model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Int J
Cardiol. 148:91–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zong C, Song G, Yao S, et al:
Administration of hydrogen-saturated saline decreases plasma
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and improves
high-density lipoprotein function in high-fat diet-fed hamsters.
Metabolism. 61:794–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schoenfeld MP, Ansari RR, Zakrajsek JF, et
al: Hydrogen therapy may reduce the risks related to
radiation-induced oxidative stress in space flight. Med Hypotheses.
76:117–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hess DA and Hegele RA: Linking diabetes
with oxidative stress, adipokines, and impaired endothelial
precursor cell dunction. Can J Cardiol. 28:629–630. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sharpe PC, Liu WH, Yue KK, et al:
Glucose-induced oxidative stress in vascular contractile cells:
comparison of aortic smooth muscle cells and retinal pericytes.
Diabetes. 47:801–809. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li BY, Li XL, Cai Q, et al: Induction of
lactadherin mediates the apoptosis of endothelial cells in response
to advanced glycation end products and protective effects of grape
seed procyanidin B2 and resveratrol. Apoptosis. 16:732–745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deng X, Gao F and May WS Jr: Bcl2 retards
G1/S cell cycle transition by regulating intracellular ROS. Blood.
102:3179–3185. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|