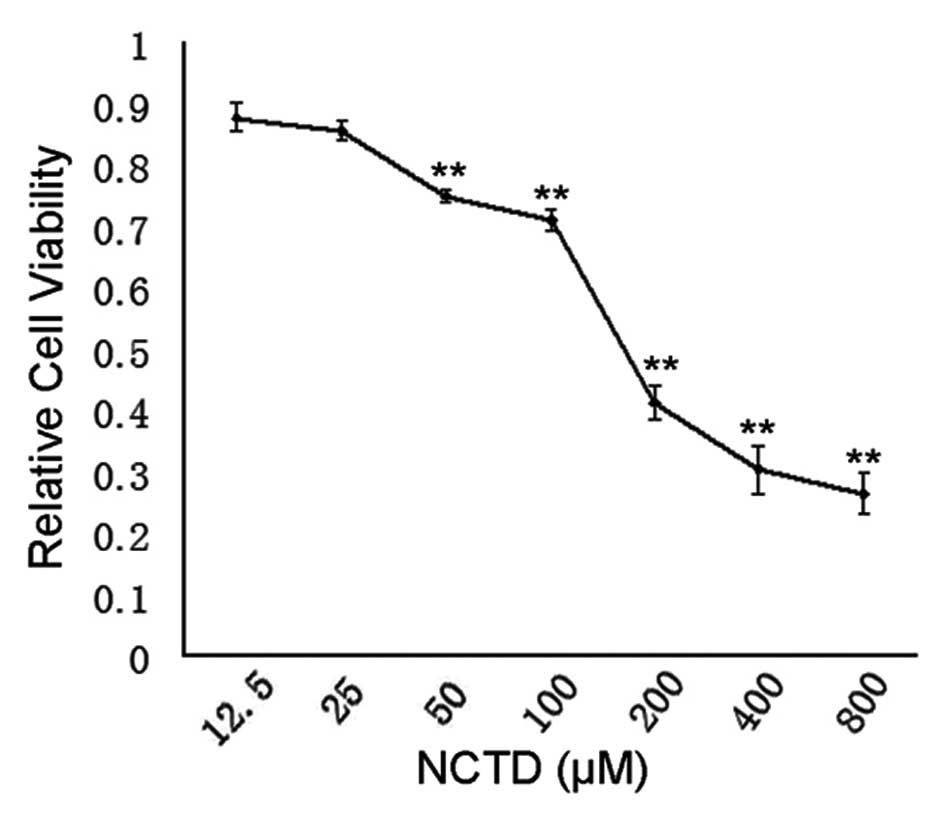
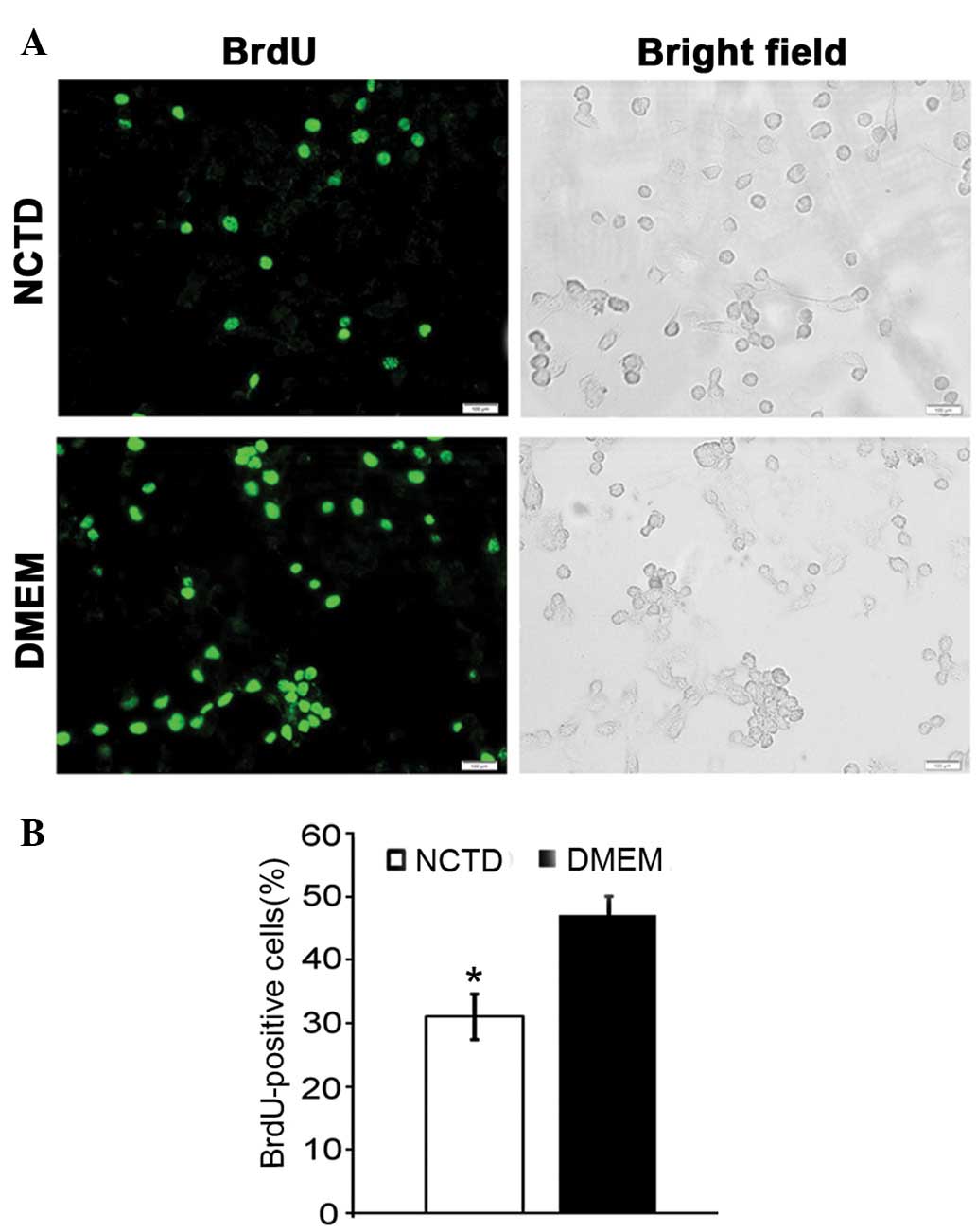
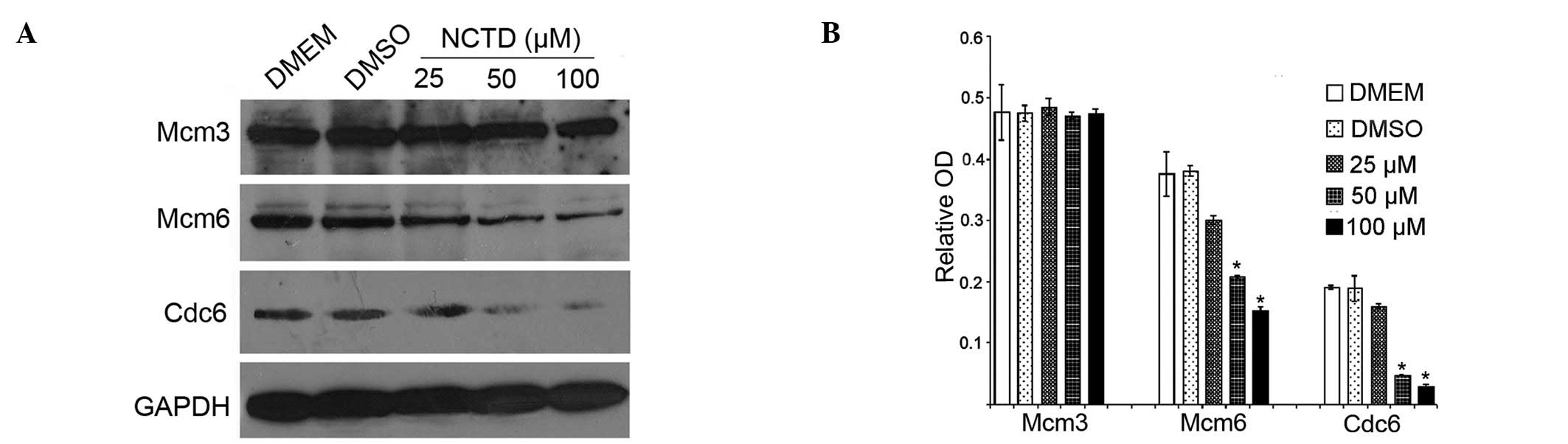
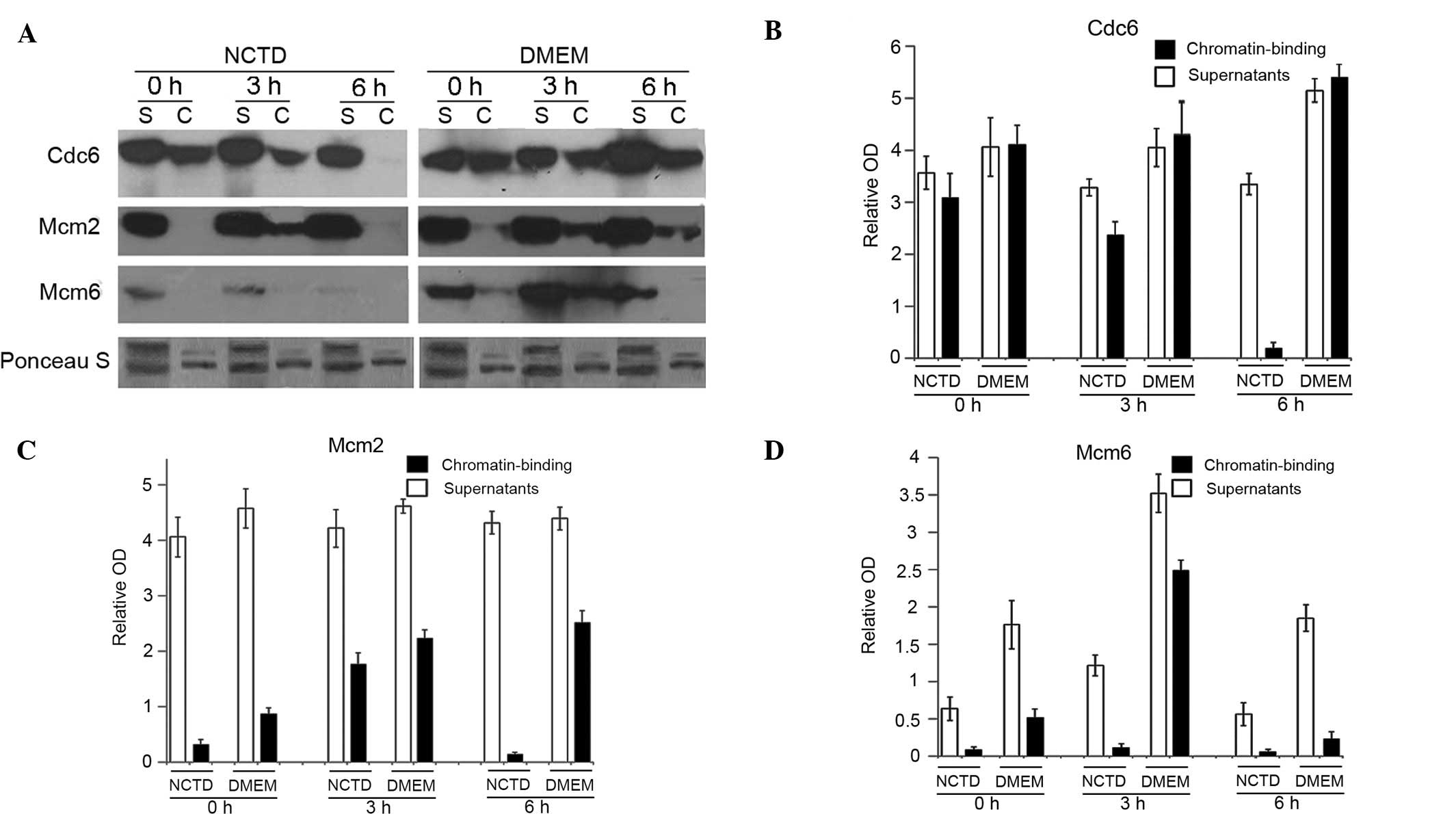
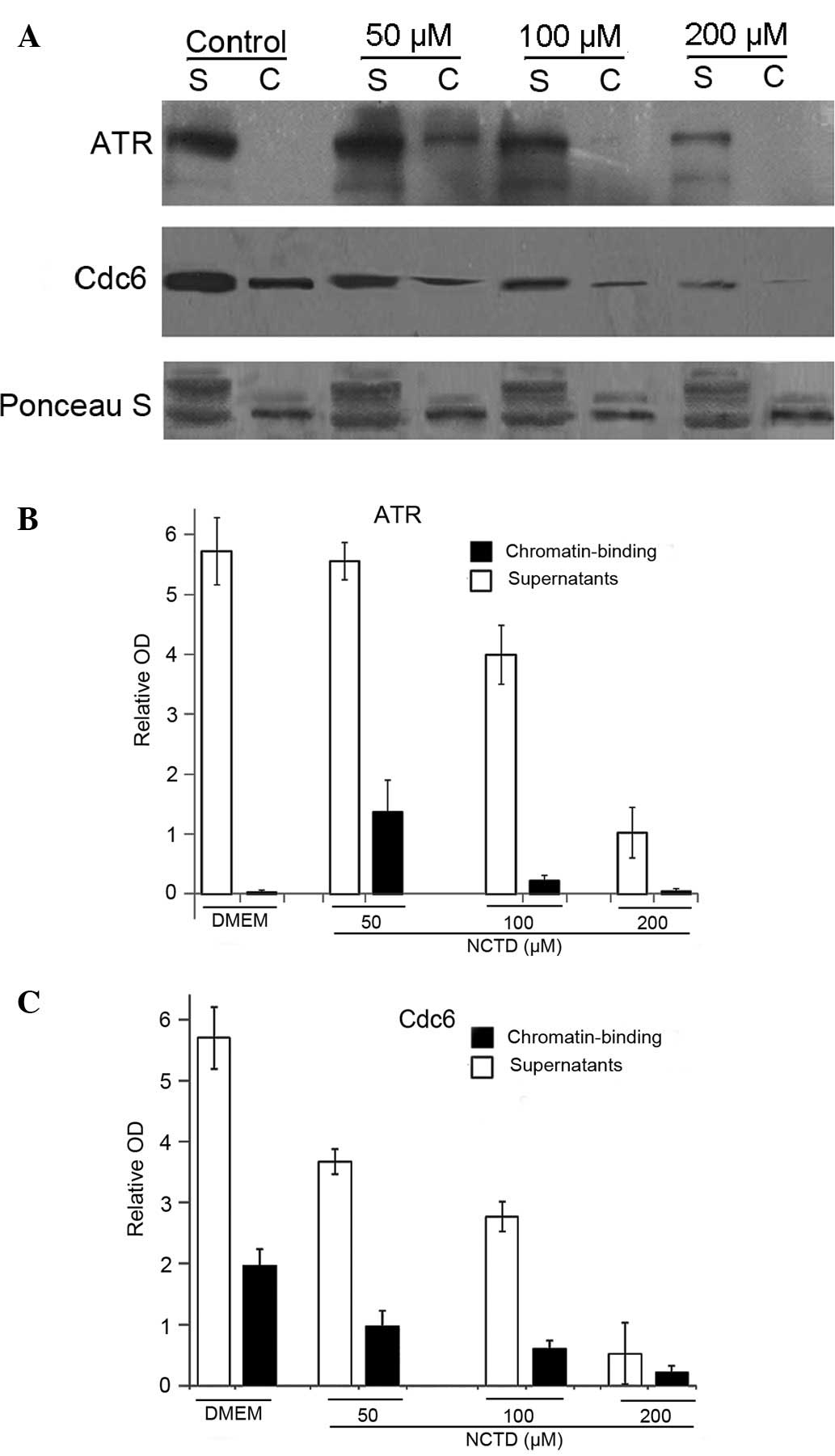
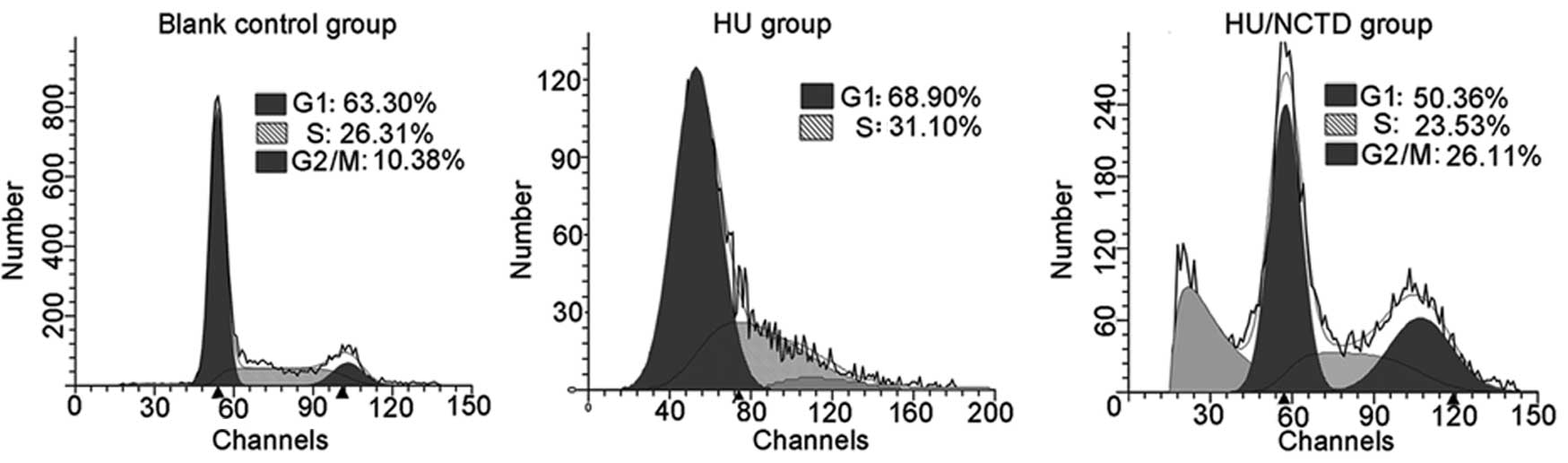
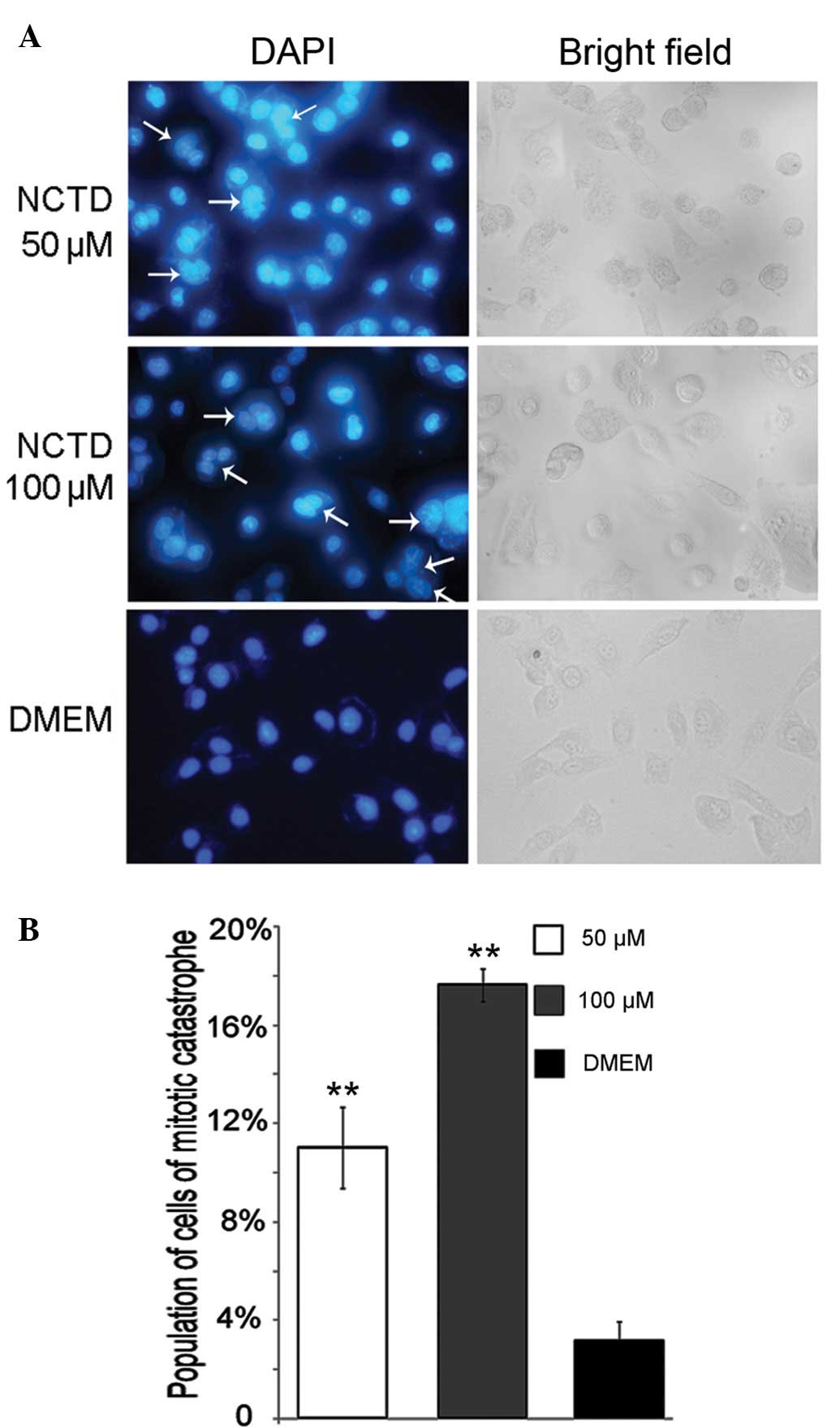
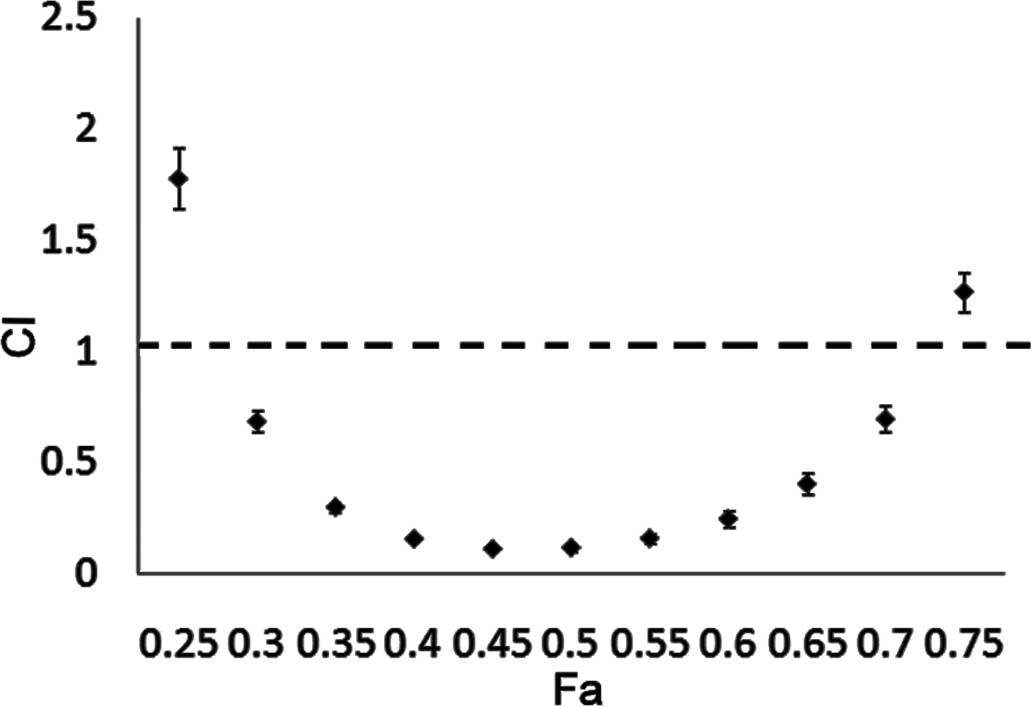
|
1.
|
Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S and Wingo
PA: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 50:7–33. 2000.
|
|
2.
|
Quinn M and Babb P: Patterns and trends in
prostate cancer incidence, survival, prevalence and mortality. Part
I: international comparisons. BJU Int. 90:162–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Cude KJ, Dixon SC, Guo Y, Lisella J and
Figg WD: The androgen receptor: genetic considerations in the
development and treatment of prostate cancer. J Mol Med (Berl).
77:419–426. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Robles LD, Frost AR, Davila M, Hutson AD,
Grizzle WE and Chakrabarti R: Down-regulation of Cdc6, a cell cycle
regulatory gene, in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 277:25431–25438.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Mallik I, Davila M, Tapia T, Schanen B and
Chakrabarti R: Androgen regulates Cdc6 transcription through
interactions between androgen receptor and E2F transcription factor
in prostate cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1783:1737–1744.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Claessens F, Verrijdt G, Schoenmakers E,
et al: Selective DNA binding by the androgen receptor as a
mechanism for hormone-specific gene regulation. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 76:23–30. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wang Q, Li W, Liu XS, et al: A
hierarchical network of transcription factors governs androgen
receptor-dependent prostate cancer growth. Mol Cell. 27:380–392.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bolton EC, So AY, Chaivorapol C, Haqq CM,
Li H and Yamamoto KR: Cell- and gene-specific regulation of primary
target genes by the androgen receptor. Genes Dev. 21:2005–2017.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Massie CE, Adryan B, Barbosa-Morais NL, et
al: New androgen receptor genomic targets show an interaction with
the ETS1 transcription factor. EMBO Rep. 8:871–878. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Jin F and Fondell JD: A novel androgen
receptor-binding element modulates Cdc6 transcription in prostate
cancer cells during cell-cycle progression. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:4826–4838. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Cook JG: Replication licensing and the DNA
damage checkpoint. Front Biosci. 14:5013–5030. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Stillman B: Cell cycle control of DNA
replication. Science. 274:1659–1664. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Saxena S and Dutta A: Geminin-Cdt1 balance
is critical for genetic stability. Mutat Res. 569:111–121. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lei M and Tye BK: Initiating DNA
synthesis: from recruiting to activating the MCM complex. J Cell
Sci. 114:1447–1454. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yoshida K, Sugimoto N, Iwahori S, et al:
CDC6 interaction with ATR regulates activation of a replication
checkpoint in higher eukaryotic cells. J Cell Sci. 123:225–235.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wang GS: Medical uses of Mylabris
in ancient China and recent studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 26:147–162.
1989.
|
|
17.
|
Chang C, Zhu Y, Tang X and Tao W: The
anti-proliferative effects of norcantharidin on human HepG2 cells
in cell culture. Mol Biol Rep. 38:163–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Luan J, Duan H, Liu Q, Yagasaki K and
Zhang G: Inhibitory effects of norcantharidin against human lung
cancer cell growth and migration. Cytotechnology. 62:349–355. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Chen YJ, Chang WM, Liu YW, et al: A
small-molecule metastasis inhibitor, norcantharidin, downregulates
matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting Sp1
transcriptional activity in colorectal cancer cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 181:440–446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Huang Y, Liu Q, Liu K, Yagasaki K and
Zhang G: Suppression of growth of highly-metastatic human breast
cancer cells by norcantharidin and its mechanisms of action.
Cytotechnology. 59:2092009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Kok SH, Cheng SJ, Hong CY, et al:
Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis in oral cancer cells is associated
with an increase of proapoptotic to antiapoptotic protein ratio.
Cancer Lett. 217:43–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liu XH, Blazsek I, Comisso M, et al:
Effects of norcantharidin, a protein phosphatase type-2A inhibitor,
on the growth of normal and malignant haemopoietic cells. Eur J
Cancer. 31A:953–963. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ofir Y, Sagee S, Guttmann-Raviv N, Pnueli
L and Kassir Y: The role and regulation of the preRC component Cdc6
in the initiation of premeiotic DNA replication. Mol Biol Cell.
15:2230–2242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Forsburg SL: Eukaryotic MCM proteins:
beyond replication initiation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:109–131.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lau E, Zhu C, Abraham RT and Jiang W: The
functional role of Cdc6 in S-G2/M in mammalian cells. EMBO Rep.
7:425–430. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Liu Q, Guntuku S, Cui XS, et al: Chk1 is
an essential kinase that is regulated by Atr and required for the
G(2)/M DNA damage checkpoint. Genes Dev. 14:1448–1459.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Clay-Farrace L, Pelizon C, Santamaria D,
Pines J and Laskey RA: Human replication protein Cdc6 prevents
mitosis through a checkpoint mechanism that implicates Chk1. EMBO
J. 22:704–712. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M and Zhivotovsky
B: Death through a tragedy: mitotic catastrophe. Cell Death Differ.
15:1153–1162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, et
al: Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity
in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med.
111:273–279. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Horwitz SB: Taxol (paclitaxel): mechanisms
of action. Ann Oncol. 5(Suppl 6): S3–S6. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Stewart ZA, Westfall MD and Pietenpol JA:
Cell-cycle dysregulation and anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:139–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Chen YN, Chen JC, Yin SC, et al: Effector
mechanisms of norcantharidin-induced mitotic arrest and apoptosis
in human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer. 100:158–165. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Chen YN, Cheng CC, Chen JC, Tsauer W and
Hsu SL: Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis is via the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase signaling
pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Br J Pharmacol.
140:461–470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|