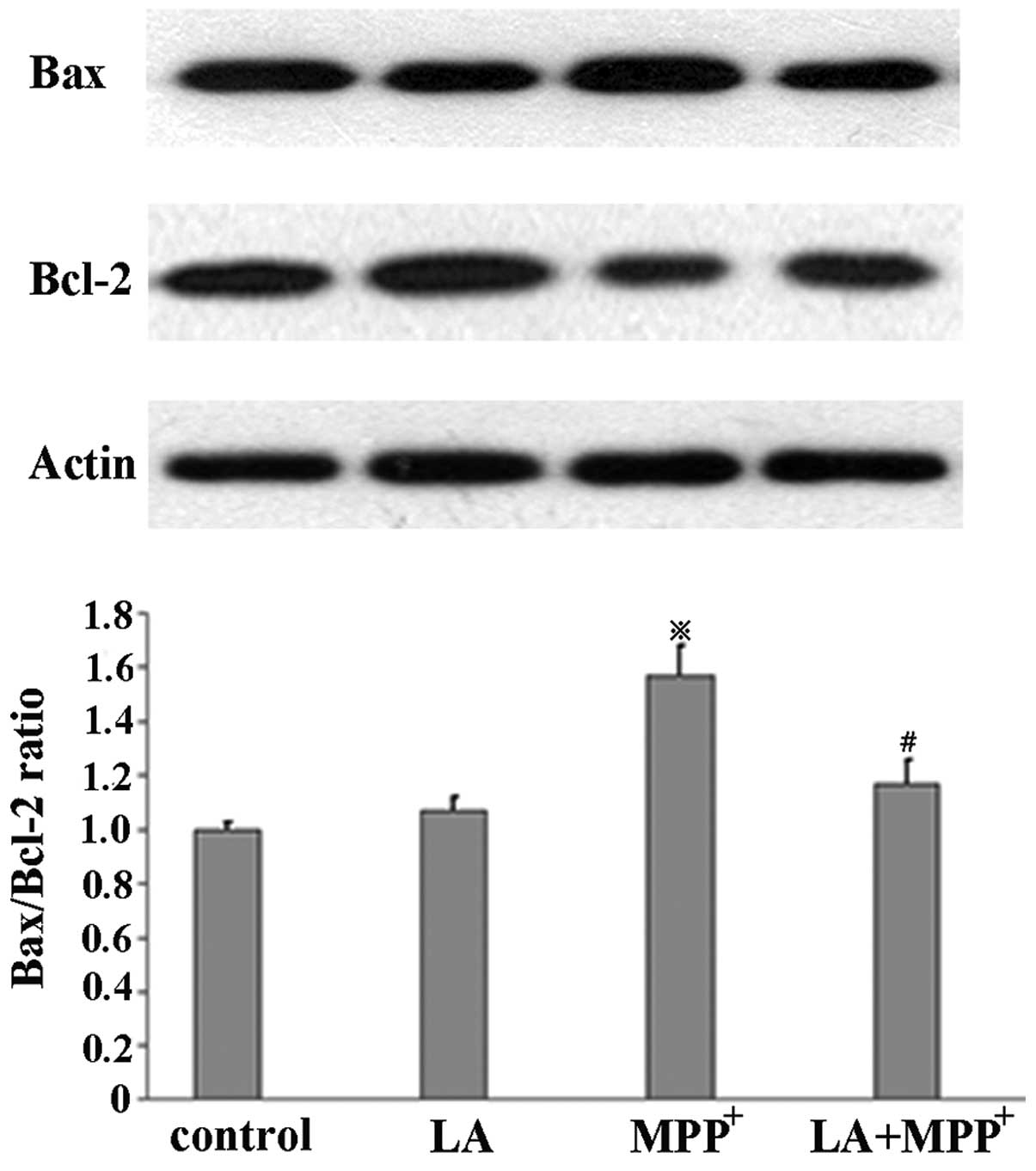
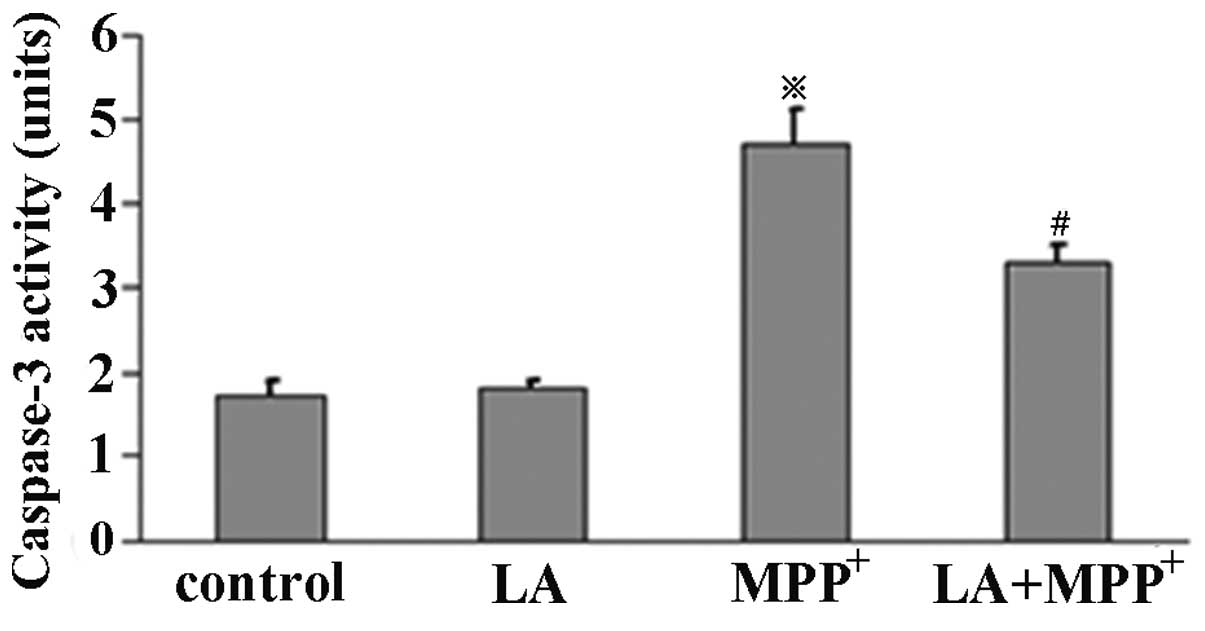
|
1.
|
Fleury C, Mignotte B and Vayssiere JL:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling.
Biochimie. 84:131–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Jenner P: Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s
disease. Ann Neurol. 53(Suppl 3): S26–S38. 2003.
|
|
3.
|
Hatanaka H: Nerve growth factor-mediated
stimulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in a clonal rat
pheochromocytoma cell line. Brain Res. 222:225–233. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Rebois RV, Reynolds EE, Toll L and Howard
BD: Storage of dopamine and acetylcholine in granules of PC12, a
clonal pheochromocytoma cell line. Biochemistry. 19:1240–1248.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Langston JW and Irwin I: MPTP: current
concepts and controversies. Clin Neuropharmacol. 9:485–507. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kopin IJ and Markey SP: MPTP toxicity:
implications for research in Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 11:81–96. 1988.
|
|
7.
|
Heikkila RE, Sieber BA, Manzino L and
Sonsalla PK: Some features of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic
neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in
the mouse. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 10:171–183. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Calon F, Lavertu N, Lemieux AM, et al:
Effect of MPTP-induced denervation on basal ganglia GABA(B)
receptors: correlation with dopamine concentrations and dopamine
transporter. Synapse. 40:225–234. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Chiba K, Trevor A and Castagnoli N Jr:
Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain
monoamine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 120:574–578. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Javitch JA, D’Amato RJ, Strittmatter SM
and Snyder SH: Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin,
N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the
metabolite N-methyl- 4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains
selective toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:2173–2177. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Hartley A, Stone JM, Heron C, Cooper JM
and Schapira AH: Complex I inhibitors induce dose-dependent
apoptosis in PC12 cells: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J
Neurochem. 63:1987–1990. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Packer L, Witt EH and Tritschler HJ:
Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med.
19:227–250. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Packer L, Tritschler HJ and Wessel K:
Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid.
Free Radic Biol Med. 22:359–378. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bustamante J, Lodge JK, Marcocci L,
Tritschler HJ, Packer L and Rihn BH: Alpha-lipoic acid in liver
metabolism and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 24:1023–1039. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Han D, Tritschler HJ and Packer L:
Alpha-lipoic acid increases intracellular glutathione in a human
T-lymphocyte Jurkat cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
207:258–264. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bast A and Haenen GR: Interplay between
lipoic acid and glutathione in the protection against microsomal
lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 963:558–561. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Busse E, Zimmer G, Schopohl B and
Kornhuber B: Influence of alpha-lipoic acid on intracellular
glutathione in vitro and in vivo. Arzneimittelforschung.
42:829–831. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Hagen TM, Ingersoll RT, Lykkesfeldt J, et
al: (R)-alpha-lipoic acid-supplemented old rats have improved
mitochondrial function, decreased oxidative damage, and increased
metabolic rate. FASEB J. 13:411–418. 1999.
|
|
19.
|
Packer L, Kraemer K and Rimbach G:
Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes
complications. Nutrition. 17:888–895. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Yilmaz O, Ozkan Y, Yildirim M, Ozturk AI
and Ersan Y: Effects of alpha lipoic acid, ascorbic
acid-6-palmitate, and fish oil on the glutathione, malonaldehyde,
and fatty acids levels in erythrocytes of streptozotocin induced
diabetic male rats. J Cell Biochem. 86:530–539. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wollin SD and Jones PJ: Alpha-lipoic acid
and cardiovascular disease. J Nutr. 133:3327–3330. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
McNeilly AM, Davison GW, Murphy MH, et al:
Effect of α-lipoic acid and exercise training on cardiovascular
disease risk in obesity with impaired glucose tolerance. Lipids
Health Dis. 10:2172011.
|
|
23.
|
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, et al:
Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the
anti-oxidant alpha-lipoic acid. A 3-week multicentre randomized
controlled trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia. 38:1425–1433. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, et al:
Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the
antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized
controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group
Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care.
22:1296–1301. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Andreyev AY, Kushnareva YE and Starkov AA:
Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 70:200–214. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Turrens JF: Mitochondrial formation of
reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 552:335–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Balaban RS, Nemoto S and Finkel T:
Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell. 120:483–495. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Adam-Vizi V and Chinopoulos C:
Bioenergetics and the formation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 27:639–645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Brookes PS: Mitochondrial H(+) leak and
ROS generation: an odd couple. Free Radic Biol Med. 38:12–23.
2005.
|
|
30.
|
Kussmaul L and Hirst J: The mechanism of
superoxide production by NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex
I) from bovine heart mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:7607–7612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Sipos I, Tretter L and Adam-Vizi V:
Quantitative relationship between inhibition of respiratory
complexes and formation of reactive oxygen species in isolated
nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 84:112–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson’s
disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
|
|
33.
|
Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V, Djaldetti
R, et al: The parkinsonian toxin MPTP: action and mechanism. Restor
Neurol Neurosci. 16:135–142. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kataoka H: Chromatographic analysis of
lipoic acid and related compounds. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl.
717:247–262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, Suh JH
and Hagen TM: Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic
diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem.
11:1135–1146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Scott BC, Aruoma OI, Evans PJ, et al:
Lipoic and dihydrolipoic acids as antioxidants. A critical
evaluation. Free Radic Res. 20:119–133. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Liu J, Head E, Gharib AM, et al: Memory
loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and
RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-L-carnitine
and/or R-alpha-lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:2356–2361.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Han D, Sen CK, Roy S, Kobayashi MS,
Tritschler HJ and Packer L: Protection against glutamate-induced
cytotoxicity in C6 glial cells by thiol antioxidants. Am J Physiol.
273:R1771–R1778. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Droge W: Free radicals in the
physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 82:47–95.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Reddy PH: Mitochondrial medicine for aging
and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromol Med. 10:291–315. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Beal MF: Mitochondria take center stage in
aging and neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol. 58:495–505. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Lin MT and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Nature. 443:787–795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Reddy PH, Mao P and Manczak M:
Mitochondrial structural and functional dynamics in Huntington’s
disease. Brain Res Rev. 61:33–48. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Selvaraj S, Watt JA and Singh BB: TRPC1
inhibits apoptotic cell degeneration induced by dopaminergic
neurotoxin MPTP/MPP(+). Cell Calcium. 46:209–218. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Abou-Sleiman PM, Muqit MM and Wood NW:
Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s
disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:207–219. 2006.
|
|
46.
|
Shiba-Fukushima K, Imai Y, Yoshida S, et
al: PINK1-mediated phosphorylation of the Parkin ubiquitin-like
domain primes mitochondrial translocation of Parkin and regulates
mitophagy. Sci Rep. 2:10022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Lee BW, Kwon SJ, Chae HY, et al:
Dose-related cytoprotective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on hydrogen
peroxide-induced oxidative stress to pancreatic beta cells. Free
Radic Res. 43:68–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: VDAC regulation
by the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Cell Death Differ. 7:1174–1181.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Gollapudi S, McCormick MJ and Gupta S:
Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial mass
occur independent of the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3
during CD95-mediated apoptosis in peripheral blood T cells. Int J
Oncol. 22:597–600. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Wu Y, Shang Y, Sun SG, Liu RG and Yang WQ:
Protective effect of erythropoietin against
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurodegenaration in PC12
cells. Neurosci Bull. 23:156–164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Shay KP, Moreau RF, Smith EJ, Smith AR and
Hagen TM: Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1790:1149–1160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Coleman MD, Eason RC and Bailey CJ: The
therapeutic use of lipoic acid in diabetes: a current perspective.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 10:167–172. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Panigrahi M, Sadguna Y, Shivakumar BR, et
al: alpha-Lipoic acid protects against reperfusion injury following
cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 717:184–188. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Arivazhagan P, Shila S, Kumaran S and
Panneerselvam C: Effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on the status of
lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in various brain regions
of aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 37:803–811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|