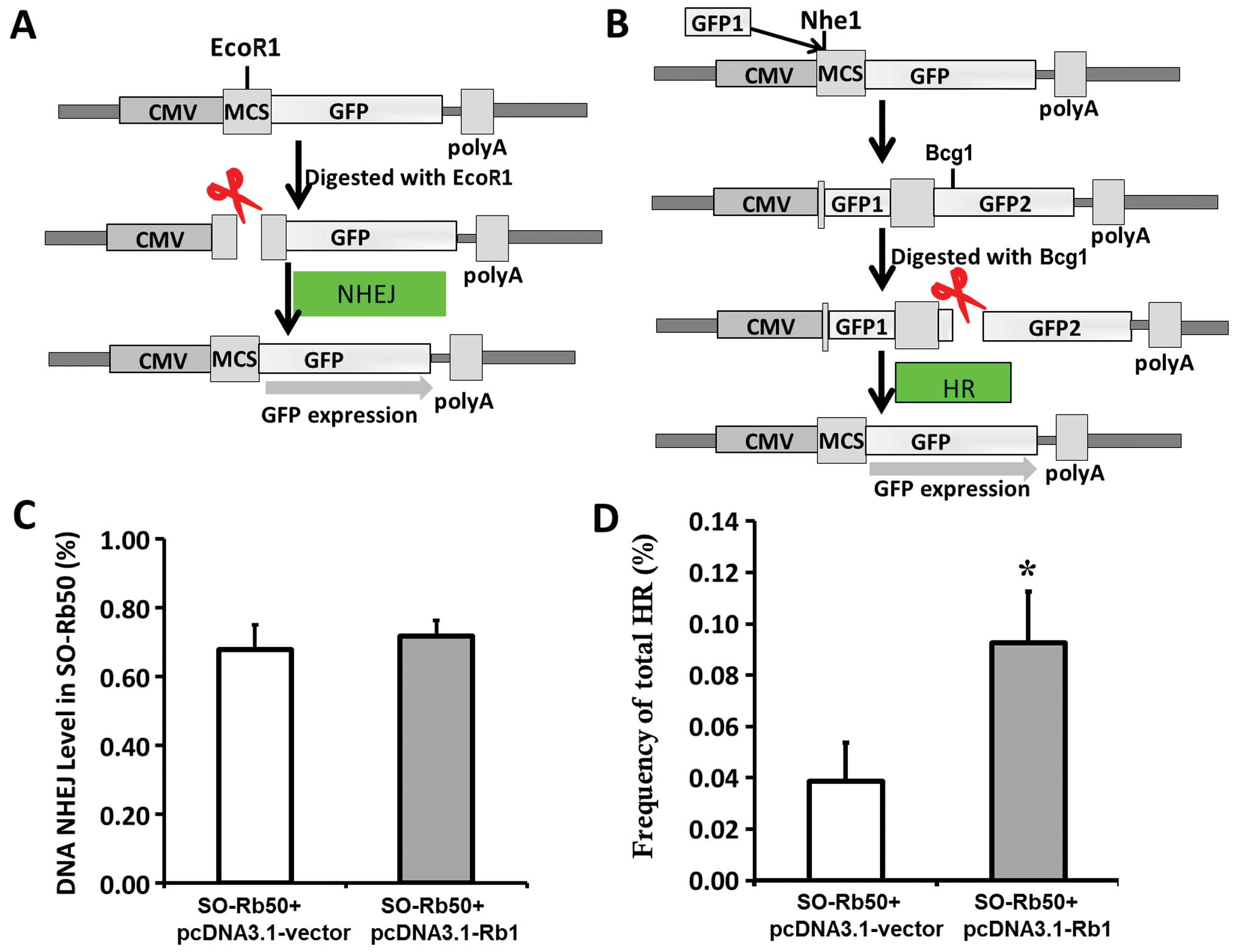
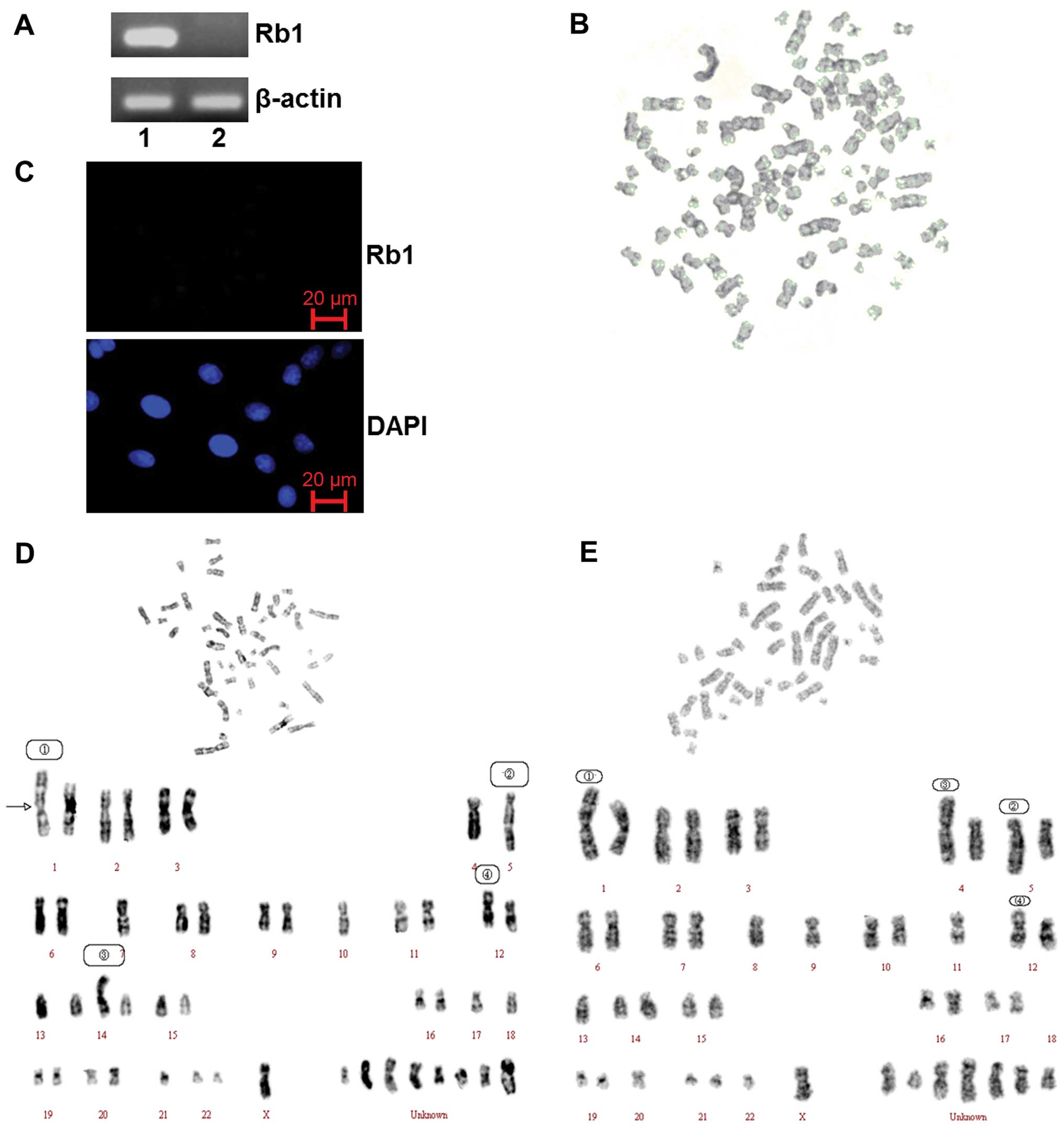
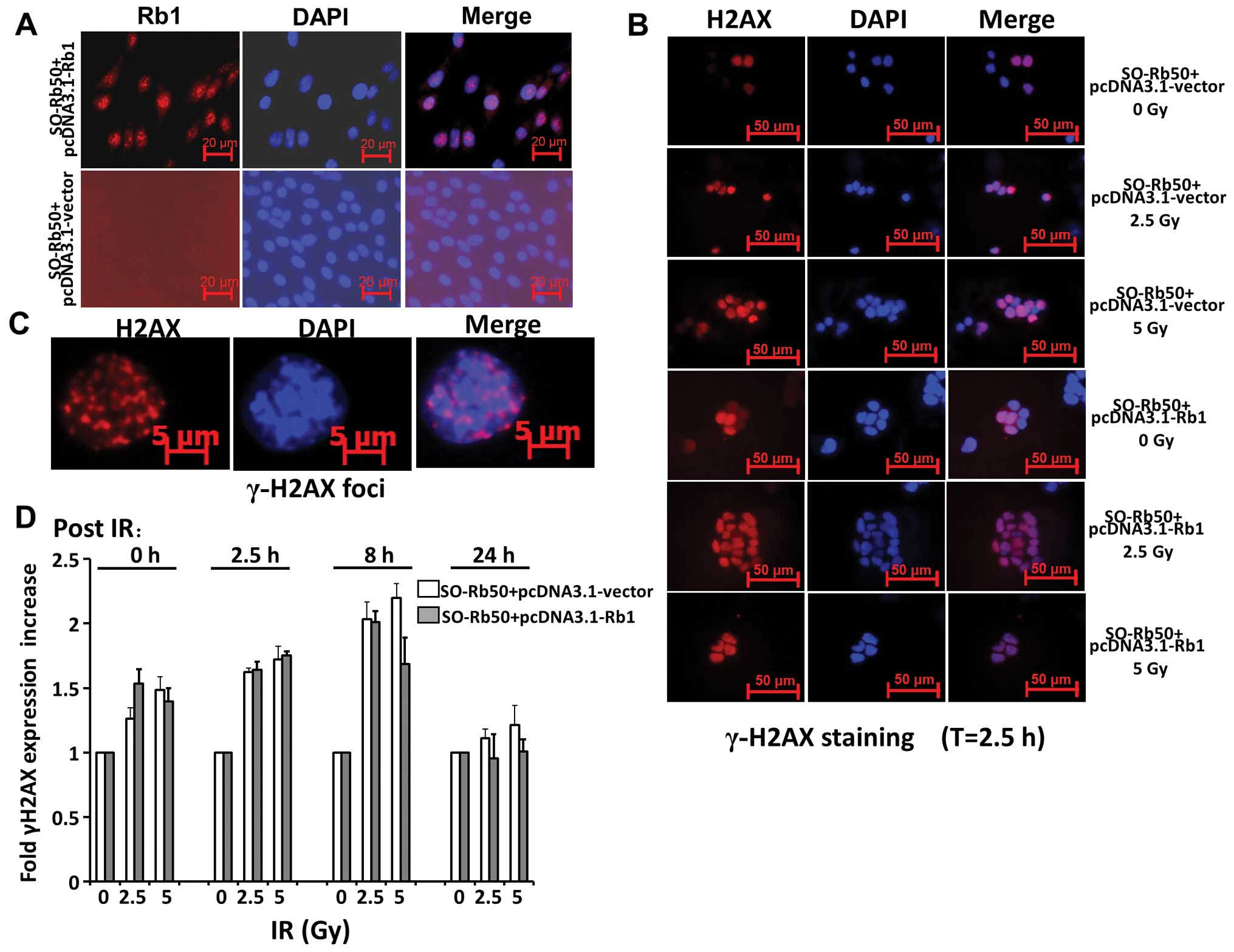
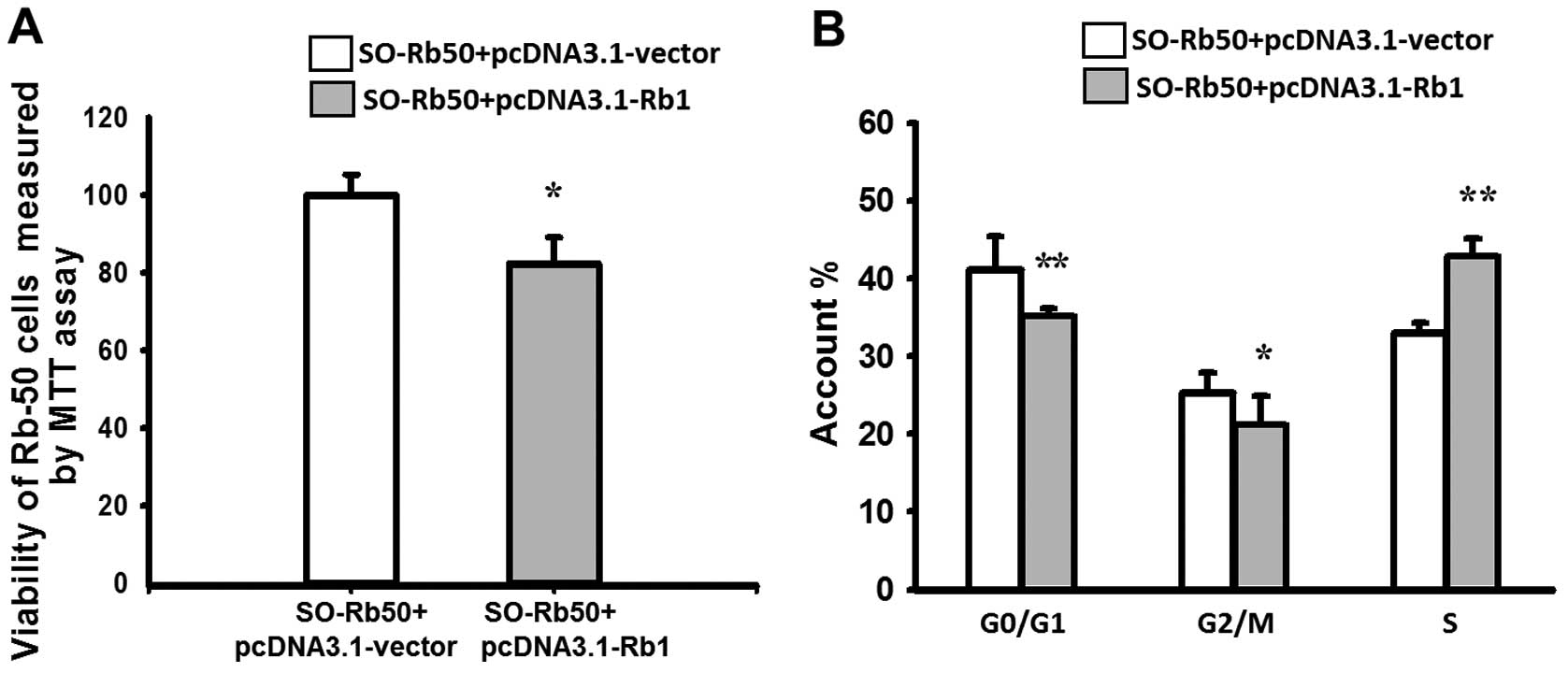
|
1.
|
Tamboli A, Podgor MJ and Horm JW: The
incidence of retinoblastoma in the United States: 1974 through
1985. Arch Ophthalmol. 108:128–132. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Diagnosis and
management of retinoblastoma. Cancer Control. 11:317–327. 2004.
|
|
3.
|
Chintagumpala M, Chevez-Barrios P, Paysse
EA, Plon SE and Hurwitz R: Retinoblastoma: review of current
management. Oncologist. 12:1237–1246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Melamud A, Palekar R and Singh A:
Retinoblastoma. Am Fam Physician. 73:1039–1044. 2006.
|
|
5.
|
Lim Z and Quah BL: Unilateral
retinoblastoma in an eye with Peters anomaly. J AAPOS. 14:184–186.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kanber D, Berulava T, Ammerpohl O, Mitter
D, Richter J, Siebert R, et al: The human retinoblastoma gene is
imprinted. PLoS Genet. 5:e10007902009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wilson PF, Nagasawa H, Fitzek MM, Little
JB and Bedford JS: G2-phase chromosomal radiosensitivity of primary
fibroblasts from hereditary retinoblastoma family members and some
apparently normal controls. Radiat Res. 173:62–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Knudsen ES, Sexton CR and Mayhew CN: Role
of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor in the maintenance of genome
integrity. Curr Mol Med. 6:749–757. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Feng G, Li H, Yi Y, Zheng J, Zhang Q, Wang
X and Du C: Study on the dynamic changes of retinoblastoma gene of
SO-Rb50 cell line. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 17:111–113. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
10.
|
Li H, Feng G, Fang Y, Li Y, Zheng J and Yi
Y: An investigation on chromosome aberration of SO-Rb50 cloned cell
strains. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 14:220–223. 1998.(In Chinese).
|
|
11.
|
Attwooll C, Lazzerini DE and Helin K: The
E2F family: specific functions and overlapping interests. EMBO J.
23:4709–4716. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Chen J, Zhu F, Weaks RL, Biswas AK, Guo R,
Li Y and Johnson DG: E2F1 promotes the recruitment of DNA repair
factors to sites of DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle.
10:1287–1294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Guo R, Chen J, Zhu F, Biswas AK, Berton
TR, Mitchell DL and Johnson DG: E2F1 localizes to sites of
UV-induced DNA damage to enhance nucleotide excision repair. J Biol
Chem. 285:19308–19315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bosco EE and Knudsen ES: Differential role
of RB in response to UV and IR damage. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:1581–1592. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Modesti M and Kanaar R: Homologous
recombination: from model organisms to human disease. Genome Biol.
2:reviews10142001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
West SC: Molecular views of recombination
proteins and their control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:435–445. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lieber MR, Ma Y, Pannicke U and Schwarz K:
Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:712–720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhuang J, Jiang G, Willers H and Xia F:
Exonuclease function of human Mre11 promotes deletional
nonhomologous end joining. J Biol Chem. 284:30565–30573. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Lucas JM, Bryans M, Lo K, Wilkie NM,
Freshney M, Thornton D and Lang JC: The FGF-4 promoter is required
for transformation and is active in both embryonal and somatic
cells. Oncol Res. 6:139–149. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Qu B, Zhuo Z, Yi Y, Feng G, Zheng J, Liang
Q and Li Y: Dynamic investigation on chromosome aberration of a
human retinoblastoma cell line So-Rb50. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 9:38–39.
37:1993
|
|
21.
|
Mao Z, Bozzella M, Seluanov A and
Gorbunova V: Comparison of nonhomologous end joining and homologous
recombination in human cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 7:1765–1771. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Boeckman HJ, Trego KS and Turchi JJ:
Cisplatin sensitizes cancer cells to ionizing radiation via
inhibition of nonhomologous end joining. Mol Cancer Res. 3:277–285.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Ganguly A, Nichols KE, Grant G, Rappaport
E and Shields C: Molecular karyotype of sporadic unilateral
retinoblastoma tumors. Retina. 29:1002–1012. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wang X, Zeng F, Xu Z, Zheng Y and Wang L:
Detection of tumor suppressor gene and oncogene in So-Rb50 human
retinoblastoma cell line. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 9:34–37. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS
and Bonner WM: DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX
phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 273:5858–5868. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Stucki M, Clapperton JA, Mohammad D, Yaffe
MB, Smerdon SJ and Jackson SP: MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated
histone H2AX to regulate cellular responses to DNA double-strand
breaks. Cell. 123:1213–1226. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hinz JM, Yamada NA, Salazar EP, Tebbs RS
and Thompson LH: Influence of double-strand-break repair pathways
on radiosensitivity throughout the cell cycle in CHO cells. DNA
Repair (Amst). 4:782–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Branzei D and Foiani M: Regulation of DNA
repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:297–308.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Helleday T, Lo J, van Gent DC and
Engelward BP: DNA double-strand break repair: from mechanistic
understanding to cancer treatment. DNA Repair (Amst). 6:923–935.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Mahaney BL, Meek K and Lees-Miller SP:
Repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks by
non-homologous end-joining. Biochem J. 417:639–650. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Haber JE: Partners and pathwaysrepairing a
double-strand break. Trends Genet. 16:259–264. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Karran P: DNA double strand break repair
in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 10:144–150. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Thompson LH and Schild D: Recombinational
DNA repair and human disease. Mutat Res. 509:49–78. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Chellappan SP, Hiebert S, Mudryj M,
Horowitz JM and Nevins JR: The E2F transcription factor is a
cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 65:1053–1061. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Stevaux O and Dyson NJ: A revised picture
of the E2F transcriptional network and RB function. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 14:684–691. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|