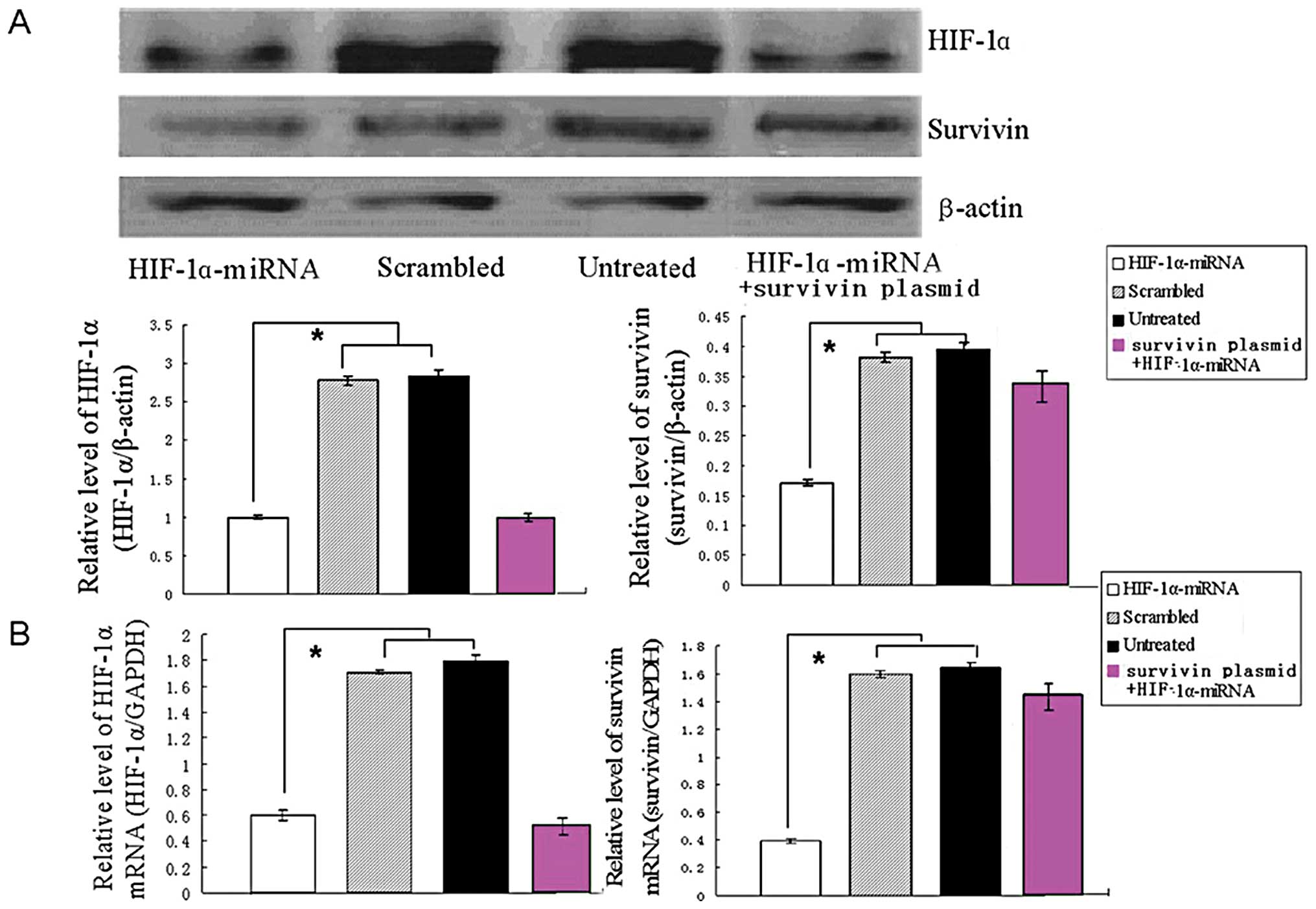
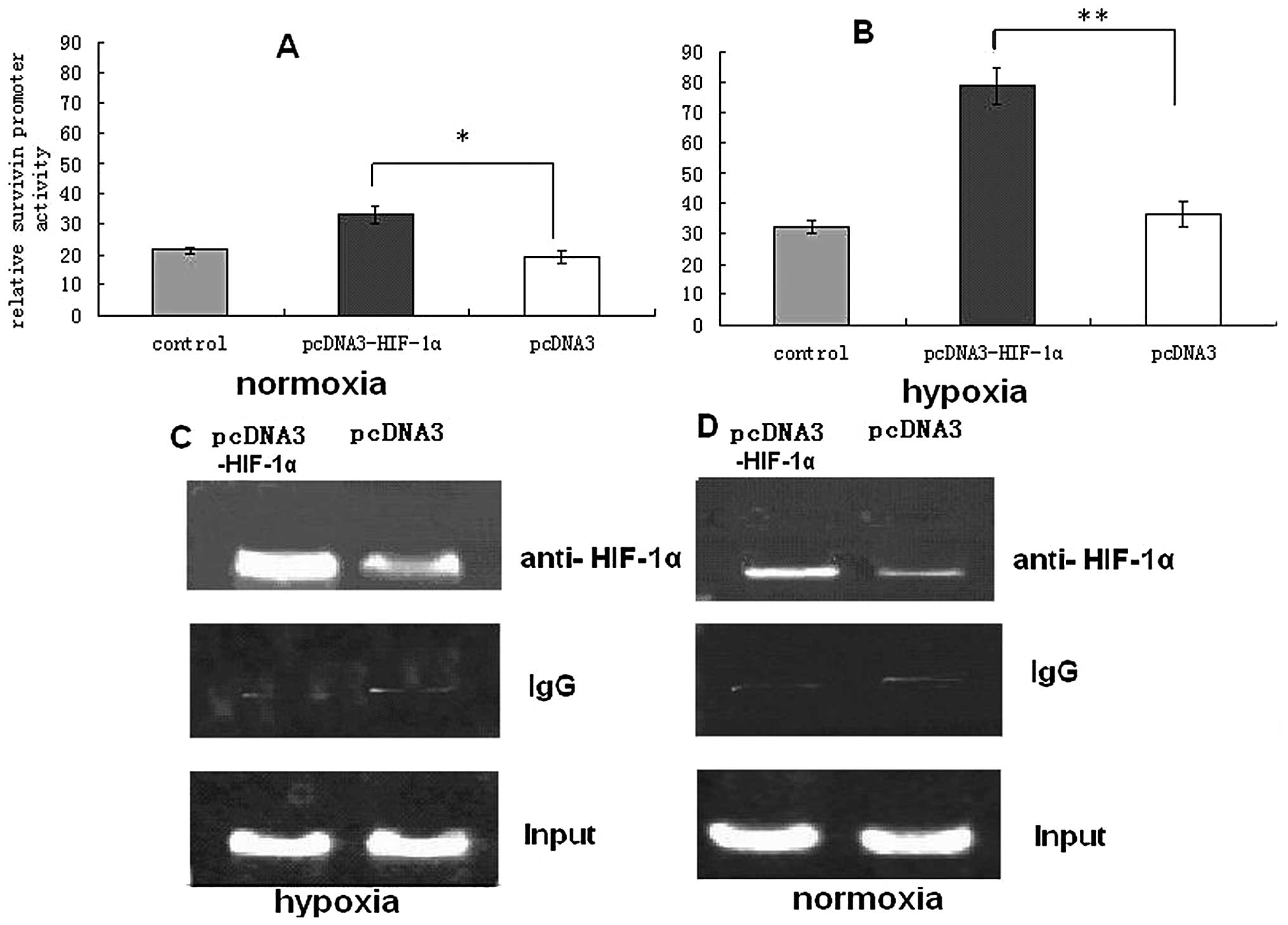
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: Apoptosis: mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Ann
Hematol. 84:627–639. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li F and Ling X: Survivin study: an update
of ‘what is the next wave’? J Cell Physiol. 208:476–486. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Altieri DC: The molecular basis and
potential role of survivin in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Trends
Mol Med. 7:542–547. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodel F, Hoffmann J, Distel L, et al:
Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and
therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res.
65:4881–4887. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altieri DC: Validating survivin as a
cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:46–54. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Knowles HJ and Harris AL: Hypoxia and
oxidative stress in breast cancer. Hypoxia and tumourigenesis.
Breast Cancer Res. 3:318–322. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harrison L and Blackwell K: Hypoxia and
anemia: factors in decreased sensitivity to radiation therapy and
chemotherapy. Oncologist. 9:31–40. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Denko NC: Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose
metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:705–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ogawa K, Chiba I, Morioka T, et al:
Clinical significance of HIF-1α expression in patients with
esophageal cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy.
Anticancer Res. 31:2351–2359. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Hochachka PW, Buck LT, Doll CJ and Land
SC: Unifying theory of hypoxia tolerance: molecular/metabolic
defense and rescue mechanisms for surviving oxygen lack. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:9493–9498. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Semenza GL: Regulation of mammalian
O2homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev
Cell Dev Biol. 15:551–578. 1999.
|
|
13
|
Jiang CQ, Fan LF, Liu ZS, et al:
Expression levels and significance of hypoxia inducible factor-1
alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in human colorectal
adenocarcinoma. Chin Med J. 117:1541–1546. 2004.
|
|
14
|
Chen YQ, Zhao CL and Li W: Effect of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha on transcription of survivin in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:292009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L, Cao Z, Li F, et al: Tumor-specific
gene expression using the survivin promoter is further increased by
hypoxia. Gene Ther. 11:1215–1223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Estève PO, Chin HG and Pradhan S:
Molecular mechanisms of transactivation and doxorubicin-mediated
repression of survivin gene in cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
282:2615–2625. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawamura K, Yu L, Tomizawa M, et al:
Transcriptional regulatory regions of the survivin gene
activate an exogenous suicide gene in human tumors and enhance the
sensitivity to a prodrug. Anticancer Res. 27:89–93. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen Y, Wang X, Li W, et al: Sp1
upregulates survivin expression in adenocarcinoma of lung cell line
A549. Anat Rec. 294:774–780. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng XH, Karna P, Cao Z, Jiang BH, Zhou M
and Yang L: Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signal pathways increases resistance to
apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression. J Biol Chem.
281:25903–25914. 2006.
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Li D, Liu H, et al: Notch-1
signaling facilitates survivin expression in human non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:14–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Semenza GL, Agani F, Feldser D, et al:
Hypoxia, HIF-1, and the pathophysiology of common human diseases.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 475:123–130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Chen YQ, Sun Y, Zhao CL and Wang XJ:
Regulation of survivin expression by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in
non-small cell lung cancer. Chin Oncol. 21:567–574. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Yu EZ, Li YY, Liu XH, Kagan E and McCarron
RM: Antiapoptotic action of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human
endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 84:553–561. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Malhotra R and Brosius FC: Glucose uptake
and glycolysis reduce hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cultured
neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 274:12567–12575. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luo F, Liu X, Yan N, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α promotes hypoxia-induced
A549 apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the glycolysis
pathway. BMC Cancer. 6:262006.
|
|
26
|
Nakahara K and Carthew RW: Expanding roles
for miRNAs and siRNAs in cell regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:127–133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK,
Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP and Bartel DP: MicroRNA targeting
specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell.
27:91–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shyu KG, Hsu FL, Wang MJ, Wang BW and Lin
S: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α regulates lung adenocarcinoma cell
invasion. Exp Cell Res. 313:1181–1191. 2007.
|
|
29
|
Liu GF, Zhao QG, Si L, Cao YG, Li GY and
Wang LX: Effects of survivin interference RNA on non-small cell
lung carcinoma. Clin Invest Med. 32:E2252009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|