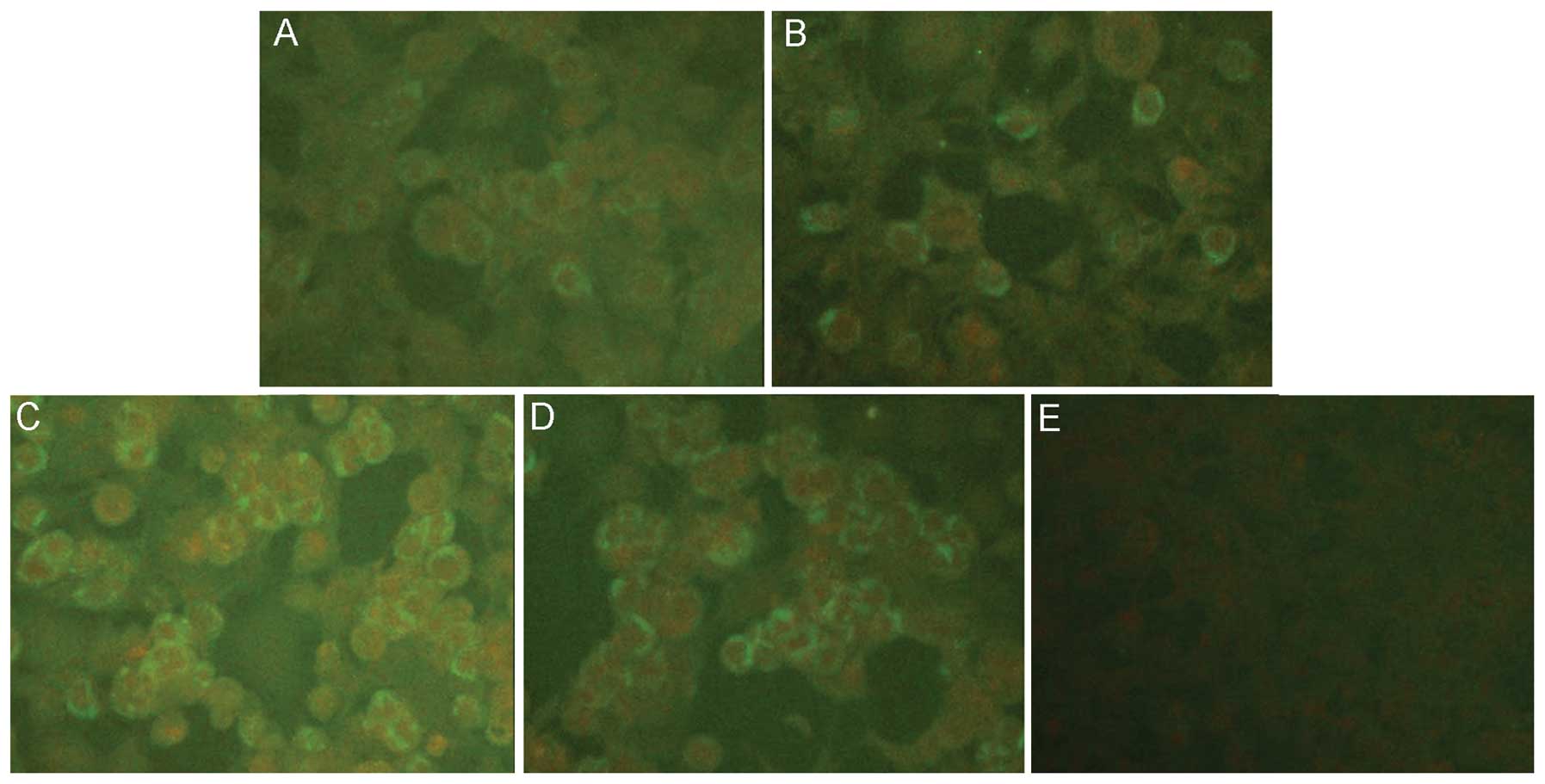
Spandidos Publications style
Li K, Li P, Wu X, Zhang L, Liu Z, Yu L, Zhang L, Cheng L, Bai W, Zhang F, Zhang F, et al: Induction of Hantaan virus-specific immune responses in C57BL/6 mice by immunization with a modified recombinant adenovirus containing the chimeric gene, GcS0.7. Int J Mol Med 32: 709-716, 2013.
APA
Li, K., Li, P., Wu, X., Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Yu, L. ... Xu, Z. (2013). Induction of Hantaan virus-specific immune responses in C57BL/6 mice by immunization with a modified recombinant adenovirus containing the chimeric gene, GcS0.7. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 32, 709-716. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1421
MLA
Li, K., Li, P., Wu, X., Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Yu, L., Zhang, L., Cheng, L., Bai, W., Zhang, F., Xu, Z."Induction of Hantaan virus-specific immune responses in C57BL/6 mice by immunization with a modified recombinant adenovirus containing the chimeric gene, GcS0.7". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 32.3 (2013): 709-716.
Chicago
Li, K., Li, P., Wu, X., Zhang, L., Liu, Z., Yu, L., Zhang, L., Cheng, L., Bai, W., Zhang, F., Xu, Z."Induction of Hantaan virus-specific immune responses in C57BL/6 mice by immunization with a modified recombinant adenovirus containing the chimeric gene, GcS0.7". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 32, no. 3 (2013): 709-716. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1421