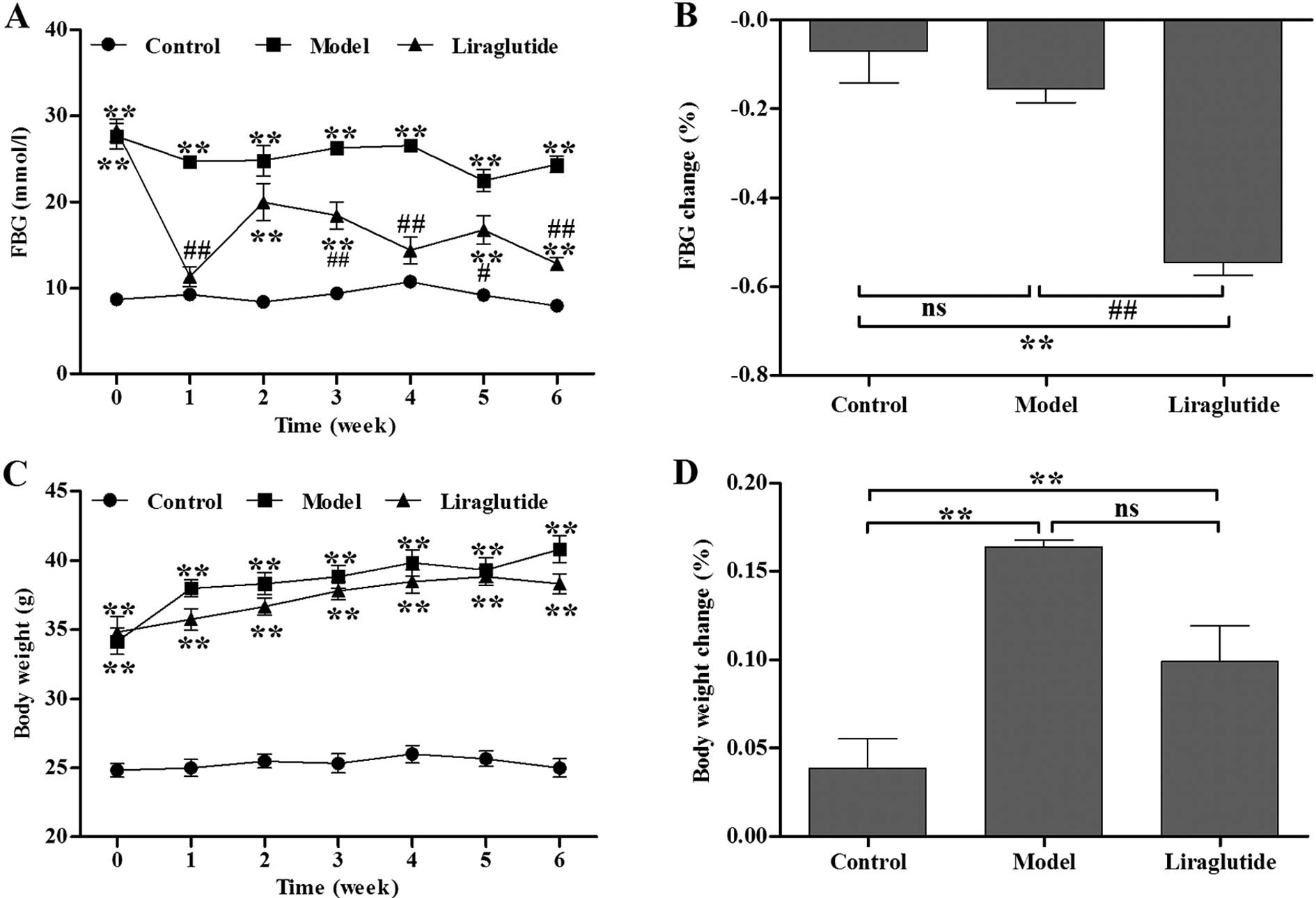
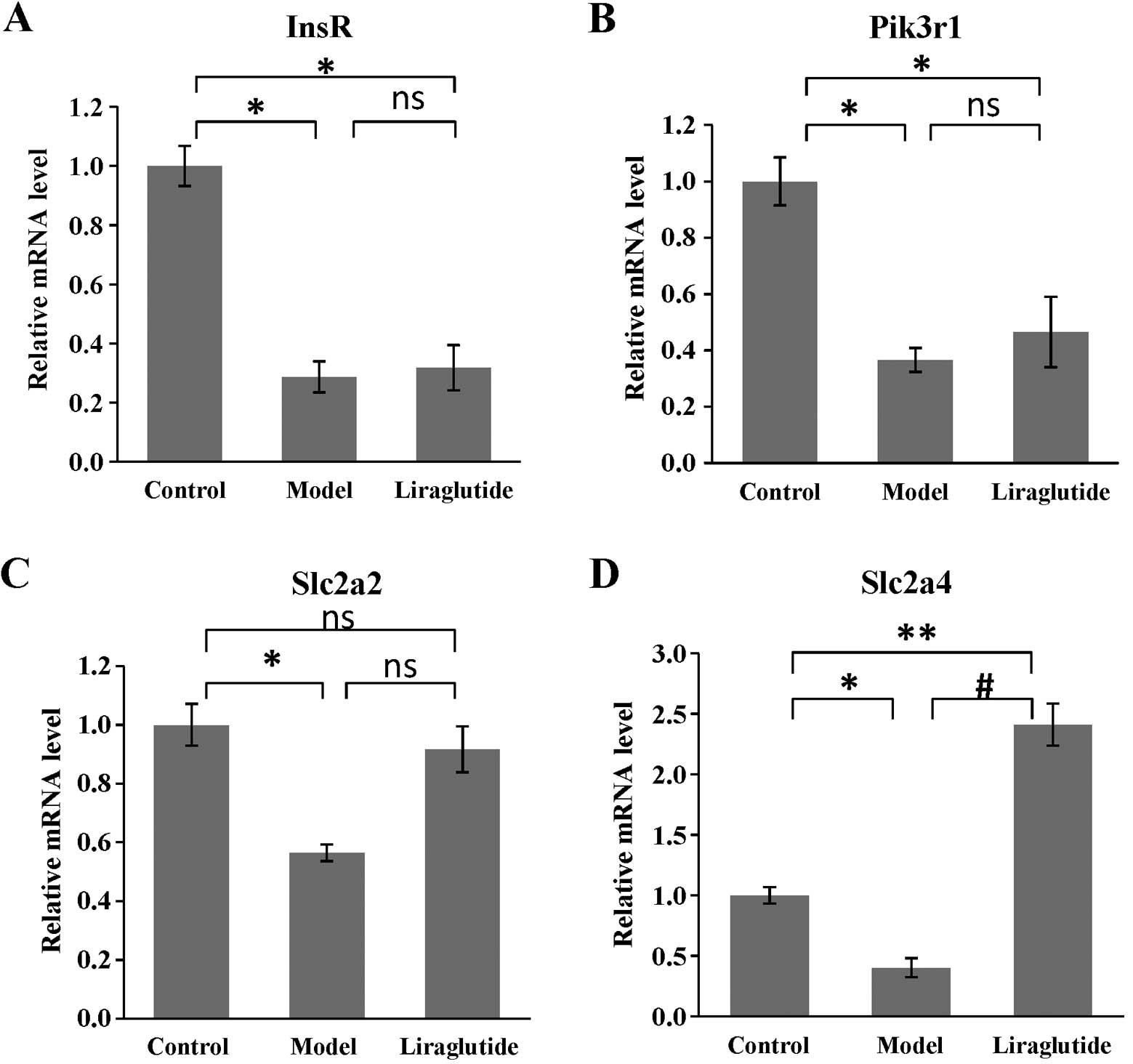
|
1
|
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R and
King H: Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000
and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 27:1047–1053.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geraldes P and King GL: Activation of
protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications.
Circ Res. 106:1319–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abdin AA, Baalash AA and Hamooda HE:
Effects of rosiglitazone and aspirin on experimental model of
induced type 2 diabetes in rats: focus on insulin resistance and
inflammatory markers. J Diabetes Complications. 24:168–178. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayden MR and Sowers JR: Treating
hypertension while protecting the vulnerable islet in the
cardiometabolic syndrome. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2:239–266. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li L, Miao Z, Liu R, Yang M, Liu H and
Yang G: Liraglutide prevents hypoadiponectinemia-induced insulin
resistance and alterations of gene expression involved in glucose
and lipid metabolism. Mol Med. 17:1168–1178. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mundil D, Cameron-Vendrig A and Husain M:
GLP-1 receptor agonists: a clinical perspective on cardiovascular
effects. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 9:95–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Senda M, Ogawa S, Nako K, Okamura M,
Sakamoto T and Ito S: The glucagon-like peptide-1 analog
liraglutide suppresses ghrelin and controls diabetes in a patient
with Prader-Willi syndrome. Endocr J. 59:889–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hunter K and Hölscher C: Drugs developed
to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood
brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 13:332012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kesavadev J, Shankar A, Krishnan G and
Jothydev S: Liraglutide therapy beyond glycemic control: an
observational study in Indian patients with type 2 diabetes in real
world setting. Int J Gen Med. 5:317–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fujishima Y, Maeda N, Inoue K, et al:
Efficacy of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
analogue, on body weight, eating behavior, and glycemic control, in
Japanese obese type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 11:1072012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fukushima T, Arai T, Ariga-Nedachi M, et
al: Insulin receptor substrates form high-molecular-mass complexes
that modulate their availability to insulin/insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor tyrosine kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
404:767–773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu Y, Pereira RO, O’Neill BT, et al:
Cardiac PI3K-Akt impairs insulin-stimulated glucose uptake
independent of mTORC1 and GLUT4 translocation. Mol Endocrinol.
27:172–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen S, Wasserman DH, MacKintosh C and
Sakamoto K: Mice with AS160/TBC1D4-Thr649Ala knockin mutation are
glucose intolerant with reduced insulin sensitivity and altered
GLUT4 trafficking. Cell Metab. 13:68–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Munkonda MN, Lapointe M, Miegueu P, et al:
Recombinant acylation stimulating protein administration to
C3−/− mice increases insulin resistance via adipocyte
inflammatory mechanisms. PLoS One. 7:e468832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei X, Wang D, Yang Y, et al:
Cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside improves obesity and triglyceride
metabolism in KK-Ay mice by regulating lipoprotein lipase activity.
J Sci Food Agric. 91:1006–1013. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Li PP, Shan S, Chen YT, et al: The
PPARalpha/gamma dual agonist chiglitazar improves insulin
resistance and dyslipidemia in MSG obese rats. Br J Pharmacol.
148:610–618. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin
hormones. Cell Metab. 3:153–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Porter DW, Kerr BD, Flatt PR, Holscher C
and Gault VA: Four weeks administration of Liraglutide improves
memory and learning as well as glycaemic control in mice with high
fat dietary-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 12:891–899. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gault VA, Kerr BD, Harriott P and Flatt
PR: Administration of an acylated GLP-1 and GIP preparation
provides added beneficial glucose-lowering and insulinotropic
actions over single incretins in mice with type 2 diabetes and
obesity. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:107–117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shimoda M, Kanda Y, Hamamoto S, et al: The
human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue liraglutide preserves
pancreatic beta cells via regulation of cell kinetics and
suppression of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a
mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia. 54:1098–1108. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Magnoni LJ, Vraskou Y, Palstra AP and
Planas JV: AMP-activated protein kinase plays an important
evolutionary conserved role in the regulation of glucose metabolism
in fish skeletal muscle cells. PLoS One. 7:e312192012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Oosterveer MH, Mataki C, Yamamoto H, et
al: LRH-1-dependent glucose sensing determines intermediary
metabolism in liver. J Clin Invest. 122:2817–2826. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ros S, García-Rocha M, Calbó J and
Guinovart JJ: Restoration of hepatic glycogen deposition reduces
hyperglycaemia, hyperphagia and gluconeogenic enzymes in a
streptozotocin-induced model of diabetes in rats. Diabetologia.
54:2639–2648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
John S, Weiss JN and Ribalet B:
Subcellular localization of hexokinases I and II directs the
metabolic fate of glucose. PLoS One. 6:e176742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun L, Shukair S, Naik TJ, Moazed F and
Ardehali H: Glucose phosphorylation and mitochondrial binding are
required for the protective effects of hexokinases I and II. Mol
Cell Biol. 28:1007–1017. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Holyoak T, Zhang B, Deng J, Tang Q,
Prasannan CB and Fenton AW: Energetic coupling between an
oxidizable cysteine and the phosphorylatable N-terminus of human
liver pyruvate kinase. Biochemistry. 52:466–476. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cortés-Cros M, Hemmerlin C, Ferretti S, et
al: M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is dispensable for tumor
maintenance and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:489–494.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun Q, Chen X, Ma J, et al: Mammalian
target of rapamycin up-regulation of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type
M2 is critical for aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:4129–4134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye J, Mancuso A, Tong X, et al: Pyruvate
kinase M2 promotes de novo serine synthesis to sustain mTORC1
activity and cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:6904–6909. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shirakawa J, Tanami R, Togashi Y, et al:
Effects of liraglutide on beta-cell-specific glucokinase-deficient
neonatal mice. Endocrinology. 153:3066–3075. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Janghorbani M and Amini M: Incidence of
metabolic syndrome and its risk factors among type 2 diabetes
clinic attenders in Isfahan, Iran. Endokrynol Pol. 63:372–380.
2012.
|
|
32
|
Ohshima K, Mogi M, Jing F, et al: Direct
angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation ameliorates insulin
resistance in type 2 diabetes mice with PPARγ activation. PLoS One.
7:e483872012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rosengren AH, Braun M, Mahdi T, et al:
Reduced insulin exocytosis in human pancreatic β-cells with gene
variants linked to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 61:1726–1733.
2012.
|
|
34
|
Tersey SA, Nishiki Y, Templin AT, et al:
Islet β-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress precedes the onset of
type 1 diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse model. Diabetes.
61:818–827. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Emamaullee JA, Merani S, Toso C, et al:
Porcine marginal mass islet autografts resist metabolic failure
over time and are enhanced by early treatment with liraglutide.
Endocrinology. 150:2145–2152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sturis J, Gotfredsen CF, Rømer J, et al:
GLP-1 derivative liraglutide in rats with beta-cell deficiencies:
influence of metabolic state on beta-cell mass dynamics. Br J
Pharmacol. 140:123–132. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Knudsen LB: Liraglutide: the therapeutic
promise from animal models. Int J Clin Pract. 167:4–11. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kawamori R: Insulin resistance seen in
non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Hypertens
Res. 19(Suppl 1): S61–S64. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tomimoto S, Ojika T, Shintani N, et al:
Markedly reduced white adipose tissue and increased insulin
sensitivity in adcyap1-deficient mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 107:41–48.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B and Kahn CR:
Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin
action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:85–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Inokuchi J: Membrane microdomains and
insulin resistance. Febs Lett. 584:1864–1871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang YC and Chuang LM: The role of
oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes: from
molecular mechanism to clinical implication. Am J Transl Res.
2:316–331. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Muniyappa R, Montagnani M, Koh KK and Quon
MJ: Cardiovascular actions of insulin. Endocr Rev. 28:463–491.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee JO, Song YH, Kim MW, et al: A
sub-1-volt nanoelectromechanical switching device. Nat Nanotechnol.
8:36–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Giannocco G, Oliveira KC, Crajoinas RO, et
al: Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition upregulates GLUT4
translocation and expression in heart and skeletal muscle of
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 698:74–86. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Nieto-Vazquez I, Fernández-Veledo S, de
Alvaro C and Lorenzo M: Dual role of interleukin-6 in regulating
insulin sensitivity in murine skeletal muscle. Diabetes.
57:3211–3221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang WY, Lee JJ, Kim IS, Kim Y, Park JS
and Myung CS: 7-O-methylaromadendrin stimulates glucose uptake and
improves insulin resistance in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:1494–1499. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|