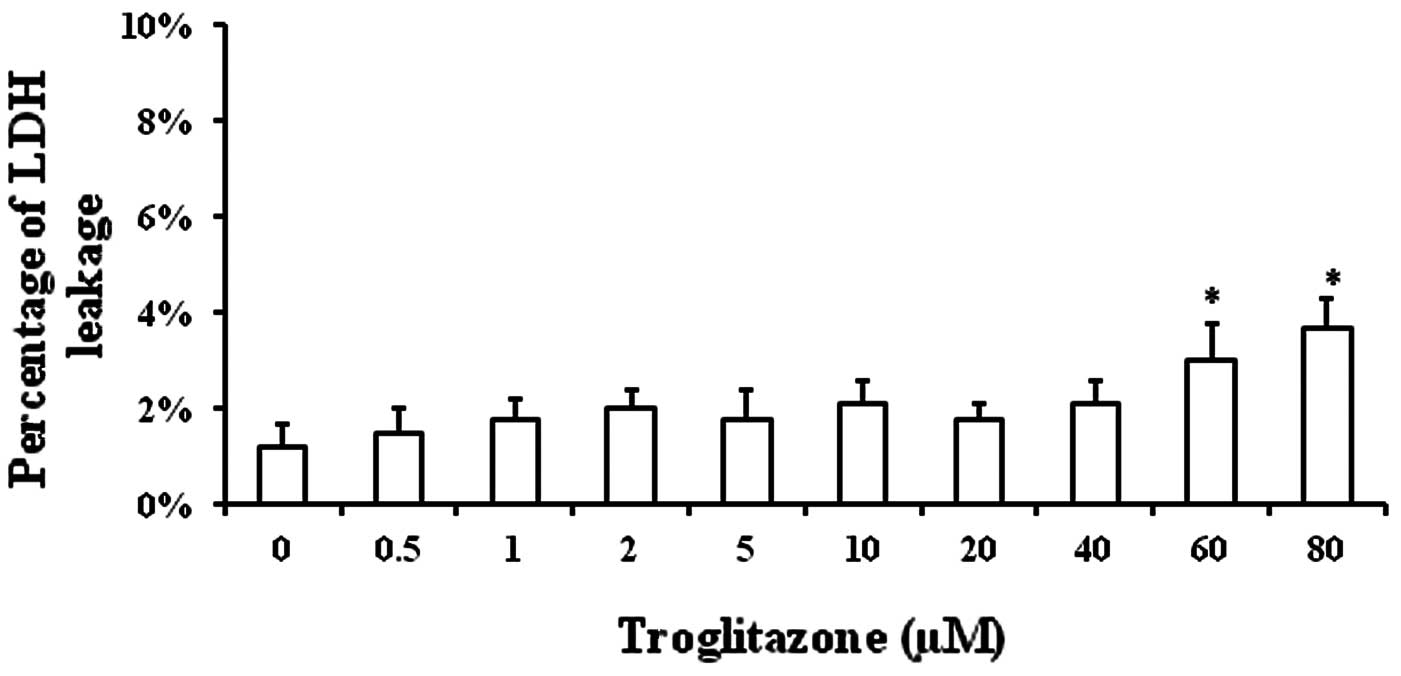
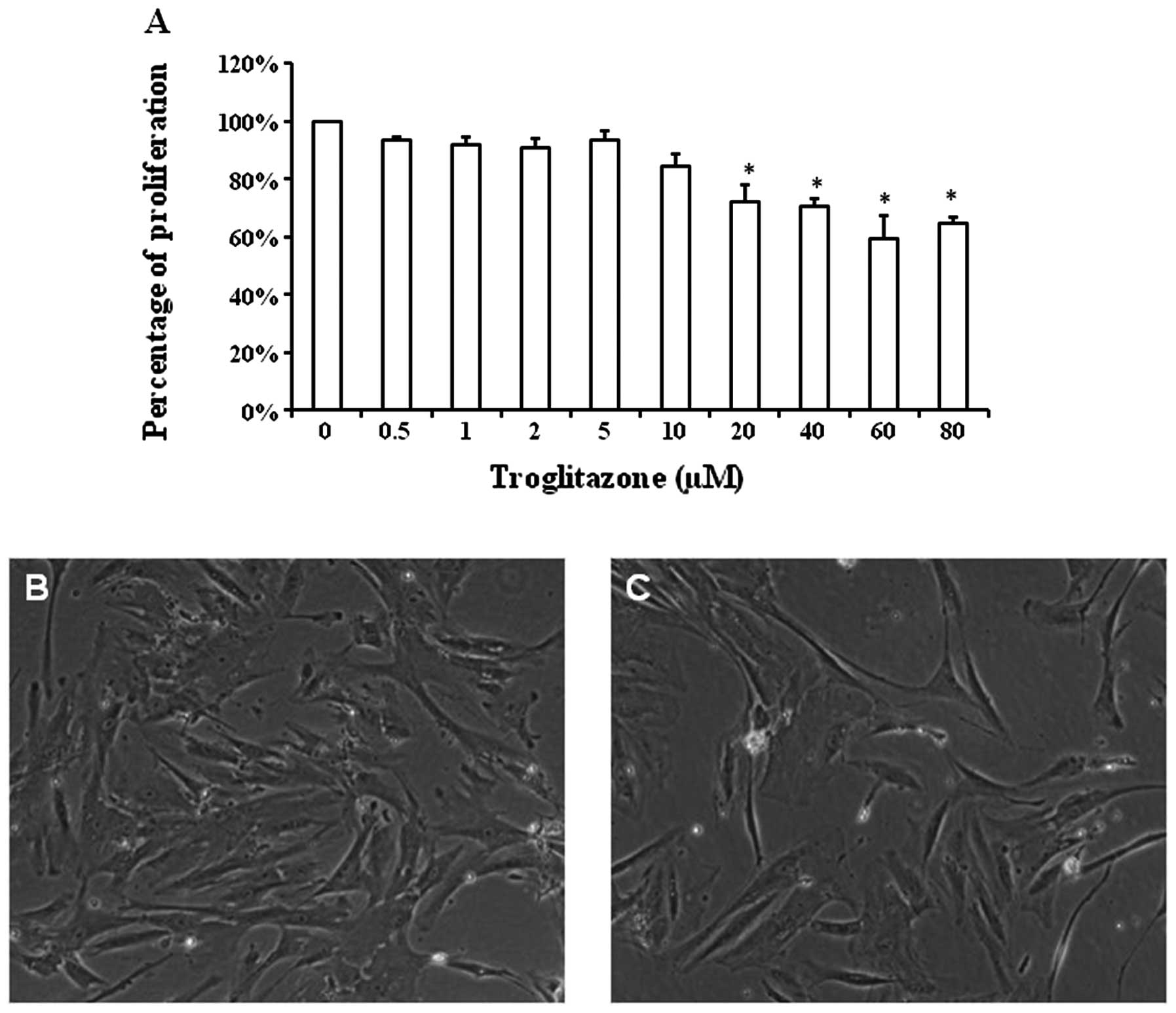
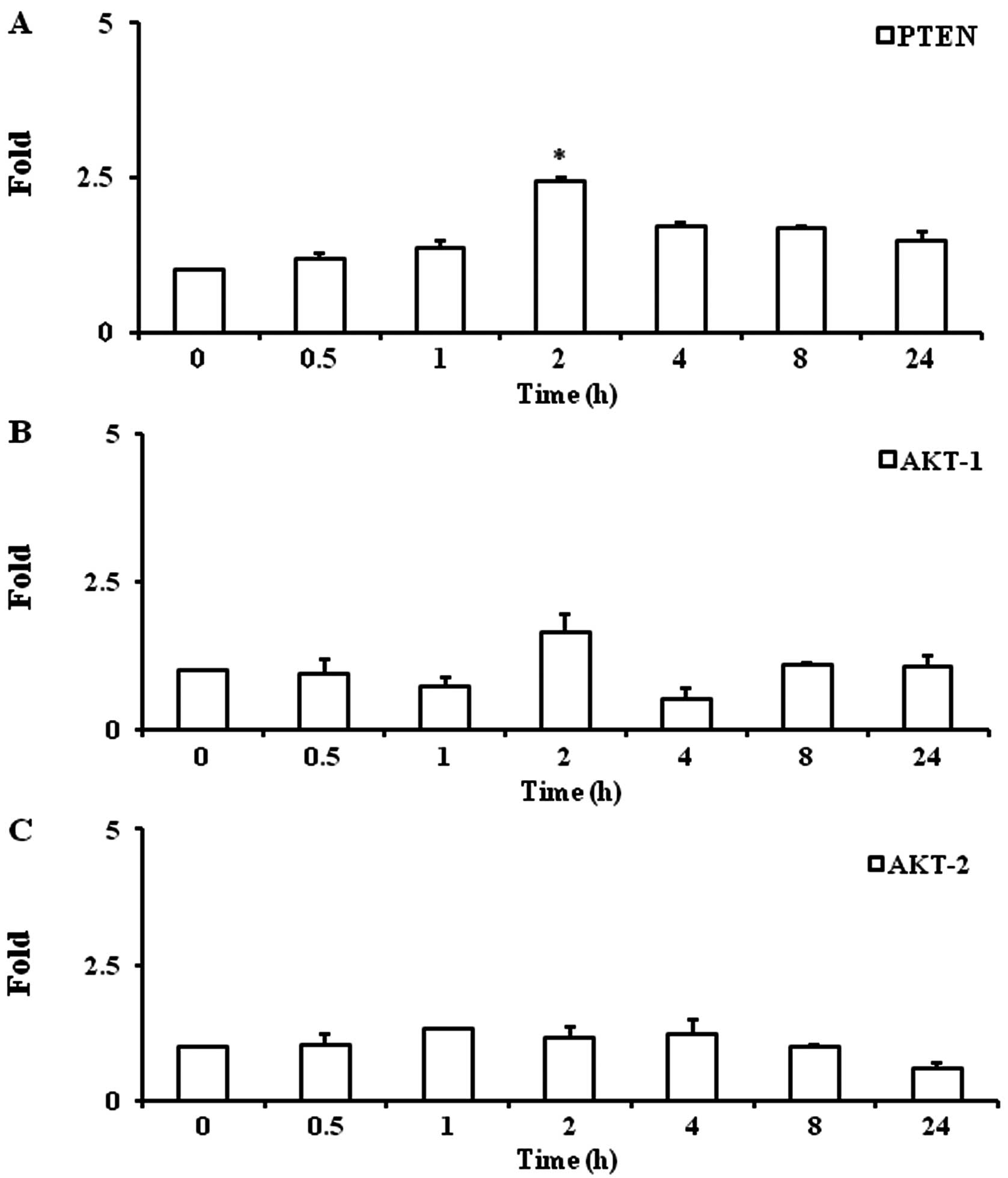
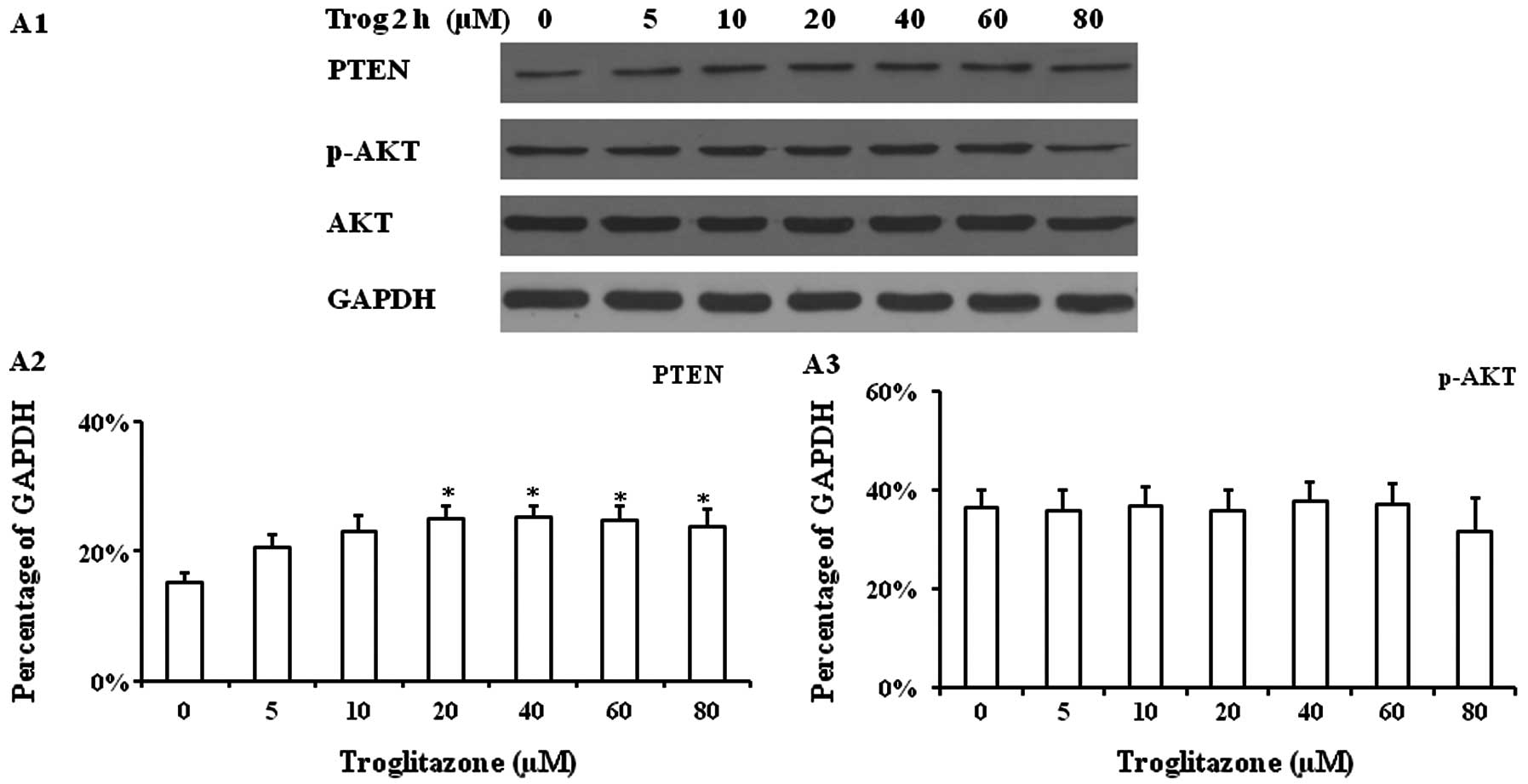
|
1
|
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, et
al: ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary
hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology
Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the
American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the
American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society,
Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Circulation.
119:2250–2294. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Pietra GG, Edwards WD, Kay JM, et al:
Histopathology of primary pulmonary hypertension. A qualitative and
quantitative study of pulmonary blood vessels from 58 patients in
the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Primary Pulmonary
Hypertension Registry. Circulation. 80:1198–1206. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nakaoka T, Gonda K, Ogita T, et al:
Inhibition of rat vascular smooth muscle proliferation in vitro and
in vivo by bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Clin Invest.
100:2824–2832. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hansmann G, de Jesus Perez VA, Alastalo
TP, et al: An antiproliferative BMP-2/PPARgamma/apoE axis in human
and murine SMCs and its role in pulmonary hypertension. J Clin
Invest. 118:1846–1857. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nisbet RE, Bland JM, Kleinhenz DJ, et al:
Rosiglitazone attenuates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension in a mouse model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
42:482–490. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee KS, Park SJ, Hwang PH, Yi HK, Song CH,
Chai OH, Kim JS, Lee MK and Lee YC: PPAR-gamma modulates allergic
inflammation through up-regulation of PTEN. FASEB J. 19:1033–1035.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang W, Wu N, Li ZX, Wang LY, Jin JW and
Zha XL: PPARgamma activator rosiglitazone inhibits cell migration
via upregulation of PTEN in human hepatocarcinoma cell line
BEL-7404. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1008–1014. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye L, Haider KhH, Esa WB, et al:
Liposome-based vascular endothelial growth factor-165 transfection
with skeletal myoblast for treatment of ischaemic limb disease. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:323–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ye L, Lee KO, Su LP, et al: Skeletal
myoblast transplantation for attenuation of hyperglycaemia,
hyperinsulinaemia and glucose intolerance in a mouse model of type
2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 52:1925–1934. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang S, Fantozzi I, Tigno DD, et al: Bone
morphogenetic proteins induce apoptosis in human pulmonary vascular
smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
285:L740–L754. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O,
Krowka MJ, Olschewski H and Gaine S: Diagnosis and differential
assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol.
43:40S–47S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ameshima S, Golpon H, Cool CD, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma)
expression is decreased in pulmonary hypertension and affects
endothelial cell growth. Circ Res. 92:1162–1169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Michalik L, Auwerx J, Berger JP, et al:
International Union of Pharmacology. LXI Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 58:726–741. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsuda Y, Hoshikawa Y, Ameshima S, et al:
Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands
on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Nihon
Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 43:283–288. 2005.(In Japanese).
|
|
15
|
Crossno JT Jr, Garat CV, Reusch JE, et al:
Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
remodeling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L885–L897.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hansmann G, Wagner RA, Schellong S, et al:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension is linked to insulin resistance and
reversed by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
activation. Circulation. 115:1275–1284. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Teresi RE, Shaiu C, Chen C, Chatterjee K,
Waite KA and Eng C: Increased PTEN expression due to
transcriptional activation of PPARgamma by Lovastatin and
Rosiglitazone. Int J Cancer. 118:2390–2398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Minamino T, Mitsialis SA and Kourembanas
S: Hypoxia extends the life span of vascular smooth muscle cells
through telomerase activation. Mol Cell Biol. 21:3336–3342. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maehama T and Dixon JE: The tumor
suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second
messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem.
273:13375–13378. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|