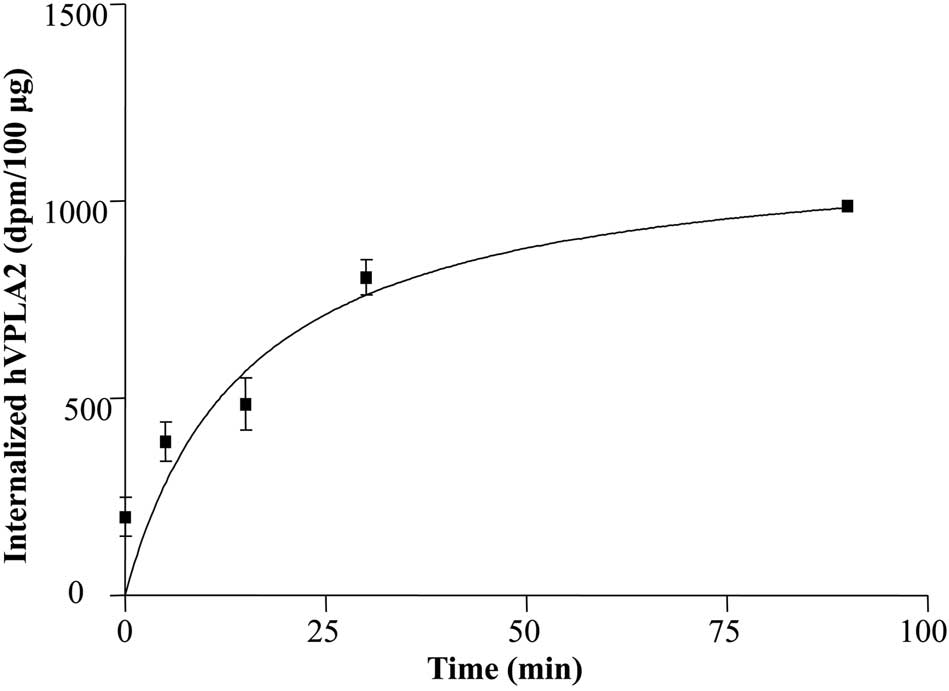
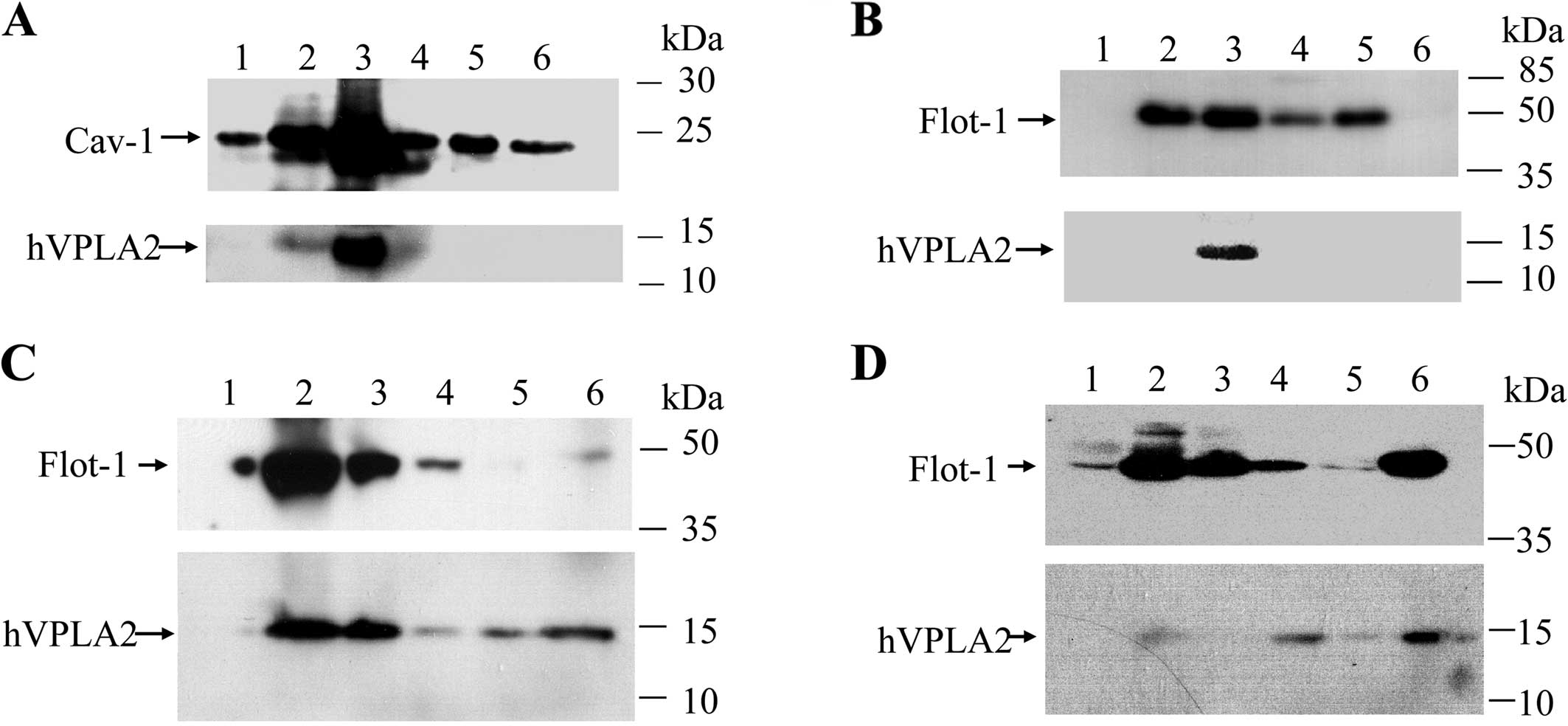
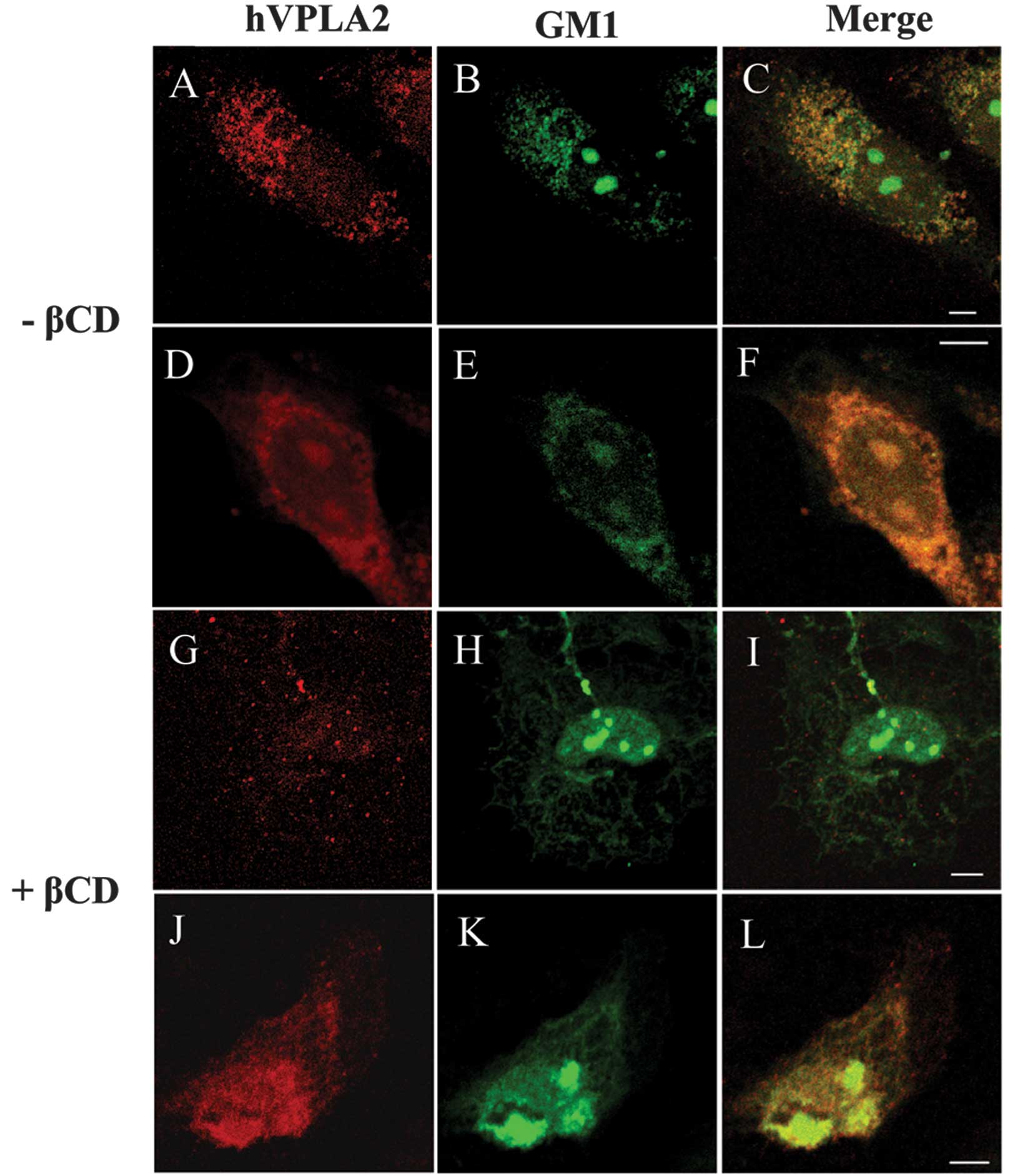
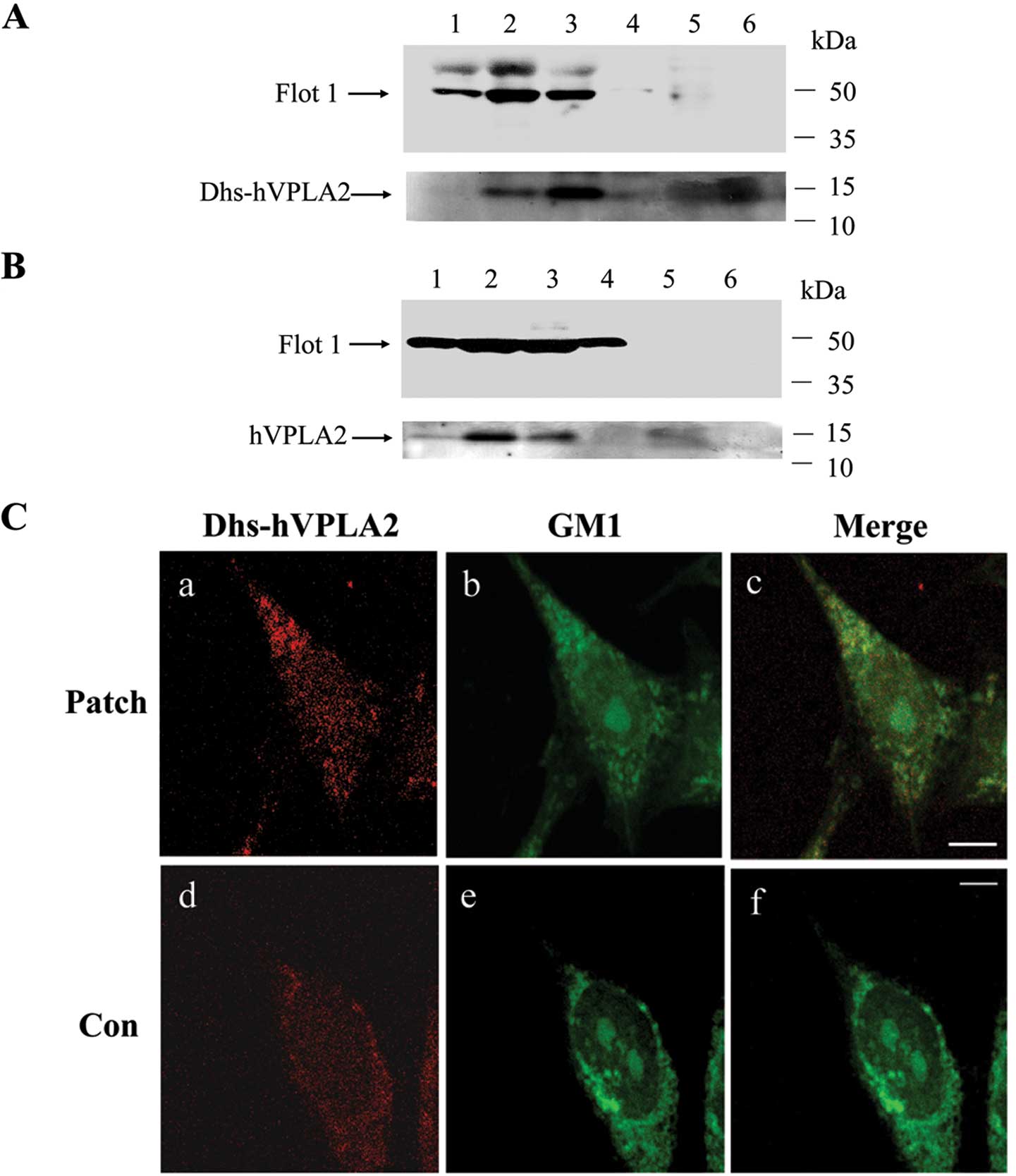
|
1
|
Schaloske RH and Dennis EA: The
phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering
system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1761:1246–1259. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lambeau G and Gelb MH: Biochemistry and
physiology of mammalian secreted phospholipases A2. Annu
Rev Biochem. 77:495–520. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Han WK, Sapirstein A, Hung CC,
Alessandrini A and Bonventre JV: Cross-talk between cytosolic
phospholipase A2 alpha (cPLA2 alpha) and
secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) in
hydrogen peroxide-induced arachidonic acid release in murine
mesangial cells: sPLA2 regulates cPLA2 alpha
activity that is responsible for arachidonic acid release. J Biol
Chem. 278:24153–24163. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murakami M, Kambe T, Shimbara S, Yamamoto
S, Kuwata H and Kudo I: Functional association of type IIA
secretory phospholipase A(2) with the
glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored heparan sulfate proteoglycan
in the cyclooxygenase-2-mediated delayed prostanoid-biosynthetic
pathway. J Biol Chem. 274:29927–29936. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fleisch JH, Armstrong CT, Roman CR, et al:
Recombinant human secretory phospholipase A2 released thromboxane
from guinea pig bronchoalveolar lavage cells: in vitro and ex vivo
evaluation of a novel secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitor. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 278:252–257. 1996.
|
|
6
|
Kim YJ, Kim KP, Han SK, et al: Group V
phospholipase A2 induces leukotriene biosynthesis in
human neutrophils through the activation of group IVA phospholipase
A2. J Biol Chem. 277:36479–36488. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muñoz NM, Kim YJ, Meliton AY, et al: Human
group V phospholipase A2 induces group IVA phospholipase
A2-independent cysteinyl leukotriene synthesis in human
eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 278:38813–38820. 2003.
|
|
8
|
Bezzine S, Koduri RS, Valentin E, et al:
Exogenously added human group X secreted phospholipase A(2) but not
the group IB, IIA, and V enzymes efficiently release arachidonic
acid from adherent mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 275:3179–3191.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Murakami M, Koduri RS, Enomoto A, et al:
Distinct arachidonate-releasing functions of mammalian secreted
phospholipase A2s in human embryonic kidney 293 and rat mastocytoma
RBL-2H3 cells through heparan sulfate shuttling and external plasma
membrane mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 276:10083–10096. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wijewickrama GT, Kim JH, Kim YJ, et al:
Systematic evaluation of transcellular activities of secretory
phospholipases A2. High activity of group V
phospholipases A2 to induce eicosanoid biosynthesis in
neighboring inflammatory cells. J Biol Chem. 281:10935–10944.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reddy ST and Herschman HR: Transcellular
prostaglandin production following mast cell activation is mediated
by proximal secretory phospholipase A2 and distal
prostaglandin synthase 1. J Biol Chem. 271:186–191. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murakami M, Kambe T, Shimbara S and Kudo
I: Functional coupling between various phospholipase A2s
and cyclooxygenases in immediate and delayed prostanoid
biosynthetic pathways. J Biol Chem. 274:3103–3115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
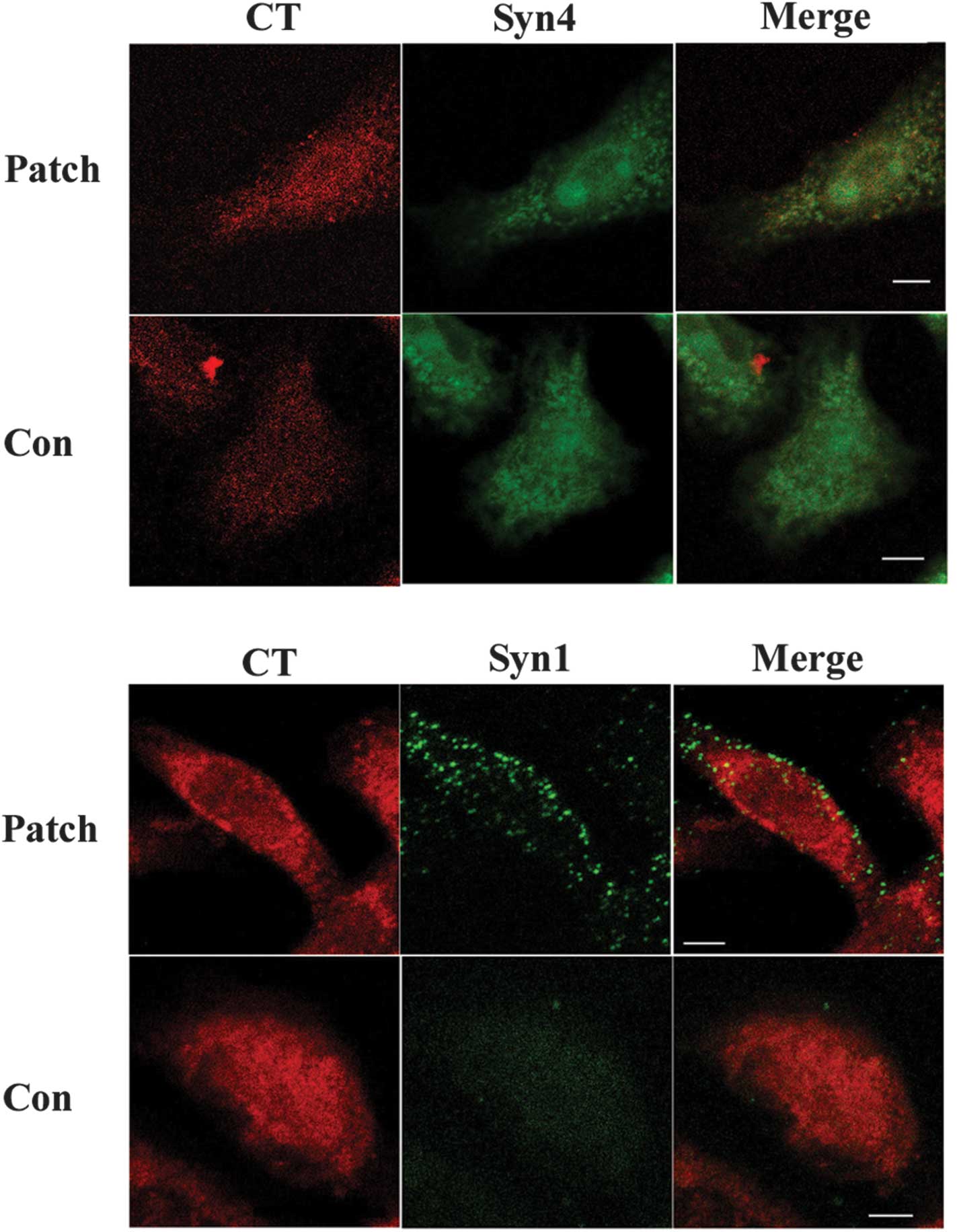
Balboa MA, Shirai Y, Gaietta G, Ellisman
MH, Balsinde J and Dennis EA: Localization of group V phospholipase
A2 in caveolin-enriched granules in activated
P388D1 macrophage-like cells. J Biol Chem.
278:48059–48065. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
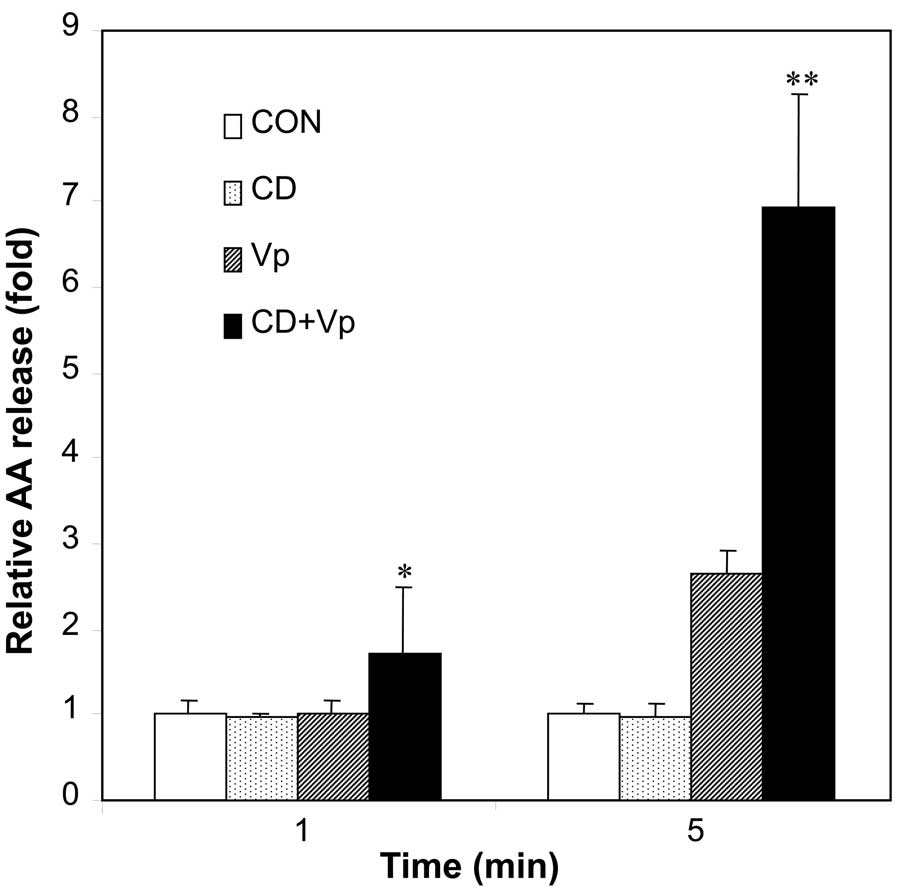
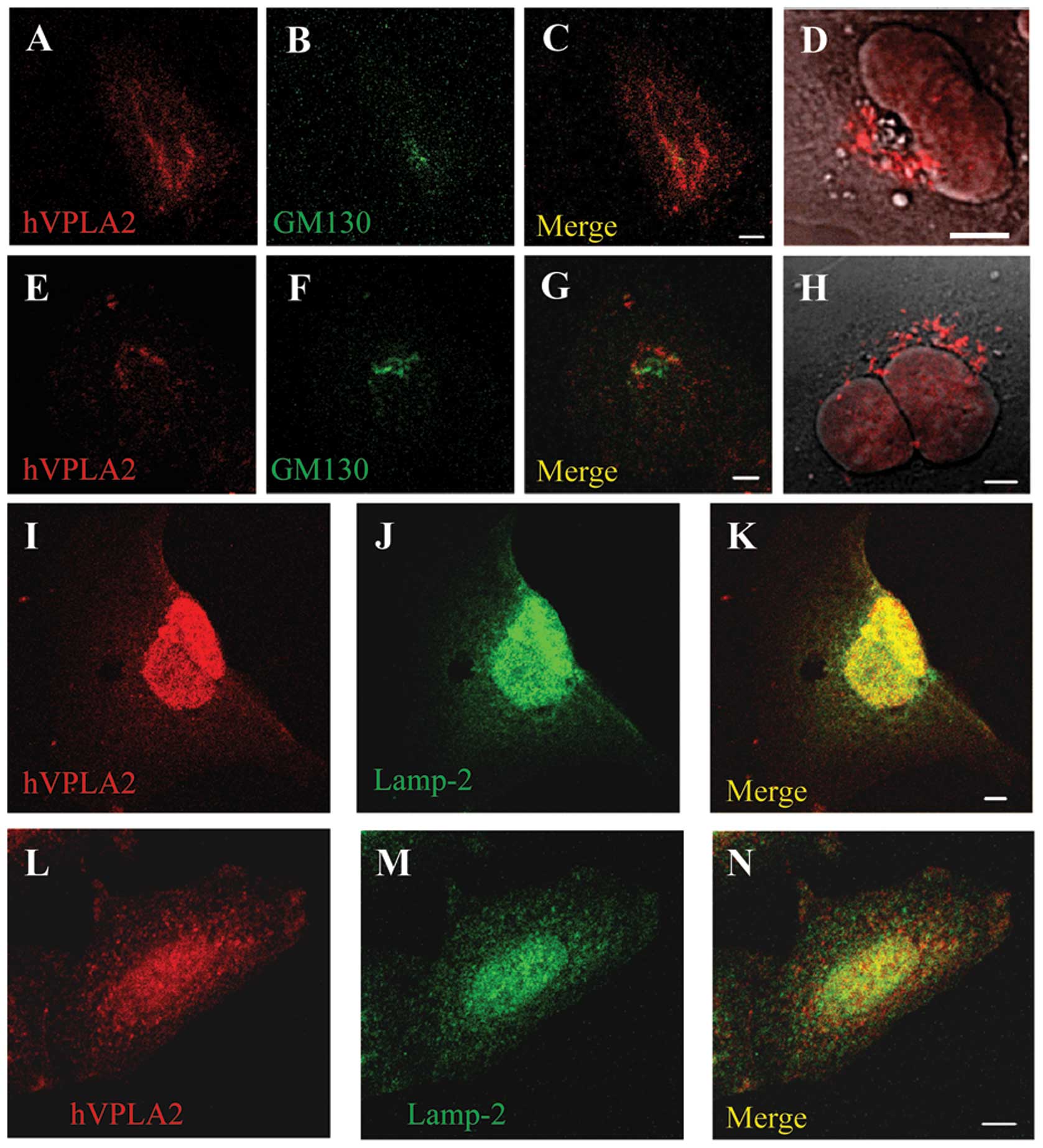
Kim YJ, Kim KP, Rhee HJ, et al:
Internalized group V secretory phospholipase A2 acts on
the perinuclear membranes. J Biol Chem. 277:9358–9365. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han SK, Kim KP, Koduri R, et al: Roles of
Trp31 in high membrane binding and proinflammatory activity of
human group V phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem.
274:11881–11888. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
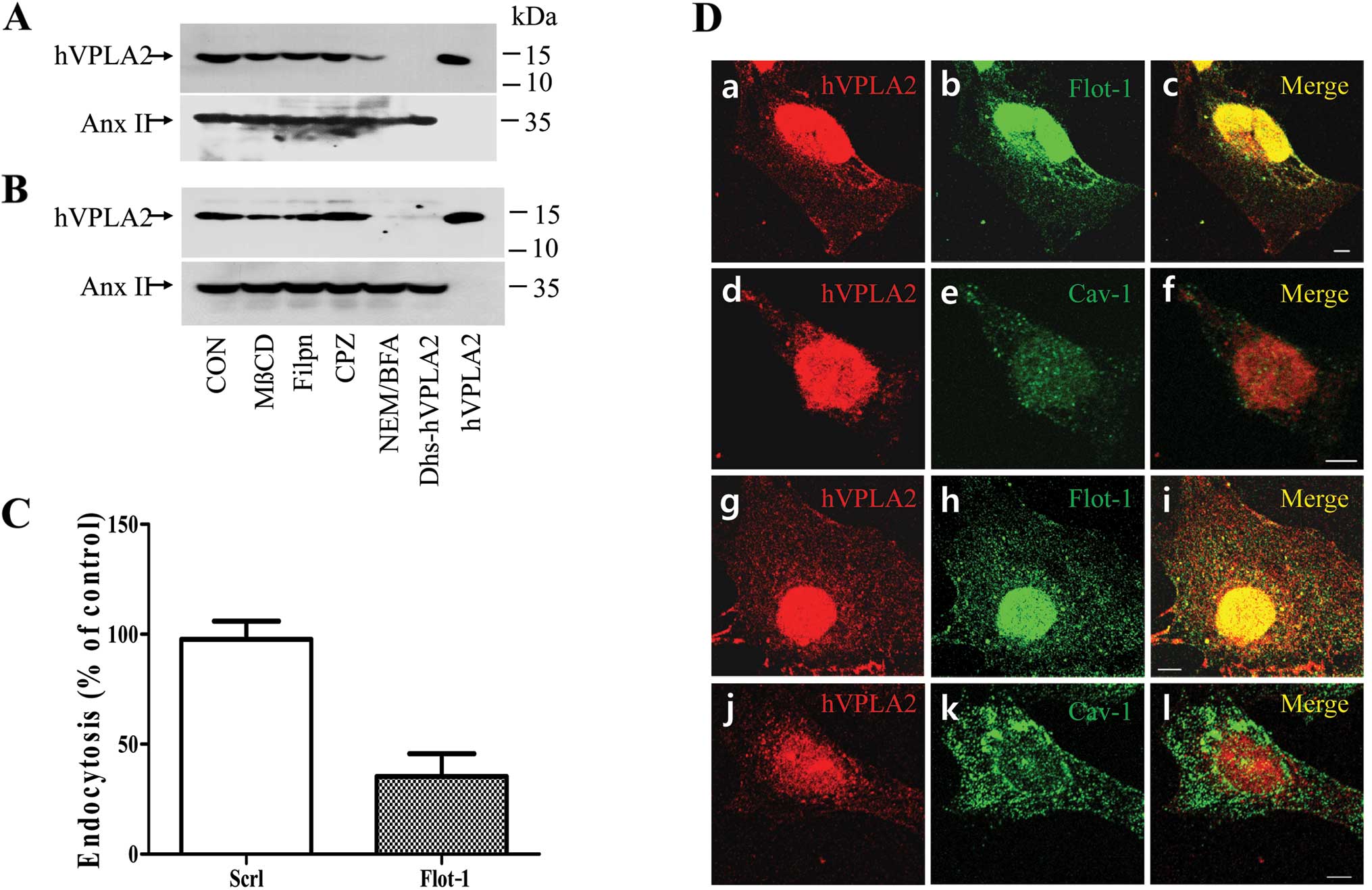
Glebov OO, Bright NA and Nichols BJ:
Flotillin-1 defines a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway in
mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol. 8:46–54. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harder T, Scheiffele P, Verkade P and
Simons K: Lipid domain structure of the plasma membrane revealed by
patching of membrane components. J Cell Biol. 141:929–942. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Janes PW, Ley SC and Magee AI: Aggregation
of lipid rafts accompanies signaling via the T cell antigen
receptor. J Cell Biol. 147:447–461. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ringerike T, Blystad FD, Levy FO, Madshus
IH and Stang E: Cholesterol is important in control of EGF receptor
kinase activity but EGF receptors are not concentrated in caveolae.
J Cell Sci. 115:1331–1340. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roepstorff K, Thomsen P, Sandvig K and van
Deurs B: Sequestration of epidermal growth factor receptors in
non-caveolar lipid rafts inhibits ligand binding. J Biol Chem.
277:18954–18960. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim KP, Rafter JD, Bittova L, et al:
Mechanism of human group V phospholipase A2
(PLA2)-induced leukotriene biosynthesis in human
neutrophils. A potential role of heparan sulfate binding in
PLA2 internalization and degradation. J Biol Chem.
276:11126–11134. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan TC, Chang HT, Chen IW, Wang HY and
Chang MD: A heparan sulfate-facilitated and raft-dependent
macropinocytosis of eosinophil cationic protein. Traffic.
8:1778–1795. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taylor DR, Whitehouse IJ and Hooper NM:
Glypican-1 mediates both prion protein lipid raft association and
disease isoform formation. PLoS Pathog. 5:e10006662009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Podyma-Inoue KA, Hara-Yokoyama M,
Shinomura T, Kimura T and Yanagishita M: Syndecans reside in
sphingomyelin-enriched low-density fractions of the plasma membrane
isolated from a parathyroid cell line. PloS One. 7:e323512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Payne CK, Jones SA, Chen C and Zhuang X:
Internalization and trafficking of cell surface proteoglycans and
proteoglycan-binding ligands. Traffic. 8:389–401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vercauteren D, Piest M, van der Aa LJ, et
al: Flotillin-dependent endocytosis and a phagocytosis-like
mechanism for cellular internalization of disulfide-based
poly(amido amine)/DNA polyplexes. Biomaterials. 32:3072–3084. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|