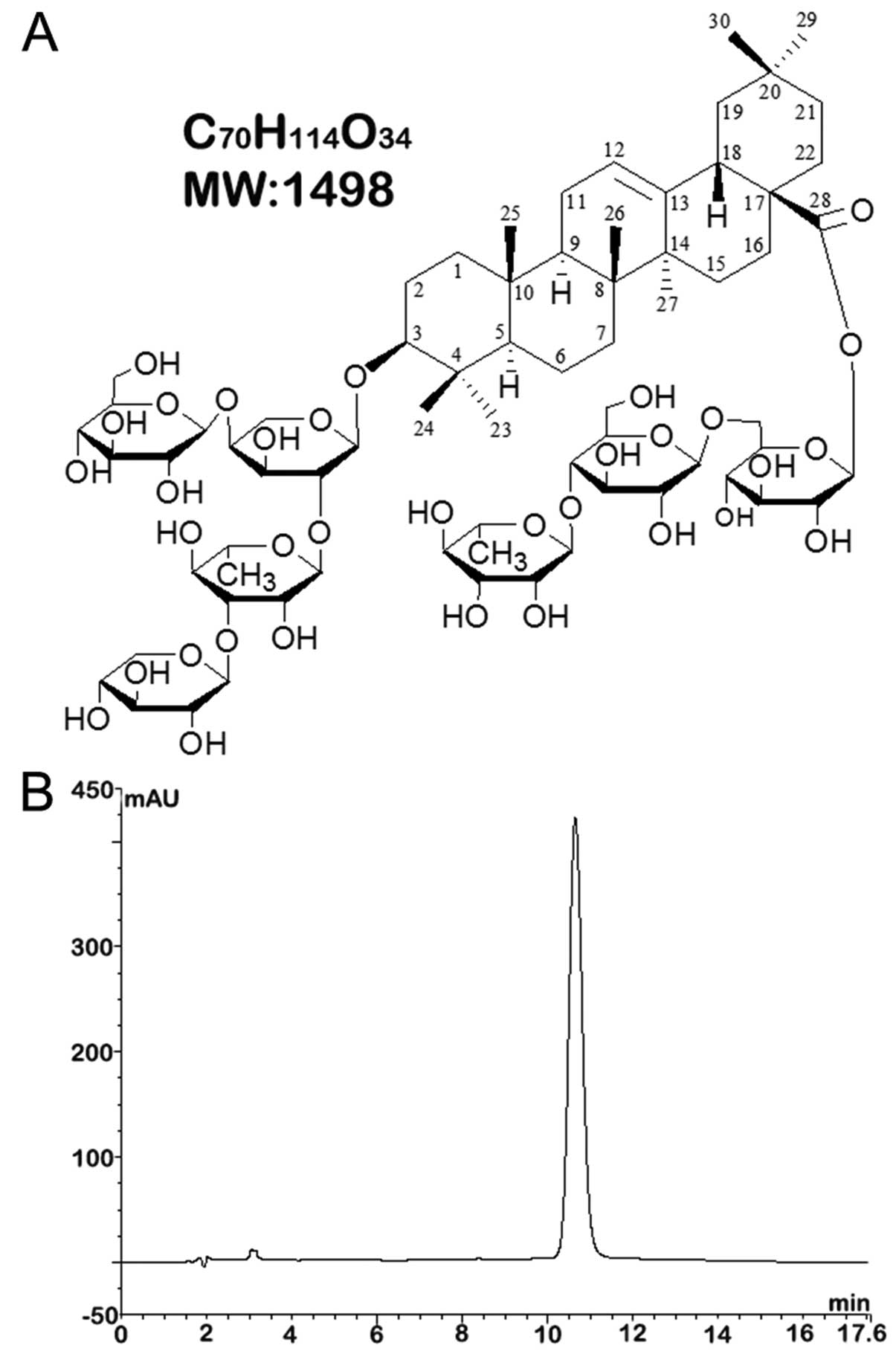
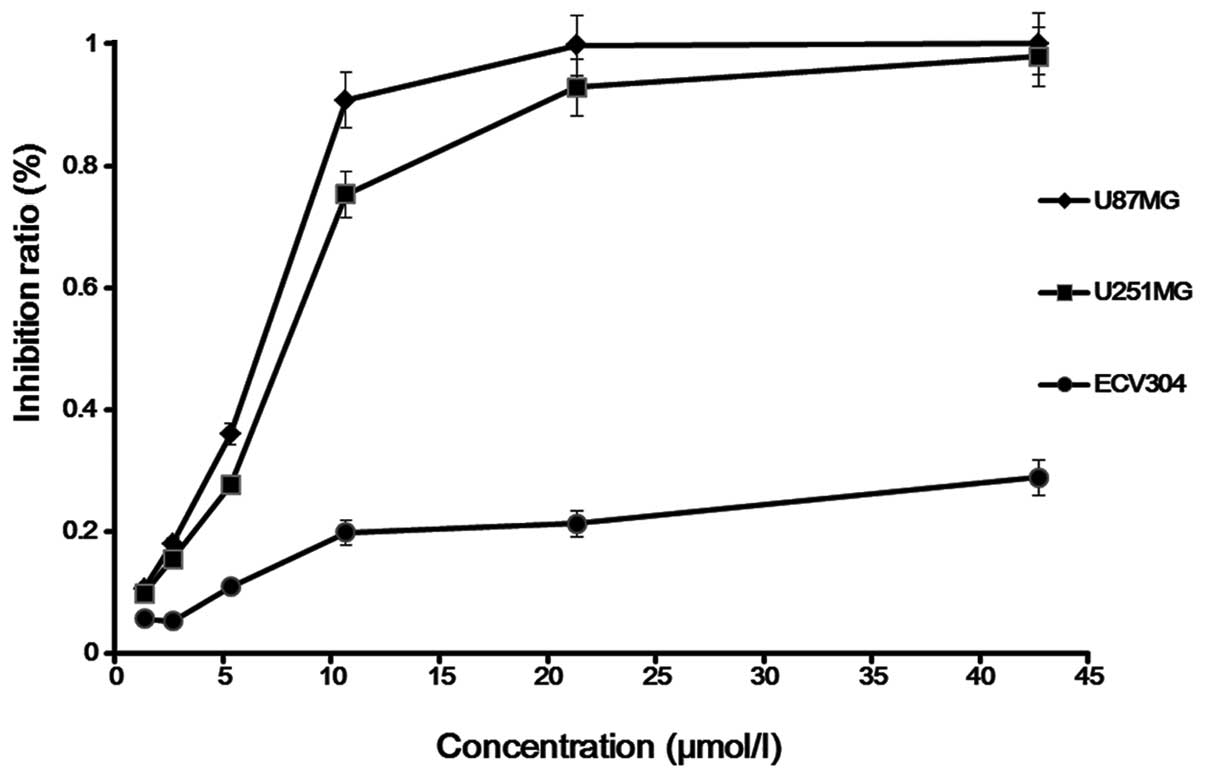
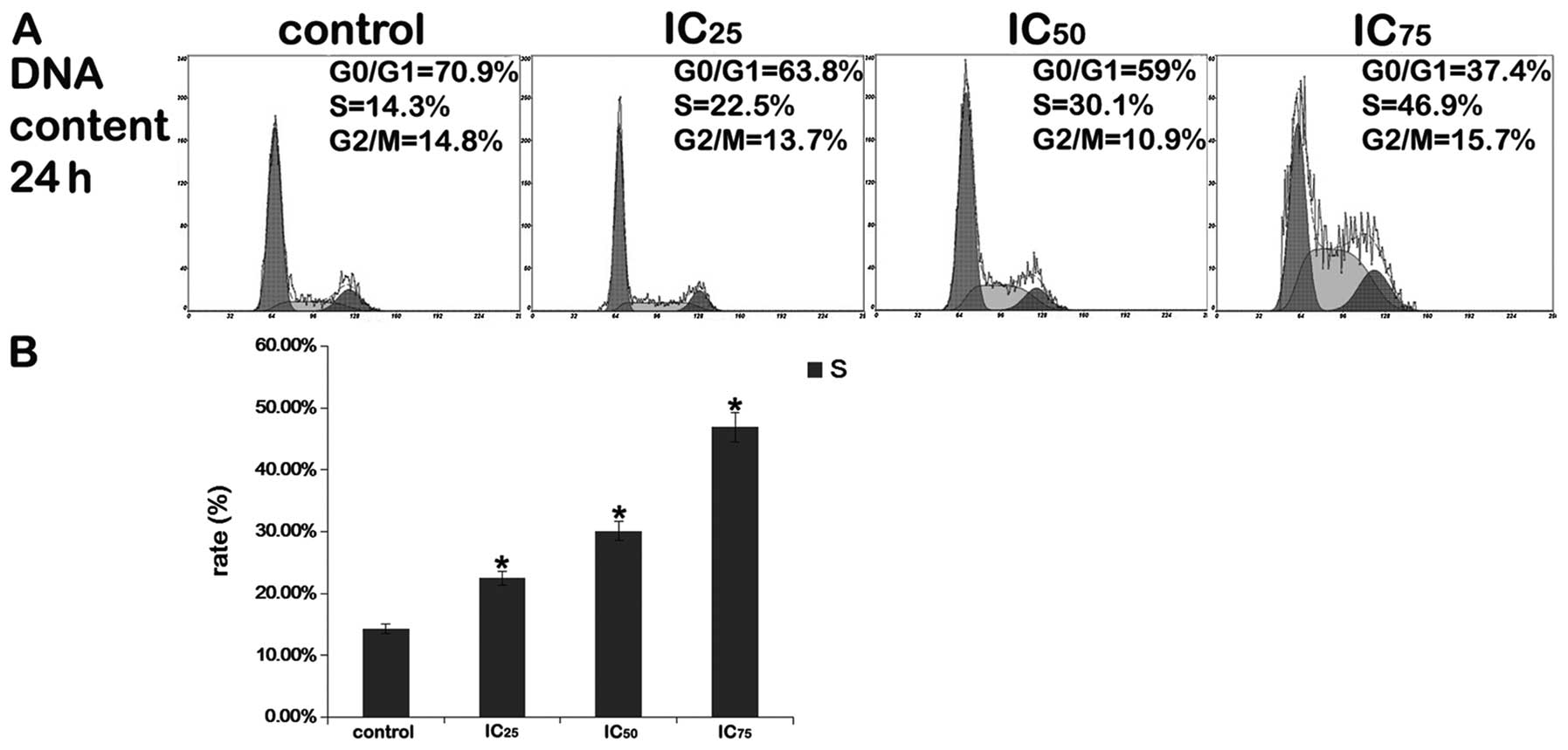
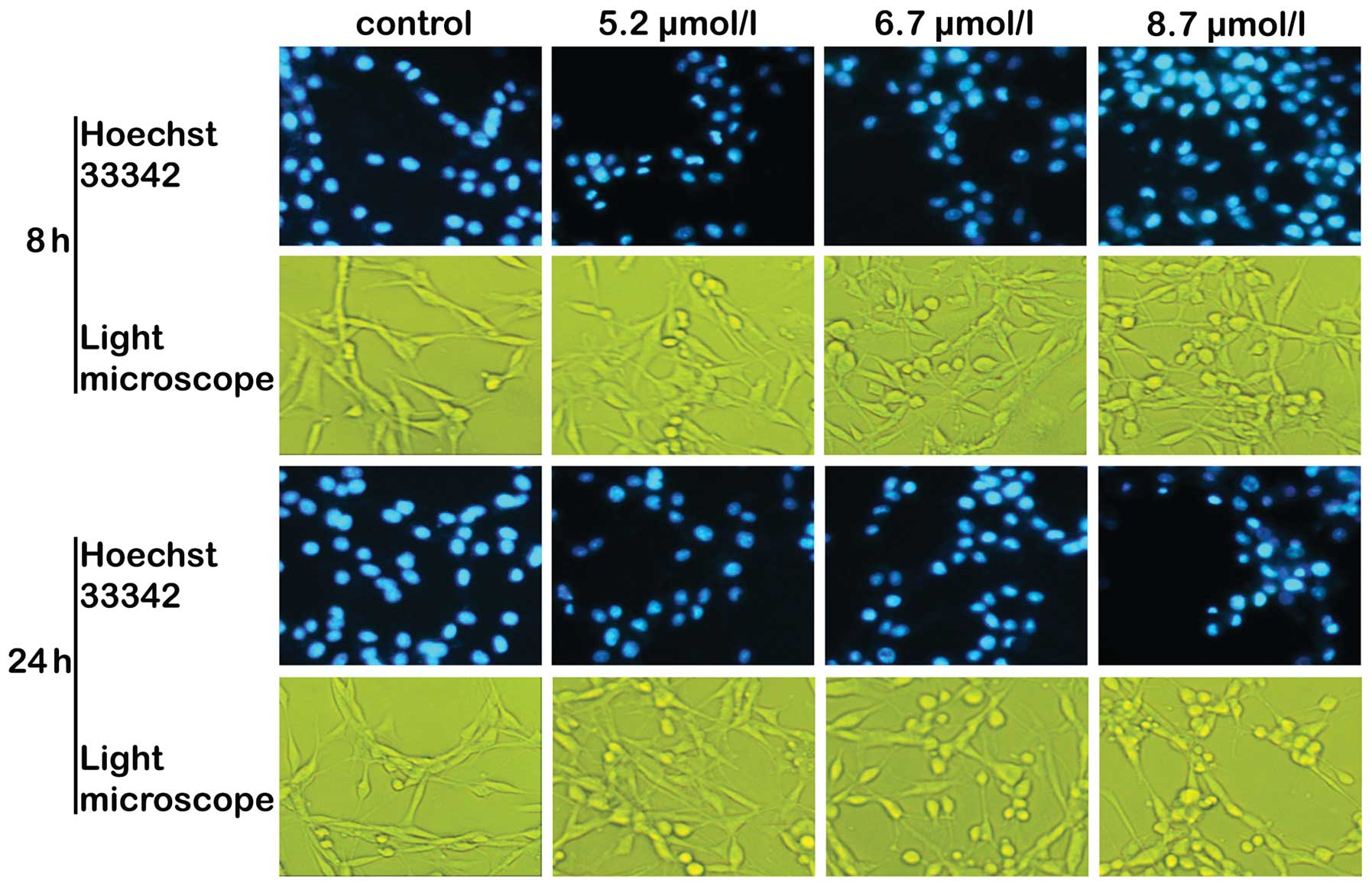
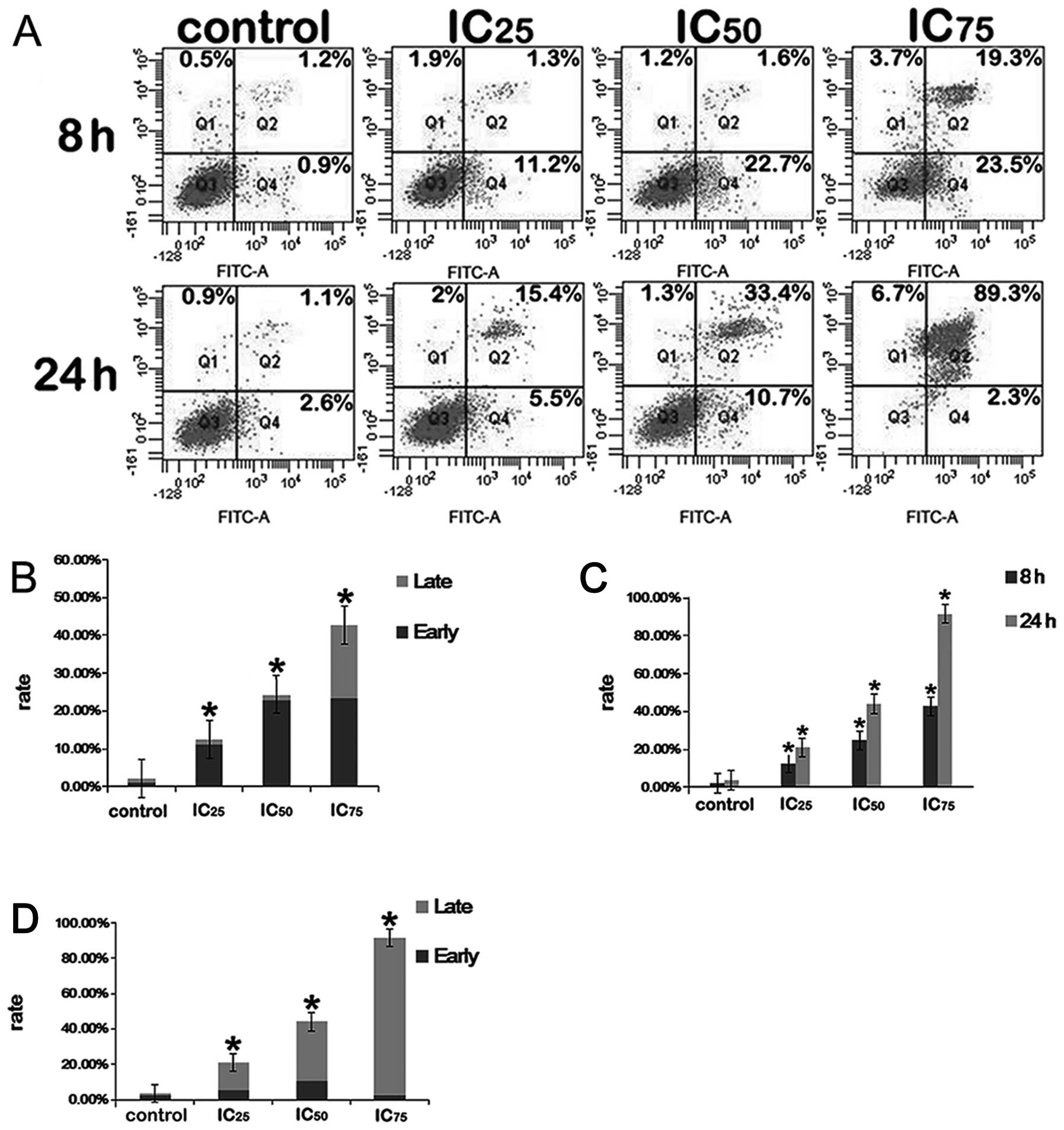
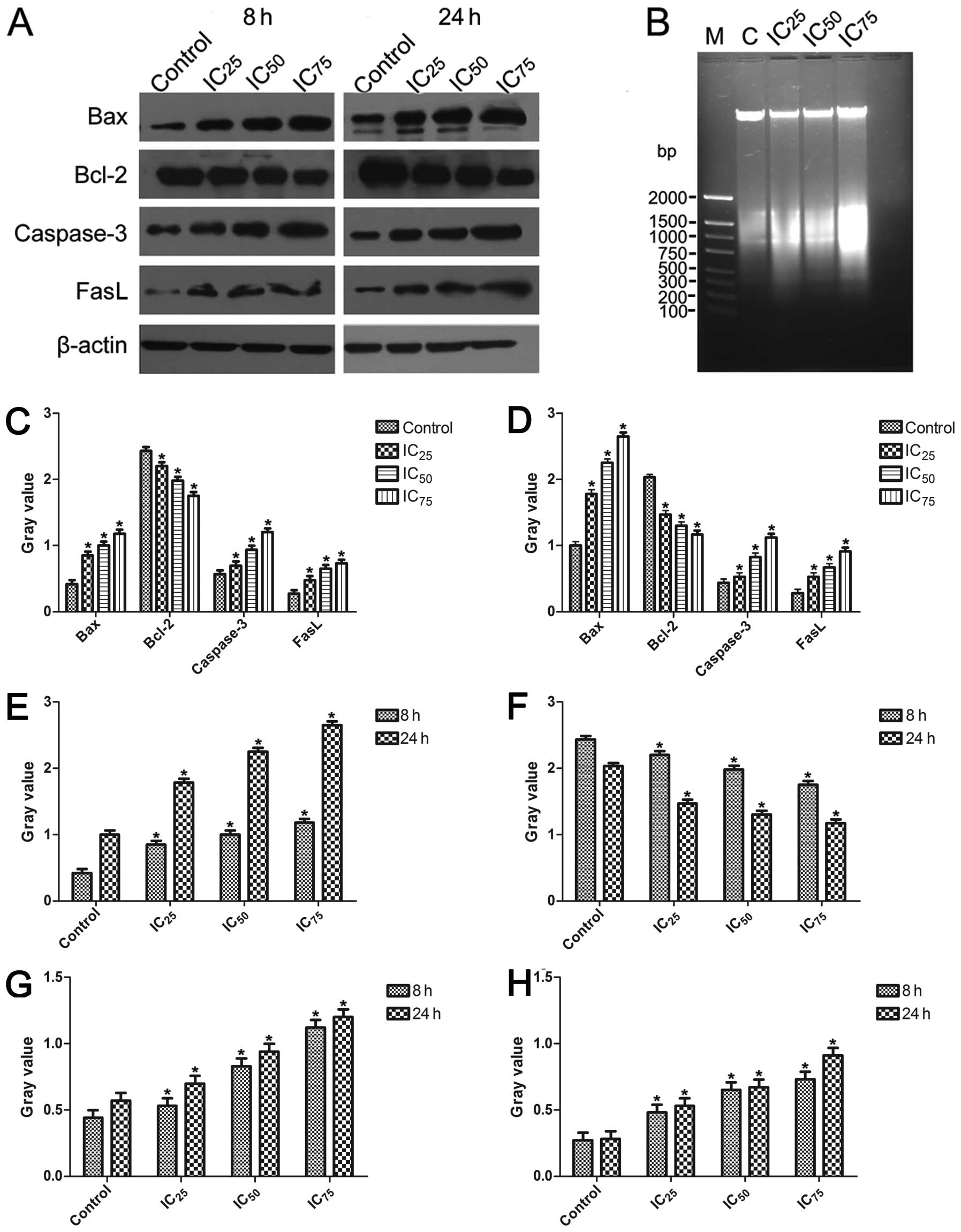
|
1
|
DeAngelis LM: Brain tumors. N Engl J Med.
344:114–123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A,
Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E and Mirimanoff RO:
Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ballman KV, Buckner JC, Brown PD, Giannini
C, Flynn PJ, LaPlant BR and Jaeckle KA: The relationship between
six-month progression-free survival and 12-month overall survival
end points for phase II trials in patients with glioblastoma
multiforme. Neuro Oncol. 9:29–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lamborn KR, Yung WK, Chang SM, Wen PY,
Cloughesy TF, DeAngelis LM, Robins HI, Lieberman FS, Fine HA, Fink
KL, Junck L, Abrey L, Gilbert MR, Mehta M, Kuhn JG, Aldape KD,
Hibberts J, Peterson PM and Prados MD: Progression-free survival:
an important end point in evaluating therapy for recurrent
high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 10:162–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Curtin JF, King GD, Candolfi M, Greeno RB,
Kroeger KM, Lowenstein PR and Castro MG: Combining cytotoxic and
immune-mediated gene therapy to treat brain tumors. Curr Top Med
Chem. 5:1151–1170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fulda S, Jeremias I, Steiner HH, Pietsch T
and Debatin KM: Betulinic acid: a new cytotoxic agent against
malignant brain-tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 82:435–441. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee YS, Jin DQ, Kwon EJ, Park SH, Lee ES,
Jeong TC, Nam DH, Huh K and Kim JA: Asiatic acid, a triterpene,
induces apoptosis through intracellular Ca2+ release and
enhanced expression of p53 in HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 186:83–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Plants as a source
of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol. 100:72–79. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang XY, Chen XL, Tang HF, Gao H, Tian XR
and Zhang PH: Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from the rhizomes of
Anemone taipaiensis. Planta Med. 77:1550–1554. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Geske FJ and Gerschenson LE: The biology
of apoptosis. Hum Pathol. 32:1029–1038. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kumar R, Herbert PE and Warrens AN: An
introduction to death receptors in apoptosis. Int J Surg.
3:268–277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abd-Elrahman I, Hershko K, Neuman T,
Nachmias B, Perlman R and Ben-Yehuda D: The inhibitor of apoptosis
protein Livin (ML-IAP) plays a dual role in tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:5475–5480. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mickisch G, Fajta S, Keilhauer G, Schlick
E, Tschada R and Alken P: Chemosensitivity testing of primary human
renal cell carcinoma by a tetrazolium based microculture assay
(MTT). Urol Res. 18:131–136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vindelov L and Christensen IJ: An
integrated set of methods for routine flow cytometric DNA analysis.
Methods Cell Biol. 33:127–137. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scaife RM: G2 cell cycle arrest,
down-regulation of cyclin B, and induction of mitotic catastrophe
by the flavoprotein inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:1229–1237. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Handrick R, Rudner J, Muller I, Eibl H,
Belka C and Jendrossek V: Bcl-2 mediated inhibition of
erucylphosphocholine-induced apoptosis depends on its subcellular
localisation. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:837–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Narayan P, Mentzer RJ and Lasley RD:
Annexin V staining during reperfusion detects cardiomyocytes with
unique properties. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
281:H1931–H1937. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huigsloot M, Tijdens IB, Mulder GJ and van
de Water B: Differential regulation of doxorubicin-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis by Bcl-2 in mammary
adenocarcinoma (MTLn3) cells. J Biol Chem. 277:35869–35879. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Malerba I, Gribaldo L, Diodovich C,
Carloni M, Meschini R, Bowe G and Collotta A: Induction of
apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity in human bone
marrow and HL-60 p53 null cells treated with anti-cancer drugs.
Toxicol In Vitro. 19:523–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng G, Zhang X, Tang HF, Zhang Y, Zhang
XH, Cao WD, Gao DK, Wang XL and Jin BQ: Asterosaponin 1, a
cytostatic compound from the starfish Culcita novaeguineae,
functions by inducing apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG cells.
J Neurooncol. 79:235–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, Ba Q, Li M, Ni
SJ, Wang LS and Du X: Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric
cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ha ES, Lee EO, Yoon TJ, Kim JH, Park JO,
Lim NC, Jung SK, Yoon BS and Kim SH: Methylene chloride fraction of
Spatholobi Caulis induces apoptosis via caspase dependent
pathway in U937 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:1348–1352.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Edinger AL and Thompson CB: Death by
design: apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:663–669. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sperandio S, de Belle I and Bredesen DE:
An alternative, nonapoptotic form of programmed cell death. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:14376–14381. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhai D, Jin C, Huang Z, Satterthwait AC
and Reed JC: Differential regulation of Bax and Bak by
anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins Bcl-B and Mcl-1. J Biol Chem.
283:9580–9586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rega MF, Leone M, Jung D, Cotton NJ,
Stebbins JL and Pellecchia M: Structure-based discovery of a new
class of Bcl-xL antagonists. Bioorg Chem. 35:344–353. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson
MG, Chen J, Jin S, Johnson EF, Marsh KC, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P,
Roberts L, Tahir SK, Xiao Y, Yang X, Zhang H, Fesik S, Rosenberg SH
and Elmore SW: ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2
family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 68:3421–3428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leist M and Jaattela M: Four deaths and a
funeral: from caspases to alternative mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 2:589–598. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lovborg H, Nygren P and Larsson R:
Multiparametric evaluation of apoptosis: effects of standard
cytotoxic agents and the cyanoguanidine CHS 828. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:521–526. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Narayan P, Mentzer RJ and Lasley RD:
Annexin V staining during reperfusion detects cardiomyocytes with
unique properties. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
281:H1931–H1937. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kaur B, Tan C, Brat DJ, Post DE and Van
Meir EG: Genetic and hypoxic regulation of angiogenesis in gliomas.
J Neurooncol. 70:229–243. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod.
70:461–477. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shackelford RE, Kaufmann WK and Paules RS:
Cell cycle control, checkpoint mechanisms, and genotoxic stress.
Environ Health Perspect. 107(Suppl 1): 5–24. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mork CN, Faller DV and Spanjaard RA: A
mechanistic approach to anticancer therapy: targeting the cell
cycle with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des.
11:1091–1104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou J, Cheng G, Cheng G, Tang HF and
Zhang X: Novaeguinoside II inhibits cell proliferation and induces
apoptosis of human brain glioblastoma U87MG cells through the
mitochondrial pathway. Brain Res. 1372:22–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee SH, Meng XW, Flatten KS, Loegering DA
and Kaufmann SH: Phosphatidylserine exposure during apoptosis
reflects bidirectional trafficking between plasma membrane and
cytoplasm. Cell Death Differ. 20:64–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry
DE and Oltvai ZN: Bcl-2/Bax: a rheostat that regulates an
anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 4:327–332.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Juin P, Geneste O, Raimbaud E and Hickman
JA: Shooting at survivors: Bcl-2 family members as drug targets for
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:251–260. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ziegler DS and Kung AL: Therapeutic
targeting of apoptosis pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol.
20:97–103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kleibl Z, Raisová M, Novotný J, Pohlreich
P and Matous B: Apoptosis and its importance in the development and
therapy of tumors (review). Sb Lek. 103:1–13. 2002.(In Czech).
|
|
43
|
Sulejczak D, Grieb P, Walski M and
Frontczak-Baniewicz M: Apoptotic death of cortical neurons
following surgical brain injury. Folia Neuropathol. 46:213–219.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|