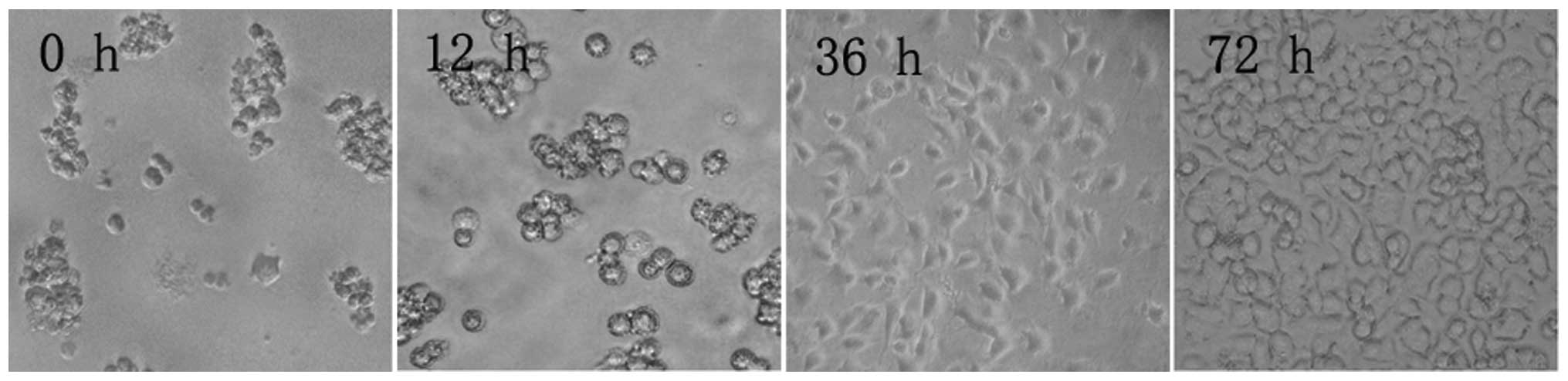
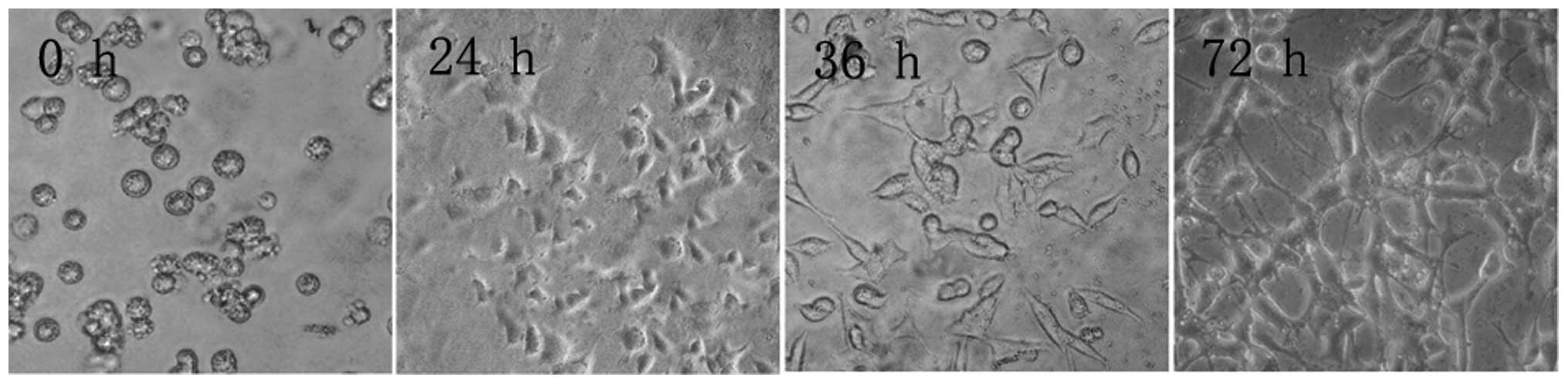
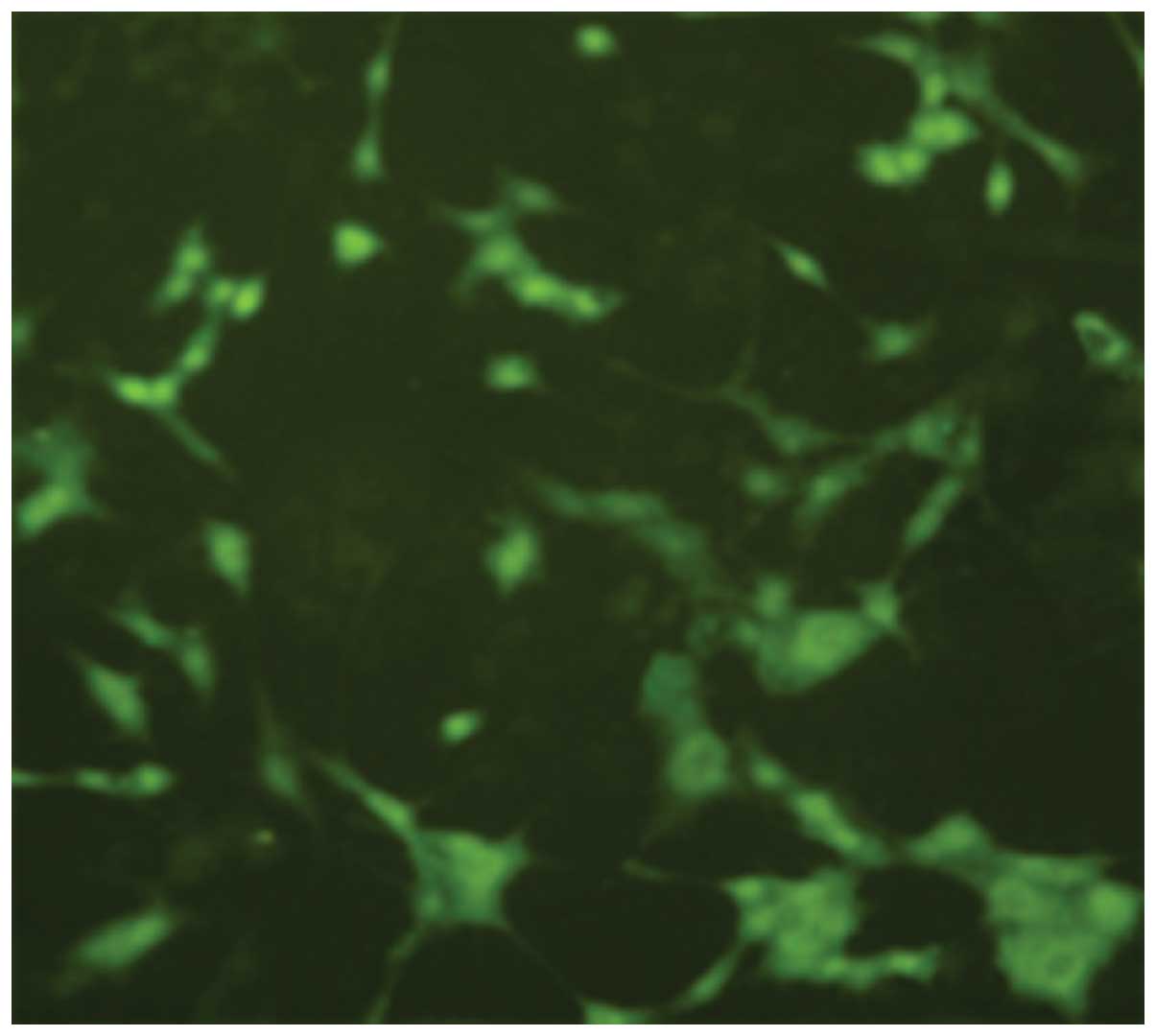
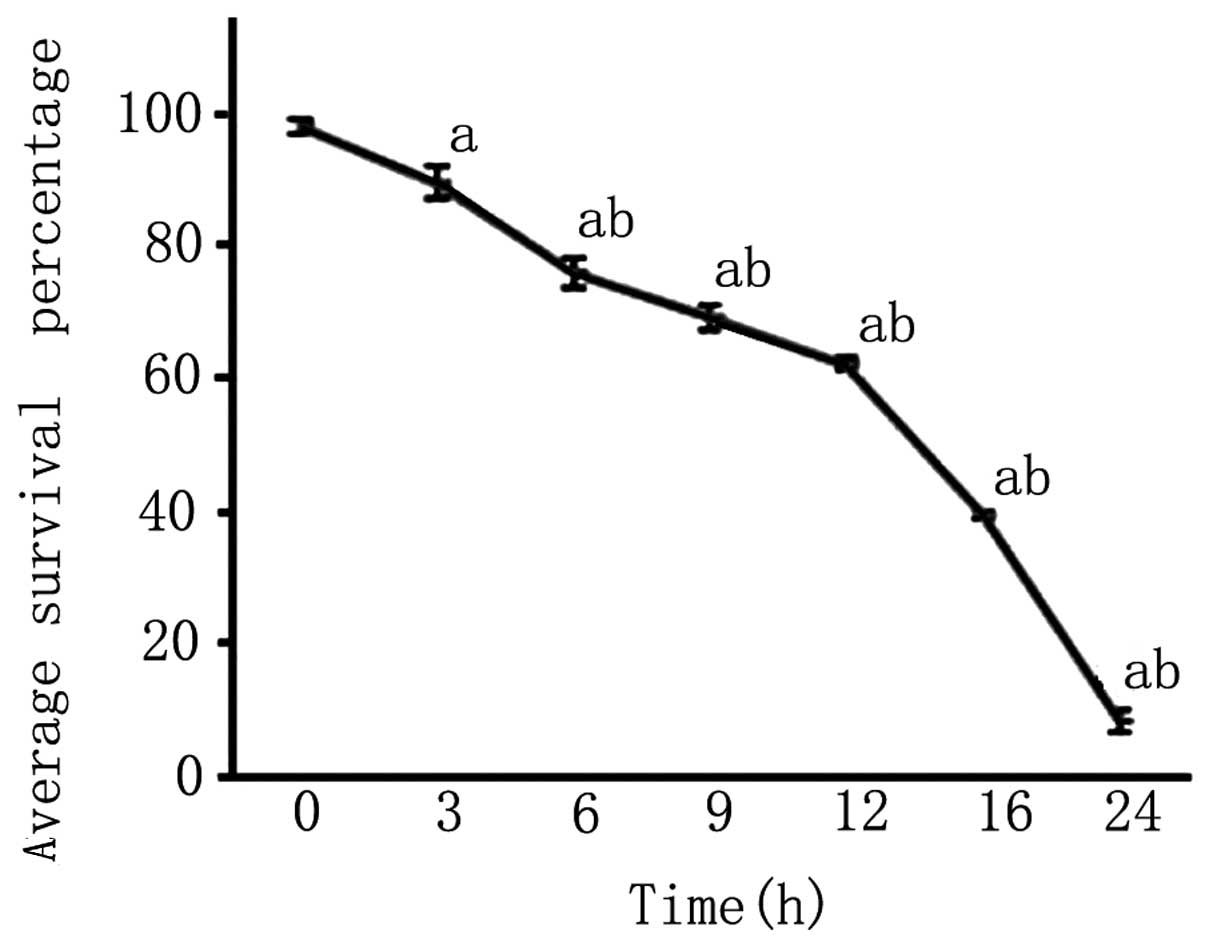
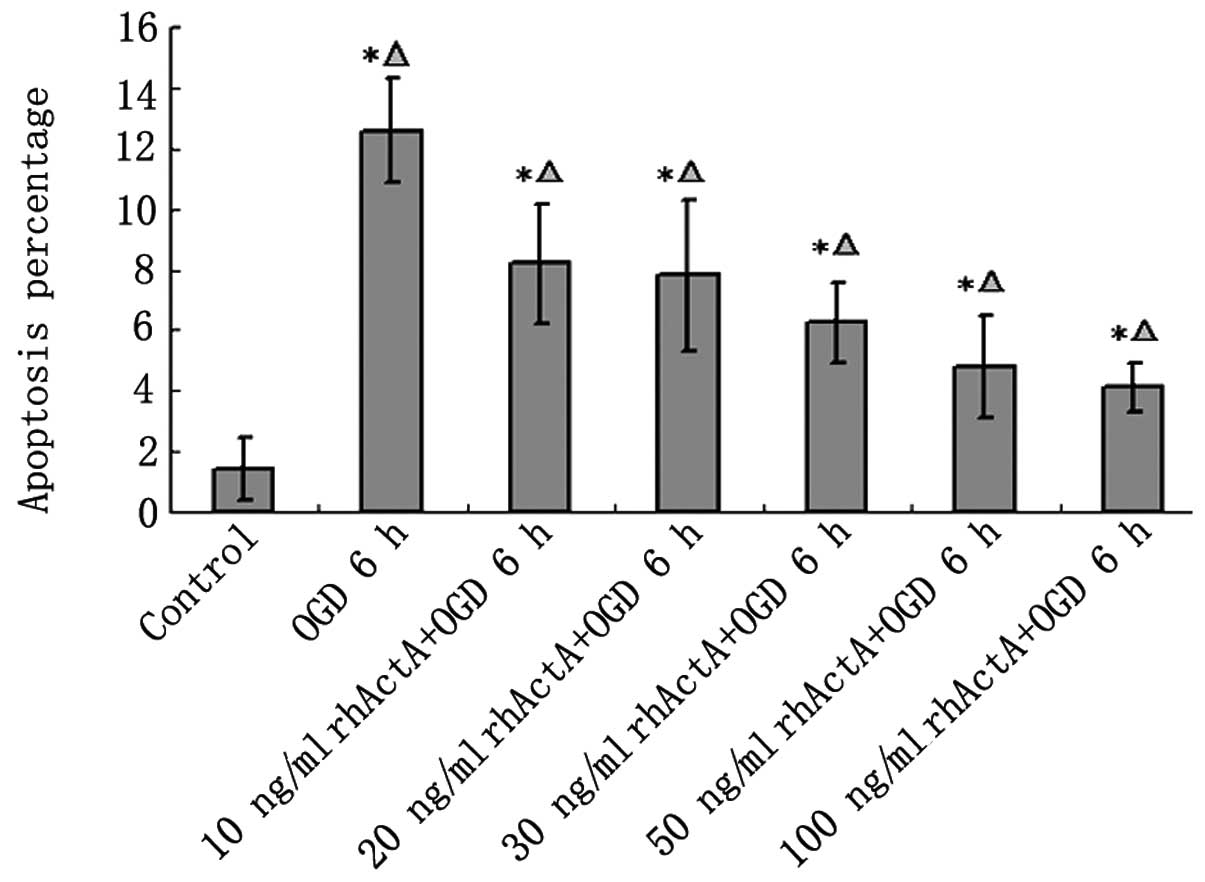
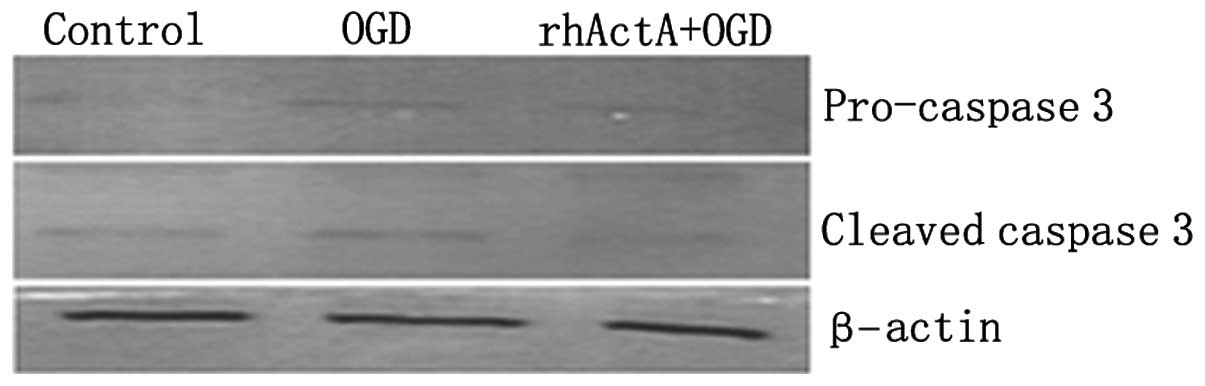
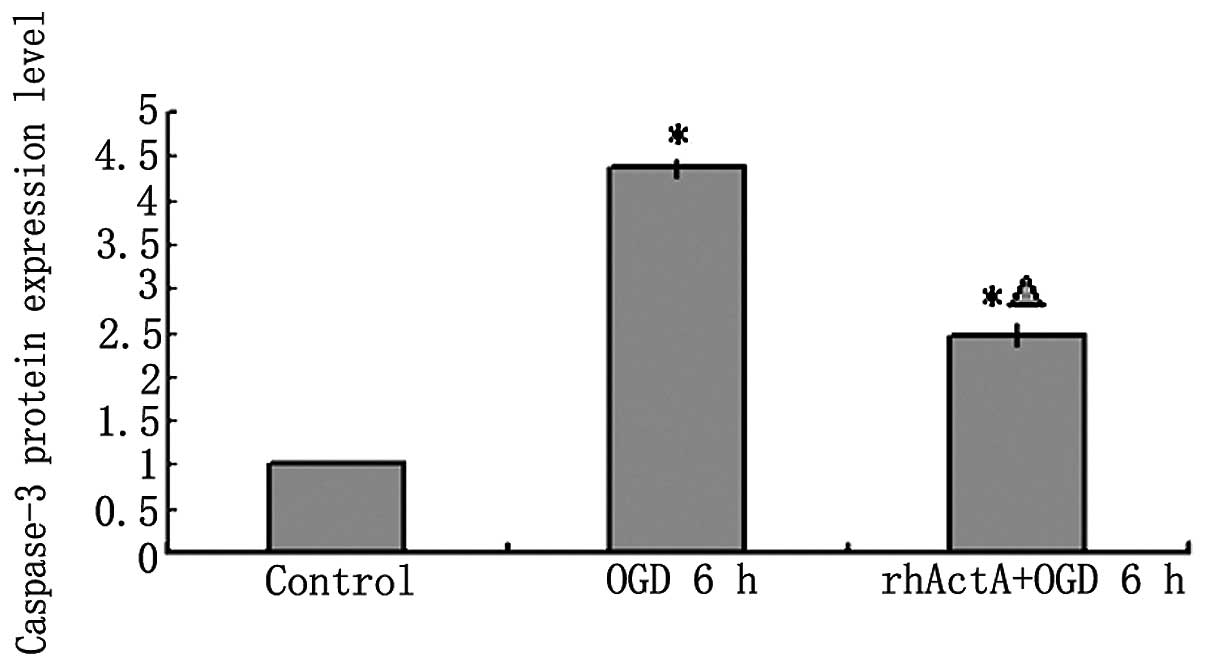
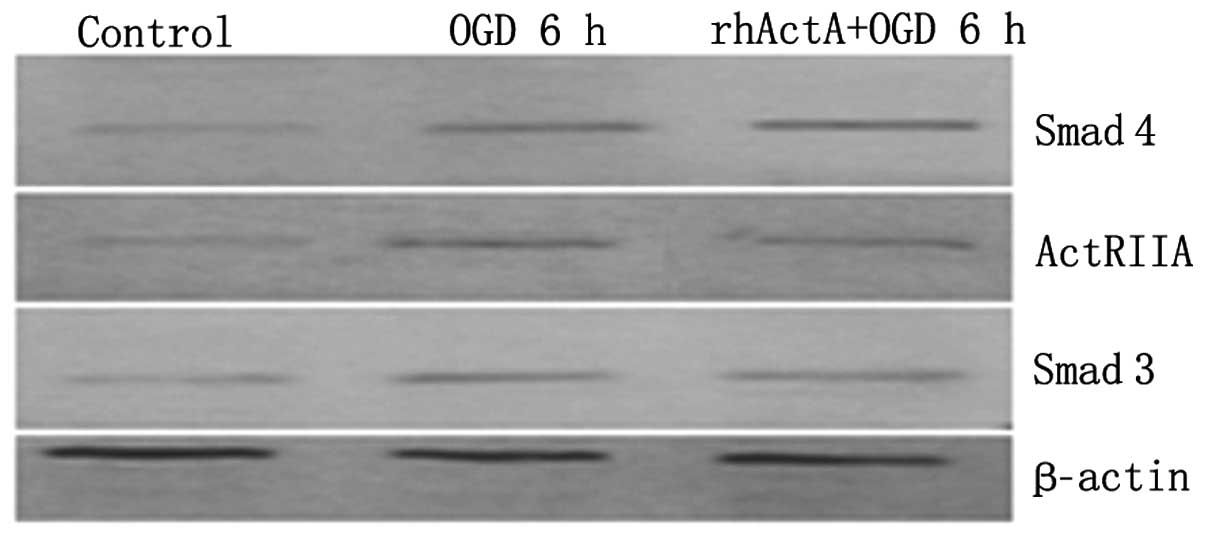
|
1
|
Massagué J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Tretter YP, Hertel M, Munz B, ten
Bruggencate G, Werner S and Alzheimer C: Induction of activin A is
essential for the neuroprotective action of basic fibroblast growth
factor in vivo. Nat Med. 6:812–815. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin X, Duan X, Liang YY, et al: PPM1A
functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate TGFbeta signaling.
Cell. 125:915–928. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ling N, Ueno N, Ying SY, et al: Inhibins
and activins. Vitam Horm. 44:1–46. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Munz B, Tretter YP, Hertel M, Engelhardt
F, Alzheimer C and Werner S: The roles of activins in repair
processes of the skin and the brain. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
180:169–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ageta H, Murayama A, Migishima R, et al:
Activin in the brain modulates anxiety-related behavior and adult
neurogenesis. PLoS One. 3:e18692008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsuchida K, Nakatani M, Uezumi A, Murakami
T and Cui X: Signal transduction pathway through activin receptors
as a therapeutic target of musculoskeletal diseases and cancer.
Endocr J. 55:11–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schneyer AL, Sidis Y, Gulati A, Sun JL,
Keutmann H and Krasney PA: Differential antagonism of activin,
myostatin and growth and differentiation factor 11 by wild-type and
mutant follistatin. Endocrinology. 149:4589–4595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou WJ and Hu ZP: Expression of Smad 2
and Smad 4 proteins in brain tissue following cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in gerbils. Guoji Shenjing Bing Xue Shenjing
Waike Zazhi. 35:112–114. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Tsuchida K, Nakatani M, Hitachi K, et al:
Activin signaling as an emerging target for therapeutic
interventions. Cell Commun Signal. 7:152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shoji-Kasai Y, Ageta H, Hasegawa Y,
Tsuchida K, Sugino H and Inokuchi K: Activin increases the number
of synaptic contacts and the length of dendritic spine necks by
modulating spinal actin dynamics. J Cell Sci. 120:3830–3837. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mukerji SS, Katsman EA, Wilber C, Haner
NA, Selman WR and Hall AK: Activin is a neuronal survival factor
that is rapidly increased after transient cerebral ischemia and
hypoxia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:1161–1172. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li XQ, Verge VM, Johnston JM and Zochodne
DW: CGRP peptide and regenerating sensory axons. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 63:1092–1103. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cruise BA, Xu P and Hall AK: Wounds
increase activin in skin and a vasoactive neuropeptide in sensory
ganglia. Dev Biol. 271:1–10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu P, Van Slambrouck C, Berti-Mattera L
and Hall AK: Activin induces tactile allodynia and increases
calcitonin gene-related peptide after peripheral inflammation. J
Neurosci. 25:9227–9235. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Müller MR, Zheng F, Werner S and Alzheimer
C: Transgenic mice expressing dominant-negative activin receptor IB
in forebrain neurons reveal novel functions of activin at
glutamatergic synapses. J Biol Chem. 281:29076–29084.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasuda H, Mine T, Shibata H, et al:
Activin A: an autocrine inhibitor of initiation of DNA synthesis in
rat hepatocytes. J Clin Invest. 92:1491–1496. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen W, Woodruff TK and Mayo KE: Activin A
induced Hep G2 liver cell apoptosis: involvement of activin
receptors and smad proteins. Endocrinology. 141:1263–1272.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan J and Yankner BA: Apoptosis in the
nervous system. Nature. 407:802–809. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gurney ME, Tomasselli AG and Heinrikson
RL: Neurobiology. Stay the executioner’s hand. Science.
288:283–284. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Lee JM, Grabb MC, Zipfel GJ and Choi DW:
Brain tissue responses to ischemia. J Clin Invest. 106:723–731.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benchoua A, Guégan C, Couriaud C, et al:
Specific caspase pathways are activated in the two stages of
cerebral infarction. J Neurosci. 21:7127–7134. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harrison DC, Davis RP, Bond BC, et al:
Caspase mRNA expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 89:133–146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo HL, Xu ZX and Li XH: Use of RNAi
silencing to target preconditioned glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor in neuronal apoptosis. Neural Regen Res.
6:510–516. 2011.
|