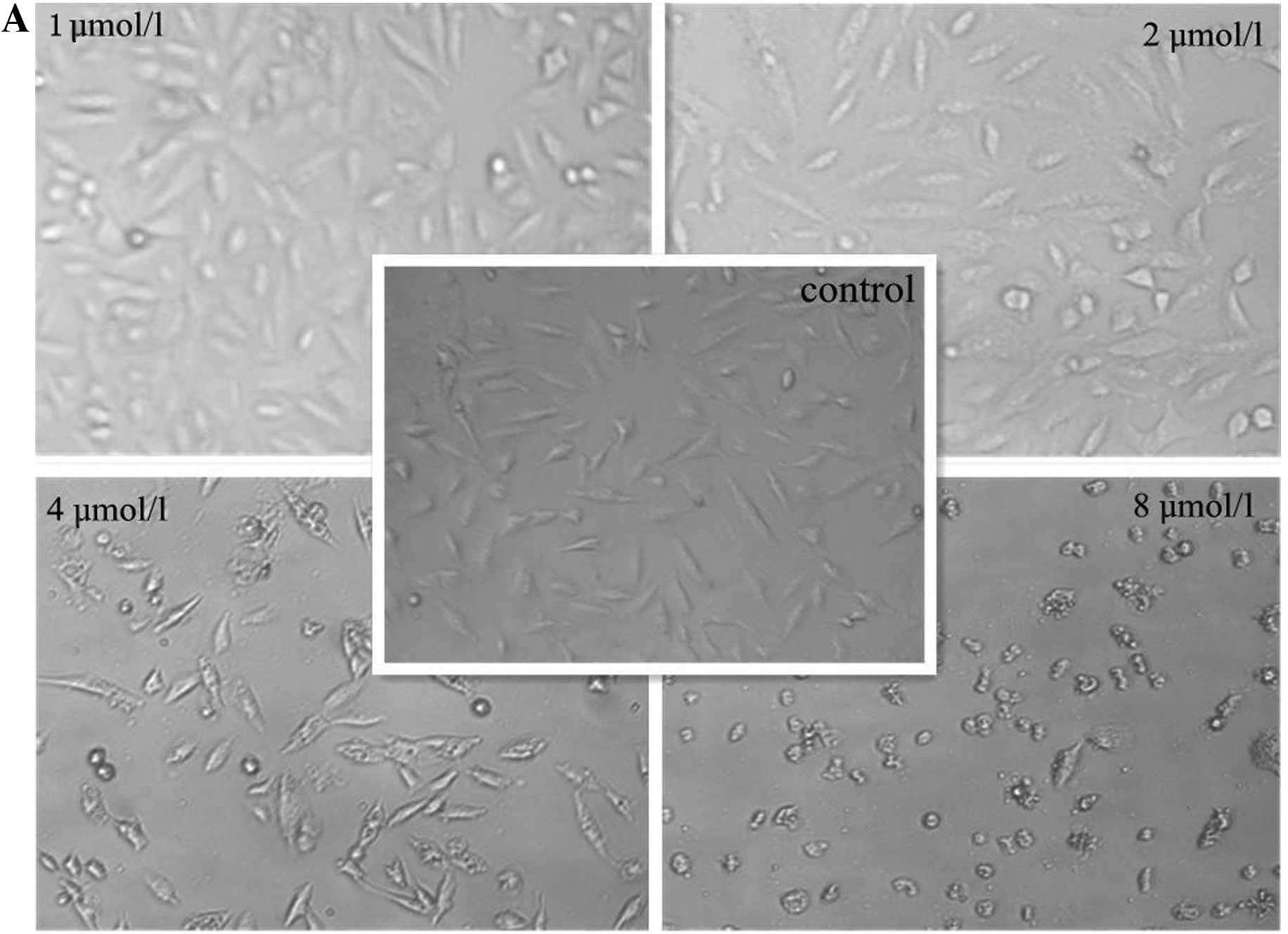
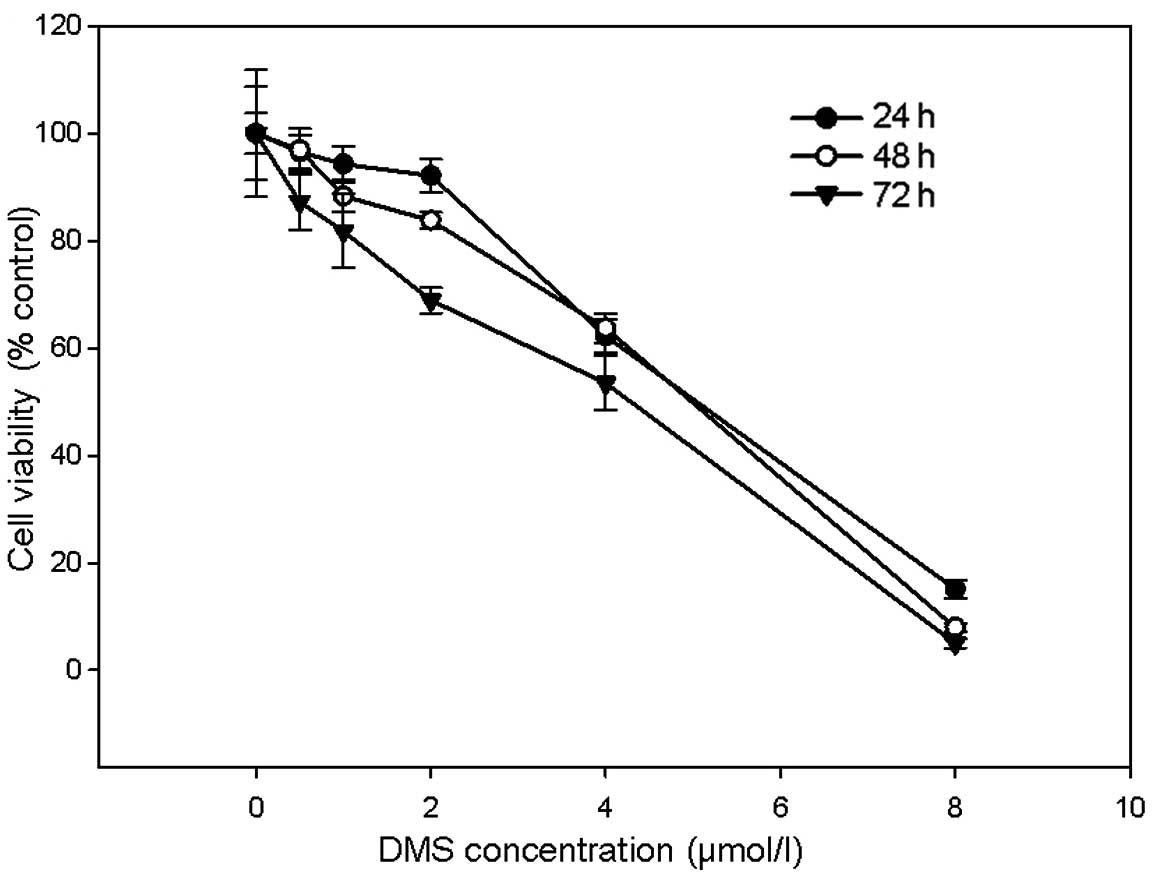
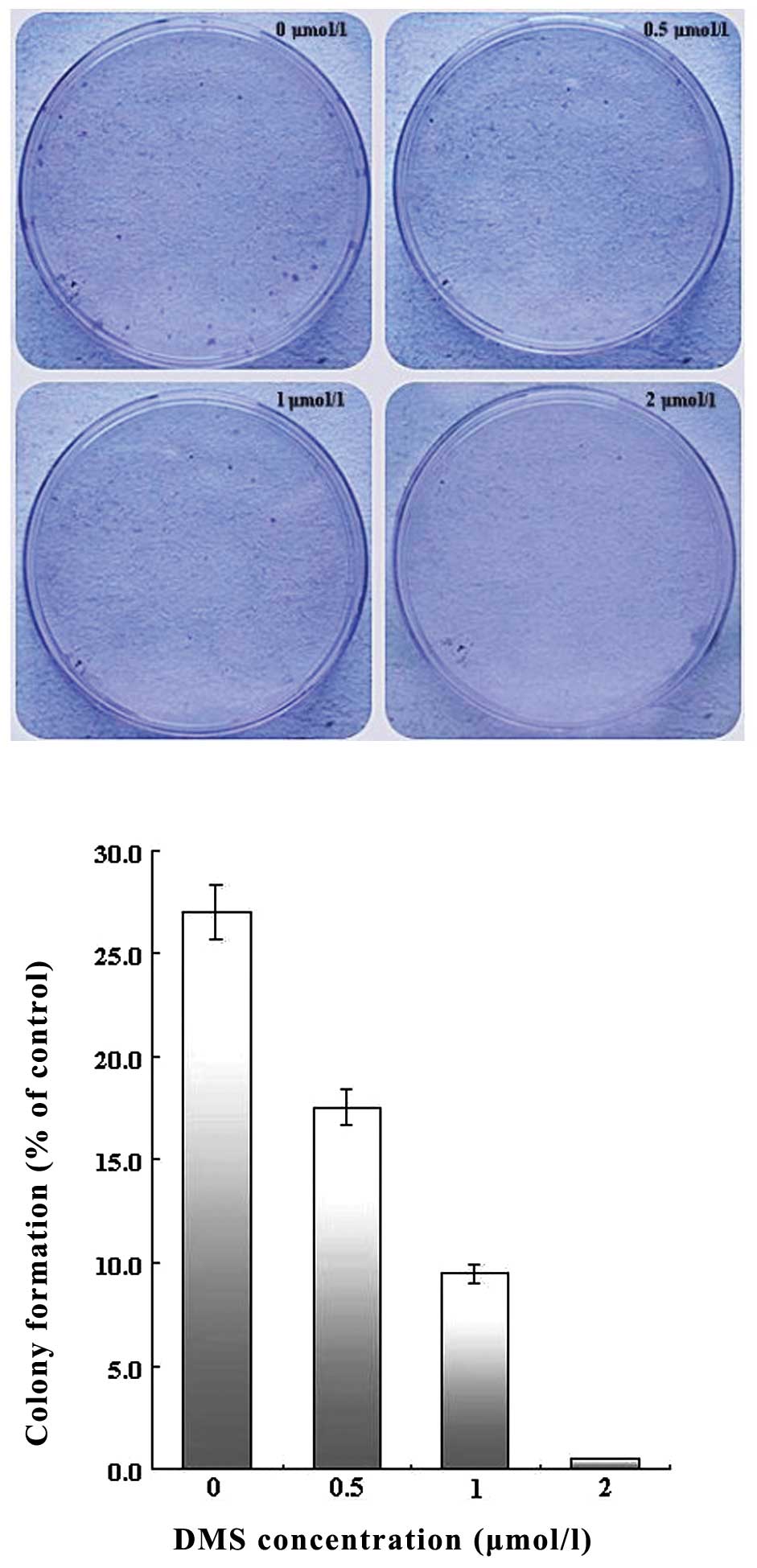
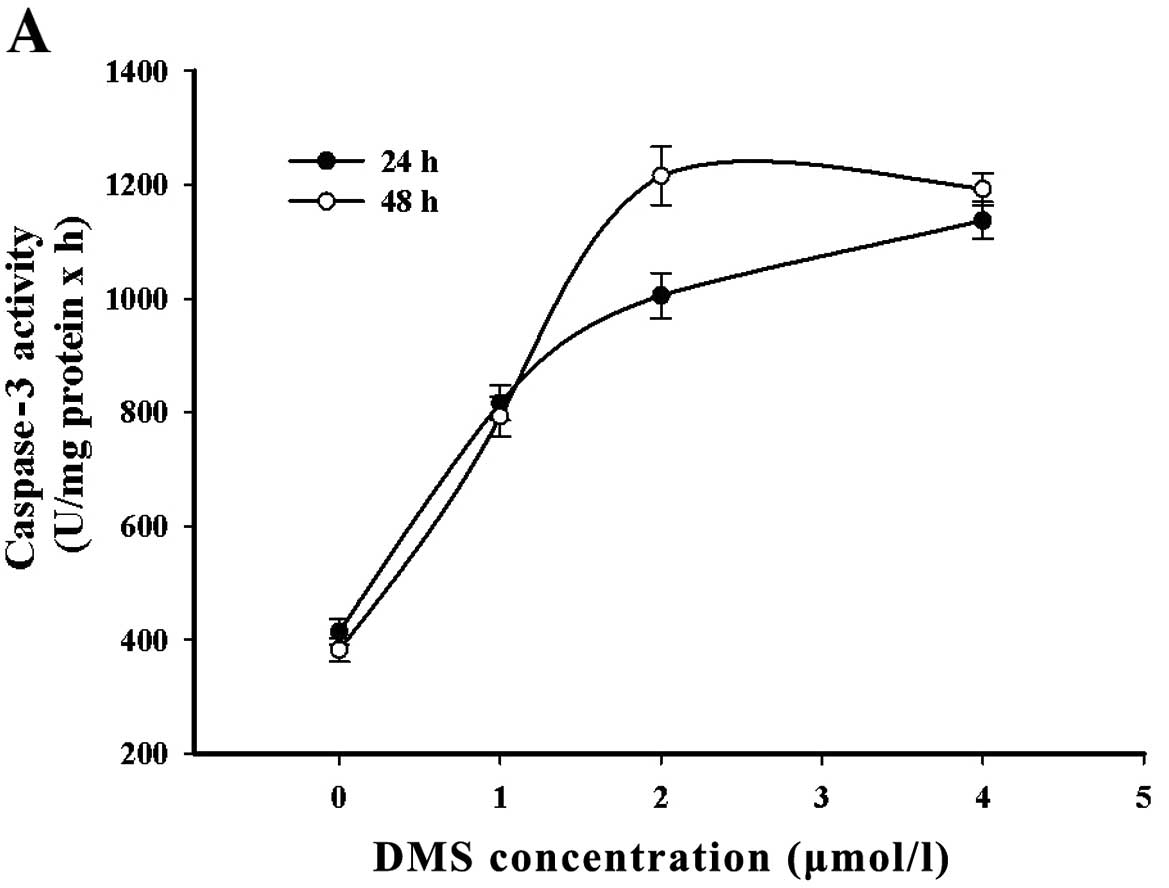
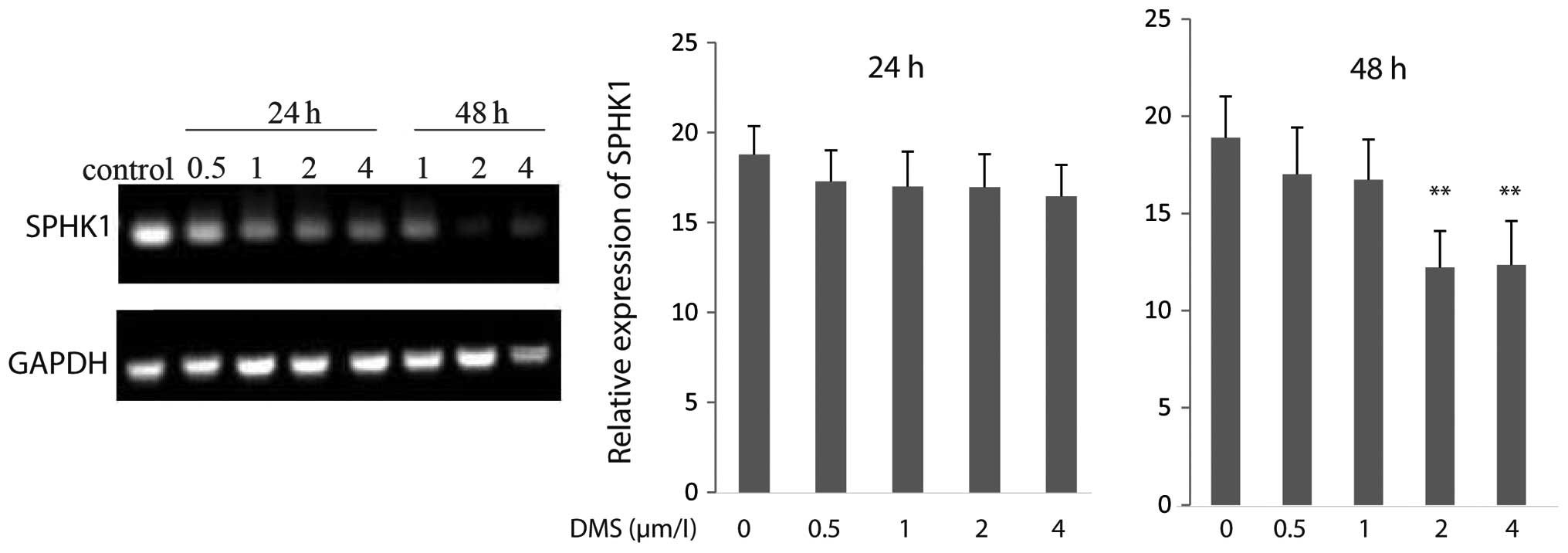
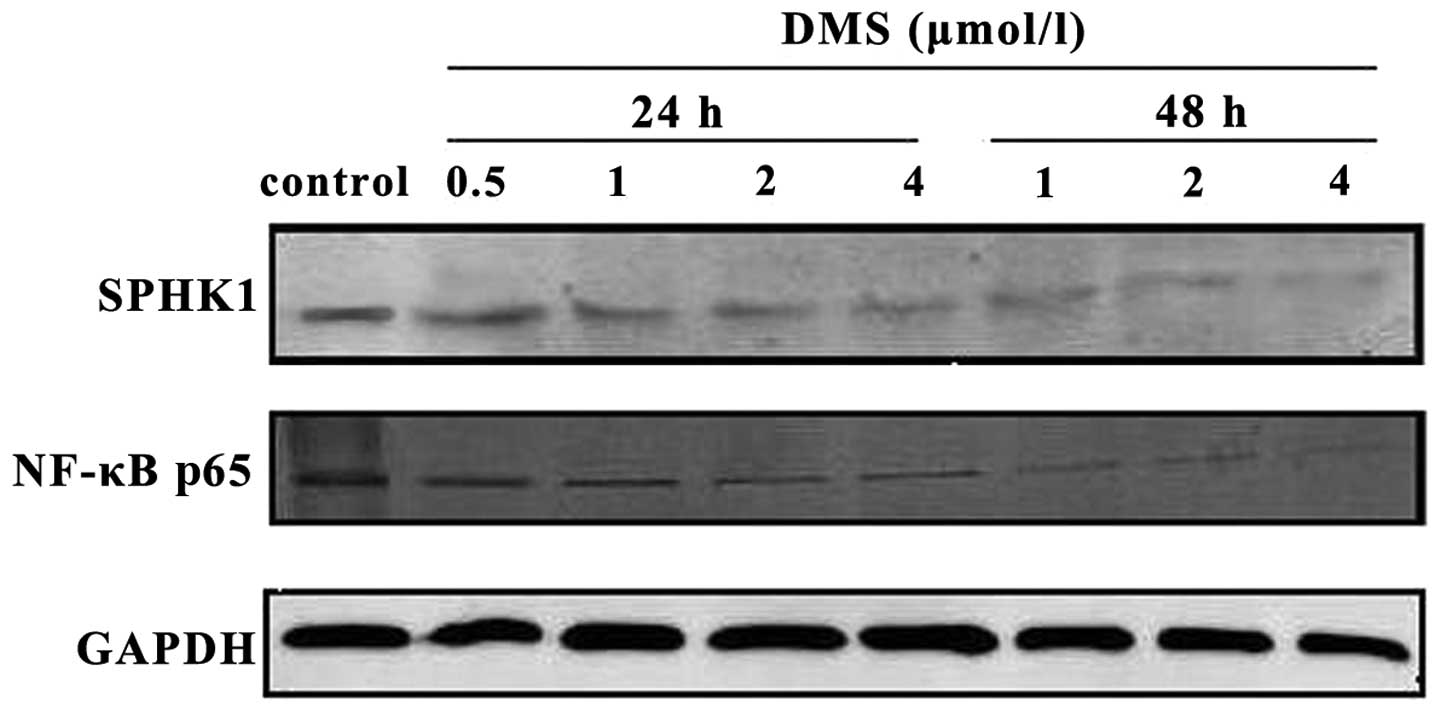
|
1
|
Igarashi Y and Hakomori S: Enzymatic
synthesis of N, N-dimethyl-sphingosine: demonstration of the
sphingosine: N-methyltransferase in mouse brain. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 164:1411–1416. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Megidish T, Cooper J, Zhang L, Fu H and
Hakomori S: A novel sphingosine-dependent protein kinase (SDK1)
specifically phosphorylates certain isoforms of 14-3-3 protein. J
Biol Chem. 273:21834–21845. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
zu Heringdorf DM, Lass H, Alemany R, et
al: Sphingosine kinase-mediated Ca2+signalling by
G-protein-coupled receptors. EMBO J. 17:2830–2837. 1998.
|
|
4
|
Edsall LC, Van Brocklyn JR, Cuvillier O,
Kleuser B and Spiegel S: N,N-dimethylsphingosine is a potent
competitive inhibitor of sphingosine kinase but not of protein
kinase C: modulation of cellular levels of sphingosine 1-phosphate
and ceramide. Biochemistry. 37:12892–12898. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakakura C, Sweeney EA, Shirahama T, et
al: Selectivity of sphingosine-induced apoptosis. Lack of activity
of DL-erythyro-dihydrosphingosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
246:827–830. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cuvillier O, Pirianov G, Kleuser B, et al:
Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by
sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature. 381:800–803. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Antoon JW, White MD, Slaughter EM, et al:
Targeting NFκB mediated breast cancer chemoresistance through
selective inhibition of sphingosine kinase-2. Cancer Biol Ther.
11:678–689. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Billich A, Bornancin F, Mechtcheriakova D,
Natt F, Huesken D and Baumruker T: Basal and induced sphingosine
kinase 1 activity in A549 carcinoma cells: function in cell
survival and IL-1beta and TNF-alpha induced production of
inflammatory mediators. Cell Signal. 17:1203–1217. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alfonso A, De la Rosa L, Vieytes M and
Botana L: Dimethylsphingosine increases cytosolic calcium and
intracellular pH in human T lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol.
65:465–478. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee EH, Lee YK, Im YJ, Kim JH, Okajima F
and Im DS: Dimethylsphingosine regulates intracellular pH and
Ca(2+) in human monocytes. J Pharmacol Sci. 100:289–296. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Shin Y, Daly J and Choi O: Diverse effects
of sphingosine on calcium mobilization and influx in differentiated
HL-60 cells. Cell Calcium. 27:269–280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang YJ, Lee YK, Lee EH, Park JJ, Chung
SK and Im DS: Structure-activity relationships of
dimethylsphingosine (DMS) derivatives and their effects on
intracellular pH and Ca2+in the U937 monocyte cell line.
Arch Pharm Res. 29:657–665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim HL and Im DS:
N,N-dimethyl-D-erythro-sphingosine increases intracellular
Ca2+concentration via
Na+-Ca2+-exchanger in HCT116 human colon
cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:54–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pchejetski D, Golzio M, Bonhoure E, et al:
Sphingosine kinase-1 as a chemotherapy sensor in prostate
adenocarcinoma cell and mouse models. Cancer Res. 65:11667–11675.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morales A, Paris R, Villanueva A, Llacuna
L, Garcia-Ruiz C and Fernandez-Checa J: Pharmacological inhibition
or small interfering RNA targeting acid ceramidase sensitizes
hepatoma cells to chemotherapy and reduces tumor growth in vivo.
Oncogene. 26:905–916. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bonhoure E, Pchejetski D, Aouali N, et al:
Overcoming MDR-associated chemoresistance in HL-60 acute myeloid
leukemia cells by targeting shingosine kinase-1. Leukemia.
20:95–102. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vadas M, Xia P, McCaughan G and Gamble J:
The role of sphingosine kinase 1 in cancer: Oncogene or
non-oncogene addiction? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA).
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1781:442–447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nava VE, Cuvillier O, Edsall LC, et al:
Sphingosine enhances apoptosis of radiation-resistant prostate
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 60:4468–4474. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nava VE, Hobson JP, Murthy S, Milstien S
and Spiegel S: Sphingosine kinase type 1 promotes
estrogen-dependent tumorigenesis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Exp
Cell Res. 281:115–127. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sweeney EA, Sakakura C, Shirahama T, et
al: Sphingosine and its methylated derivative
N,N-dimethylsphingosine (DMS) induce apoptosis in a variety of
human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 66:358–366. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu H, Sugiura M, Nava VE, et al:
Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel
mammalian sphingosine kinase type 2 isoform. J Biol Chem.
275:19513–19520. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Olivera A, Kohama T, Tu Z, Milstien S and
Spiegel S: Purification and characterization of rat kidney
sphingosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 273:12576–12583. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ruckhäberle E, Rody A, Engels K, et al:
Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals
prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 112:41–52. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
French KJ, Schrecengost RS, Lee BD, et al:
Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human sphingosine kinase.
Cancer Res. 63:5962–5969. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
French KJ, Upson JJ, Keller SN, Zhuang Y,
Yun JK and Smith CD: Antitumor activity of sphingosine kinase
inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 318:596–603. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akao Y, Banno Y, Nakagawa Y, et al: High
expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and S1P receptors in
chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells and their
camptothecin-induced up-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
342:1284–1290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Leroux M, Auzenne E, Evans R, et al:
Sphingolipids and the sphingosine kinase inhibitor, SKI II, induce
BCL-2-independent apoptosis in human prostatic adenocarcinoma
cells. Prostate. 67:1699–1717. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sutphen R, Xu Y, Wilbanks GD, et al:
Lysophospholipids are potential biomarkers of ovarian cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:1185–1191. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Brocklyn JR, Jackson CA, Pearl DK,
Kotur MS, Snyder PJ and Prior TW: Sphingosine kinase-1 expression
correlates with poor survival of patients with glioblastoma
multiforme: roles of sphingosine kinase isoforms in growth of
glioblastoma cell lines. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 64:695–705.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzuki H, Riley RT and Sharma RP:
Inducible nitric oxide has protective effect on fumonisin B1
hepatotoxicity in mice via modulation of sphingosine kinase.
Toxicology. 229:42–53. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawamori T, Osta W, Johnson KR, et al:
Sphingosine kinase 1 is up-regulated in colon carcinogenesis. FASEB
J. 20:386–388. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sobue S, Nemoto S, Murakami M, et al:
Implications of sphingosine kinase 1 expression level for the
cellular sphingolipid rheostat: relevance as a marker for
daunorubicin sensitivity of leukemia cells. Int J Hematol.
87:266–275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson KR, Johnson KY, Crellin HG, et al:
Immunohistochemical distribution of sphingosine kinase 1 in normal
and tumor lung tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 53:1159–1166. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Min J, Van Veldhoven PP, Zhang L, Hanigan
MH, Alexander H and Alexander S: Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase
regulates sensitivity of human cells to select chemotherapy drugs
in a p38-dependent manner. Mol Cancer Res. 3:287–296. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sauer B, Ruwisch L and Kleuser B:
Antiapoptotic action of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in primary
human melanocytes. Melanoma Res. 13:339–347. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bektas M, Jolly PS, Müller C, Eberle J,
Spiegel S and Geilen CC: Sphingosine kinase activity counteracts
ceramide-mediated cell death in human melanoma cells: role of Bcl-2
expression. Oncogene. 24:178–187. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han S and Roman J: Suppression of
prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP2 by PPARgamma ligands inhibits
human lung carcinoma cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
314:1093–1099. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mukogawa T, Koyama F, Tachibana M, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated gene transduction of truncated I kappa B alpha
enhances radiosensitivity in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
94:745–750. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weaver KD, Yeyeodu S, Cusack JC Jr,
Baldwin AS Jr and Ewend MG: Potentiation of chemotherapeutic agents
following antagonism of nuclear factor kappa B in human gliomas. J
Neurooncol. 61:187–196. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin JC, Yang SC, Hong TM, et al:
Phenanthrene-based tylophorine-1 (PBT-1) inhibits lung cancer cell
growth through the Akt and NF-kappaB pathways. J Med Chem.
52:1903–1911. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gong G, Waris G, Tanveer R and Siddiqui A:
Human hepatitis C virus NS5A protein alters intracellular calcium
levels, induces oxidative stress, and activates STAT-3 and NF-kappa
B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:9599–9604. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|